Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Week 1 Introduction and Overview PDF
Week 1 Introduction and Overview PDF
Uploaded by
Sin TungOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Week 1 Introduction and Overview PDF
Week 1 Introduction and Overview PDF
Uploaded by
Sin TungCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction to Financial
Services and Operations
Suri Gurumurthi, Ph.D. (2020) 1
Financial Services Firms and Institutions
• A service that enables and executes financial transactions
• Agents for a market for money and asset transactions
• Examples?
• Central banks (of a country)
• Banks (commercial, retail)
• Investment banks
• Credit unions
• Insurance companies
• Fund management companies
• Security firms
• Credit card companies, payment companies
• …
Suri Gurumurthi, Ph.D. (2020) 2
Macro-Markets: Central Banks
Promotes
Employment
Issues Maintains
Currency Stability
Central
Sets Growth
Bank Lends to
Targets Governments
Sets Interest Inflation
Rates Targets
Suri Gurumurthi, Ph.D. (2020) 3
Central Banks: History
• Swedish Riksbank, 1668
• Post US Revolution: The First Bank of the US, 1790
• Central Banks are the governing institutions behind commercial and
investment banks
• Typically independent of political government
• Support the economy
• Maintains an objective national or even world macroeconomic view
• European Central Bank and Deutsche Bundesbank
• Prominent roles in the Greek financial crisis of 2009-2018
Suri Gurumurthi, Ph.D. (2020) 4
Commercial and Investment Banks
Assets US Trillions
Netherlands ING Group
Italy Intesa Sanpaolo
Canada Toronto-Dominion Bank
Canada Royal Bank of Canada
Germany Deutsche Bank
France Groupe BPCE
France Société Générale
Japan Mizuho Financial Group
United States Citigroup Inc.
Japan Japan Post Bank
France BNP Paribas
United States JPMorgan Chase
Japan Mitsubishi UFJ Financial Group
China Agricultural Bank of China
China Industrial and Commercial Bank of China
0.00 0.50 Suri1.00 1.50
Gurumurthi, 2.00
Ph.D. (2020) 2.50 3.00 3.50 4.00 4.50 5 5.00
Micro-Markets: Commercial and Retail Banks
• Accept deposits from public (individuals or corporations) and make
loans to the public, including local and central governments
• Retail banks:
• serving individual customers or households – accept deposits, make loans, facilitate
payments,
• Commercial banks (also merchant banks):
• Serving corporations and governments, accept deposits, provide loans (buy goods,
expand business operations, paying off debts, facilitate payments), currency exchange,
• Wholesale banks:
• Serving between merchant banks and other financial institutions; deal with large
institutions, and large amounts per transactions
Suri Gurumurthi, Ph.D. (2020) 6
Micro-Markets: Investment Banks
• Take deposit from institutional and private investors
• Services to investors and borrowers
• underwriting of debts and equity offerings (IPO)
• large public and private share offerings,
• mergers and acquisitions (M&A)…
• Glass-Steagall Act of 1933
• Separated US investment banking operations from commercial banking
• High risk (investment bank) vs low risk (commercial banks
• Glass-Steagall Repealed in 1999
• Led to financial crisis of 2008
• Dodd–Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, 2010
Suri Gurumurthi, Ph.D. (2020) 7
Retail and Commercial Banking Framework
Branches, Agents, Customer Analytics, Statutory
SWIFT, BACS,
Mail, Call Center, Life Cycle Execution, Risk
CHAPS
Salesforce Management Management
Customer Relationship Management Regulatory
ENGINES
Core Banking, Insurance, Asset Finance, Capital Markets, Fund Management, Credit and
Debit Cards, Mortgages, Stock Broking
Suri Gurumurthi, Ph.D. (2020) 8
Functional View of Retail/Commercial Banking
Leadership
Operations Collections Finance
Transaction Information Facilities Design Real Estate/
Investments Trading
Processing Systems and Layout Mortgage
Check
clearing/collectio Data Security Maintenance Vault and Safes Securities Private Clients Loans/Debt Proprietary Clients
ns
Suri Gurumurthi, Ph.D. (2020) 9
Investment Banking Operations
Back Office: Admin and Infrastructure
Middle Office: Business Operations and Risk Management
Front Office: Client Management, Sales and Trading
Capture Trade Settle
News, Value
Report
added Market
services
Clients
Control
Institutional Corporate Wealth
Market Business Risk
Execution Delivery
Analysis Intelligence Management
