Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hooke's States That, When A Material Is Loaded Within The Elastic Limit The Stress Is Linearly Proportional To Strain. Therefore
Uploaded by
Sathiez Sathish0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesOriginal Title
UNIT 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesHooke's States That, When A Material Is Loaded Within The Elastic Limit The Stress Is Linearly Proportional To Strain. Therefore
Uploaded by
Sathiez SathishCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
1. Define stress.
The resistance per unit area offered by a body against deformation is called stress.
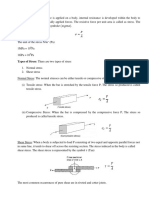
2. Define shear stress.
When a body is subjected to tangential force, a resistance to deformation per unit
area is generated. It is called Shear stress. 9. Give the relation between modulus of elasticity and bulk modulus.
Where K – Bulk Modulus (N/mm2), E- modulus of elasticity (N/mm2), µ - Poisson
Ratio.
10. Define bulk modulus.
3. State Hooke’s law. Ratio of direct stress to volumetric strain when the body is subjected to two
Hooke’s states that, when a material is loaded within the elastic limit the stress is mutually perpendicular forces.
linearly proportional to strain. Therefore
Stress Strain
σ=Ee
where, E = Young’s Modulus (N/mm2). ‘E’ is also called as elastic constant.
4. Define thermal stress. 11. Define principal plane and principal stress.
Stress generated in a body due to change in temperature when the body is not The plane in which the shear stress is zero is called principal plane.
allowed to expand or contract freely is called thermal stress. The normal stress which is acting on the principal plane is called
Thermal stress principal stress.
5. Define composite bar. 12. A material has a young’s modulus of 1.25 x 105 N/mm2 and poisson ratio of
A compound bar is an assembly of more than one bar of equal length made of 0.25. Calculate the modulus of rigidity.
different materials. It behaves as a single unit as it is fixed at the same end.
6. Differentiate elasticity and elastic limit
Elasticity is a property of a material to Elastic Limit is the maximum
regain its original shape and size when deformation of a body, before which
load is removed. there will be no permanent deformation.
7. Define principle of super position.
When a body is subjected to a number of external forces, the forces are split up,
and their effects are considered on individual sections. The resulting deformation,
of the body is equal to the algebraic sum of the deformations of the individual
sections.
8. Derive the relation for change in length of a bar hanging freely under its own
weight.
Formula’s
Stress
Relation between Youngs moduls and Bulk Modulus
Relation between Youngs modulus and Rigidity modulus
Volumetric strain
You might also like
- Course Code: Physics - E Course Description: Pysics For Egieers (Calculus-Based) Mudule 8Document15 pagesCourse Code: Physics - E Course Description: Pysics For Egieers (Calculus-Based) Mudule 8Nathaniel ClementeNo ratings yet
- The Mechanical Properties of Wood: Including a Discussion of the Factors Affecting the Mechanical Properties, and Methods of Timber TestingFrom EverandThe Mechanical Properties of Wood: Including a Discussion of the Factors Affecting the Mechanical Properties, and Methods of Timber TestingNo ratings yet
- CE6306-Strength of Materials Part-A EditDocument15 pagesCE6306-Strength of Materials Part-A EditgoldencometNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Physics Revision Notes - Mechanical Properties of SolidsDocument10 pagesClass 11 Physics Revision Notes - Mechanical Properties of SolidsArjun UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Mos 2 MarksDocument19 pagesMos 2 Markssathiya21No ratings yet
- PHY 103 Note 2020-21Document56 pagesPHY 103 Note 2020-21demiladeajakayeNo ratings yet
