Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pneumonia
Uploaded by
Albean DelojeroOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pneumonia
Uploaded by
Albean DelojeroCopyright:
Available Formats
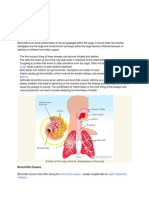
Pneumonia is an infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs.
The air
sacs may fill with fluid or pus (purulent material), causing cough with phlegm or
pus, fever, chills, and difficulty breathing. A variety of organisms, including
bacteria, viruses and fungi, can cause pneumonia.
Viral pneumonia usually goes away on its own. Therefore, treatment focuses on
easing some of the symptoms. A person with viral pneumonia should get
sufficient rest and stay hydrated by drinking plenty of fluids. A doctor may
prescribe cough-relieving medication to help ease coughing.
Pneumonia can become severe if left untreated. People with severe
pneumonia experience higher fevers along with gastrointestinal symptoms, such
as vomiting and diarrhea. Sweating, rapid heart rate, and a bluish tint to lips and
nails are also signs of severe pneumonia.
You might also like
- BronchitisDocument3 pagesBronchitiscorsaruNo ratings yet
- Nasal Discharge - Symptom EvaluationDocument2 pagesNasal Discharge - Symptom EvaluationUjwal NarayanNo ratings yet
- Sign and SymptomsDocument8 pagesSign and SymptomsCaral Grace Gatdula-PenalbaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Notes On UrtiDocument9 pagesLesson Notes On UrtiNeethupaulNo ratings yet
- What Is Acute BronchitisDocument11 pagesWhat Is Acute BronchitisKerri-DojhnHallNo ratings yet
- Ent Lesson 4Document64 pagesEnt Lesson 4favourednancie9No ratings yet
- Common ColdDocument17 pagesCommon ColdNyakie MotlalaneNo ratings yet
- Upper Respiratory Infection Definition and FactsDocument2 pagesUpper Respiratory Infection Definition and FactsBerlian PurnamasariNo ratings yet
- Influenza: By: Fitriana Khusnul.KDocument7 pagesInfluenza: By: Fitriana Khusnul.KFitri Thu Bundanya FendiNo ratings yet
- Upper Respiratory Tract Infection (Urti)Document2 pagesUpper Respiratory Tract Infection (Urti)wen_pilNo ratings yet
- 3RD Quarter - Most Common Communicable Diseases and Its Prevention and ControlDocument7 pages3RD Quarter - Most Common Communicable Diseases and Its Prevention and ControlJocel May TaboradaNo ratings yet
- Upper Respiratory Tract InfectionDocument3 pagesUpper Respiratory Tract Infectionmcvirgo014100% (1)
- Common Cold, Influenza or Flu - Whooping Cough (Pertussis)Document2 pagesCommon Cold, Influenza or Flu - Whooping Cough (Pertussis)EllaAdayaMendiolaNo ratings yet
- Core Clinical Problems: Cough and FeverDocument28 pagesCore Clinical Problems: Cough and FeverChro MANo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Respiratory SystemDocument47 pagesDisorders of The Respiratory SystemShweta RamolaNo ratings yet
- Air Borne DiseasesDocument3 pagesAir Borne DiseasesMuhammad Anwar GulNo ratings yet
- Acute Upper Respiratory Infection (AURI)Document58 pagesAcute Upper Respiratory Infection (AURI)api-19916399No ratings yet
- Pneumonia Is An Inflammatory Condition of The Lung Affecting Primarily The AlveoliDocument3 pagesPneumonia Is An Inflammatory Condition of The Lung Affecting Primarily The AlveolimakkosetteNo ratings yet
- Clinical Finalterm (9th Sem)Document52 pagesClinical Finalterm (9th Sem)sarwar sonsNo ratings yet
- LESSON 1.3-Common Diseases and Disorders of The Respiratory SystemDocument22 pagesLESSON 1.3-Common Diseases and Disorders of The Respiratory SystemRin HxHNo ratings yet
- The Toddler / Preschooler With:: Early Childhood CareDocument17 pagesThe Toddler / Preschooler With:: Early Childhood CareJazyr Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 HSBDocument22 pagesGrade 11 HSBkevorn gentlesNo ratings yet
- QUARTER 3 - Communicablediseasesfinal-EditedDocument66 pagesQUARTER 3 - Communicablediseasesfinal-EditedJocel May TaboradaNo ratings yet
- Types of PneumoniaDocument6 pagesTypes of PneumoniasakuraleeshaoranNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Tract InfectionDocument30 pagesRespiratory Tract InfectionNaresh JoshiNo ratings yet
- Clearing The Throat: Coughs Affected PartDocument6 pagesClearing The Throat: Coughs Affected Partkarla callejaNo ratings yet
- Fever and Sore ThroatDocument2 pagesFever and Sore Throatkarthivisu2009No ratings yet
- BHS Ingg BronkitisDocument12 pagesBHS Ingg BronkitisdeyrikaNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Upper Airway InfectionsDocument45 pages1.0 Upper Airway InfectionsMariahNo ratings yet
- PNEUMONIA NotesDocument4 pagesPNEUMONIA NotesKate HizonNo ratings yet
