Professional Documents
Culture Documents
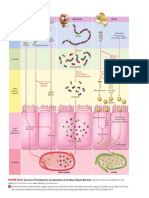
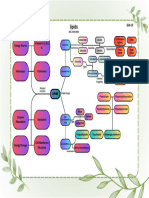
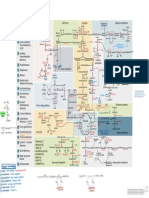
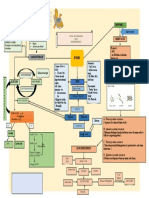
Macronutrients Concept Map
Uploaded by
Ana LuisaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Macronutrients Concept Map
Uploaded by
Ana LuisaCopyright:
Available Formats
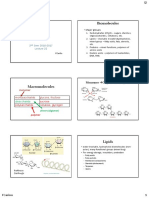
Provide energy, supply
essential fatty acids,
support reabsorption of
fat-soluble vitamins,
storage source of
energy, transmission of
insoluble in water,
nerve impulses Physical greasy to touch
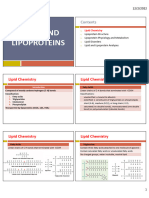
PHYSICAL & CHEMICAL carbon
CHARACTERISTICS
Chemical hydrogen
oxygen
Chain Length
Saturated
FATTY ACIDS Monounsaturated
Glucose CHARACTERISTICS Saturation Omega 3
Fructose MONOSACCHARIDES FAT Polyunsaturated
Omega 6
Linoleic acid
Galactose Energy source, α-linoleic acid
glycogen-carbohydrate
Sucrose storage, protein- Linoleic acid
sparing action,
antiketogenic diet,
ESSENTIAL FATTY ACIDS
Lactose DISACCHARIDES α-linoleic acid
heart action, central
Maltose nervous system
stored fatty acids in the human body;
serve as multiple functions throughout the body
Starch TRIGLYCERIDES
appear in the body cells as oily droplets
Resistant Starch
called Lipoproteins
CARBOHYDRATES MACRONUTRIENTS
Glycogen Digestible
Cholesterol
Dextrins POLYSACCHARIDES
LIPID-RELATED COMPOUNDS
Lipoproteins
Oligosaccharides
Dietary fiber
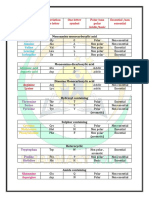
Non-digestible Histidine
Functional fiber Isoleucine
Leucine
Sorbitol Lysine
Mannitol OTHER FORMS
ESSENTIAL AMINO ACIDS Methioinine
Phenylalanine
Xylitol Threonine
Tryptophan
Valine
Alanine
PROTEIN Aspartic acid
NON-ESSENTIAL Asparagine
Glutamic acid
Serine
growth tissue Arginine
building, form
neurotransmitters,
Cysteine
form amino acids, Glutamine
form hormones,
CONDITIONALLY ESSENTIAL GLycine
support immune Proline
function, treat
catabolic illness,
Tyrosine
contributes to
overall energy
metabolism
You might also like
- Kenneth Saladin - Anatomy & Physiology - The Unity of Form and Function-McGraw-Hill Education (2020) (1) - 1Document1 pageKenneth Saladin - Anatomy & Physiology - The Unity of Form and Function-McGraw-Hill Education (2020) (1) - 1Guilherme RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Vitamins and Minerals Directly Involved in Energy MetabolismDocument5 pagesVitamins and Minerals Directly Involved in Energy MetabolismBaber Amin100% (1)
- LIPIDS graphic organizerDocument1 pageLIPIDS graphic organizerJuancho OsorioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document34 pagesChapter 14rafelNo ratings yet
- Vegetales, Portadores y Emolientes Datos Maestros de Aceites HLBDocument4 pagesVegetales, Portadores y Emolientes Datos Maestros de Aceites HLBHamsa RyuuganNo ratings yet
- PM SPM Metabolic PathwaysDocument1 pagePM SPM Metabolic PathwaysWill EdenNo ratings yet
- Ee Minimap 17Document1 pageEe Minimap 17阮 孟强No ratings yet
- Concept Map2Document1 pageConcept Map2Adrian idpalinaNo ratings yet
- Macro Molecules - Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins and Nucleic AcidsDocument2 pagesMacro Molecules - Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins and Nucleic Acidscbs123abc0% (1)