Suri Gurumurthi, Ph.D. (2020) 10
Insurance Company Operations
Sales and Marketing Customer acquisition, growth, and retention
• Online transactions
• Relationships with insurance brokers
• Advertise, develop relationships with customers
Underwriting Rate Making and Risk Pricing
• Evaluate exposure to customer risks
• Accept or reject customer risks
• Improve risk profile
Reinsurance Transferring portfolio risk
• Re-package risks into broader portfolios
• Hedging against systemic risks by re-insuring portfolios
Production Claims and Customer service
• Support customers during risk events, and evaluate their losses
• Absorb minimum warranted losses for customers
• Arbitration with third party insurance companies; follow up with customers
Investing Managing cash flows
• Investing customer premiums
• Generating returns to support claim payments
Suri Gurumurthi, Ph.D. (2020) 11
Credit Card Value Chain Perspectives
Information Core Card Interfacing and
Suppliers Governance
Services Operations Communications
New customer
Admin Customer Data and merchant Account security Audit committees
accounts
Risk profiles and Transaction Consumer
Bank Branches Fraud alerts
reports processing Protection
Merchant
Statements and Regulatory
Courier Services Lending rates payment and
reminders compliance
settlements
Fund processors Contracts and Dispute Risk exposure
Dispute resolution
(Visa/Mastercard) terms management management
Internal reports Privacy rights
Suri Gurumurthi, Ph.D. (2020) 12
Financial Markets Overview
Interbank (lending) Foreign exchange markets The Stock Market The Bond market
• Institutional borrowing – mostly • Governs trade and supply chains • Capital access to firms • Debt access to firms
short term • Risk access to investors • Lower risk assets for investors
• Maintains liquidity
The Insurance Market The Commodities Market The Futures market The Money Market
• Trading and exchange of risks • Access to industrial resources • Hedging against price risks • Market for cash
• Enables firms to take on risk and agricultural products • Access to Derivatives • Access to liquidity for firms
• Enables market pricing of mass • Inventory of surplus cash flows
resources
Suri Gurumurthi, Ph.D. (2020) 13
Stock Market Capitalization (2017-18)
Suri Gurumurthi, Ph.D. (2020) 14
China Market Cap 2003-2018
Suri Gurumurthi, Ph.D. (2020) 15
Corporate Government
• Secured • T-Bills
Bond Markets • Unsecured • Municipal
Mortgage Backed Collateralized Debt
• Residential • Cash
• Commercial • Synthetic
Issuers: Organizations that sell bonds to raise funds for their operations (banks, corporations,
municipal and central governments)
Underwriters: Mainly investment banks and leading FI in the investing business. They perform
the key role of middlemen and perform the critical activities like preparing legal documents,
prospectus, and other collaterals to simplify transactions. (Packaging the bond.) They are also
responsible for the validity of the information related directly to the bond.
Purchasers: Corporations and governments that buy the bonds, fund management companies
(like mutual fund management companies, trusts, etc. where individual investors can invest in
their products: including unit-investment trusts, bond funds, ..)
Suri Gurumurthi, Ph.D. (2020) 16
Global Bond Markets
Suri Gurumurthi, Ph.D. (2020) 17
Foreign Exchange Markets
Suri Gurumurthi, Ph.D. (2020) 18
Money Markets
• A financial market where buyers and sellers buy or issue/sell short term loans (less than a year). These
bonds/securities are also known as financial instruments (called papers).
• Supply Chain and trade finance, operating capital
• Smoothen functioning of banks;
• increase the efficiency of the central bank…
• Participants: Banks, retail money market funds, trading companies, central banks, trading companies, cash
management funds
• Products
• Commercial paper (shirt term loans)
• T-Bills
• Letter of credit for supply chain financing
• Repurchase agreements (Repos)- overnight borrowing
• Money markets freezing causes liquidity problems for the economy
• 2008 Financial crisis
• Barometer of banking confidence
Suri Gurumurthi, Ph.D. (2020) 19
Top Commodity Markets (2018)
Brent crude (oil) • Commodity Market:
Steel • A physical or virtual market-place where buyers
WTI crude (oil) and sellers trade raw or primary products or the
Soybean future contracts of these products.