- SOM Mechanics of Solids 1 - by EasyEngineering - Net 04 PDFDocument78 pagesSOM Mechanics of Solids 1 - by EasyEngineering - Net 04 PDFPrakash BudhaNo ratings yet
- Bab 1-Force On MaterialDocument25 pagesBab 1-Force On MaterialMARIA NATASYANo ratings yet
- Simple Stresses: Types of Stress: There Are Two Types of StressDocument12 pagesSimple Stresses: Types of Stress: There Are Two Types of StressSanjeev dahiyaNo ratings yet
- 2 Marks SOM RejinpaulDocument12 pages2 Marks SOM Rejinpaull8o8r8d8s8i8v8No ratings yet
- ELASTICITYDocument3 pagesELASTICITYBLESSIE ARCENIONo ratings yet
- Young's Modulus DoneDocument9 pagesYoung's Modulus Donejim1234uNo ratings yet
- CE6306-Strength of Materials Part-ADocument15 pagesCE6306-Strength of Materials Part-AAmal MechanicNo ratings yet
- Stress and StrainDocument2 pagesStress and StrainbabeNo ratings yet
- Relationship Between Stress and StrainDocument2 pagesRelationship Between Stress and Strainbabe100% (4)
- Mechanical Properties of Materials ClassNoteDocument9 pagesMechanical Properties of Materials ClassNoteTousik IqbalNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of Solids Class 11 Notes Physics Chapter 9 - Learn CBSEDocument9 pagesMechanical Properties of Solids Class 11 Notes Physics Chapter 9 - Learn CBSEAjith kNo ratings yet
- Me-8395-Strength of Materials For Mechanical EngineersDocument59 pagesMe-8395-Strength of Materials For Mechanical EngineersKarthikeyan RajamaniNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials - 2marks PDFDocument37 pagesStrength of Materials - 2marks PDFAjith KumarNo ratings yet
- Defomation of Solids (Full Note)Document12 pagesDefomation of Solids (Full Note)Shayani PereraNo ratings yet
- Ce8301 - QB - 2markDocument25 pagesCe8301 - QB - 2markflora sharaNo ratings yet
- StiffnessDocument3 pagesStiffnessAkashNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of Solids and Mechanical Properties of FluidsDocument19 pagesMechanical Properties of Solids and Mechanical Properties of FluidsSasidaran SasiNo ratings yet
- ME 1201-Lecture 1Document33 pagesME 1201-Lecture 1Bau MandalNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 and 2Document22 pagesLesson 1 and 2Mark MarkNo ratings yet
- 02.UNIT-1 - Properties of Matter PDFDocument30 pages02.UNIT-1 - Properties of Matter PDFsindhuja100% (6)
- Ce8301 2 Marks - SomDocument12 pagesCe8301 2 Marks - SomPrakash BudhaNo ratings yet
- Strength: Classification of LoadsDocument16 pagesStrength: Classification of Loadsphb1986No ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of MaterialsDocument28 pagesMechanical Properties of Materialshoda melhemNo ratings yet
- SOM 2 MarksDocument8 pagesSOM 2 MarksSiva ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Ce83491 - QB SomDocument18 pagesCe83491 - QB SomchakravarthimeNo ratings yet
- CE6306 Strength of Materials Two Mark Questions With AnswersDocument24 pagesCE6306 Strength of Materials Two Mark Questions With AnswersSrini VasanNo ratings yet
- Material Is Called Stress.: Sample Questions For Material PropertiesDocument5 pagesMaterial Is Called Stress.: Sample Questions For Material PropertiesIbrahim HossainNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Cbse PhysicsDocument7 pagesClass 11 Cbse PhysicsShabnam ZakirNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials ModulesDocument30 pagesStrength of Materials ModulesJaninne SalesNo ratings yet
- LESSON NO. 1 in Machine Design 1Document9 pagesLESSON NO. 1 in Machine Design 1Carl JavierNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 PhysicsLesson Note May 27,2020Document9 pagesGrade 11 PhysicsLesson Note May 27,2020yigermalamanuel32No ratings yet
- B.Sc. Physics - I Year: Djk1A: Properties of MatterDocument79 pagesB.Sc. Physics - I Year: Djk1A: Properties of MatterThatOneGuyNo ratings yet