- Enzyme Models and BiomoleculesDocument3 pagesEnzyme Models and BiomoleculesJeffrey DaclanNo ratings yet
- Faal LambungDocument3 pagesFaal LambungAde RahmanNo ratings yet
- SOL review Biochemistry and water classificationDocument1 pageSOL review Biochemistry and water classificationAlayna SheltonNo ratings yet
- Metabolic PathwayDocument8 pagesMetabolic PathwaysadadsadNo ratings yet
- WWW MindmeisterDocument1 pageWWW MindmeisterDanu Handrian Firdaus XII MIPA 4No ratings yet
- Digestive System Anatomy and FunctionsDocument2 pagesDigestive System Anatomy and FunctionsHanako AranillaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and Diet Therapy: Macronutrients - Fats and LipidsDocument3 pagesNutrition and Diet Therapy: Macronutrients - Fats and LipidsJilliary AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Vocab PuzzleDocument1 pageBiochemistry Vocab PuzzleLelaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Secondary Metabolism and The Biosynthesis of Natural ProductsDocument64 pagesIntroduction To Secondary Metabolism and The Biosynthesis of Natural ProductsRobby ZidnyNo ratings yet
- Vegetable Oils Master Data for Skin Care ApplicationsDocument6 pagesVegetable Oils Master Data for Skin Care ApplicationsKaterina KaradikNo ratings yet
- Mind Maps in Biochemistry - (Metabolism of Carbohydrates)Document23 pagesMind Maps in Biochemistry - (Metabolism of Carbohydrates)Gus LionsNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Macromolecules HomeworkDocument4 pages2.2 Macromolecules HomeworkKarolina RachwalNo ratings yet
- 030 Intro To Secondary Metabolism and BiosynthesisDocument64 pages030 Intro To Secondary Metabolism and BiosynthesisRadi TyoNo ratings yet
- Pathway Asidosis MetabolikDocument1 pagePathway Asidosis MetabolikdianmardianiNo ratings yet
- Cas FCCDocument53 pagesCas FCCadfNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates Sugar S Lipids/Fatty Acids Proteins Amino Acids Nucleic Acids NucleotidesDocument2 pagesCarbohydrates Sugar S Lipids/Fatty Acids Proteins Amino Acids Nucleic Acids NucleotideslhabNo ratings yet
- 1 & 2 Gangg MetabolismeDocument117 pages1 & 2 Gangg MetabolismerahmedNo ratings yet
- Macromolecule Comparison Table PDFDocument1 pageMacromolecule Comparison Table PDFMariel Lolinco0% (1)
- Matabolism at A GlanceDocument1 pageMatabolism at A GlanceMoshiur RahmanNo ratings yet
- 1.3 LipidsDocument1 page1.3 LipidsBlitzSZNNo ratings yet
- Metabolism MapDocument1 pageMetabolism Mapyinose7198No ratings yet
- jDocument1 pagejKarthikNo ratings yet
- Copy ofDocument3 pagesCopy ofXyla HapatingaNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid Metabolism: (Palmitate, A 16C FA)Document1 pageFatty Acid Metabolism: (Palmitate, A 16C FA)Muhammad AbubakarNo ratings yet
- Advanced Dairy Chemistry: DR - Ganesh Kumar MSC (Dairy Tech) PH.D (Dairy Tech)Document40 pagesAdvanced Dairy Chemistry: DR - Ganesh Kumar MSC (Dairy Tech) PH.D (Dairy Tech)Alemayehu YohanesNo ratings yet
- Cargo Chart Sample PDFDocument1 pageCargo Chart Sample PDFRGCNo ratings yet
- Cargo Compatibility Chart: Reactive GroupsDocument1 pageCargo Compatibility Chart: Reactive GroupsRGCNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument1 pageBiomoleculesAshish GuleriaNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument1 pageBiomoleculesRaunak JayaswalNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid BiosynthesisDocument7 pagesFatty Acid BiosynthesisJeremiah Eyo AmanamNo ratings yet
