Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dynamics 1 Discussion
Uploaded by
jlOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Dynamics 1 Discussion
Uploaded by
jlCopyright:
Available Formats
Dynamics 1
Sunday, 6 September 2020
10:28 PM
• Dynamics includes:
• Kinematics: study of the geometry of motion.
Kinematics is used to relate displacement, velocity,
acceleration, and time without reference to the
cause of motion.
• Kinetics: study of the relations existing between the
forces acting on a body, the mass of the body, and
the motion of the body. Kinetics is used to predict
the motion caused by given forces or to determine
the forces required to produce a given motion.
• Rectilinear motion: position, velocity, and acceleration of a particle as it
moves along a straight line.
• Curvilinear motion: position, velocity, and acceleration of a particle as it
moves along a curved line in two or three dimensions.
New Section 1 Page 1
dx
v constant
dt
Rectilinear Motion with Constant Acceleration
x t
Sunday, 6 September 2020
dx 11:21
v PMdt
x0 For0particle in uniform rectilinear motion, the acceleration is zero
x x0 and
vt the velocity is constant.
x x0 vt
v t
dv
a constant dv a dt v v0 at
dt v0 0
v v0 at
x t 11 - 4
dx
v0 at dx
0v at dt x x 0 v 0 2 at
t 1 2
dt x0 0
For particle in uniformly accelerated rectilinear motion, the acceleration
xparticle
ofxthe 0 v0 t is2 constant.
1 at 2
v 2 v02 ax x0
v x
dv
v a constant v dv a dx 1
2
dx v0 x0
v 2
v02 2 a x x0
New Section 1 Page 2
Situation 1
Sunday, 6 September 2020
11:26 PM
A motorcycle at a gasoline station
stays there for 10 minutes after his
buddy in a car passes at an average
speed of 40 mph.
a) How long will it take for the
motorcycle at an average speed of
50 mph to reach his buddy’s car.?
b) What must be the total distance
travelled by the motorcycle to
up.?
New Section 1 Page 3
Situation 2
Sunday, 6 September 2020
11:28 PM
A truck traveling along a straight road at speed of 20 kph, increases its
speed to 120 kph in 15 sec.
a) What is the truck's acceleration?
b) Determine the distance travelled?
New Section 1 Page 4
Situation
Monday, 7 September 2020
12:03 AM
An automobile moving at a constant
velocity of 15 m/s passes a gasoline
station. Two seconds later, another
automobile leaves the gasoline station
and accelerates at a constant rate of 2
m/s2. How soon will the second
automobile overtake the first?
16.787 s
New Section 1 Page 5
Situation
Monday, 7 September 2020
12:09 AM
A boatman rows to a place 48 miles
distant and back in 14 hours but find
that he can row 4 miles with the
stream in the same time as 3 miles
against the stream. Find the rate of the
stream.
1mph
New Section 1 Page 6
Situation
Monday, 7 September 2020
12:11 AM
A man driving his car at a constant
speed of 42 mph suddenly sees a cow
crossing the road 60 ft ahead. At what
constant deceleration ( in ft/s2) is
required to avoid hitting the animal?
Assume a reaction time of 0.3 seconds
before the man applied the brake.
45.695
New Section 1 Page 7
Situation 3
Monday, 7 September 2020
12:00 AM
A stone is thrown vertically upward
and returns to earth in 12 seconds
A. Determine its initial velocity.
B. How high did it go?
C. At what time did it travel until it
reaches the highest point?
58.86 176.58 6
New Section 1 Page 8
Monday, 7 September 2020
12:15 AM
A ball is thrown vertically into the air
at 120 m/s. After 3 seconds, another
ball is thrown vertically. What is the
velocity must the second ball have to
pass the first ball at 100 m from the
ground?
105.89
New Section 1 Page 9
Monday, 7 September 2020
12:18 AM
A ball is thrown vertically upwatd from
the ground and a student gazing out of
the window sees it moving upward
him at 5 m/s. The window is 10 m
the ground. How high does the ball go
above the ground?
