Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Types of shock surgery updates
Uploaded by
skOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Types of shock surgery updates
Uploaded by
skCopyright:
Available Formats
Surgery
Updates
RECENT TOPICS OF 2017-18 EXAMS
PAGE
1
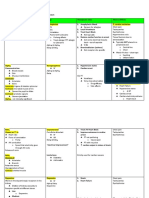
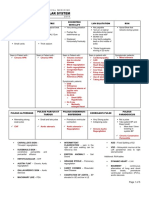
TYPES OF SHOCK
P
Types Causes Pathophysiology Clinical feature Treatment
Afterlod
R
ES
Hypovolemic Hemorrhage, Preload ↓ HR ↑ Prevent losses,
Dehydration Contractility normal or ↑ BP ↓ Secure large bore IV access, Fluid
Afterlod (SVR) ↑ Cardiac output ↓ rescucitation with crystalloids
CRT Delayed,
Extremities cool & pale
i
Weak thready pulse
AT
Distributive M
1. Septic Infections, sepsis Preload ↓ HR ↑ IV Antibiotics, Fluids
Contractility normal or ↓ BP ↓ IV Noradrinaline .... drug of choice
afterload ↓
PD Cardiac output ↓
CRT Flash/delayed
E
Extremities warm & pink
2. Anaphylactic Anaphylaxis Preload ↓ HR ↑ IV Epinephrine, Fluids
Contractility variable BP ↓
Afterlod ↑↓ Cardiac output ↓
CRT Flash/delayed
S
Extremities warm
U
TU
3. Neurogenic Spinal cord injury, Preload ↓ HR ↓ (BRADYCARDIA) High flow O2,
Traumatic brain Contractility normal BP ↓ Fluid rescucitation
injury (TBI) Afterlod (SVR) ↓
Loss of sympathetic tone
Cardiac output ↓
CRT Flash/normal
Vassopressors
P
Extremities warm
Cardiogenic Myocarditis,
Dysrhythmia
Preload ↓
Contractility ↓
HR ↑
BP ↓
Inotropes (Inj Dopamine)
Cautious use of fluids, ECMO
P
Afterlod (SVR) Cardiac output ↓
N
↑ (Rt ventricular)
↓ (Left ventricular)
CRT delayed
L
CE
Obstructive Tamponade,
Tension
Preload ↓
Contractility normal
HR ↑
BP ↓
Pericardiocentasis,
chest tube
E
pneumothorax, Afterlod (SVR) ↑ Cardiac output ↓
pulmonary
embolus,
CRT Delayed
Extremities cool
M
chest trauma
RE
Dissociative CO poisoning,
Cyanide
variable HR ↑
BP Normal or ↑
Antidotes,
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy,
E
Cardiac output ↑
CRT normal
Extremities normal
N
T
These Updates are from Primes Supplement 2018
You might also like
- Pa ToDocument2 pagesPa Tokz392No ratings yet
- Myocardial Infarction (MI) ComplicationsDocument4 pagesMyocardial Infarction (MI) ComplicationsPäw YusophNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Concept MapDocument1 pageHypertension Concept Mapjyd parreñoNo ratings yet
- Ischemic Heart Disease DrugsDocument3 pagesIschemic Heart Disease DrugsRiyam WannasNo ratings yet
- Cardiac DisordersDocument4 pagesCardiac DisordersEUNICE CORILLONo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis and Care Plan for Headache PatientDocument10 pagesNursing Diagnosis and Care Plan for Headache PatientZaky IbadurrahmanNo ratings yet
- Antianginal Drugs: Classes Therapeutic Uses MOA Adverse EffectsDocument3 pagesAntianginal Drugs: Classes Therapeutic Uses MOA Adverse EffectsNadhirah ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- 6.22 Urinary SystemDocument9 pages6.22 Urinary SystemGhianx Carlox PioquintoxNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord InjuryDocument1 pageSpinal Cord Injurymaglangitjoannamarie1920No ratings yet
- Cardiac Output (Page Print 1-5)Document6 pagesCardiac Output (Page Print 1-5)hihariv794No ratings yet