- Lipids overview and fatty acid typesDocument14 pagesLipids overview and fatty acid typesBeverlyNo ratings yet
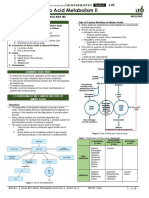
- Amino Acid Metabolsm 2Document12 pagesAmino Acid Metabolsm 2Manila Med100% (1)
- Lipids Midterm Exam BreakdownDocument4 pagesLipids Midterm Exam BreakdownKUZONo ratings yet
- Sailor Chemistry InfographicDocument1 pageSailor Chemistry Infographicapi-438770732No ratings yet
- Gel Filtration Selection GuideDocument1 pageGel Filtration Selection GuideDolphingNo ratings yet
- Structure of Human DigestionDocument3 pagesStructure of Human DigestionChong Yu AnNo ratings yet
- WaxesDocument3 pagesWaxesAshwani YadavNo ratings yet
- 1.lipid Metabolism - Catabolism Oct 16,2019 - For StudentsDocument1 page1.lipid Metabolism - Catabolism Oct 16,2019 - For StudentsAlif BaloNo ratings yet
- 1st Sec. (1st Part Summary)Document9 pages1st Sec. (1st Part Summary)RebelMLMlNo ratings yet
- Macromolecule ReviewDocument1 pageMacromolecule ReviewSebastian RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Final Review OutlinesDocument22 pagesBiochemistry Final Review Outlineslacey100% (1)
- bio mapDocument2 pagesbio mapdqnxfdw6bjNo ratings yet
- Lipids - An OverviewDocument16 pagesLipids - An OverviewKelvin ChipezeniNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins TableDocument1 pageCarbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins TableCarmela VargasNo ratings yet
- Chem 1: BiomoleculesDocument8 pagesChem 1: BiomoleculesApple GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Digestion+Absorption Mind MapDocument1 pageDigestion+Absorption Mind MapNo-Face. PersonaNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument10 pagesLipidsMelanie ParisNo ratings yet
- BBC 17 12 PDFDocument40 pagesBBC 17 12 PDFElleazar Immanuel MarcusNo ratings yet
- Digest in Body Complex Carbs Example:oat, Pumkin, Sweet PotatoDocument1 pageDigest in Body Complex Carbs Example:oat, Pumkin, Sweet PotatoSushi TangNo ratings yet
- Mindmap 2 MoleculesDocument1 pageMindmap 2 MoleculesAndrew ColvilleNo ratings yet
- PhysicianDocument2 pagesPhysicianAna LuisaNo ratings yet
- Tuesdayyy Submission!!!!!!!!!!Document2 pagesTuesdayyy Submission!!!!!!!!!!Ana LuisaNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Nursing Health HistoryDocument1 pageComprehensive Nursing Health HistoryAna LuisaNo ratings yet
- CESAREANDocument14 pagesCESAREANAna LuisaNo ratings yet
- VDRL Non Reactive Hiv I & Ii Non ReactiveDocument1 pageVDRL Non Reactive Hiv I & Ii Non ReactiveAna LuisaNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Nursing Health HistoryDocument1 pageComprehensive Nursing Health HistoryAna LuisaNo ratings yet
- PharmaDocument4 pagesPharmaAna LuisaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Interventions to Manage Postpartum Pain and Prevent ComplicationsDocument6 pagesNursing Interventions to Manage Postpartum Pain and Prevent ComplicationsAna LuisaNo ratings yet