• Hard commodities: gold, oil, copper, …
Iron
• Soft commodities: agricultural products like wheat, rice,
Corn sugar, cocoa, coffee, pork, …
Gold • There are over 50 commodity markets over the world
Copper • China alone has over 1000 of these markets all over the
Aluminum country
Silver
Suri Gurumurthi, Ph.D. (2020) 20
Derivative Markets
• National Stock Exchange of • Derivative markets
India (India)
• Contract between two or more parties agreeing on selling/buying certain
• Chicago Mercantile Exchange assets.
(US)
• Security with a price derived (or dependent upon) from a set of underlying
• Intercontinental Exchange assets: stocks, bonds, currencies, interest rates, commodities, market
(US)
indexes…
• CBOE Holdings (US)
• Futures market (standardized and regulated)
• 5 Eurex (Europe)
• over the counter (OTC) market. (non-standardized and not regulated)
• NASDAQ (US+ Europe)
• Notional value can be 10xGDP, but face value is smaller
• Moscow Exchange (Russia)
• Korea Exchange (South • Futures market (futures exchange)
Korea) • Participants trade standardized futures contracts (options e.g.)
• Shanghai Futures Exchange • Specific quantities of a commodity or securities at a specified price with
(China)
delivery at a specific time in the future.
Suri Gurumurthi, Ph.D. (2020) 21
You might also like
- Mba III Financial Services (14mbafm302) NotesDocument93 pagesMba III Financial Services (14mbafm302) NotesSyeda GazalaNo ratings yet
- Emerging Market Bank Lending and Credit Risk Control: Evolving Strategies to Mitigate Credit Risk, Optimize Lending Portfolios, and Check Delinquent LoansFrom EverandEmerging Market Bank Lending and Credit Risk Control: Evolving Strategies to Mitigate Credit Risk, Optimize Lending Portfolios, and Check Delinquent LoansRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (3)
- Fast No Credit Check LoansDocument3 pagesFast No Credit Check LoansRobinson52KristensenNo ratings yet
- Objectives: at The End of The Session You Will Be Able ToDocument70 pagesObjectives: at The End of The Session You Will Be Able ToShashidhar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Investment Banking NoteDocument6 pagesInvestment Banking NoteShwetank RaiNo ratings yet
- UT MBA Day in The Life 11.06Document18 pagesUT MBA Day in The Life 11.06Hardik JainNo ratings yet
- Practical Investment BankingDocument30 pagesPractical Investment Bankingw_fibNo ratings yet
- Careers in FinanceDocument22 pagesCareers in Financethobiasetc2710No ratings yet
- Intervention StrasbourgDocument85 pagesIntervention StrasbourgChaimae Rahmani AfifNo ratings yet
- Intervention StrasbourgDocument77 pagesIntervention StrasbourgChaimae Rahmani AfifNo ratings yet
- W2 WCorporateDocument14 pagesW2 WCorporateWay2 WealthNo ratings yet
- Industrial Analysis-Financial Services: Presented To - Prof. Tarun Agarwal SirDocument19 pagesIndustrial Analysis-Financial Services: Presented To - Prof. Tarun Agarwal SirGEETESH KUMAR JAINNo ratings yet
- 66576bos53772 cp5Document75 pages66576bos53772 cp5HemanthNo ratings yet
- GLB IBDDocument16 pagesGLB IBDRaimond DuflotNo ratings yet
- Measuring Financial Distress of IDBI Using Altman Z-Score ModelDocument9 pagesMeasuring Financial Distress of IDBI Using Altman Z-Score Modelkingbyom3896No ratings yet
- New PPT Ia Group 5Document22 pagesNew PPT Ia Group 5GEETESH KUMAR JAINNo ratings yet
- Banking Industry Is Most Concerned With Direct Saving and LendingDocument8 pagesBanking Industry Is Most Concerned With Direct Saving and LendingabyrnNo ratings yet
- Banking Industry Is Most Concerned With Direct Saving and LendingDocument8 pagesBanking Industry Is Most Concerned With Direct Saving and LendingturnNo ratings yet
- Implementation of Universal Banking in Icici: Presented By: Surya Prakash Sanhita SarkarDocument12 pagesImplementation of Universal Banking in Icici: Presented By: Surya Prakash Sanhita Sarkartanu25No ratings yet
- CBPTM S01-02Document39 pagesCBPTM S01-02SuvajitLaikNo ratings yet
