Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biomolecules
Uploaded by
Raunak JayaswalCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biomolecules
Uploaded by
Raunak JayaswalCopyright:
Available Formats
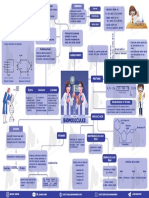
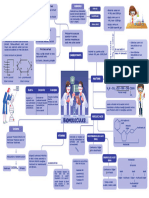
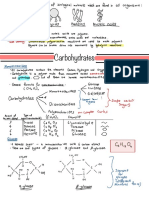
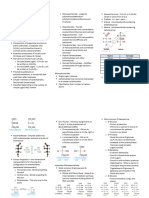
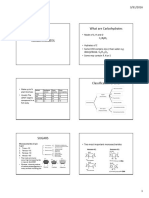
MonoSaccharides HORMONES
Glucose Further hydrolysis is not possible
Steroids
Neutral: equal no.
Preparation:- Molecules that are
(simple sugar).
H+ synthesised by endocrine of -NH2 and -COOH group.
Sucrose →Glucose +Fructose Ex: Glucose, Fructose, Ribose glands to control and Polypeptides
regulate the functioning Basic: More no. of
starch + NH2 O Glucose -NH2 then -COOH group.
of specific organs.
Chemical properties:- Amino Acids Acidic: more no.
∆, HI n-Hexane of-COOH than-NH2 group.
NH2OH OligoSaccharides
Oxime
Glucose Br2/water Yields two to ten Polyhydroxy aldehyde
number of -NH2 and -COOH group
Gluconic acid
Acetic anhydride monosaccharides. (aldose) or ketone
Glucosepenta-acetate Ex: Sucrose, Maltose, Lactose (ketose) containing at
least one chiral center Essential amino acids can
Cyclic structure of glucvose
be synthesized in the
On the relative
body.
PolySaccharides On the basis of
Polymer of α-amino acids that Non-essential amino acids
Yields a large number of contain -NH2 and -COOH group place of synthesis
cH2OH CARBOHYDRATE are synthesized in the
monosaccharides units. body.
O Ex: Starch, Cellulose, Glycogen
H H H
H
H
4 1
HO O
OH H ON the basis 1. Fibrous: fibre like
H OH OH
structure
H
3 2 of shape
CH2OH H OH 2. Globular protein.
[α-D(+)- Glucose] α-D-(+)-Glycopyranose Classification
PROTEINS
(Fischer Formula) (Haworth structure)
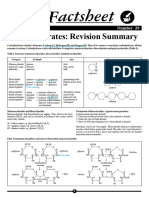
Starch Cellulose Glycogen
H2 N − CH2 − CO− NH− CH− COOH
Peptide linkage
This is known as CH3
Polymer of It is found in animal starch. It is
α-glucose with plants. present in liver,
two components It contains muscle and brain. Denaturation of protein
amylose(15-20%) β−D- glucose units It's structure is
connected vice similar to
When a protein in its native form is
and amylopectin
(80-85%) glycosidic linkage amylopectin. subjected to physical change, globules unfold,
and proteins loses it's biological activity.
NUCLEIC ACID
BIOMOLECULES Nitrogenous
base
Pentose
sugar Phosphate GP
Enzyme N
Globular proteins that are VITAMINS DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID
specific to a particular Particles of nucleus of (DNA)
reaction and for a substrate. the cell responsible for
heredity are called Nucleoside
chromosomes Compound of sugar
β-D-2 deoxyribose
Mechanism of enzyme action Organic compounds required
in diet in small amounts to
RIBONUCLEIC ACID
perform specific biological (RNA)
CLASSIFICATION Bases that at make up nucleic acid chain
functions for maintenance DNA and RNA
Substrate
Enzyme and growth.
