Professional Documents
Culture Documents
General Psychology Midterm Exam
Uploaded by
SaaB PanaraagCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
General Psychology Midterm Exam
Uploaded by
SaaB PanaraagCopyright:
Available Formats
Musa-ab A.
Panara-ag
BSCA-IV
General Psychology Midterm Exam
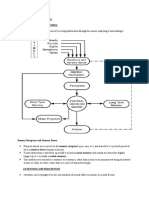
I.
1. Perceptions
2. Thoughts
3. Sense
4. Memories
5. William James
6. Awareness
7. Consciousness
8. Internal
9. External
10. Environment
11. Plans
12. Initiate
13. Execute
13. Conscious
14. Behavior
15. PRECONSCIOUSNESS
16.
17.
18. Altered State of Consciousness
19. Memory
20. Encoding
21. Memory
22. Retrieval
23. Intelligence
24. Take out
25. Learning
II.
KINDS OF LEARNING
1. Classical conditioning
2. Operant Conditioning
3. Cognitive Social Approaches
4.
5. Experience Learning
THEORIES OF INTELLIGENCE
6. PSYCHOMETRICS
7. Cognitive Social Approaches
INTELLIGENCE GIVEN BY STERNBERG
8. Analytical intelligence
9. Creative intelligence
10.
THREE STAGES OF MEMORY
11.
12. Short term memory
13. Long term memory
THE SUBTYPES OF LONG TERM MEMORY
14. Episodic memories
15. Procedural memories
III.
A. BRIEFLY EXPLAIN THE KINDS OF LEARNING
1. Operant Conditioning -is a type of learning in which a voluntary response is strengthened or
weakened , depending on its favorable or unfavorable consequences.
2. Classical conditioning- is a form of learning whereby a conditioned stimulus becomes associated with
an unrelated unconditioned stimulus in order to produce a behavioral response known as a conditioned
response.
3. Cognitive-Social Approches-
4. Observational Learning- Observational learning is learning that occurs through observing the behavior
of others.
5.
B. DIFFERENTIATE THE THREE STAGES OF MEMORY
Sensory memory is understood as the initial, momentary storage of information, lasting only for an
instant while the Short-term memory is the capacity for holding, but not manipulating, a small amount
of information in mind in an active, readily available state for a short period of time. and the Long-term
memory refers to the storage of information over an extended period.
C. BRIEFLY DISCUSS THE EXAMPLES OF ALTERED STATES OF CONSCIOUSNESS
1. Sleep is a condition of body and mind that typically recurs for several hours every night, in which the
nervous system is relatively inactive, the eyes closed, the postural muscles relaxed, and consciousness
practically suspended.
2. HYPNOSIS- came from the Greek god of sleep, Hypnos, which means sleep.
3. MEDITATION is practiced for relaxation. It lowers the rate of metabolism, blood pressure, and muscle
tension and focuses on breathing.
4.
5.
You might also like
- PSY2012 Test 2Document9 pagesPSY2012 Test 2Amanda BartleyNo ratings yet
- School of ThoughtDocument61 pagesSchool of ThoughtRADHIKA JAISWALNo ratings yet
- University of Lagos: Name: Ogunjimi Joel OluseyiDocument12 pagesUniversity of Lagos: Name: Ogunjimi Joel OluseyiIkponmwosa EseosaNo ratings yet
- Advanced General Psychology - I (SPPY101) - Assessment - 1Document4 pagesAdvanced General Psychology - I (SPPY101) - Assessment - 1dilipdts89No ratings yet
- Theories of LearningDocument20 pagesTheories of LearningUzaina QaziNo ratings yet
- SleepDocument3 pagesSleepTONo ratings yet
- 4 TH QRev PERDEVDocument3 pages4 TH QRev PERDEVTristan KyleNo ratings yet
- Learning and Memory UbcomDocument23 pagesLearning and Memory UbcomAdamu IsaNo ratings yet
- MemoryDocument13 pagesMemoryalishbaajaz148No ratings yet
- Soal SAPDocument6 pagesSoal SAPdevinasalmaniaNo ratings yet
- Accelerated Learning and Unlimited Memory Techniques and Strategies: Real Coaching from a Real Expert. Tips & Tricks for Students and AdultsFrom EverandAccelerated Learning and Unlimited Memory Techniques and Strategies: Real Coaching from a Real Expert. Tips & Tricks for Students and AdultsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Biology Investigatory ProjectDocument29 pagesBiology Investigatory ProjectBalaji KNo ratings yet