- Intro Mon Pol - Oct 19 ABRDocument150 pagesIntro Mon Pol - Oct 19 ABRSoumya JainNo ratings yet
- Mergers & Inquisitions - Financial Institutions Group - FIG Investment Banking GuideDocument43 pagesMergers & Inquisitions - Financial Institutions Group - FIG Investment Banking GuideGABRIEL SALONICHIOSNo ratings yet
- Corporate Banking IndusInd Bank Investor Day 20221122Document26 pagesCorporate Banking IndusInd Bank Investor Day 20221122Ankit DhanukaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document15 pagesAssignment 1Jhilik PradhanNo ratings yet
- Security AgreementsDocument18 pagesSecurity AgreementsEINSTEIN2DNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01Document24 pagesChapter 01munatasneemNo ratings yet
- Audit Meth PresentDocument81 pagesAudit Meth PresentFajar Putra JakartaNo ratings yet
- 1 Careers in Investments I - IB 31jan08Document19 pages1 Careers in Investments I - IB 31jan08Amit MishraNo ratings yet
- Research and Marketing of Financial ServicesDocument26 pagesResearch and Marketing of Financial ServicesHIGGSBOSON304No ratings yet
- Strategic Analysis of Investment Banking in IndiaDocument19 pagesStrategic Analysis of Investment Banking in Indiaanuradha100% (7)
- Icici Mutual Funds Business ModelDocument6 pagesIcici Mutual Funds Business ModelsnehashisNo ratings yet
- Sakthi - HR PresentationDocument22 pagesSakthi - HR PresentationSakthi VelNo ratings yet
- Overview of Changing Financial ServicesDocument14 pagesOverview of Changing Financial ServicesNazmul H. PalashNo ratings yet
- Business Plan ReferenceDocument18 pagesBusiness Plan ReferenceAditya KothiwalNo ratings yet
- Z.ib 1Q23 Investment Banks From The Inside VFDocument36 pagesZ.ib 1Q23 Investment Banks From The Inside VFLuis Soldevilla MorenoNo ratings yet
- Fs Data and AnalyticsDocument5 pagesFs Data and Analyticsvcpc2008No ratings yet
- Wholesale BankingDocument7 pagesWholesale BankingSrinath SmartNo ratings yet
- Introduction To IB PDFDocument31 pagesIntroduction To IB PDFsanjayNo ratings yet
- The World's Most Admired Bank: Who We Are: A Leading Global BankDocument10 pagesThe World's Most Admired Bank: Who We Are: A Leading Global BankwhartonfinanceclubNo ratings yet
- Everything About Investment Banking!Document10 pagesEverything About Investment Banking!debasis.datta65No ratings yet
- Notes On Introduction To Financial ServicesDocument18 pagesNotes On Introduction To Financial ServicesKirti Giyamalani100% (1)
- Financial Services in India: Learning ObjectivesDocument48 pagesFinancial Services in India: Learning ObjectivesrbmjainNo ratings yet
- Capstone Partners Financial Technology Payments MA Coverage Report March 2022Document31 pagesCapstone Partners Financial Technology Payments MA Coverage Report March 2022Juan Nicolás BarretoNo ratings yet
- BRDDocument5 pagesBRDanon_7975025No ratings yet
- CSB Project Chapter 2Document38 pagesCSB Project Chapter 2Nithin Mathew Jose MBA 2020No ratings yet
- Supply Chain of IciciDocument17 pagesSupply Chain of Icicishan birla100% (1)
- 19351sm SFM Finalnew cp8 PDFDocument40 pages19351sm SFM Finalnew cp8 PDFtimirkantaNo ratings yet
- Redefining Possibilities - Strategy & Way ForwardDocument12 pagesRedefining Possibilities - Strategy & Way ForwardSeshagiri Vasa SavaramNo ratings yet
- Investment Banking Strategies and Key Issues: Kaan Sarıaydın 23 November 2009, Bilgi UniversityDocument57 pagesInvestment Banking Strategies and Key Issues: Kaan Sarıaydın 23 November 2009, Bilgi UniversityAshish SharmaNo ratings yet
- Financial ServicesDocument42 pagesFinancial ServicesGururaj Av100% (1)
- BankDocument2 pagesBankAshish AgarwalNo ratings yet
- CHP 1 Intro To FS TextbkDocument31 pagesCHP 1 Intro To FS TextbkVenom BhaiyaNo ratings yet
- Axis Mission Statement:: PortfolioDocument5 pagesAxis Mission Statement:: PortfolioHimesh BhaiNo ratings yet
- Commercial Banks and Investment BanksDocument15 pagesCommercial Banks and Investment BanksRemalyn AmmakNo ratings yet