Product Compound of Sugar
Adenine (A) Base Base Base
Guanine (G) β-D-ribose
Cytosine (C) Sugar - Phosphate - [sugar - phosphate]-sugar
n
Water Soluble: B group and Fat Soluble: Soluble in Thymine (T)
fats and oils but Types of RNA:
vitamin C are soluble in insoluble in water Uracil (U)
water. (vitamins A, D, E and K) m-RNA, r-RNA, t-RNA
You might also like
- BiomoleculesDocument1 pageBiomoleculesAshish GuleriaNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules: GlucoseDocument1 pageBiomolecules: GlucoseGargi PathakNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument1 pageBiomoleculessarthakyedlawar04No ratings yet
- Designed: by PanchalDocument18 pagesDesigned: by PanchalJatinder SinghNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Macromolecules HomeworkDocument4 pages2.2 Macromolecules HomeworkKarolina RachwalNo ratings yet
- digestiveDocument1 pagedigestivenina.kol222No ratings yet
- N Acetyl-Coa: Overview: Lipids To SucroseDocument1 pageN Acetyl-Coa: Overview: Lipids To SucroseLuke ShantiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For Biologist 1A Parts 1& 2Document17 pagesChemistry For Biologist 1A Parts 1& 2body fayezNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules RevisionDocument12 pagesBiomolecules Revisionpk2637932No ratings yet
- Chem Ch14 NIE Premium NOtesDocument19 pagesChem Ch14 NIE Premium NOtessnigdhagulhane0922No ratings yet
- Class 12 BiomoleculesDocument9 pagesClass 12 BiomoleculesArpit LambaNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument3 pagesBiologys0xynpark18No ratings yet
- Carbohydrates structure and propertiesDocument1 pageCarbohydrates structure and propertiesS3CH-14 Choy Pak MingNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration FlowchartDocument1 pageCellular Respiration FlowchartAndrew100% (5)
- Chapter2 Carbohydrates 1Document66 pagesChapter2 Carbohydrates 1Alice C. RiveraNo ratings yet
- BioMolecules in One ShotDocument46 pagesBioMolecules in One ShotKESHAV KUMARNo ratings yet
- Bio Molecules Part 1 Short Notes 1 YbNZvpO1rMiZ3B5YDocument19 pagesBio Molecules Part 1 Short Notes 1 YbNZvpO1rMiZ3B5YBob the clasherNo ratings yet
- Polysaccharides: SugarsDocument7 pagesPolysaccharides: SugarsBikash YadavNo ratings yet
- Lecture 22 11-17-22Document19 pagesLecture 22 11-17-22Caleb HeNo ratings yet
- L6 ElectronsDocument12 pagesL6 ElectronsCheng FuNo ratings yet
- Bio Molecules ReviewerDocument5 pagesBio Molecules ReviewerFIORELA LAZARONo ratings yet
- Biochem FinalsDocument3 pagesBiochem FinalsElyon Jirehel AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry CarbsDocument78 pagesClinical Chemistry CarbsvnicasantiagoNo ratings yet
- Classification According To Number of Carbons Fischer Projection Formula (Linear)Document2 pagesClassification According To Number of Carbons Fischer Projection Formula (Linear)bunso padillaNo ratings yet
- Biological MoleculesDocument11 pagesBiological Moleculesparisa khoshhalNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument6 pagesBiology NoteselviiNo ratings yet
- Glycoside IntroDocument5 pagesGlycoside IntroNomiNo ratings yet
- Enzymatic Types in MetabolismDocument9 pagesEnzymatic Types in MetabolismSara JensenNo ratings yet
- Chapt07 Lecture 2015F-3Document65 pagesChapt07 Lecture 2015F-3PaulNo ratings yet
- (Biochem A) 1.1 Carbohydrate Chemistry (Asis)Document8 pages(Biochem A) 1.1 Carbohydrate Chemistry (Asis)Faye AquinoNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates NotesDocument9 pagesCarbohydrates NotesAshley Saron100% (1)
- The Hexanoyl-Coa Precursor For Cannabinoid Biosynthesis Is Formed by An Acyl-Activating Enzyme in Cannabis Sativa TrichomesDocument13 pagesThe Hexanoyl-Coa Precursor For Cannabinoid Biosynthesis Is Formed by An Acyl-Activating Enzyme in Cannabis Sativa TrichomesAnonymous 9oH7eQ2TNo ratings yet
- 04 Terpenoides CompilationDocument209 pages04 Terpenoides Compilationrustyryan77No ratings yet
- Cho Chemistry: The Genius in Biochemistry Dr. Mohamed AghaDocument13 pagesCho Chemistry: The Genius in Biochemistry Dr. Mohamed AghaAbd Al Razzaq Said100% (1)
- 1.2 CarbohydratesDocument1 page1.2 CarbohydratesBlitzSZNNo ratings yet
- Matabolic PathwaysDocument11 pagesMatabolic PathwaysLevi100% (2)
- Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle: DR Imran SiddiquiDocument10 pagesTricarboxylic Acid Cycle: DR Imran Siddiquiapi-19824406No ratings yet
- Carbohydrates - FactRecallDocument5 pagesCarbohydrates - FactRecallRawan Al-tahanNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument24 pagesChemistryLee LuceroNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates MIDTERMDocument9 pagesCarbohydrates MIDTERMLeiNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULES MHT CET SynopsisDocument4 pagesBIOMOLECULES MHT CET SynopsisAbhishek Mandlik100% (3)
- Carbohydrates: Structure, Classification and ImportanceDocument3 pagesCarbohydrates: Structure, Classification and ImportanceRanit MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- 3 CarbohydratesDocument6 pages3 Carbohydrates211525No ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument79 pagesBiomolecules9929raoyadav6No ratings yet