- WWW - Learnengineering.In: Important QuestionsDocument48 pagesWWW - Learnengineering.In: Important Questionsm,narNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Mechanical Properties of Solids PDFDocument6 pagesChapter 9 - Mechanical Properties of Solids PDFVikrant KelkarNo ratings yet
- CS6306Document9 pagesCS6306reddyprasadNo ratings yet
- sOM NotesDocument48 pagessOM NotesmaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Mechanical Properties of SolidsDocument7 pagesChapter 9 Mechanical Properties of SolidsAdrenq QuandrentNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Questions With AnswerDocument5 pagesUnit 1 Questions With AnsweranishNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6. Mechanical Properties of MetalsDocument6 pagesChapter 6. Mechanical Properties of MetalsyshokeenNo ratings yet
- PH8151 - Engineering Physics 01 - by LearnEngineering - inDocument130 pagesPH8151 - Engineering Physics 01 - by LearnEngineering - inRathodNo ratings yet
- CE8395 - 2M QB - by WWW - Easyengineering.net 1aDocument18 pagesCE8395 - 2M QB - by WWW - Easyengineering.net 1aரகுபதி குNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgB6GwA6 6Syop3h7fBK kKwLiybzwADG2SVDxFPsoKkblp1hjjQVmcGX6s6V DmBb37YNecIgU9d1DPqaGY5vKEcp3be8yFUMn0yA SFf20F5yWdV-Dml7F-qcpszUoXW7PvhU965y XDLZDocument3 pagesACFrOgB6GwA6 6Syop3h7fBK kKwLiybzwADG2SVDxFPsoKkblp1hjjQVmcGX6s6V DmBb37YNecIgU9d1DPqaGY5vKEcp3be8yFUMn0yA SFf20F5yWdV-Dml7F-qcpszUoXW7PvhU965y XDLZmalanga.bangaNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials - Lec01Document25 pagesStrength of Materials - Lec01Dheyaa Al-JubouriNo ratings yet
- Som All Theory Question and Answers Shaikh Sir NotesDocument7 pagesSom All Theory Question and Answers Shaikh Sir NotesSwapnil JadhavNo ratings yet
- Stress Force F Area A: LasticityDocument6 pagesStress Force F Area A: LasticityLalunio Catapang JayveeNo ratings yet
- SOM UNIT IV 2 Mark & 8 Mark QBDocument47 pagesSOM UNIT IV 2 Mark & 8 Mark QBkumaraguru SNo ratings yet
- Types of Engineering Analysis-2Document2 pagesTypes of Engineering Analysis-2Goutam AcharjeeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 and 2-1 PDFDocument22 pagesLesson 1 and 2-1 PDFDenver NieverasNo ratings yet
- WWW - Learnengineering.In: Unit I Stress, Strain and Deformation of Solids Part ADocument18 pagesWWW - Learnengineering.In: Unit I Stress, Strain and Deformation of Solids Part Am,narNo ratings yet
- BFBM Unit - 3Document38 pagesBFBM Unit - 3Kripa NNo ratings yet
- Statics and Dynamics 1. It Is A Study of The External Effects Upon RigidDocument6 pagesStatics and Dynamics 1. It Is A Study of The External Effects Upon RigidPeter Carl BurgosNo ratings yet
- ElasticityDocument8 pagesElasticityPRATYUSH JADHAVNo ratings yet
- Stucor Me8594-WoDocument118 pagesStucor Me8594-WoSathiez SathishNo ratings yet
- H&P UNIT TEST 1 QPDocument1 pageH&P UNIT TEST 1 QPSathiez SathishNo ratings yet
- CE8395/ Strength of Materials For Mechanical Engineers: (Answer For Any THREE Questions)Document1 pageCE8395/ Strength of Materials For Mechanical Engineers: (Answer For Any THREE Questions)Sathiez SathishNo ratings yet
- H&P UNIT TEST 2 QPDocument1 pageH&P UNIT TEST 2 QPSathiez SathishNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument1 pageQuestion BankSathiez SathishNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument1 pageQuestion BankSathiez SathishNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Machinery NOTESDocument92 pagesDynamics of Machinery NOTESMudavath Baburam100% (1)
- Nodia and Company: Gate Solved Paper Mechanical Engineering 2015-2Document12 pagesNodia and Company: Gate Solved Paper Mechanical Engineering 2015-2Sounak BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Gearboxes PDFDocument10 pagesGearboxes PDFSathiez SathishNo ratings yet
- Iii Year V Sem Other College ComparisonDocument5 pagesIii Year V Sem Other College ComparisonSathiez SathishNo ratings yet