11.3
New Section 1 Page 10
Monday, 7 September 2020
12:21 AM
A wrench is dropped from the top of a
tower 100 m high at the same instant a
ball is thrown upward from the ground.
If the two items meet each other at a
point 60 m above the ground.
Determine the initial velocity of the
35.02
New Section 1 Page 11
Monday, 7 September 2020
12:23 AM
A man dropped a stone into a well.
Four seconds later the sound of a
water splash is heard. Assuming soud
travels at a speed of 330 m/s,
determine how deep is the well.
70.34
New Section 1 Page 12
Monday, 7 September 2020
12:25 AM
A workman drops a wrench from the
roof of a tall building 90 m above the
street and at the same instant shouts a
warning to men below. If sound travels
342 m/s, how long after the warning is
heard below does the wrench strike?
4.02s
New Section 1 Page 13
Rectilinear Motion with Variable Acceleration
Sunday, 6 September 2020
11:21 PM
New Section 1 Page 14
Monday, 7 September 2020
12:31 AM
The position of a particle along a
straight line is given by
s = t3 - 9t 2 + 15t.
a) Determine the velocity when t = 10
b) What is the acceleration when t = 10
sec?
135 42
New Section 1 Page 15
Monday, 7 September 2020
12:32 AM
The rectilinear motion of a particle is
given by s = v2 – 9 where s in meter and
v in m/s. When t = 0, s = 0 and v = 3m/s
a) Determine the particle’s velocity when
= 2 sec.
b) What is the distance traveled at t = 3
sec?
4
11.25
New Section 1 Page 16
Monday, 7 September 2020
12:42 AM
The velocity of a particle is governed
by the relation v= 2 - 4t + 5t^3/2 where
is in seconds and v in m/s. When t = 0, s
= 3m.
a. Determine the particle's position
when t = 3 seconds.
b. Determine the particle's
when t = 3 seconds
22.2
9
New Section 1 Page 17
Monday, 7 September 2020
12:49 AM
Starting from rest, a bicyclist travels
around a horizontal circular path of
radius 10, at a speed v=0.09t 2 + 0.1t.
a) Determine the magnitude of his
when he traveled a distance of 3 m.
b) Determine the magnitudes of his
acceleration when he has traveled a
distance of 3 m.
1.96
0.93 (resultant)
New Section 1 Page 18
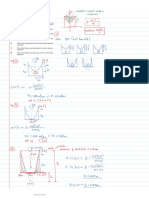
Graphical Solution of Rectilinear Motion Problems
Monday, 7 September 2020
12:56 AM
Graphical Solution of Rectilinear-
Motion Problems
• Given the x-t curve, the v-t curve is equal to
the x-t curve slope.
• Given the v-t curve, the a-t curve is equal to
the v-t curve slope.
• Given the a-t curve, the change in velocity between t1 and t2 is
equal to the area under the a-t curve between t1 and t2.
• Given the v-t curve, the change in position between t1 and t2 is
equal to the area under the v-t curve between t1 and t2.
New Section 1 Page 19
Monday, 7 September 2020
12:58 AM
A subway car leaves station A; it gains speed at the
rate of 4 ft/s2 for 6 s and then at the rate of 6ft/s 2
until it has reached the speed of 48 ft/s. The car
maintains the same speed until it approaches station
B; brakes are then applied, giving the car a constant
deceleration and bringing it to a stop in 6 seconds.
The total running time from A to B is 40s.. Draw the
a-t, v-t, and x-t curves, and determine the distance
between stations A and B.
New Section 1 Page 20
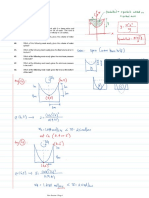
Monday, 7 September 2020
12:59 AM
A car starts from rest and reaches a speed of 48m/s
in 15 sec. The acceleration increases from zero
uniformly with time for the first 6 seconds after which
it remains constant.
a. What is the constant acceleration
b. What is the velocity after 6 seconds
c. What is the distance traveled in 15 seconds
4
12
294
New Section 1 Page 21
Monday, 7 September 2020
1:32 AM
A car accelerates from intial veloctiy of 10 m/s. The
acceleration is increasing uniformly from zero to 8
m/s2 in 6 seconds. During the next 2 seconds, the car
decelerates at a constant rate of 2 m/s2.
a. What is the velocity after 8 seconds
b. Determine the total distance traveled after 8
seconds.