- Psy 101 All Past Quiz EsDocument28 pagesPsy 101 All Past Quiz EsAsma RafiqNo ratings yet
- Genpsy 1ST SemDocument28 pagesGenpsy 1ST SemAubrey RosalesNo ratings yet
- Intro To Psych L5Document6 pagesIntro To Psych L5Abigail MorfeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Intro-Psyc of Learning StudentDocument54 pagesLecture 1 Intro-Psyc of Learning StudentCherliyntiaNo ratings yet
- General Psychology PPT (2023)Document70 pagesGeneral Psychology PPT (2023)Gatluak Thalow KuethNo ratings yet
- Memory Processes and Learning Theory DR Abeer Almarzouki MD, PHD 2017-2018Document32 pagesMemory Processes and Learning Theory DR Abeer Almarzouki MD, PHD 2017-2018Elyas MehdarNo ratings yet
- Managing and Caring For The SelfDocument33 pagesManaging and Caring For The SelfLea Victoria Pronuevo100% (2)
- CH 7 - Altered States of Consciousness - NotesDocument8 pagesCH 7 - Altered States of Consciousness - NotesEilla Marie GomosNo ratings yet
- PSYC2650 Exam ReviewDocument67 pagesPSYC2650 Exam ReviewSaraNo ratings yet
- HF Subjective Questions 1. Information ProcessingDocument5 pagesHF Subjective Questions 1. Information ProcessingraviNo ratings yet
- CH 06Document104 pagesCH 06BISHALNo ratings yet
- PSY Memory Assignment NewDocument9 pagesPSY Memory Assignment NewFarukIslamNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 7 MemoryDocument7 pagesChapter - 7 Memoryfariha khanNo ratings yet
- Biol/Psy 105: Class 19, MemoryDocument47 pagesBiol/Psy 105: Class 19, MemoryandersonalbertNo ratings yet
- 7 Memory Attention and Mental WorkloadDocument30 pages7 Memory Attention and Mental WorkloadGretchen Laurente100% (4)
- Biological Basis of Memory: Dr. Karrar Husain Moderator: Dr. Piyush P. SinghDocument72 pagesBiological Basis of Memory: Dr. Karrar Husain Moderator: Dr. Piyush P. SinghAshvin WaghmareNo ratings yet
- Stages of Sleep and Sleep DisorderDocument18 pagesStages of Sleep and Sleep DisorderLiya ThaaraNo ratings yet
- Processing Theory by Atkinson and ShiffrinDocument18 pagesProcessing Theory by Atkinson and ShiffrinChrispina SorianoNo ratings yet
- Pyschology: Branches of PsychologyDocument12 pagesPyschology: Branches of Psychologyjids06No ratings yet
- Memory and Its ProcessDocument70 pagesMemory and Its ProcessAnnapoornahariNo ratings yet
- GUIA PSICOLOGIA (1) TermDocument13 pagesGUIA PSICOLOGIA (1) Termvernesto780No ratings yet
- Basic Psychological Processes CIA - 3: SAI Harini Vegiraju 2120820 1 BBA HDocument6 pagesBasic Psychological Processes CIA - 3: SAI Harini Vegiraju 2120820 1 BBA HRicky ThanmaiNo ratings yet
- Serial No. Description Page NoDocument10 pagesSerial No. Description Page NoRina MarakNo ratings yet
- Information Pro Wps OfficeDocument10 pagesInformation Pro Wps OfficeLyra Cristel DaitolNo ratings yet
- CognitionDocument12 pagesCognitionBilal PervaizNo ratings yet
- Articulo KANDEL - The Molecular and Systems Biology of Memory PDFDocument29 pagesArticulo KANDEL - The Molecular and Systems Biology of Memory PDFKarina NoelNo ratings yet
- Physiological Aspects of MemoryDocument13 pagesPhysiological Aspects of Memorypkm16499No ratings yet
- Question Bank PSYC F.A Part I 1Document8 pagesQuestion Bank PSYC F.A Part I 1Linda SelvarajNo ratings yet
- Encoding and Retrieval From Long-Term MemoryDocument47 pagesEncoding and Retrieval From Long-Term Memorydsekulic_1100% (1)
- Language, Learning, and MemoryDocument78 pagesLanguage, Learning, and MemoryRonalyn A.No ratings yet
- Psychology Chapter 7: Human MemoryDocument26 pagesPsychology Chapter 7: Human MemoryZubaidahNo ratings yet
- U2L1 Student GuideDocument4 pagesU2L1 Student GuidethomasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document31 pagesChapter 1Mohammad Nabi EbrahimiNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 8.psych ReviewerDocument4 pagesCHAPTER 8.psych ReviewerEdralyn EgaelNo ratings yet
- Psychology 5Document7 pagesPsychology 5Block AaronNo ratings yet
- Physiology Brain Bloc 16Document80 pagesPhysiology Brain Bloc 16iqiqiqiqiqNo ratings yet
- Psychology Final ReviewDocument5 pagesPsychology Final Reviewhiddencreations93No ratings yet
- Crim Chapter 2 NotesDocument6 pagesCrim Chapter 2 NotesBhavneet ToorNo ratings yet
- Psychology Notes Revised by Ayesha YounasDocument56 pagesPsychology Notes Revised by Ayesha YounasAyesha100% (1)
- Psychology ExperimentDocument11 pagesPsychology ExperimentZunair IlyasNo ratings yet
- 12 Remembering and Forgetting Lecture 2013.Ppt Yr1Document40 pages12 Remembering and Forgetting Lecture 2013.Ppt Yr1Sambili Tonny100% (2)
- U1L2 Student GuideDocument8 pagesU1L2 Student Guideria wuNo ratings yet
- Abnormal PsychologyDocument23 pagesAbnormal PsychologySimon RaoNo ratings yet
- General Psychology AssignmentDocument4 pagesGeneral Psychology AssignmentSaaB PanaraagNo ratings yet
- HBO Case AnalysisDocument2 pagesHBO Case AnalysisSaaB PanaraagNo ratings yet
- Special Duties Midterm ExamDocument2 pagesSpecial Duties Midterm ExamSaaB PanaraagNo ratings yet
- HBO Case QuizDocument1 pageHBO Case QuizSaaB PanaraagNo ratings yet
- General Psychology Midterm Activity No.2Document1 pageGeneral Psychology Midterm Activity No.2SaaB PanaraagNo ratings yet
- General Psychology Midterm Activity No.2Document1 pageGeneral Psychology Midterm Activity No.2SaaB PanaraagNo ratings yet
- Marketing Activity 2Document1 pageMarketing Activity 2SaaB PanaraagNo ratings yet
- General Psychology Prelim ExamDocument11 pagesGeneral Psychology Prelim ExamSaaB PanaraagNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Criminal InvestigationDocument2 pagesFundamentals of Criminal InvestigationSaaB PanaraagNo ratings yet
- General Psychology AssignmentDocument4 pagesGeneral Psychology AssignmentSaaB PanaraagNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Criminal InvestigationDocument2 pagesFundamentals of Criminal InvestigationSaaB PanaraagNo ratings yet
- General Psychology Prelim ExamDocument11 pagesGeneral Psychology Prelim ExamSaaB PanaraagNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Criminal InvestigationDocument2 pagesFundamentals of Criminal InvestigationSaaB PanaraagNo ratings yet
- Police IntelligenceDocument2 pagesPolice IntelligenceSaaB PanaraagNo ratings yet
- Police IntelligenceDocument2 pagesPolice IntelligenceSaaB PanaraagNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Criminal InvestigationDocument2 pagesFundamentals of Criminal InvestigationSaaB PanaraagNo ratings yet
- The Bone of Contention Case AnalysisDocument36 pagesThe Bone of Contention Case AnalysisJames Cullen80% (10)
- Police IntelligenceDocument2 pagesPolice IntelligenceSaaB PanaraagNo ratings yet
- KatkatDocument3 pagesKatkatSaaB PanaraagNo ratings yet
- HBO Case AnalysisDocument2 pagesHBO Case AnalysisSaaB PanaraagNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Criminal InvestigationDocument2 pagesFundamentals of Criminal InvestigationSaaB PanaraagNo ratings yet
- General Psychology AssignmentDocument4 pagesGeneral Psychology AssignmentSaaB PanaraagNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Criminal InvestigationDocument2 pagesFundamentals of Criminal InvestigationSaaB PanaraagNo ratings yet
- Formation of Genetically Modified Organisms GMODocument18 pagesFormation of Genetically Modified Organisms GMOSaaB PanaraagNo ratings yet
- How The World and Manking Were Created PowerPoint Period 4Document10 pagesHow The World and Manking Were Created PowerPoint Period 4SaaB PanaraagNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic Cell1Document31 pagesProkaryotic Cell1SaaB PanaraagNo ratings yet
- Police IntelligenceDocument2 pagesPolice IntelligenceSaaB PanaraagNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Criminal InvestigationDocument2 pagesFundamentals of Criminal InvestigationSaaB PanaraagNo ratings yet
- Formation of EarthDocument21 pagesFormation of EarthSaaB PanaraagNo ratings yet