- Tuesdayyy Submission!!!!!!!!!!Document2 pagesTuesdayyy Submission!!!!!!!!!!Ana LuisaNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Drug Class Mechanism Indications Contra-Side Effetcs/ Nursing of Action Indications Adverse Reactions ConsiderationsDocument5 pagesDrug Name Drug Class Mechanism Indications Contra-Side Effetcs/ Nursing of Action Indications Adverse Reactions ConsiderationsAna LuisaNo ratings yet
- PhysicianDocument2 pagesPhysicianAna LuisaNo ratings yet
- Sci ReportDocument8 pagesSci ReportAna LuisaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Interventions to Manage Postpartum Pain and Prevent ComplicationsDocument6 pagesNursing Interventions to Manage Postpartum Pain and Prevent ComplicationsAna LuisaNo ratings yet
- Physical AsessmentDocument2 pagesPhysical AsessmentAna LuisaNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Nursing Health HistoryDocument1 pageComprehensive Nursing Health HistoryAna LuisaNo ratings yet
- Tuesdayyy Submission!!!!!!!!!!Document2 pagesTuesdayyy Submission!!!!!!!!!!Ana LuisaNo ratings yet
- PhysicianDocument2 pagesPhysicianAna LuisaNo ratings yet
- New Medication Calculation PresentationDocument70 pagesNew Medication Calculation PresentationAna Luisa100% (1)
- Final Case Study IndividualDocument38 pagesFinal Case Study IndividualAna LuisaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Case Study ApaleDocument16 pagesNursing Case Study ApaleAna LuisaNo ratings yet
- Over 40 drugs for antineoplastics, cardiovascular, hematological & moreDocument5 pagesOver 40 drugs for antineoplastics, cardiovascular, hematological & moreAna LuisaNo ratings yet
- OdrehDocument1 pageOdrehAna LuisaNo ratings yet
- Learning Feedback Diary: Time ActivityDocument3 pagesLearning Feedback Diary: Time ActivityAna LuisaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Interventions to Manage Postpartum Pain and Prevent ComplicationsDocument6 pagesNursing Interventions to Manage Postpartum Pain and Prevent ComplicationsAna LuisaNo ratings yet
- Laurente, Ana Proteins: Figure 1. Protein SynthesisDocument11 pagesLaurente, Ana Proteins: Figure 1. Protein SynthesisAna LuisaNo ratings yet
- Group3 SurveyQuestionnaire-Block1Document3 pagesGroup3 SurveyQuestionnaire-Block1Ana LuisaNo ratings yet
- Uprooting Plastic Pollution: An Raw Material That Dissolve in WaterDocument2 pagesUprooting Plastic Pollution: An Raw Material That Dissolve in WaterAna LuisaNo ratings yet
- Historical Timeline of Philippine NursingDocument5 pagesHistorical Timeline of Philippine NursingAna LuisaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 5: Amino AcidsDocument6 pagesExperiment No. 5: Amino AcidsAna LuisaNo ratings yet
- Medical Certificate: Ormoc District HospitalDocument1 pageMedical Certificate: Ormoc District HospitalAna LuisaNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle and Cell ProliferationDocument49 pagesThe Cell Cycle and Cell ProliferationLeah BeningtonNo ratings yet
- G-Protein Coupled ReceptorsDocument8 pagesG-Protein Coupled ReceptorsHyunji KimNo ratings yet
- Protein Structure - Lecture 3Document18 pagesProtein Structure - Lecture 3Aakash HaiderNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Review Worksheet: Name: . DateDocument4 pagesEnzymes Review Worksheet: Name: . Dateapi-233187566100% (1)
