Professional Documents
Culture Documents
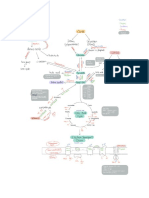
Digest in Body Complex Carbs Example:oat, Pumkin, Sweet Potato
Uploaded by
Sushi TangOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Digest in Body Complex Carbs Example:oat, Pumkin, Sweet Potato
Uploaded by
Sushi TangCopyright:
Available Formats
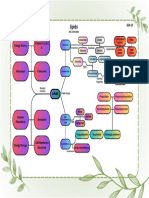
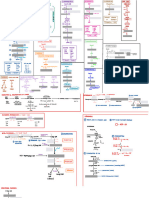
PROTEIN
COMPLEX CARBS
Example:oat,pumkin, Digest in body
Sweet potato
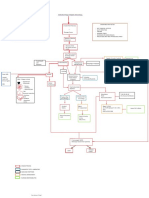
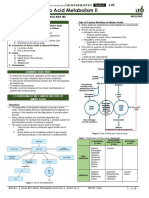
TAJUK: METABOLISMA
TIGA AMINO ACID
SIMPLE CARBS MAKROMOLEKUL
Digest
Example: icecream,biscuit Absorb into blood
chocolate Essential :
- 9/20
- ex. Histidine, isoleucine,
CARBOHYDRATE FOOD leucine, etc.
Non-Essential :
Saturated : - 11/20
2 types of fat in - “bad” for us - ex. Alanine, asparagine, etc.
body : - Solid at room
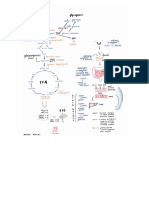
Glucose storage Visceral fat : temp
GLYCOGENESIS
-Stored around - Ex. Meat, fish,
G important internal and dairy Polypeptide
L GLUCOSE GLYCOGEN
organ LIPID
U
C -Ex. Liver, Unsaturated : Gest in body
GLYCOGENOLYSIS pancreas, etc. Digest in body - “Better” for us
O
N Subcutaneous -Liquid at room
E fat : TRIGLYCERIDES tempt
O -Ex. Plant oils
G GLYCOLYSIS -Jilligy fat visible
E just under the skin
N - Normally
E harmless Lipolysis
S
I PYRUVATE in
S Cytoplasma Glycerol Fatty acid
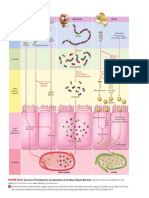
( 3 carbon x 2 ) A. Primary protein structure
Ketones
( Sequence of a chain of Amino Acid )
X O2 √ O2 Lipogenesis
B. Secondary protein structure
Lactate ( Hydrogen bonding of people backbone causes the amino acids to
Acetyl - CoA Acetly - CoA
fold into a repeating pattern )
2 ATP Krebs Cycle In C. Tertiary protein structure
Lactic acid
Mitochondria ( Three-dimensional folding pattern of a protein due to side chain
GLUCONEOGENESIS interactions )
Electron Transport
Chain (38 ATPS) D. Quaternary protein structure
Fatty ( Protein consisting more than one amino acid chain )
Acid Acetyl - CoA
Energy (ATP)
Amino Acid Pyruvate Lactate
Liver
Kidney
Amino acid GLYCOLYSIS Glucose 6-Phosphate GLUCOSE
Glycerol
You might also like
- Metabolism MapDocument1 pageMetabolism Mapyinose7198No ratings yet
- NPLEX Biochem NutritionalDocument6 pagesNPLEX Biochem Nutritionalapi-26938624No ratings yet
- Dka Patho DiagramDocument1 pageDka Patho DiagramGrae TaclobNo ratings yet
- List of AbbreviationsDocument3 pagesList of Abbreviationsjuwita latiefahNo ratings yet
- Liver Cirrhosis PathophysiologyDocument1 pageLiver Cirrhosis PathophysiologyCaren ReyesNo ratings yet
- Lectures On EnzymesDocument123 pagesLectures On EnzymesProf Rakesh Sharma100% (2)
- Lipid BiosynthesisDocument67 pagesLipid Biosynthesissaraniya100% (3)
- Molecular Gastronomy: Introduction ToDocument12 pagesMolecular Gastronomy: Introduction ToTatiana100% (2)
- Metabolism of Fatty AcidDocument5 pagesMetabolism of Fatty AcidmanikchawlaplusoneNo ratings yet
- Perhitungan Nutrisi Parenteral SortedDocument50 pagesPerhitungan Nutrisi Parenteral SortedAtiik AjalaahNo ratings yet
- AttachmentDocument15 pagesAttachmentkedirNo ratings yet
- Session 3 L1Document23 pagesSession 3 L1Nidar LoqmanNo ratings yet
- Complete Amino Acid MixDocument1 pageComplete Amino Acid MixEva Devita SariNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument1 pageCarbohydrate MetabolismdaefaegagNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus ManagementDocument6 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Managementmouxritsa_83No ratings yet
- 1 & 2 Gangg MetabolismeDocument117 pages1 & 2 Gangg MetabolismerahmedNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules Carbohydrates 2 (1) - InvertDocument40 pagesBiomolecules Carbohydrates 2 (1) - InvertelluresonyNo ratings yet