- Analisa Harga SatuanDocument8 pagesAnalisa Harga SatuanMbeda NayNo ratings yet
- PlasticsDocument69 pagesPlasticsMyrna TabernillaNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet-CF.S10Document1 pageData Sheet-CF.S10nicolasNo ratings yet
- Design and Installation of Chemical-Resistant Protection Systems For Concrete Surfaces (BASED ON EN 14879-PARTS 1, 3, 5 AND 6)Document22 pagesDesign and Installation of Chemical-Resistant Protection Systems For Concrete Surfaces (BASED ON EN 14879-PARTS 1, 3, 5 AND 6)sudeep9666No ratings yet
- COA MetforminDocument12 pagesCOA MetforminPrasad Babu A100% (1)
- Beam Column - IS 800Document2 pagesBeam Column - IS 800parishith0% (1)
- BS en 438-4-2016Document16 pagesBS en 438-4-2016anh tho100% (1)
- Compression Deflection Hardness Chart: Shore OODocument1 pageCompression Deflection Hardness Chart: Shore OOAisya IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - 3145 - 01 - 6RP - AFP - tcm143-665876 PDFDocument20 pagesKami Export - 3145 - 01 - 6RP - AFP - tcm143-665876 PDFMa'an Al Sabri100% (1)
- VLSI Technology Dr. Nandita Dasgupta Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 38 CMOS TechnologyDocument25 pagesVLSI Technology Dr. Nandita Dasgupta Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 38 CMOS TechnologysrividyabadavathNo ratings yet
- Hilti HIT HY 70 Injection Mortar For MasonryDocument26 pagesHilti HIT HY 70 Injection Mortar For MasonryVenkatesh PadmanabhanNo ratings yet
- Reodata41 PDFDocument68 pagesReodata41 PDFMunzuara AktherNo ratings yet
- Mil L 46010BDocument18 pagesMil L 46010BaguNo ratings yet
- AlibagDocument2 pagesAlibagKuldeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Concrete & RCC (BMC 3)Document41 pagesConcrete & RCC (BMC 3)Arsh ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Hysys PrintDocument1 pageHysys Printlebiatan89No ratings yet
- Detailed Estimates: Construction of Welcome Arch New Little Baguio, Brgy. Magsaysay, Infanta, QuezonDocument8 pagesDetailed Estimates: Construction of Welcome Arch New Little Baguio, Brgy. Magsaysay, Infanta, QuezonAiresh GoNo ratings yet
- Design Software and Supporting Tool: Hydranautics - NittoDocument25 pagesDesign Software and Supporting Tool: Hydranautics - NittoAbdelhakim AkroucheNo ratings yet
- 2 2 3 Aa RecyclingFactsDocument5 pages2 2 3 Aa RecyclingFactsRyan CedergrenNo ratings yet
- Determination of Bod of Waste Water: Submitted by Shuva Chandra Bose ID: 161116Document8 pagesDetermination of Bod of Waste Water: Submitted by Shuva Chandra Bose ID: 161116shuvobosu262No ratings yet
- Surface & Coatings Technology: J. VetterDocument28 pagesSurface & Coatings Technology: J. VetterAlireza BagherpourNo ratings yet
- Civil Green ConcreteDocument18 pagesCivil Green Concretesharukh88% (8)
- 03 - API Cements and AdditivesDocument15 pages03 - API Cements and AdditivesangelacanchonNo ratings yet
- Composite Materials Used For UAVDocument3 pagesComposite Materials Used For UAVAkashNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 PDFDocument20 pagesChapter 4 PDFSiti Arbaiyah AhmadNo ratings yet
- Thin-Walled Pressure VesselsDocument18 pagesThin-Walled Pressure Vesselsjomarie apolinarioNo ratings yet
- Oluseyi Presentation SoilmechanicsDocument186 pagesOluseyi Presentation SoilmechanicsOluseyi AbegundeNo ratings yet
- Oral RecitationDocument2 pagesOral RecitationEarl Cris RiggsNo ratings yet
- Design For TorsionDocument4 pagesDesign For TorsionChhim RothyNo ratings yet
- Construciton SupervisorDocument16 pagesConstruciton SupervisorkinleyNo ratings yet
- A Welder’s Handbook to Robotic ProgrammingFrom EverandA Welder’s Handbook to Robotic ProgrammingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Dark Aeon: Transhumanism and the War Against HumanityFrom EverandDark Aeon: Transhumanism and the War Against HumanityRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Artificial Intelligence: From Medieval Robots to Neural NetworksFrom EverandArtificial Intelligence: From Medieval Robots to Neural NetworksRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- ChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindFrom EverandChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindNo ratings yet