30
196
New Section 1 Page 22
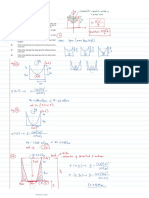
Monday, 7 September 2020
8:52 AM
A car starting from rest accelerates uniformly from
zero at B to 3 m/s2 for 5 seconds at C, then
decelerates uniformly at 2 m/s2 and stop at D.
Determine the time elapsed the car gas traveled from
B to D.
8.75 s
New Section 1 Page 23
Monday, 7 September 2020
9:15 AM
A subway train travels between two of its
station stops with the acceleration schedule
shown.
18. Determine the velocity after 12 sec.
a. 20 m/s c. 12 m/s
b. 8 m/s d. 0 m/s
19. Determine the time interval “t” during the
brakes to a stop with deceleration of 2m/s 2.
a. 4 sec c. 8 sec
b. 10 sec d. 6 sec
20. Determine the distance between stations.
a. 614 m c. 461 m
b. 146 m d. 416 m
New Section 1 Page 24
Projectile Motion
Monday, 7 September 2020
9:00 AM
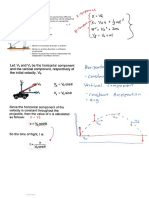
• Rectangular components particularly effective
when component accelerations can be integrated
independently, e.g., motion of a projectile,
a x x 0 a y y g a z z 0
with initial conditions,
Integrating twice yields
x0 y 0 z 0 0 v x 0 , v y 0 , v z 0 0
• Motion in horizontal direction is uniform.
• Motion in vertical direction is uniformly
accelerated.
• Motion of projectile could be replaced by two
independent rectilinear motions. v v
x x 0 0 gt
vy vy vz 0
x v x 0 t
y v y y 12 gt 2
0
z0
New Section 1 Page 25
New Section 1 Page 26
New Section 1 Page 27
You might also like
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Final Requirement On Ce 523: Situation IDocument4 pagesFinal Requirement On Ce 523: Situation ICzindy MoradosNo ratings yet
- Cee 109 - First ExamDocument43 pagesCee 109 - First ExamRonald Renon QuiranteNo ratings yet
- Assignment TemplateDocument3 pagesAssignment TemplateAina Margauxe JacintoNo ratings yet
- Math Samples PDFDocument1 pageMath Samples PDFArwin VillegasNo ratings yet
- Engineering Economy: Ma. Leona Maye B. Pepito, MEDocument72 pagesEngineering Economy: Ma. Leona Maye B. Pepito, MELouie Ludeña VillegasNo ratings yet
- Evaluation Exam 1Document5 pagesEvaluation Exam 1MICHAEL CORETICONo ratings yet
- May 2005 Board ExamDocument6 pagesMay 2005 Board ExamAndrei AlidoNo ratings yet
- A Closed Cylindrical Tank With Axis VerticalDocument8 pagesA Closed Cylindrical Tank With Axis VerticalVini Marie MadrigalNo ratings yet
- CE Practice ProblemsDocument5 pagesCE Practice ProblemsLyra GurimbaoNo ratings yet
- Design of Doubly Reinf and - T-BeamsDocument13 pagesDesign of Doubly Reinf and - T-BeamsGrace Ann CabanbanNo ratings yet
- Q3Document4 pagesQ3Ritsu Tainaka0% (1)
- Umay DesignDocument55 pagesUmay DesignMhel CenidozaNo ratings yet
- Ce0061 Professional Course 4 - (Specialized 2) Ste Track: Prestressed Concrete DesignDocument40 pagesCe0061 Professional Course 4 - (Specialized 2) Ste Track: Prestressed Concrete DesignjerichoNo ratings yet
- Chap-1Revised and FinalDocument35 pagesChap-1Revised and Finalshiva100% (1)
- 2.probable Error Item No. 1 2 3Document7 pages2.probable Error Item No. 1 2 3Elyse LedesmaNo ratings yet
- Unsolved Problems (Math)Document2 pagesUnsolved Problems (Math)Chan FamilyNo ratings yet
- Ce1 Compilation of LessonsDocument107 pagesCe1 Compilation of LessonsFides CastelltortNo ratings yet
- Evals in Surveying and Transpo Answer SheetDocument11 pagesEvals in Surveying and Transpo Answer SheetYedda M IlaganNo ratings yet
