0% found this document useful (0 votes)
359 views11 pagesPre Calculus Circles
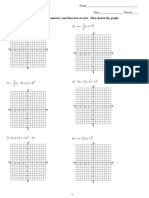
The document contains practice problems identifying the standard and general equations of circles based on given properties such as the center and radius, points the circle passes through, or tangency conditions. The problems cover identifying and sketching circles from equations, finding the standard and general forms of circles given conditions about the center, radius, and tangents/points, and solving systems of equations related to circles.
Uploaded by
Paul Asi HitaliaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
359 views11 pagesPre Calculus Circles
The document contains practice problems identifying the standard and general equations of circles based on given properties such as the center and radius, points the circle passes through, or tangency conditions. The problems cover identifying and sketching circles from equations, finding the standard and general forms of circles given conditions about the center, radius, and tangents/points, and solving systems of equations related to circles.
Uploaded by
Paul Asi HitaliaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd