Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Twelve-Month Profit and Loss Projection: Notes On Preparation
Uploaded by
Vorn Ra VuthOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Twelve-Month Profit and Loss Projection: Notes On Preparation
Uploaded by
Vorn Ra VuthCopyright:
Available Formats
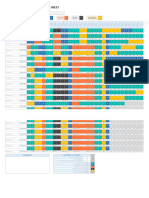
Twelve-month profit and loss projection Enter your Company Name here Fiscal Year Begins Jan-04
Notes on Preparation
LY
.%
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
B/A
4
y-0
g-0
AR
v-0
c-0
p-0
r-0
b-0
n-0
r-0
n-0
t-0
l-0
IND
Note: You may want to print this information to use as reference later. To delete these
%
%
%
Ma
Ma
Ap
Au
Oc
No
YE
De
Se
Fe
Ju
Ju
Ja
%
instructions, click the border of this text box and then press the DELETE key.
Revenue (Sales)
Category 1 - - You should change
- -
"category 1, category -
2", etc. labels -
to the actual names -
of your sales - - - - - -
Category 2 - - categories. Enter
- sales for each category
- for each month.
- The spreadsheet
- will add up total
- - - - - - -
annual sales. In the "%" columns, the spreadsheet will show the % of total sales contributed
Category 3 - - - - - - - - - - - - -
by each category.
Category 4 - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Category 5 - - COST OF GOODS
- SOLD (also called
- Cost of Sales- or COGS): COGS- are those expenses
- - - - - - -
Category 6 - - directly related to
- producing or buying
- your products- or services. For example,
- purchases
- of - - - - - -
inventory or raw materials, as well as the wages (and payroll taxes) of employees directly
Category 7 - - - - - - - - - - - - -
involved in producing your products/services, are included in COGS. These expenses usually
Total Revenue (Sales) 0 0.0 0 0.0 go up and 0 down
0.0 along with0the volume
0.0 0 0.0 or sales. Study
of production 0 0.0
your records0to 0.0 0 0.0 0 0.0 0 0.0 0 0.0 0 0.0 0 0.0
determine COGS for each sales category. Control of COGS is the key to profitability for most
Cost of Sales businesses, so approach this part of your forecast with great care. For each category of
Category 1 - - product/service,- analyze the elements
- of COGS: how - much for labor, for
- materials, for - - - - - - -
Category 2 - -
packing, for shipping,
-
for sales commissions,
-
etc.? Compare
-
the Cost -of Goods Sold and - - - - - - -
Gross Profit of your various sales categories. Which are most profitable, and which are least -
Category 3 - - -
and why? Underestimating COGS- can lead to under- pricing, which can - destroy your ability
- to - - - - - -
Category 4 - - earn a profit. Research
- carefully and
- be realistic. Enter
- the COGS for each - category of sales
- - - - - - -
Category 5 - - for each month.- In the "%" columns, - the spreadsheet - will show the COGS- as a % of sales
- - - - - - -
dollars for that category.
Category 6 - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Category 7 - - GROSS PROFIT:
- Gross Profit is Total
- Sales minus -Total COGS. In the
- "%" columns, the
- - - - - - -
Total Cost of Sales 0 - 0 - spreadsheet
0 will- show Gross
0 Profit
- as a % of0Total Sales.
- 0 - 0 - 0 - 0 - 0 - 0 - 0 - 0 -
Gross Profit 0 - 0 - OPERATING 0 EXPENSES
- (also called
0 - Overhead):
0 These
- are necessary
0 - expenses0 which,- 0 - 0 - 0 - 0 - 0 - 0 -
however, are not directly related to making or buying your products/services. Rent, utilities,
Expenses telephone, interest, and the salaries (and payroll taxes) of office and management employees
Salary expenses - - are examples. Change
- the names- of the Expense categories
- to suit your
- type of business- - - - - - -
and your accounting system. You may need to combine some categories, however, to stay
Payroll expenses - - - - -
within the 20 line limit of the spreadsheet. Most operating expenses remain- -
reasonably fixed - - - - - -
Outside services - - regardless of changes
- in sales volume.
- Some, like sales
- commissions,- may vary with sales.
- - - - - - -
Supplies (office and Some, like utilities, may vary with the time of year. Your projections should reflect these
- -
operating) fluctuations. The only rule is that the projections should simulate your financial reality as-
- - - - - - - - - -
nearly as possible. In the "%" columns, the spreadsheet will show Operating Expenses as a
Repairs and maintenance - - - - - - - - - - - - -
% of Total Sales.
Advertising - - - - - - - - - - - - -
NET PROFIT: The spreadsheet will subtract Total Operating Expenses from Gross Profit to
Car, delivery and travel - - - - - - - - - - - - -
calculate Net Profit. In the "%" columns, it will show Net Profit as a % of Total Sales.
Accounting and legal - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Rent - - INDUSTRY AVERAGES:
- The first- column, labeled "IND.
- %" is for posting
- average cost - - - - - - -
Telephone - - factors for firms-of your size in your
- industry. Industry
- average data is- commonly available
- - - - - - -
from industry associations, major manufacturers who are suppliers to your industry, and local
Utilities - - colleges, Chambers
- - and public libraries.
of Commerce, - One common -source is the book- - - - - - -
Insurance - - Statement Studies
- published annually
- -
by Robert Morris Associates. It -can be found in major
- - - - - - -
Taxes (real estate, etc.) - - libraries, and your
- banker almost surely
- has a copy.- It is unlikely that your
- expenses will -be - - - - - -
exactly in line with industry averages, but they can be helpful in areas in which expenses may
Interest - - - - - - - - - - - - -
be out of line.
Depreciation - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Other expenses (specify) - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Other expenses (specify) - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Other expenses (specify) - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Misc. (unspecified) - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Total Expenses 0 - 0 - 0 - 0 - 0 - 0 - 0 - 0 - 0 - 0 - 0 - 0 - 0 -
Net Profit 0 - 0 - 0 - 0 - 0 - 0 - 0 - 0 - 0 - 0 - 0 - 0 - 0 -
You might also like
- Fill Your Glass With Gold-When It's Half-Full or Even Completely ShatteredFrom EverandFill Your Glass With Gold-When It's Half-Full or Even Completely ShatteredNo ratings yet
- 12month P&L ProjectionDocument1 page12month P&L Projectionapi-3809857No ratings yet
- 12 Month Cash Flow Statement1AZXDocument1 page12 Month Cash Flow Statement1AZXahmed HOSNYNo ratings yet
- 12 Month Cash Flow statement1AZXDocument1 page12 Month Cash Flow statement1AZXUmer FiazNo ratings yet
- Twelve-month profit projectionDocument1 pageTwelve-month profit projectionSayed Abo ElkhairNo ratings yet
- Yanni, BlueDocument8 pagesYanni, BlueSarmad Ke100% (10)
- EL CAMINO DE LA VIDA - UkuleleDocument3 pagesEL CAMINO DE LA VIDA - UkulelePENSANDO EN ANIMACIONNo ratings yet
- Spanish CaravanDocument1 pageSpanish CaravanMarco LonghiNo ratings yet
- 6shflàfdwlrqiru Fruurvlrquhvlvwlqjvwhho Pxvkurrpkhdghg Vorwwhggulyherowv Vwuhqjwkfodvv03DDocument12 pages6shflàfdwlrqiru Fruurvlrquhvlvwlqjvwhho Pxvkurrpkhdghg Vorwwhggulyherowv Vwuhqjwkfodvv03Dson gokuNo ratings yet
- IC-Monthly-Employee-Attendance-Sheet-11664Document8 pagesIC-Monthly-Employee-Attendance-Sheet-11664THE CPRNo ratings yet
- Standard tuning for Amilie guitarDocument3 pagesStandard tuning for Amilie guitarAmirhoosein MeshginiNo ratings yet
- دائره ثلاث محركات تبديل بتايمر واحدDocument1 pageدائره ثلاث محركات تبديل بتايمر واحدBrahim CherguiNo ratings yet
- Left Alone TabsDocument8 pagesLeft Alone TabsbruheNo ratings yet
- Étude in ADocument6 pagesÉtude in AEvanNo ratings yet
- Caiaphas Debate Over Jesus' ImportanceDocument5 pagesCaiaphas Debate Over Jesus' Importancechilaquiles123No ratings yet
- Mariage Damour PDFDocument7 pagesMariage Damour PDFAntigoni Basdeki100% (3)
- Grande Valsa BrilhanteDocument12 pagesGrande Valsa BrilhanteAndréNo ratings yet
- Standard guitar tuning chart under 40 charactersDocument1 pageStandard guitar tuning chart under 40 charactersHazel Anne LopezNo ratings yet
- PaciênciaDocument3 pagesPaciênciaandrels89No ratings yet
- 03 - Sons de Carrilhões (J.Pernambuco)Document2 pages03 - Sons de Carrilhões (J.Pernambuco)Paulo0% (1)
- Grieg's Notturno Lyric PieceDocument5 pagesGrieg's Notturno Lyric PieceArturo MeleroNo ratings yet
- Francisco Tárrega - Capricho Árabe Serenata PDFDocument4 pagesFrancisco Tárrega - Capricho Árabe Serenata PDFFernanda Torres Aguirre33% (3)
- Frederic Chopin - Opus 64 No 2 (Valse No 7) - Guitar TabsDocument14 pagesFrederic Chopin - Opus 64 No 2 (Valse No 7) - Guitar TabsLeison MachadoNo ratings yet
- ') X'P) 'A) VD) VX'P ) D (X) MD (:) 2 (D) : !ND:XMX:) XD' MD (Document7 pages') X'P) 'A) VD) VX'P ) D (X) MD (:) 2 (D) : !ND:XMX:) XD' MD (Samwel TarimoNo ratings yet
- Henry Purcell - Jig PDFDocument2 pagesHenry Purcell - Jig PDFFrank Black100% (1)
- Purcell Jig GPDocument2 pagesPurcell Jig GPLUIS ALVAREZ RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- ESTUDIO 34 Manuel Diaz CanoDocument2 pagesESTUDIO 34 Manuel Diaz CanoLaurent SpadaNo ratings yet
- Guitar Solo by Francisco Tárrega - Isabel ValsDocument2 pagesGuitar Solo by Francisco Tárrega - Isabel ValsAldo MedinaNo ratings yet
- Francisco Tárrega: IsabelDocument2 pagesFrancisco Tárrega: IsabelHerberth Botero100% (1)
- Tarrega Franciso Isabel PDFDocument2 pagesTarrega Franciso Isabel PDFmateoNo ratings yet
- ') X'P) 'A) VD) VX'P ) D (X) MD (:) 2 (D) : !ND:XMX:) XD' MD (Document8 pages') X'P) 'A) VD) VX'P ) D (X) MD (:) 2 (D) : !ND:XMX:) XD' MD (Samwel TarimoNo ratings yet
- 522067-A-Main Buildig_TOILET.pdfDocument1 page522067-A-Main Buildig_TOILET.pdfmonaliNo ratings yet
- Les Betises Piano-SoloDocument3 pagesLes Betises Piano-SoloAnneSophieNo ratings yet
- 01 What A Wonderful World - FluteDocument1 page01 What A Wonderful World - FlutekwhiteNo ratings yet
- 12A - Up on the Housetop 在屋頂上&C練習曲Document1 page12A - Up on the Housetop 在屋頂上&C練習曲ChakNeng SouNo ratings yet
- MARRIAGE D AMOUR PDS PDFDocument7 pagesMARRIAGE D AMOUR PDS PDFKylin WangNo ratings yet
- MARRIAGE D AMOUR PDS PDFDocument7 pagesMARRIAGE D AMOUR PDS PDFKylin WangNo ratings yet
- MARRIAGE D AMOUR PDS PDFDocument7 pagesMARRIAGE D AMOUR PDS PDFKylin WangNo ratings yet
- Indian War Dance Sheet MusicDocument2 pagesIndian War Dance Sheet MusicMichaela Peanut-Butter Van BlerkNo ratings yet
- GPeixe Mirim PartesDocument6 pagesGPeixe Mirim PartesMarlon MolinaNo ratings yet
- Mallorcan Lullaby Sheet MusicDocument1 pageMallorcan Lullaby Sheet MusicAna OliverosNo ratings yet
- Mafua Ze MenezesDocument3 pagesMafua Ze MenezesleoliveiraguitarNo ratings yet
- Marching Band Show - Moana WIPDocument5 pagesMarching Band Show - Moana WIPNopi BhartezNo ratings yet
- be_computer-engineering_semester-6_2023_may_internet-of-thingsrev-2019-c-schemeDocument1 pagebe_computer-engineering_semester-6_2023_may_internet-of-thingsrev-2019-c-schemevaishaliNo ratings yet
- Concertino A Minor in Russian Style OpDocument3 pagesConcertino A Minor in Russian Style Op8pn4xjm8n5No ratings yet
- HappyDocument20 pagesHappyAlexeyNo ratings yet
- Vicente Amigo - RomaDocument7 pagesVicente Amigo - RomaCristobal Pérez MonteroNo ratings yet
- RHYTHM - Midnight Drive Groove Guitar Backing Track Jam in B MinorDocument2 pagesRHYTHM - Midnight Drive Groove Guitar Backing Track Jam in B MinorSam BNo ratings yet
- Etude 4Document1 pageEtude 4Александра ЖуковаNo ratings yet
- Moderate = 96 Вступление Часть 1: Standard tuningDocument3 pagesModerate = 96 Вступление Часть 1: Standard tuningMoreSvetaNo ratings yet
- Dom Quixote: Egberto Gismonti Adaptação Daniel MurrayDocument4 pagesDom Quixote: Egberto Gismonti Adaptação Daniel MurrayGiliard CoelhoNo ratings yet
- Eqŭus Templari PDFDocument6 pagesEqŭus Templari PDFartesvelazquezNo ratings yet
- La Catedral BarriosDocument10 pagesLa Catedral Barrios8dgvdfmcd2No ratings yet
- Saint Seya Ending Blue Dream Sheet MusicDocument2 pagesSaint Seya Ending Blue Dream Sheet MusicDanielNo ratings yet
- Flute Sonata in E-Flat Major BWV 1031 Johann Sebastian BachDocument3 pagesFlute Sonata in E-Flat Major BWV 1031 Johann Sebastian BachmarketaNo ratings yet
- 04 - Vals Venezolano No.1 (A.lauro)Document2 pages04 - Vals Venezolano No.1 (A.lauro)Paulo100% (1)
- Wa0004 PDFDocument2 pagesWa0004 PDFpastelinNo ratings yet
- La Catedral (3rd Movement)Document5 pagesLa Catedral (3rd Movement)OWEN MARCELIUS KEANENo ratings yet
- Kayser Etude 1 Op.20Document1 pageKayser Etude 1 Op.20Neo ComposerNo ratings yet
- 1b-Content (Done)Document7 pages1b-Content (Done)Vorn Ra VuthNo ratings yet
- Data RR3 - K7 To K8Document20 pagesData RR3 - K7 To K8Vorn Ra VuthNo ratings yet
- Concrete Quantity of Box Culvert 2x3x3 Reinforcement Calculation For BC 2X3X3Document3 pagesConcrete Quantity of Box Culvert 2x3x3 Reinforcement Calculation For BC 2X3X3Vorn Ra VuthNo ratings yet
- Annex 25 COVID Guide For Workplace 14.7.2020 After PKPDocument9 pagesAnnex 25 COVID Guide For Workplace 14.7.2020 After PKPVorn Ra VuthNo ratings yet
- All Type of Joints - Concrete PavementDocument23 pagesAll Type of Joints - Concrete PavementVorn Ra VuthNo ratings yet
- MPWT - Defect WorkDocument118 pagesMPWT - Defect WorkVorn Ra VuthNo ratings yet
- WHO 2019 NCoV Adjusting PH Measures Workplaces 2020.1 EngDocument6 pagesWHO 2019 NCoV Adjusting PH Measures Workplaces 2020.1 EngViktória BozanaNo ratings yet
- Guidelines for Detailing ReinforcementDocument216 pagesGuidelines for Detailing ReinforcementAndreas Ragus100% (1)
- Balance-Sheet US GAAPDocument1 pageBalance-Sheet US GAAPvishnuNo ratings yet
- Materials in SketchUp - EnscapeDocument19 pagesMaterials in SketchUp - EnscapeVorn Ra VuthNo ratings yet
- Balance-Sheet US GAAPDocument1 pageBalance-Sheet US GAAPvishnuNo ratings yet
- Inspe-Remove Existing DBST-294Document2 pagesInspe-Remove Existing DBST-294Vorn Ra VuthNo ratings yet
- 12 Month Cash Flow statement1AZX PDFDocument1 page12 Month Cash Flow statement1AZX PDFVorn Ra VuthNo ratings yet
- WHO 2019 nCoV Adjusting - PH - Measures Schools 2020.1 Eng PDFDocument6 pagesWHO 2019 nCoV Adjusting - PH - Measures Schools 2020.1 Eng PDFAndres EspindolaNo ratings yet
- Mix Designs: #106, Mao Tse Tung BLVD, Khan Chamkamorn, Phnom Penh, Cambodia Tel: + (855-23) 958 958, M: + (855-67) 555 721Document1 pageMix Designs: #106, Mao Tse Tung BLVD, Khan Chamkamorn, Phnom Penh, Cambodia Tel: + (855-23) 958 958, M: + (855-67) 555 721Vorn Ra VuthNo ratings yet
- Insp-Proof Rolling Existing Road-235Document3 pagesInsp-Proof Rolling Existing Road-235Vorn Ra VuthNo ratings yet
- Request For InspectionDocument24 pagesRequest For InspectionVorn Ra VuthNo ratings yet
- 12 Month Cash Flow Statement1Document1 page12 Month Cash Flow Statement1Vorn Ra VuthNo ratings yet
- Inspe-Filling Shoulder 0+000-1+500BHS-299Document2 pagesInspe-Filling Shoulder 0+000-1+500BHS-299Vorn Ra VuthNo ratings yet
- Inspe-Proof Rolling Roundabout Gardens-201Document2 pagesInspe-Proof Rolling Roundabout Gardens-201Vorn Ra VuthNo ratings yet
- Insp-Filling Soil Embankment of Shoulder-301Document7 pagesInsp-Filling Soil Embankment of Shoulder-301Vorn Ra VuthNo ratings yet
- 12 Month Cash Flow StatementDocument1 page12 Month Cash Flow StatementiPakistan100% (2)
- Inspe-Proof Rolling Roundabout Gardens-201Document2 pagesInspe-Proof Rolling Roundabout Gardens-201Vorn Ra VuthNo ratings yet
- Inspe-FDT Top Subgrade-203Document2 pagesInspe-FDT Top Subgrade-203Vorn Ra VuthNo ratings yet
- Inspe-Clearing Near Roundabout Gardens-293Document2 pagesInspe-Clearing Near Roundabout Gardens-293Vorn Ra VuthNo ratings yet
- Insp-Clearing Roundabout Gardening-287Document2 pagesInsp-Clearing Roundabout Gardening-287Vorn Ra VuthNo ratings yet
- Inspe-Filling Shoulder 0+000-1+500BHS-299 PDFDocument2 pagesInspe-Filling Shoulder 0+000-1+500BHS-299 PDFVorn Ra VuthNo ratings yet
- TAX REMEDIES PART 3 BDocument2 pagesTAX REMEDIES PART 3 BIris BalucanNo ratings yet
- Section A - Accounting questions and answersTITLE Section B - Partnership accounts problems and journal entriesTITLE Section C - Statement of profit or loss and final accounts for single entry systemDocument6 pagesSection A - Accounting questions and answersTITLE Section B - Partnership accounts problems and journal entriesTITLE Section C - Statement of profit or loss and final accounts for single entry systemGSNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Corporate Expansion and Strategic ActionsDocument17 pagesChapter 6 Corporate Expansion and Strategic ActionsApril Joy SevillaNo ratings yet
- Sample Problems INTACC-3 - PART-2Document6 pagesSample Problems INTACC-3 - PART-2Angela AlarconNo ratings yet