- Statistics: Measure of Central Tendency MeanDocument25 pagesStatistics: Measure of Central Tendency MeanjlNo ratings yet
- Keyanalytic ExamDocument5 pagesKeyanalytic ExamIvy Vanessa OlapNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Rigid Bodies CE 002 (TIP Reviewer)Document7 pagesDynamics of Rigid Bodies CE 002 (TIP Reviewer)James LindoNo ratings yet
- Highway and Railroad Engineering: Compound CurvesDocument9 pagesHighway and Railroad Engineering: Compound CurvesDirect XNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 1 Surveying Instruments and Tools: ObjectiveDocument11 pagesActivity No. 1 Surveying Instruments and Tools: ObjectiverafaelNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - MeasurementsDocument6 pagesAssignment 1 - MeasurementsIrish Joy Gales GanzanNo ratings yet
- Geometry 100-200Document14 pagesGeometry 100-200Franz Anfernee Felipe GenerosoNo ratings yet
- HydraulicsDocument12 pagesHydraulicsMugiwara Sparrow0% (1)
- Le1 12102022 PMDocument1 pageLe1 12102022 PMRyiehmNo ratings yet
- 112Document10 pages112Memo LyNo ratings yet
- Probability, Surveyng, Transpotation EngringDocument13 pagesProbability, Surveyng, Transpotation EngringCaro Kan LopezNo ratings yet
- 4 PrintDocument8 pages4 PrintsubyNo ratings yet
- Module 2 TranspoDocument95 pagesModule 2 TranspomarcusluismacusiNo ratings yet
- Practice Exam in Survurveying Converted 1Document5 pagesPractice Exam in Survurveying Converted 1Darlene Mae VenturanzaNo ratings yet
- Sison, Marcus Ceazar - Module 3 - SurveyingDocument3 pagesSison, Marcus Ceazar - Module 3 - SurveyingMarcus Ceazar SisonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 - Curvature and Refraction, Measuring Vertical DistancesDocument10 pagesLesson 8 - Curvature and Refraction, Measuring Vertical DistancesDumalag Banaay JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Activity # 3 Trigonometry-MathematicsDocument4 pagesActivity # 3 Trigonometry-MathematicsEurydiceNo ratings yet
- Circulo de Morh PytelDocument51 pagesCirculo de Morh PytelJohn Royer Araúz FuentesNo ratings yet
- Ce353 Part 3 HydrologyDocument24 pagesCe353 Part 3 HydrologyAnnie TheExplorerNo ratings yet
- Probability Review NotesDocument3 pagesProbability Review NotesNaigell SolomonNo ratings yet
- 16Document1 page16Mark Ruby Opawon100% (1)
- HGE#003-Hydraulics Engineering 3Document3 pagesHGE#003-Hydraulics Engineering 3Kim Ryan PomarNo ratings yet
- SolutionDocument13 pagesSolutionAngelo CompetenteNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Distance Correction Problem SolvingDocument1 pageLecture 1 Distance Correction Problem SolvingErych E. SinadNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials 1 PDFDocument3 pagesStrength of Materials 1 PDFMaxNo ratings yet
- Ce234 Topic 09-10Document58 pagesCe234 Topic 09-10Nicholas Bonn SingNo ratings yet
- Chap12 (3) 3Document65 pagesChap12 (3) 3Vince HarrisNo ratings yet
- Algebra Exam ContributionDocument2 pagesAlgebra Exam ContributionDan CasuraoNo ratings yet
- Pamantasan NG Lungsod NG ValenzuelaDocument2 pagesPamantasan NG Lungsod NG ValenzuelaDiane de OcampoNo ratings yet
- 7 AREA by DMD and DPDDocument4 pages7 AREA by DMD and DPDBryanHarold BrooNo ratings yet
- SIM CEE 108 Week 1-3 PDFDocument28 pagesSIM CEE 108 Week 1-3 PDFIah Belleza MedelNo ratings yet