- Bronchitis: Bronchitis Is An Inflammation of The Bronchial Tubes, TheDocument6 pagesBronchitis: Bronchitis Is An Inflammation of The Bronchial Tubes, TheRoy VergaraNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Tract InfectionsDocument17 pagesRespiratory Tract InfectionsPriya bhattiNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument12 pagesRespiratory Systemshubham royalNo ratings yet
- Meaning of Different Types of SputumDocument10 pagesMeaning of Different Types of SputumCharlotte's WebNo ratings yet
- Legionnaires' Disease: Respiratory DiseasesDocument4 pagesLegionnaires' Disease: Respiratory DiseasesClarence BuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- BronchopneumoniaDocument3 pagesBronchopneumoniaGrn MynjrkxzNo ratings yet
- Name: Chintiya Cahaya Putri NIM: P20637020008 Class: 1A Prodi: Diii RmikDocument37 pagesName: Chintiya Cahaya Putri NIM: P20637020008 Class: 1A Prodi: Diii RmikChintiya PutriNo ratings yet
- BronchitisDocument15 pagesBronchitisAakanksha vaishnav100% (1)
- Upper Respiratory Tract InfectionsDocument13 pagesUpper Respiratory Tract InfectionsJavaid Mustuffa100% (1)
- Psa CloversDocument10 pagesPsa Cloversapi-324647832No ratings yet
- Lungs InfectionsDocument7 pagesLungs InfectionsMac PhersonNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Is An Inflammation of The Lungs Caused by An Infection. It Is Also Called Pneumonitis orDocument6 pagesPneumonia Is An Inflammation of The Lungs Caused by An Infection. It Is Also Called Pneumonitis orOtrebron BatisanNo ratings yet
- Respiratorydisease 170426125838Document69 pagesRespiratorydisease 170426125838Hayder MaqsadNo ratings yet
- Broncho PneumoniaDocument5 pagesBroncho PneumoniamarkkkkkkkheeessNo ratings yet
- "Bronchitis": Respiratory DisorderDocument40 pages"Bronchitis": Respiratory Disorderaswin379No ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument10 pagesPneumoniaKarylle ZairahNo ratings yet
- BronchitisDocument3 pagesBronchitisjosanne938No ratings yet
- Cardio AssignmentDocument4 pagesCardio AssignmentNeha SarfrazNo ratings yet
- Acute TracheobronchitisDocument2 pagesAcute TracheobronchitisNicole Shannon CariñoNo ratings yet
- Article About CaughDocument8 pagesArticle About CaughNour AlhazzaaNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia: Ma. Concepcion Badar Liezl Joy Stanfa Marilyn BuctuanDocument29 pagesPneumonia: Ma. Concepcion Badar Liezl Joy Stanfa Marilyn Buctuanarl777No ratings yet
- Upper Respiratory Tract InfectionDocument45 pagesUpper Respiratory Tract InfectionNatasha Abdulla100% (2)
- Common Respiratory DiseasesDocument1 pageCommon Respiratory DiseasesJohn Angelo Ryan CarmonaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory InfectionsDocument25 pagesRespiratory InfectionsHifza KhanNo ratings yet
- Classification: PneumoniaDocument2 pagesClassification: PneumoniaAlbean DelojeroNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument1 pagePneumoniaJas PerNo ratings yet
- Upper Respiratory Tract Infections Group 1 BSN 2.3Document57 pagesUpper Respiratory Tract Infections Group 1 BSN 2.3Joedelynne Diane Endaya GarciaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory and CirculatoryDocument35 pagesRespiratory and CirculatoryTumabangNo ratings yet
- What Is Dengue Fever?Document30 pagesWhat Is Dengue Fever?Jeanie Rose AlduesoNo ratings yet
- Classification: PneumoniaDocument2 pagesClassification: PneumoniaAlbean DelojeroNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of TeachingDocument5 pagesBasic Principles of TeachingAlbean DelojeroNo ratings yet
- Myocardial InfarctionDocument2 pagesMyocardial InfarctionAlbean DelojeroNo ratings yet
- AsthmaDocument2 pagesAsthmaAlbean DelojeroNo ratings yet
- What Is PsoriasisDocument6 pagesWhat Is PsoriasisAlbean DelojeroNo ratings yet
- Coronavirus Disease 2019Document1 pageCoronavirus Disease 2019Albean DelojeroNo ratings yet
- The Nurse As An EducatorDocument4 pagesThe Nurse As An EducatorAlbean DelojeroNo ratings yet
- Overview of Education inDocument2 pagesOverview of Education inAlbean DelojeroNo ratings yet
- Good Morning Everyone, Our Topic To Tackle About Is Balantidium ColiDocument1 pageGood Morning Everyone, Our Topic To Tackle About Is Balantidium ColiAlbean DelojeroNo ratings yet
- Juliet and RomeoDocument1 pageJuliet and RomeoAlbean DelojeroNo ratings yet
- Risk For Deficient Fluid Volume Best NCPDocument2 pagesRisk For Deficient Fluid Volume Best NCPAlbean DelojeroNo ratings yet
- Choose and Encircle The Letter of The Correct AnswerDocument1 pageChoose and Encircle The Letter of The Correct AnswerAlbean DelojeroNo ratings yet
- Romeo and JulietDocument1 pageRomeo and JulietAlbean DelojeroNo ratings yet