- Gene RegulationDocument261 pagesGene RegulationPavithra ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Lista de Preturi: Subcontractat Analiza Acreditata RENARDocument9 pagesLista de Preturi: Subcontractat Analiza Acreditata RENARalexrodyNo ratings yet
- Isolasi Dan Penapisan Bakteri Penghasil Kitinase Dan Protease Yang Bersimbiosis Dengan Spons Dragmacidon SP Dari Teluk Manado, Sulawesi UtaraDocument9 pagesIsolasi Dan Penapisan Bakteri Penghasil Kitinase Dan Protease Yang Bersimbiosis Dengan Spons Dragmacidon SP Dari Teluk Manado, Sulawesi UtaraKevin NokeyaNo ratings yet
- BIO156 Enzyme Lab-Effect of Temperature On Enzyme Activity-F21Document8 pagesBIO156 Enzyme Lab-Effect of Temperature On Enzyme Activity-F21Shiloh FrederickNo ratings yet
- 11 Biosynthesis of RNADocument52 pages11 Biosynthesis of RNADayne Ocampo-SolimanNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 15-ENZYMESDocument4 pagesWorksheet 15-ENZYMESNaz BasaranNo ratings yet
- molecules: Computational Design of Macrocyclic Binders of S100B (ββ) : Novel Peptide TheranosticsDocument23 pagesmolecules: Computational Design of Macrocyclic Binders of S100B (ββ) : Novel Peptide TheranosticsГульнара ХакимоваNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid Abbreviations, Properties & Memory TricksDocument3 pagesAmino Acid Abbreviations, Properties & Memory TricksAniket SinghNo ratings yet
- Immunology - Website QuestionsDocument100 pagesImmunology - Website QuestionsMohammed AlMujaini75% (12)
- A Transcription ReinitiationDocument5 pagesA Transcription ReinitiationGeorgina HernandezNo ratings yet
- 3 LipidsDocument29 pages3 LipidsJayashree RajamaniNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Biochemistry 4th Edition Voet Test Bank DownloadDocument21 pagesFundamentals of Biochemistry 4th Edition Voet Test Bank Downloadmatildaphelim4g8100% (38)
- Differences in Energy, Macronutrients and Omega 3 of Blenderized and Commercial Enteral FormulasDocument8 pagesDifferences in Energy, Macronutrients and Omega 3 of Blenderized and Commercial Enteral FormulaszulhenniNo ratings yet
- 1.question Bank - IGMCRI (Biochemistry)Document11 pages1.question Bank - IGMCRI (Biochemistry)Anirudh BNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Form 3Document4 pagesEnzymes Form 3Ralph MuchingamiNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1567258117004Document10 pagesOrca Share Media1567258117004Monique Eloise GualizaNo ratings yet
- BCH 401 - Advanced EnzymologyDocument15 pagesBCH 401 - Advanced EnzymologyOLUWASEGUN K Afolabi100% (2)
- Biol 309 Question Bank CytoskeletonDocument6 pagesBiol 309 Question Bank CytoskeletonsharventhiriNo ratings yet
- JRRMMC Biochem Exam Answer KeyDocument4 pagesJRRMMC Biochem Exam Answer KeyBom Tna100% (2)
- Harpers 20Document9 pagesHarpers 20Dewi RatnasariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - NotesDocument22 pagesChapter 2 - NotesanusoumyaNo ratings yet
- Lipid Metabolism Notes PDFDocument3 pagesLipid Metabolism Notes PDFLoly HemmingsNo ratings yet
- Secondary HemostasisDocument14 pagesSecondary HemostasisSindhu AdhikariNo ratings yet
- 2.5 (Enzymes)Document1 page2.5 (Enzymes)bulhaNo ratings yet
- Homeopathic and herbal remedies price listDocument18 pagesHomeopathic and herbal remedies price listJOCELYN ACEVEDONo ratings yet
- Protein DenaturationDocument17 pagesProtein DenaturationnaalakiNo ratings yet