- English Units SI UnitsDocument4 pagesEnglish Units SI UnitsChristian Jay GamboaNo ratings yet
- Module 7Document16 pagesModule 7Be LoveNo ratings yet
- Structural Steel Design: Design of Tension Members 2: Universal College of ParañaqueDocument36 pagesStructural Steel Design: Design of Tension Members 2: Universal College of ParañaqueFritz LuzonNo ratings yet
- Geotech-1 Virtual Class 2021Document6 pagesGeotech-1 Virtual Class 2021Naigell SolomonNo ratings yet
- Shuffled FinalDocument54 pagesShuffled FinalAllen Robert SornitNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 - P3 - SolutionDocument6 pagesQuiz 1 - P3 - SolutionJohn Saniel J. EstacionNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 2 Compound CurveDocument12 pagesProblem Set 2 Compound Curvezhwan Anwar nooriNo ratings yet
- Rate of ChangeDocument14 pagesRate of ChangejennaNo ratings yet
- Kinematics 2Document3 pagesKinematics 2harish raghavendarNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics 4 Discussion PDFDocument16 pagesFluid Mechanics 4 Discussion PDFjlNo ratings yet
- A) B) C) D) E) 0 A:: LL .LRDocument3 pagesA) B) C) D) E) 0 A:: LL .LRjlNo ratings yet
- Probability-2: Prepared By: Engr. Jude L. Rosales, CE July 15, 2020Document22 pagesProbability-2: Prepared By: Engr. Jude L. Rosales, CE July 15, 2020jl100% (1)
- Statistics: Measure of Central Tendency MeanDocument25 pagesStatistics: Measure of Central Tendency MeanjlNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics 1 Discussion PDFDocument6 pagesFluid Mechanics 1 Discussion PDFjlNo ratings yet
- RCD LectureDocument7 pagesRCD LecturejlNo ratings yet
- Probability Virtual Review (November 2020)Document3 pagesProbability Virtual Review (November 2020)jlNo ratings yet
- Probability: Prepared By: Engr. Jude L. Rosales, CE July 14, 2020Document19 pagesProbability: Prepared By: Engr. Jude L. Rosales, CE July 14, 2020jlNo ratings yet
- Dynamics 2 DiscussionDocument24 pagesDynamics 2 DiscussionjlNo ratings yet
- Dynamics 3 Discussion PDFDocument21 pagesDynamics 3 Discussion PDFjlNo ratings yet
- Dynamics 1 DiscussionDocument27 pagesDynamics 1 DiscussionjlNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Engineering 1 DiscussionDocument45 pagesGeotechnical Engineering 1 Discussionjl86% (7)
- Prepared By: Engr. Jude L. RosalesDocument3 pagesPrepared By: Engr. Jude L. RosalesjlNo ratings yet
- Dynamics 2 DiscussionDocument24 pagesDynamics 2 DiscussionjlNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Engineering DISCUSSION SEPTEMBER 24Document45 pagesGeotechnical Engineering DISCUSSION SEPTEMBER 24jlNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics 1 Discussion PDFDocument6 pagesFluid Mechanics 1 Discussion PDFjlNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics 4 DiscussionDocument16 pagesFluid Mechanics 4 DiscussionjlNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics 3 DiscussionDocument14 pagesFluid Mechanics 3 DiscussionjlNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics 2 DiscussionDocument9 pagesFluid Mechanics 2 DiscussionjlNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics 2 Continuation DiscussionDocument7 pagesFluid Mechanics 2 Continuation DiscussionjlNo ratings yet
- AspenTech Awareness & Workshop Ebook - 2020 PDFDocument20 pagesAspenTech Awareness & Workshop Ebook - 2020 PDFĐậu BắpNo ratings yet