- GI SeminarDocument13 pagesGI SeminarshararohitNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument3 pagesBiologys0xynpark18No ratings yet
- Mouth Salivary Glands: Aranilla, Hanako S. Homework-GitDocument2 pagesMouth Salivary Glands: Aranilla, Hanako S. Homework-GitHanako AranillaNo ratings yet
- LIPIDSDocument3 pagesLIPIDSsilenkylepaoloNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry by DR - AzamDocument98 pagesBiochemistry by DR - AzamArrya DSNo ratings yet
- Kenneth Saladin - Anatomy & Physiology - The Unity of Form and Function-McGraw-Hill Education (2020) (1) - 1Document1 pageKenneth Saladin - Anatomy & Physiology - The Unity of Form and Function-McGraw-Hill Education (2020) (1) - 1Guilherme RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Metabolic & Performance Benefit L-Arginine Over GAADocument2 pagesMetabolic & Performance Benefit L-Arginine Over GAABagus HidayatNo ratings yet
- Designed: by PanchalDocument18 pagesDesigned: by PanchalJatinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Biological MoleculesDocument3 pagesBiological MoleculestrishaNo ratings yet
- Digestion - 7Document7 pagesDigestion - 7aaravrshah14No ratings yet
- Metabolic Adaptation During Prolonged StarvationDocument18 pagesMetabolic Adaptation During Prolonged StarvationThabrish rish1234No ratings yet
- EndokrinologiDocument26 pagesEndokrinologiAhmad Rafi Satrio PrayogoNo ratings yet
- Allen: Pre-Medical: BiologyDocument1 pageAllen: Pre-Medical: BiologyDevdatta PatilNo ratings yet
- Spaghetti Sauce With BeefDocument1 pageSpaghetti Sauce With Beefkristine_henry2809No ratings yet
- Physiologic Effects: B6M2 Case 5 4/ 26/ 2019 GROUP 15Document1 pagePhysiologic Effects: B6M2 Case 5 4/ 26/ 2019 GROUP 15Group15Nikki Louise PaquibotNo ratings yet
- PDF Digestion and Absorption of Carbohydrate and ProteinDocument5 pagesPDF Digestion and Absorption of Carbohydrate and ProteinHhh HhhNo ratings yet
- Metabolic PathwayDocument8 pagesMetabolic PathwaysadadsadNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid Metabolsm 2Document12 pagesAmino Acid Metabolsm 2Manila Med100% (1)
- Metabolic Pathways of GlucoseDocument11 pagesMetabolic Pathways of GlucosemanikchawlaplusoneNo ratings yet
- Farmakognosi 7Document29 pagesFarmakognosi 7Randi RasyidNo ratings yet
- Fresubin 2 Kcal Mini DrinkDocument1 pageFresubin 2 Kcal Mini DrinkMohammed HaiderNo ratings yet
- BASF Emulsifier CheatSheet - LResDocument2 pagesBASF Emulsifier CheatSheet - LResdwiwidyapNo ratings yet
- LIPIDS Graphic OrganizerDocument1 pageLIPIDS Graphic OrganizerJuancho OsorioNo ratings yet
- Alba TinDocument3 pagesAlba TinRojas Evert AlonsoNo ratings yet
- Fats Fats: How Fat Can Be How Fat Can Be Good... Good..Document11 pagesFats Fats: How Fat Can Be How Fat Can Be Good... Good..mizyunieNo ratings yet
- Macronutrients Concept MapDocument1 pageMacronutrients Concept MapAna LuisaNo ratings yet
- TOP 50 BIO Questipns by TetriDocument56 pagesTOP 50 BIO Questipns by TetritetriofficialNo ratings yet
- Venkatarao Mannem Pharmacy Officer, Jharkhand: Presented byDocument9 pagesVenkatarao Mannem Pharmacy Officer, Jharkhand: Presented byShivangi ChauhanNo ratings yet
- BioBiochem Lesson 1 in CC 1 Student May 2 12 (Dragged)Document1 pageBioBiochem Lesson 1 in CC 1 Student May 2 12 (Dragged)DSNo ratings yet
- Important Points For DigestionDocument2 pagesImportant Points For Digestionaaravrshah14No ratings yet
- Hyperlipidemias and Atherosclerosis Dr. ManaloDocument3 pagesHyperlipidemias and Atherosclerosis Dr. ManaloMonique Angela Turingan GanganNo ratings yet
- Janes Metro Map Pathways BLANKDocument1 pageJanes Metro Map Pathways BLANKWinston TengNo ratings yet
- C S S P: Roduct EscriptionDocument2 pagesC S S P: Roduct EscriptionFrank DagohoyNo ratings yet
- Digestion of CarbohydratesDocument1 pageDigestion of Carbohydrateskay yNo ratings yet
- Drug CounsellingDocument4 pagesDrug CounsellingAnkit PandeyNo ratings yet