- Corporate PresentationDocument41 pagesCorporate PresentationMoHd AliNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Financial ServicesDocument60 pages1.1 Financial ServicesPrachi AsawaNo ratings yet
- State Bank of Indias Osaka Experience PDFDocument11 pagesState Bank of Indias Osaka Experience PDFakashigupta26No ratings yet
- Holder's Name No of Shares % Share Holding: Mr. Sunil MehtaDocument7 pagesHolder's Name No of Shares % Share Holding: Mr. Sunil Mehtashraddha anandNo ratings yet
- Bank Fundamentals: An Introduction to the World of Finance and BankingFrom EverandBank Fundamentals: An Introduction to the World of Finance and BankingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Credit Derivatives: Techniques to Manage Credit Risk for Financial ProfessionalsFrom EverandCredit Derivatives: Techniques to Manage Credit Risk for Financial ProfessionalsNo ratings yet
- Banking 2020: Transform yourself in the new era of financial servicesFrom EverandBanking 2020: Transform yourself in the new era of financial servicesNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Materials (Part 2)Document18 pagesTopic 4 Materials (Part 2)Sin TungNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Materials (Part 1)Document13 pagesTopic 4 Materials (Part 1)Sin TungNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 QuestionsDocument14 pagesTopic 4 QuestionsSin TungNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Materials (Part 2)Document26 pagesTopic 3 Materials (Part 2)Sin TungNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Part IIDocument17 pagesWeek 5 Part IISin TungNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Part IDocument29 pagesWeek 5 Part ISin TungNo ratings yet
- Week 4 - Product Mix DecisionsDocument17 pagesWeek 4 - Product Mix DecisionsSin TungNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Part IDocument24 pagesWeek 6 Part ISin TungNo ratings yet
- And In-Depth Analysis To Score Full Credit.: Spring 2020 ISOM3730 Final Exam SolutionDocument5 pagesAnd In-Depth Analysis To Score Full Credit.: Spring 2020 ISOM3730 Final Exam SolutionSin TungNo ratings yet
- ISOM 3730 Quality and Process Management Dr. Ki Ling Cheung Samsung Electronics: Analyzing Qualitative Complaint DataDocument1 pageISOM 3730 Quality and Process Management Dr. Ki Ling Cheung Samsung Electronics: Analyzing Qualitative Complaint DataSin Tung0% (1)
- Basic Seven ToolsDocument33 pagesBasic Seven ToolsSin TungNo ratings yet
- Week 4 - Cont. Week 3 Slides - UpdatedDocument43 pagesWeek 4 - Cont. Week 3 Slides - UpdatedSin TungNo ratings yet
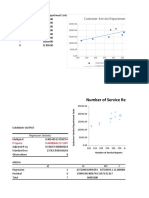
- Number of Service Reports Line Fit Plot: Customer-Service Department CostsDocument11 pagesNumber of Service Reports Line Fit Plot: Customer-Service Department CostsSin TungNo ratings yet
- Quality Wireless (A) and (B) : Process CapabilityDocument3 pagesQuality Wireless (A) and (B) : Process CapabilitySin TungNo ratings yet
- Spring 2020 ISOM3730 Quiz Solution: Depth Analysis To Score Full CreditDocument5 pagesSpring 2020 ISOM3730 Quiz Solution: Depth Analysis To Score Full CreditSin TungNo ratings yet
- SUST 1000 (L4) Introduction To Sustainability: Group 1 - MongoliaDocument3 pagesSUST 1000 (L4) Introduction To Sustainability: Group 1 - MongoliaSin TungNo ratings yet
- Acceptance SamplingDocument50 pagesAcceptance SamplingSin TungNo ratings yet
- Advanced Accounting: Business CombinationsDocument43 pagesAdvanced Accounting: Business CombinationsSin TungNo ratings yet
- 3730 Inclass Flowchart 1Document2 pages3730 Inclass Flowchart 1Sin TungNo ratings yet
- Business Combinations: Answers To Questions 1Document12 pagesBusiness Combinations: Answers To Questions 1Sin TungNo ratings yet
- Ch1 Handout QuestionsDocument2 pagesCh1 Handout QuestionsSin TungNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Affinity Diagrams and Pareto ChartsDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Affinity Diagrams and Pareto ChartsSin TungNo ratings yet