- Instability of Slender Concrete Deep BeamDocument12 pagesInstability of Slender Concrete Deep BeamFrederick TanNo ratings yet
- Predicates and ArgumentsDocument4 pagesPredicates and ArgumentsOanh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Teacher Survey - Outdoor Classroom Feedback: Please Circle All That ApplyDocument3 pagesTeacher Survey - Outdoor Classroom Feedback: Please Circle All That ApplyBrooke Doran RoeNo ratings yet
- Upfc PlacementDocument0 pagesUpfc PlacementVamsi KumarNo ratings yet
- Visibility of NursesDocument17 pagesVisibility of NursesLuke ShantiNo ratings yet
- Mutant ChroniclesDocument3 pagesMutant ChroniclesZoth BernsteinNo ratings yet
- BarDocument1 pageBarJoannalyn Libo-onNo ratings yet
- How To Plant Thoughts in Her Mind Ross Jeffries: TranscriptDocument12 pagesHow To Plant Thoughts in Her Mind Ross Jeffries: TranscriptAlcajNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledapi-223522684No ratings yet
- Assignment 1 To 7Document23 pagesAssignment 1 To 7KashishNo ratings yet
- TP PortalDocument25 pagesTP PortalSurendranNo ratings yet
- BC Caribou Recovery Program Stakeholders Teleconference MinutesDocument5 pagesBC Caribou Recovery Program Stakeholders Teleconference MinutesRevelstoke MountaineerNo ratings yet
- Cement Grouted Rock BoltsDocument28 pagesCement Grouted Rock BoltsBhaskar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Transfer Request 2022 - CBOA CHENNAIDocument5 pagesTransfer Request 2022 - CBOA CHENNAIVignesh NarayananNo ratings yet
- 978-0393617542 Research MethodsDocument18 pages978-0393617542 Research MethodsReccebacaNo ratings yet
- TelemetryDocument8 pagesTelemetryKristin WiseNo ratings yet
- Resume Arun.A: Career ObjectiveDocument2 pagesResume Arun.A: Career ObjectiveajithkumarNo ratings yet
- Inertia Physics: Defi Ni Ti OnDocument2 pagesInertia Physics: Defi Ni Ti OnSentoash NaiduNo ratings yet
- Functional Plant Manager 2. Geographical Vice PresidentDocument5 pagesFunctional Plant Manager 2. Geographical Vice PresidentVic FranciscoNo ratings yet
- EHS Audit - Review PaperDocument5 pagesEHS Audit - Review PaperYousef OlabiNo ratings yet
- 990XP Bandit ChipperDocument5 pages990XP Bandit ChipperFrancisco ConchaNo ratings yet
- Language - Introduction To The Integrated Language Arts CompetenciesDocument7 pagesLanguage - Introduction To The Integrated Language Arts CompetenciesHari Ng Sablay100% (1)
- Children Literature Evaluation Form I Aint Gonna Paint No MoreDocument4 pagesChildren Literature Evaluation Form I Aint Gonna Paint No Moreapi-548506674No ratings yet
- GW1101-1DI (3IN1) DatasheetDocument6 pagesGW1101-1DI (3IN1) DatasheetGina HuachoNo ratings yet
- Sharp MX M283 363 453 503 PDFDocument404 pagesSharp MX M283 363 453 503 PDFAlejandro Barraza100% (2)
- IQX Controller & I/O ModulesDocument12 pagesIQX Controller & I/O ModulesAnonymous XYAPaxjbYNo ratings yet
- VW 60330 2009 12 eDocument29 pagesVW 60330 2009 12 eAmir Borhanipour100% (1)
- Tahmina Ferdousy Jhumu: HND Btec Unit 15 Psychology For Health and Social CareDocument29 pagesTahmina Ferdousy Jhumu: HND Btec Unit 15 Psychology For Health and Social CareNabi BoxNo ratings yet
- Too Early! by Anton Pavlovich ChekhovDocument4 pagesToo Early! by Anton Pavlovich Chekhovapi-19787590No ratings yet