- Arduino: The complete guide to Arduino for beginners, including projects, tips, tricks, and programming!From EverandArduino: The complete guide to Arduino for beginners, including projects, tips, tricks, and programming!Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Artificial Intelligence Revolution: How AI Will Change our Society, Economy, and CultureFrom EverandArtificial Intelligence Revolution: How AI Will Change our Society, Economy, and CultureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Artificial Intelligence: The Complete Beginner’s Guide to the Future of A.I.From EverandArtificial Intelligence: The Complete Beginner’s Guide to the Future of A.I.Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Evil Robots, Killer Computers, and Other Myths: The Truth About AI and the Future of HumanityFrom EverandEvil Robots, Killer Computers, and Other Myths: The Truth About AI and the Future of HumanityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Mastering Drones - A Beginner's Guide To Start Making Money With DronesFrom EverandMastering Drones - A Beginner's Guide To Start Making Money With DronesRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- In the Age of AI: How AI and Emerging Technologies Are Disrupting Industries, Lives, and the Future of WorkFrom EverandIn the Age of AI: How AI and Emerging Technologies Are Disrupting Industries, Lives, and the Future of WorkRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Comprehensive Guide to Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Tips, Recommendations, and Strategies for SuccessFrom EverandComprehensive Guide to Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Tips, Recommendations, and Strategies for SuccessNo ratings yet
- Artificial You: AI and the Future of Your MindFrom EverandArtificial You: AI and the Future of Your MindRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- How to Survive a Robot Uprising: Tips on Defending Yourself Against the Coming RebellionFrom EverandHow to Survive a Robot Uprising: Tips on Defending Yourself Against the Coming RebellionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (129)
- Arduino: The ultimate Arduino guide for beginners, including Arduino programming, Arduino cookbook, tips, tricks, and more!From EverandArduino: The ultimate Arduino guide for beginners, including Arduino programming, Arduino cookbook, tips, tricks, and more!Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Atlas of AI: Power, Politics, and the Planetary Costs of Artificial IntelligenceFrom EverandAtlas of AI: Power, Politics, and the Planetary Costs of Artificial IntelligenceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (9)
- ChatGPT: The Future of Intelligent ConversationFrom EverandChatGPT: The Future of Intelligent ConversationRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- PLC Programming & Implementation: An Introduction to PLC Programming Methods and ApplicationsFrom EverandPLC Programming & Implementation: An Introduction to PLC Programming Methods and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Create Profitable Side Hustles with Artificial IntelligenceFrom EverandCreate Profitable Side Hustles with Artificial IntelligenceNo ratings yet
- What to Expect When You're Expecting Robots: The Future of Human-Robot CollaborationFrom EverandWhat to Expect When You're Expecting Robots: The Future of Human-Robot CollaborationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Collection of Raspberry Pi ProjectsFrom EverandCollection of Raspberry Pi ProjectsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)