- Quality and Process ManagementDocument7 pagesQuality and Process ManagementSin TungNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: 2.1 Multiple Choice Questions (Circle The Correct Answer, 2 Points Each)Document3 pagesThis Study Resource Was: 2.1 Multiple Choice Questions (Circle The Correct Answer, 2 Points Each)Sin TungNo ratings yet
- Charles Schwab Case StudyDocument1 pageCharles Schwab Case StudySin TungNo ratings yet
- Statement On The Purpose of A CorporationDocument12 pagesStatement On The Purpose of A CorporationSin TungNo ratings yet
- PLCR Notes PDFDocument2 pagesPLCR Notes PDFArti RahangdaleNo ratings yet
- Solution Chapter 13Document31 pagesSolution Chapter 13ClarisaJoy Sy100% (3)
- Ecash: What Is E-Cash?Document6 pagesEcash: What Is E-Cash?Aarchi MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Lab1 Excel VBADocument1 pageLab1 Excel VBAJonahJuniorNo ratings yet
- English EvAUDocument4 pagesEnglish EvAUNoemiNo ratings yet
- Philippine Supreme Court Jurisprudence: Home Law Firm Law Library Laws Jurisprudence Contact UsDocument6 pagesPhilippine Supreme Court Jurisprudence: Home Law Firm Law Library Laws Jurisprudence Contact Usinternation businesstradeNo ratings yet
- Tax Invoice/Bill of Supply/Cash Memo: (Original For Recipient)Document1 pageTax Invoice/Bill of Supply/Cash Memo: (Original For Recipient)Manoj LingeNo ratings yet
- ACC216 Week 2 To 3Document2 pagesACC216 Week 2 To 3Ann ToniaNo ratings yet
- Research Project - Digital Landscape India Final Final-1Document59 pagesResearch Project - Digital Landscape India Final Final-1Keshav DhootNo ratings yet
- Assets Liabilities: Cash Equipment Accounts Receivable Medical Supplies Furniture & Fixtures Accounts PayableDocument12 pagesAssets Liabilities: Cash Equipment Accounts Receivable Medical Supplies Furniture & Fixtures Accounts PayableRicah MagalsoNo ratings yet
- Individual Paper Return For Tax Year 2020: SignatureDocument26 pagesIndividual Paper Return For Tax Year 2020: SignaturejamalNo ratings yet
- 02audit of CashDocument12 pages02audit of CashJeanette FormenteraNo ratings yet
- BOC Aviation Investor Presentation - Jan-2023Document32 pagesBOC Aviation Investor Presentation - Jan-2023Jigar VikamseyNo ratings yet
- A) Financial Accounting Is Concerned With Reporting To ExternalDocument7 pagesA) Financial Accounting Is Concerned With Reporting To ExternalRuzana UtkurovaNo ratings yet
- Bank AlfalahDocument40 pagesBank Alfalahmir nida95% (21)
- Airtel N ZainDocument31 pagesAirtel N ZainPooja LilaniNo ratings yet
- NIRMAL RUBBER INDUSTRIES PraposalDocument1 pageNIRMAL RUBBER INDUSTRIES PraposalTomJohnNo ratings yet
- Tif 1Document7 pagesTif 1James BurdenNo ratings yet
- TWO: Financial Analyses and PlanningDocument18 pagesTWO: Financial Analyses and Planningsamuel kebedeNo ratings yet
- The Future of Financial System and The Money and Capital MarketsDocument29 pagesThe Future of Financial System and The Money and Capital MarketsaamirjewaniNo ratings yet
- Obligation Request: Province of Negros Oriental Provincial Legal OfficeDocument3 pagesObligation Request: Province of Negros Oriental Provincial Legal OfficeJessa Mia UyNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Accounting-Introduction To AccountingDocument14 pagesCBSE Class 11 Accounting-Introduction To AccountingRudraksh PareyNo ratings yet
- HSBC FinalDocument80 pagesHSBC FinalAhmed ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Acc Oount Statement Ra PortDocument6 pagesAcc Oount Statement Ra PortAlexandru GradinaruNo ratings yet
- TFG Luis Gonzalez Corujo PDFDocument180 pagesTFG Luis Gonzalez Corujo PDFKaran GoyalNo ratings yet
- Accounting Basics: Upsc-EpfoDocument12 pagesAccounting Basics: Upsc-EpfoAnkit Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- ch2 ExercisesDocument8 pagesch2 ExercisesDanicaEsponillaNo ratings yet
- © The Institute of Chartered Accountants of IndiaDocument50 pages© The Institute of Chartered Accountants of Indiaprabhawagarwalla9690No ratings yet