- Proteins BiochemDocument10 pagesProteins BiochemRein TopacioNo ratings yet
- MC104 Biochemistry LipidsDocument7 pagesMC104 Biochemistry LipidsAngelo GanabaNo ratings yet
- Congrat!: Circula Tory Sy StemDocument1 pageCongrat!: Circula Tory Sy StembruhNo ratings yet
- PDF Digestion Absorption 2nd PartDocument6 pagesPDF Digestion Absorption 2nd PartHhh HhhNo ratings yet
- Diapos Lab 5 BiocaDocument161 pagesDiapos Lab 5 BiocaFrancisco GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Digestion of LipidsDocument88 pagesDigestion of LipidsAbiyya AliNo ratings yet
- Fresubin 2 Kcal Fibre Mini DrinkDocument1 pageFresubin 2 Kcal Fibre Mini DrinkMohammed HaiderNo ratings yet
- Copy ofDocument3 pagesCopy ofXyla HapatingaNo ratings yet
- CC FinalsDocument29 pagesCC FinalsLOI VENUS BELMONTENo ratings yet
- Aa3 LPN 6Document4 pagesAa3 LPN 6Armaan PruthiNo ratings yet
- Gene SilencingDocument7 pagesGene SilencingMaliha JahanNo ratings yet
- 9.biomolecules 140mcq AakashDocument30 pages9.biomolecules 140mcq Aakashmd.ali.sharukhnawazNo ratings yet
- Food Chemistry: Ayyagari Archana, K. Ramesh BabuDocument6 pagesFood Chemistry: Ayyagari Archana, K. Ramesh BabuDinh Thi Kim HoaNo ratings yet
- Rna 10 924Document10 pagesRna 10 924Jyoti ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Replication, Transcription, Translation and Its Regulation: By, University of Agricultural Sciences, DharwadDocument42 pagesReplication, Transcription, Translation and Its Regulation: By, University of Agricultural Sciences, DharwadTabada NickyNo ratings yet
- (Reviewer) CMB Dna To RnaDocument9 pages(Reviewer) CMB Dna To RnaColeen ParejaNo ratings yet
- Methylation Diagram PDFDocument1 pageMethylation Diagram PDFmetNo ratings yet
- 2.6 Notes-1Document5 pages2.6 Notes-1John von steinbechNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Class 12th Project - DNA and RNA 2 (Complete Content PDFDocument34 pagesChemistry Class 12th Project - DNA and RNA 2 (Complete Content PDFKshitij RanjanNo ratings yet
- Vitamins All AboutDocument31 pagesVitamins All Aboutvu aneelaNo ratings yet
- Origins of Names of Protein Amino AcidsDocument1 pageOrigins of Names of Protein Amino AcidsadirmeedanNo ratings yet
- Virtual Lab-BuildingDNASEDocument5 pagesVirtual Lab-BuildingDNASEsmol ukeleleNo ratings yet
- 10 1126@science Abb2491Document9 pages10 1126@science Abb2491venkatavamsibharadwajNo ratings yet
- Vitamins Lecture 2 For 1st Year MBBS by DR Sadia HaroonDocument71 pagesVitamins Lecture 2 For 1st Year MBBS by DR Sadia HaroonIMDCBiochem100% (1)
- Fine Test ELISA KitsDocument376 pagesFine Test ELISA KitsDavid1002No ratings yet
- Nihms 56748Document35 pagesNihms 56748burcuu34No ratings yet
- Daftar ObatDocument1 pageDaftar Obatpuskesmas paciranNo ratings yet
- Adaptaciones Spinreact BS240 ProDocument1 pageAdaptaciones Spinreact BS240 ProClaudia Gonzalez CuisaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document6 pagesChapter 5Jackson VonkNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 SBI4U Exam Review June 2011Document3 pagesUnit 1 SBI4U Exam Review June 2011Shivi YogarajanNo ratings yet
- Why Spirulina Boosts Your Energy LevelDocument1 pageWhy Spirulina Boosts Your Energy LevelpinaslifeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 NotesDocument5 pagesChapter 3 NotesAndresNo ratings yet
- Excel HysysDocument11 pagesExcel HysysAndrie Kurniawan IndraNo ratings yet
- 6.conversion of Amino Acids To Specialized ProductsDocument8 pages6.conversion of Amino Acids To Specialized Productsقتيبه خالد دحام خلفNo ratings yet
- Molecular ChaperonesDocument14 pagesMolecular ChaperonesRomi GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Kecukupan GiziDocument110 pagesKecukupan GiziFathimah UswahNo ratings yet
- Metabolisme Protein As AminoDocument78 pagesMetabolisme Protein As AminoAgus FeriNo ratings yet