- Darunday NCM 116aDocument3 pagesDarunday NCM 116aEzra Miguel DarundayNo ratings yet
- Left Sided Heart Failure Dyspnea: Chest PainDocument2 pagesLeft Sided Heart Failure Dyspnea: Chest PainnikinoonaNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource WasDocument2 pagesThis Study Resource WasKimberly WhitesideNo ratings yet
- ST Elevation MI, STEMIDocument3 pagesST Elevation MI, STEMInmyza89No ratings yet
- Sudden Cardiac Death: Ischaemic Heart DiseaseDocument4 pagesSudden Cardiac Death: Ischaemic Heart Diseasenmyza89No ratings yet
- Hypercholesterolemia Men ( 45 Years Old) Women ( 55 Years Old) Cigarette Smoking Alcoholism Diabetes Mellitus Obesity Physical Inability Sodium Intake HereditaryDocument3 pagesHypercholesterolemia Men ( 45 Years Old) Women ( 55 Years Old) Cigarette Smoking Alcoholism Diabetes Mellitus Obesity Physical Inability Sodium Intake HereditaryMichelle Gliselle Guinto MallareNo ratings yet
- ArrhysmiasDocument1 pageArrhysmiasBell GatesNo ratings yet
- Note 2 Dec 2022Document3 pagesNote 2 Dec 2022Queen ShNo ratings yet
- HTN PathoDocument1 pageHTN PathoShelley Jade MenorNo ratings yet
- HyperpituitarismDocument3 pagesHyperpituitarismGerardLumNo ratings yet
- EMCrit RACC Pulmonary Embolism PathwayDocument1 pageEMCrit RACC Pulmonary Embolism PathwayhmsptrNo ratings yet
- Patient Information: Location DateDocument2 pagesPatient Information: Location DateGisselle PauloNo ratings yet
- What Is It? Risk Factors/ Causes My Columns For My Cardiac Spreadsheet 2 Unique Symptoms Heart Failure (General)Document3 pagesWhat Is It? Risk Factors/ Causes My Columns For My Cardiac Spreadsheet 2 Unique Symptoms Heart Failure (General)Aji PicanteNo ratings yet
- ShockDocument30 pagesShockLập Trương Minh QuốcNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Diagram of Congestive Heart FailureDocument3 pagesPathophysiology Diagram of Congestive Heart Failurea_samiane64% (11)
- Heartsound MurmurDocument2 pagesHeartsound MurmurDya AndryanNo ratings yet
- Blue Print Chapters 15-16 Autonomic NSDocument10 pagesBlue Print Chapters 15-16 Autonomic NSMarisella ReadonNo ratings yet
- Shock AmbossDocument40 pagesShock AmbossAshraf AlbhlaNo ratings yet
- Approach To Chest Pain 1Document5 pagesApproach To Chest Pain 1Sonu CanNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure (Page Print 1-4)Document4 pagesBlood Pressure (Page Print 1-4)hihariv794No ratings yet
- Mitral Valve Stenosis: Peripheral OrgansDocument1 pageMitral Valve Stenosis: Peripheral OrgansPäw YusophNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology CHFDocument3 pagesPathophysiology CHFKit LaraNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart FailureDocument13 pagesCongestive Heart Failurektae337No ratings yet
- NotesDocument6 pagesNotesCarl JuanNo ratings yet
- How To Deal Acute Pulmonary OedemDocument23 pagesHow To Deal Acute Pulmonary Oedemdhika2496No ratings yet
- Multisystem ProblemsDocument90 pagesMultisystem ProblemsAlexander Blanche PajelaNo ratings yet