- Cisco System Inc: Economic AnalysisDocument32 pagesCisco System Inc: Economic AnalysisuditmangalNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Philippine School of Business AdministrationDocument6 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Philippine School of Business AdministrationGab IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Internal Financial Control IFC Self Assessment ChecklistDocument5 pagesInternal Financial Control IFC Self Assessment ChecklistJasmine Iris Bautista100% (1)
- Ii Puc Accountancy Theory Package For 2022-23Document11 pagesIi Puc Accountancy Theory Package For 2022-23ngveeresh551No ratings yet
- Practice Homework Chapter 3 (25 Ed) FA21Document2 pagesPractice Homework Chapter 3 (25 Ed) FA21Thomas TermoteNo ratings yet
- Horizontal & Vertical Analysis of Maruti Suzuki India LtdDocument17 pagesHorizontal & Vertical Analysis of Maruti Suzuki India LtdBerkshire Hathway coldNo ratings yet
- Xerox Centre With Wire Binding and LaminationDocument12 pagesXerox Centre With Wire Binding and LaminationGolden Shower தமிழ்No ratings yet
- Dr. M. Anwar Ullah, FCMA: FIN 5134: Financial Management and PracticesDocument38 pagesDr. M. Anwar Ullah, FCMA: FIN 5134: Financial Management and Practicesasif rahanNo ratings yet
- TAX-Alhambra Cigar v. CIRDocument2 pagesTAX-Alhambra Cigar v. CIRGrezyl AmoresNo ratings yet
- Null 001.2001.issue 139 enDocument36 pagesNull 001.2001.issue 139 enMark RiveraNo ratings yet
- Marketing (NetMBA)Document23 pagesMarketing (NetMBA)dejavu77No ratings yet
- Makerere University Business School Jinja CampusDocument54 pagesMakerere University Business School Jinja CampusIanNo ratings yet
- Annex D CNPF Annual Report 2020 - Consolidated Financial StatementsDocument113 pagesAnnex D CNPF Annual Report 2020 - Consolidated Financial StatementsJC LastimosoNo ratings yet
- Arabian Drilling Co - GIB Capital Mar 2023 PDFDocument4 pagesArabian Drilling Co - GIB Capital Mar 2023 PDFikhan809No ratings yet
- R.A. No. 9679 IRRDocument21 pagesR.A. No. 9679 IRRsnhlaoNo ratings yet
- ADJUSTING-ENTRIES-PPT-Examples-and-activityDocument14 pagesADJUSTING-ENTRIES-PPT-Examples-and-activitytamorromeo908No ratings yet
- AIS Chapter 6Document5 pagesAIS Chapter 6የሞላ ልጅNo ratings yet
- LTIMINDTREEDocument8 pagesLTIMINDTREEMadhav DhanukaNo ratings yet
- Economic Analysis of Project Planning & ManagmentDocument64 pagesEconomic Analysis of Project Planning & Managmentimran_rana9437100% (3)
- I/zlanila: Section As ofDocument25 pagesI/zlanila: Section As ofGilbert AguillonNo ratings yet
- Master Budget ProblemDocument2 pagesMaster Budget ProblemCillian ReevesNo ratings yet
- Articulate AprilDocument117 pagesArticulate AprilSAURAV12345No ratings yet
- TRIAL Food Drink Marketplace Financial Model Excel Template v.1.0.122020Document90 pagesTRIAL Food Drink Marketplace Financial Model Excel Template v.1.0.122020motebangNo ratings yet
- Assign 3 - Sem 2 11-12 - RevisedDocument5 pagesAssign 3 - Sem 2 11-12 - RevisedNaly BergNo ratings yet
- Assigment Ite (Group 4) 1Document23 pagesAssigment Ite (Group 4) 1HAKIMNo ratings yet
- Simple Compound Interest Study MaterialDocument6 pagesSimple Compound Interest Study MaterialprtyushNo ratings yet