- Hytension For 16 Years Men (64 Years Old) Cigarette Smoking (32 Pack Years) Alcoholic Drinker For 32 Years Fond of Eating Fatty Foods Physical Inability Sodium Intake HereditaryDocument3 pagesHytension For 16 Years Men (64 Years Old) Cigarette Smoking (32 Pack Years) Alcoholic Drinker For 32 Years Fond of Eating Fatty Foods Physical Inability Sodium Intake HereditaryJohn Paulo CatacutanNo ratings yet
- AneurysmDocument11 pagesAneurysmNashrah HusnaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Medicine CVS Tabulated 2019Document5 pagesClinical Medicine CVS Tabulated 2019Justin TayabanNo ratings yet
- Cyanotic Congenital Heart Diseases, Etc.Document12 pagesCyanotic Congenital Heart Diseases, Etc.sarguss14100% (2)
- Generic Patient Report FormDocument1 pageGeneric Patient Report FormEssie MohammedNo ratings yet
- Acute Heart Failure PDFDocument18 pagesAcute Heart Failure PDFRiaak ImNo ratings yet
- Valvular DiseaseDocument29 pagesValvular DiseasegeminisycoraxNo ratings yet
- Course Guide Learning - CardiologyDocument1 pageCourse Guide Learning - CardiologyZahra MotorwalaNo ratings yet
- 07 Heart Pathology (Part 1 and 2)Document13 pages07 Heart Pathology (Part 1 and 2)carlgangcaNo ratings yet
- Recog Shock FlowchartDocument1 pageRecog Shock FlowchartbrendaNo ratings yet
- Drugs for Heart FailureDocument39 pagesDrugs for Heart FailureOngKahYeeNo ratings yet
- PT Management & Problems of The CV System - Part 3 Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesPT Management & Problems of The CV System - Part 3 Cheat SheetGayle MarieNo ratings yet
- Over Weight / Obesity Stress Smoking Cocaine Use / Abuse Sedentary Lifestyle Diet in Fats, Na, CholesterolDocument4 pagesOver Weight / Obesity Stress Smoking Cocaine Use / Abuse Sedentary Lifestyle Diet in Fats, Na, Cholesterollouije_mombael2000No ratings yet
- MS PentaDocument12 pagesMS PentalalaineNo ratings yet
- 7• Hyperaldosteronism [Illustrations Key]Document2 pages7• Hyperaldosteronism [Illustrations Key]Meng BekNo ratings yet
- Origination of Heart Sounds: Department of Physical Diagnostics 1 Teaching Hospital Henan Medical UniversityDocument6 pagesOrigination of Heart Sounds: Department of Physical Diagnostics 1 Teaching Hospital Henan Medical Universityapi-19916399No ratings yet
- IsoketDocument2 pagesIsoketJaessa Feliciano100% (1)
- IsoketDocument2 pagesIsoketJaessa FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 2Document2 pagesAnatomy 2Ahmed AdelNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 - Med SurgDocument7 pagesNCM 112 - Med SurgKierzteen Brianna TaromaNo ratings yet
- Syok Kardiogenik Dr. Rani Maliawan, SP JPDocument59 pagesSyok Kardiogenik Dr. Rani Maliawan, SP JPLuh Leni AriniNo ratings yet
- 6.6 CardiovascularDocument9 pages6.6 CardiovascularGhianx Carlox PioquintoxNo ratings yet
- CHNDocument28 pagesCHNVed TiwariNo ratings yet
- Derma LMRDocument11 pagesDerma LMRadiNo ratings yet
- Opthalmology Short NotesDocument14 pagesOpthalmology Short NotesChristine Nancy Ng100% (1)
- Surgery EssenceDocument31 pagesSurgery EssenceNikhilBhattNo ratings yet
- Medicine LMRDocument24 pagesMedicine LMRadiNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry One Liner PDFDocument13 pagesBiochemistry One Liner PDFMinaz PatelNo ratings yet
- XTRA Final PunchDocument314 pagesXTRA Final Punchsk100% (1)
- Patho LMRDocument16 pagesPatho LMRskNo ratings yet
- Forensic Medicine: ST STDocument17 pagesForensic Medicine: ST STAmaresha PatilNo ratings yet
- Ent PointsDocument9 pagesEnt PointsSaiNo ratings yet
- Psychiatry: IQ Range Level of IntelligenceDocument9 pagesPsychiatry: IQ Range Level of IntelligenceskNo ratings yet
- Davinci Medical AcademyDocument15 pagesDavinci Medical AcademyskNo ratings yet
- Ortho ShortDocument13 pagesOrtho Shortsubramaniam krishnamoorthiNo ratings yet
- Gen Surgery LMRDocument32 pagesGen Surgery LMRskNo ratings yet
- Last Minute RevisionDocument229 pagesLast Minute RevisionSelvaArockiamNo ratings yet
- Anatomy: ST ND TH TH Th. RD TH TH THDocument11 pagesAnatomy: ST ND TH TH Th. RD TH TH THskNo ratings yet
- Skin & STDDocument8 pagesSkin & STDskNo ratings yet
- Physiology One LinersDocument10 pagesPhysiology One LinersadiNo ratings yet
- Davinci Medical AcademyDocument10 pagesDavinci Medical Academysk100% (2)
- Surgery One Liners Imp MciDocument41 pagesSurgery One Liners Imp Mciadi100% (2)
- Sweating, Salivation, Diarrhea, Bradycardia - Diagnosis Is - OPC PoisoningDocument2 pagesSweating, Salivation, Diarrhea, Bradycardia - Diagnosis Is - OPC PoisoningskNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic One Liners Mci ImpDocument15 pagesOrthopedic One Liners Mci ImpadiNo ratings yet
- Davinci Medical AcademyDocument38 pagesDavinci Medical AcademyskNo ratings yet
- Davinci Medical AcademyDocument13 pagesDavinci Medical AcademyskNo ratings yet
- Davinci Medical AcademyDocument12 pagesDavinci Medical AcademyskNo ratings yet
- Pathology Mci One Liners MCQDocument21 pagesPathology Mci One Liners MCQadiNo ratings yet
- Davinci Medical AcademyDocument26 pagesDavinci Medical Academysk100% (2)
- Radiology Mci One Liners MCQDocument6 pagesRadiology Mci One Liners MCQadi100% (1)
- Davinci Medical AcademyDocument9 pagesDavinci Medical AcademyskNo ratings yet
- Davinci Medical Academy - Microbiology Review: RNA Viruses, EBV, Malaria, Bacterial Infections & MoreDocument14 pagesDavinci Medical Academy - Microbiology Review: RNA Viruses, EBV, Malaria, Bacterial Infections & MoreskNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis of Nephrotic SyndromeDocument33 pagesPathogenesis of Nephrotic SyndromeHari Mukti100% (1)
- Tinea CorporisDocument7 pagesTinea CorporisAziza Ulfie WijayaniNo ratings yet
- Delusional DisorderDocument12 pagesDelusional Disorderayyappan.ashok6713100% (2)
- Typhoid FeverDocument4 pagesTyphoid FeverBernice GyapongNo ratings yet
- Compendium of Instructions For Covid-19 Testing LaboratoryDocument176 pagesCompendium of Instructions For Covid-19 Testing LaboratoryasanyogNo ratings yet
- 1 Persiapan Penanganan Bayi Baru LahirDocument54 pages1 Persiapan Penanganan Bayi Baru LahirRosa NinmusuNo ratings yet
- Isolation Guidelines PDFDocument209 pagesIsolation Guidelines PDFlimiya vargheseNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument6 pagesNCPAngelaTrinidadNo ratings yet
- PDF JnFmyW1qOR70whlpf4M2Document2 pagesPDF JnFmyW1qOR70whlpf4M2SAI SMARAN INTURINo ratings yet
- Cancer Rehabilitation AssessmentDocument21 pagesCancer Rehabilitation AssessmentLiliana Carolina Guzman RiosNo ratings yet
- Case Study PneumoniaDocument8 pagesCase Study PneumoniaThesa FedericoNo ratings yet
- Migraine DiaryDocument6 pagesMigraine DiaryhumphryNo ratings yet
- Toxin Botulinum For StrabismusDocument8 pagesToxin Botulinum For StrabismusRay MaudyNo ratings yet
- Sideroblastic Anemia Guide: Causes, Symptoms & TypesDocument18 pagesSideroblastic Anemia Guide: Causes, Symptoms & TypesSonam Joshi100% (2)
- Class Presentation ON BPH: Presented By: Ruchika Kaushal M.Sc. Nursing 1 YearDocument31 pagesClass Presentation ON BPH: Presented By: Ruchika Kaushal M.Sc. Nursing 1 YearRuchika KaushalNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Tenggorokan Dan Penerapan Klinisnya: Dr. Adi Arianto, M. BiomedDocument39 pagesAnatomi Tenggorokan Dan Penerapan Klinisnya: Dr. Adi Arianto, M. BiomedAl AdinNo ratings yet
- Krok 1 Stomatology 2012Document22 pagesKrok 1 Stomatology 2012Saaha ParmarNo ratings yet
- Triplixam 10mg - 2-5mg - 10mg Film Coated Tablets (Perindopril Arginine - Indapamide - Amlodipine)Document8 pagesTriplixam 10mg - 2-5mg - 10mg Film Coated Tablets (Perindopril Arginine - Indapamide - Amlodipine)Sze Wei TanNo ratings yet
- Med-surg Restrictive and Obstructive Lung Disease: Key Presentations and TreatmentsDocument11 pagesMed-surg Restrictive and Obstructive Lung Disease: Key Presentations and Treatmentsorganictallgirl50% (2)
- Meningitis MENINGITIS Meningococcal MeningitisDocument46 pagesMeningitis MENINGITIS Meningococcal Meningitistummalapalli venkateswara raoNo ratings yet
- Human Karyotyping Lab Identifies Genetic DisordersDocument7 pagesHuman Karyotyping Lab Identifies Genetic DisordersEditorialranged CartoonistoplaneNo ratings yet
- Leg Ulcer, What Do You Stand byDocument2 pagesLeg Ulcer, What Do You Stand byFree PizzaNo ratings yet
- PATOFISIOLOGI MALARIADocument9 pagesPATOFISIOLOGI MALARIARasyid RidhaNo ratings yet
- NCP GunshotDocument13 pagesNCP GunshotMichael John F. Natividad0% (1)
- Successful Treatment of Multiple Common Warts With Intralesional OzoneDocument6 pagesSuccessful Treatment of Multiple Common Warts With Intralesional OzoneRubensNo ratings yet
- Neuropathic PainDocument40 pagesNeuropathic PainHasmirahNo ratings yet
- Mayo Clinic Consensus Report On Membranous - Nephropathy - Proposal For A Novel ClassificationDocument11 pagesMayo Clinic Consensus Report On Membranous - Nephropathy - Proposal For A Novel ClassificationAnaNo ratings yet
- Bowel Incontinence ConstipationDocument3 pagesBowel Incontinence ConstipationMatty-b AskalaniNo ratings yet
- Doproct Suppository Hydrocortisone Acetate Benzocaine Zinc Oxide IMEKS PHARMA SDN BHD 11sep2017 ENGDocument2 pagesDoproct Suppository Hydrocortisone Acetate Benzocaine Zinc Oxide IMEKS PHARMA SDN BHD 11sep2017 ENGgigiNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Disorder in Postpartum Women - Epidemiology, Clinical Features, Assessment, and Diagnosis PDFDocument14 pagesBipolar Disorder in Postpartum Women - Epidemiology, Clinical Features, Assessment, and Diagnosis PDFdreamingNo ratings yet











































![7• Hyperaldosteronism [Illustrations Key]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/725978840/149x198/433eb3f52c/1713901009?v=1)