- 10 3390@biom10071068Document18 pages10 3390@biom10071068Hillary OziokoNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate GiziDocument11 pagesCarbohydrate Gizifina26No ratings yet
- Non Energy Role of CarbohydratesDocument34 pagesNon Energy Role of CarbohydratesDr. M. Prasad NaiduNo ratings yet
- Classification of Carbohydrates: Monosaccharides, Disaccharides, and FunctionsDocument6 pagesClassification of Carbohydrates: Monosaccharides, Disaccharides, and FunctionsnnnnNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates Sugar S Lipids/Fatty Acids Proteins Amino Acids Nucleic Acids NucleotidesDocument2 pagesCarbohydrates Sugar S Lipids/Fatty Acids Proteins Amino Acids Nucleic Acids NucleotideslhabNo ratings yet
- BMM LEC 4 SN Structure Function of Carbohydrates & LipidsDocument3 pagesBMM LEC 4 SN Structure Function of Carbohydrates & LipidsSARAH SAFIAH TAJUL ARIFFINNo ratings yet
- Aakash Modules 06Document125 pagesAakash Modules 06tenn84269No ratings yet
- LEC 7 - CarbohydratesDocument5 pagesLEC 7 - Carbohydrateserikapana09No ratings yet
- Glycolysis 1: Sections 1 and 2Document11 pagesGlycolysis 1: Sections 1 and 2rukida_No ratings yet
- Bio FactsheetDocument3 pagesBio Factsheetshannongiovanny7No ratings yet
- Wax Classification 1Document5 pagesWax Classification 1Prabhu TexcomsNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Carbohydrates: Professor & Hod DR Maryam Wahid MBBS, Mphil, PH.D (Biochemistry)Document22 pagesChemistry of Carbohydrates: Professor & Hod DR Maryam Wahid MBBS, Mphil, PH.D (Biochemistry)Haseeb AlviNo ratings yet
- Metabolisme SekunderDocument27 pagesMetabolisme Sekunderjea yaumulNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde Ketones and Carboxylic AcidDocument1 pageAldehyde Ketones and Carboxylic AcidRaunak JayaswalNo ratings yet
- 15 PolymersDocument1 page15 PolymersMalola EducationNo ratings yet
- 6 General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements 1Document1 page6 General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements 1Raunak JayaswalNo ratings yet
- Gas Solif Liquid StateDocument1 pageGas Solif Liquid StateMiroNo ratings yet
- Coatings - Competitive Crossover 2013 R2Document127 pagesCoatings - Competitive Crossover 2013 R2g_milburnNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical ReviewerDocument6 pagesBiogeochemical ReviewerQuerecia IsidroNo ratings yet
- Cytotoxic, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities and Phenolic Contents of Eleven Salvia Species From IranDocument10 pagesCytotoxic, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities and Phenolic Contents of Eleven Salvia Species From IranIsmael GuardiaNo ratings yet
- Ru Du PhosDocument6 pagesRu Du Phossiti emeliaNo ratings yet
- Harmony in Wisdom: Hope in LifeDocument318 pagesHarmony in Wisdom: Hope in LifeSymon MillarNo ratings yet
- Alcohols: Year 11 Chemistry IgcseDocument12 pagesAlcohols: Year 11 Chemistry IgcseGanta BooomNo ratings yet
- 27 Alcohol Phenol Ether Formula Sheets Getmarks AppDocument15 pages27 Alcohol Phenol Ether Formula Sheets Getmarks AppFLASH FFNo ratings yet
- 10.1 Chemical Basis of Life - 05th JanDocument15 pages10.1 Chemical Basis of Life - 05th JanManupa PereraNo ratings yet
- Volume 2 Issue 10 - October 2013Document406 pagesVolume 2 Issue 10 - October 2013Tatiana Monroy MoraNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science SHS 16.3 How Organisms Obtain and Utilize EnergyDocument23 pagesEarth and Life Science SHS 16.3 How Organisms Obtain and Utilize EnergyPamela MalihanNo ratings yet
- Harga Pihak 3Document16 pagesHarga Pihak 3Aprillian AptNo ratings yet
- Activity 2B - Reactions To CarbohydratesDocument6 pagesActivity 2B - Reactions To CarbohydratesMy Roses Are RosèNo ratings yet
- Installation and Refrigerant Cutout Guide for Evaporator UnitsDocument1 pageInstallation and Refrigerant Cutout Guide for Evaporator UnitsEdmarNo ratings yet
- Fikru Zawude Orgnal WorkDocument33 pagesFikru Zawude Orgnal WorkEcy YghiNo ratings yet
- Appendix U Remedial Action Plan Part 1Document204 pagesAppendix U Remedial Action Plan Part 1Chester FengNo ratings yet
- Dairy Portfolio Solutions GBDocument6 pagesDairy Portfolio Solutions GByaigenis contrerasNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its Compounds 1Document22 pagesCarbon and Its Compounds 1Subhendu KumarNo ratings yet
- Almscare Product List 03-10-2023Document22 pagesAlmscare Product List 03-10-2023Gautam DxNo ratings yet
- 2 IR SpectrosDocument32 pages2 IR SpectrosRaunak PrasadNo ratings yet
- Lipids Classification and PropertiesDocument13 pagesLipids Classification and PropertiesAbby Dimalaluan OquendoNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet: F-29, Liquid SanitizerDocument4 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet: F-29, Liquid SanitizerNiraNo ratings yet
- Driers and Metallic Soaps 2Document5 pagesDriers and Metallic Soaps 2Juan David NavarroNo ratings yet
- Understanding Redox ReactionsDocument64 pagesUnderstanding Redox ReactionsJason Teh59% (66)
- Bania Et Al 2012 Enhanced Catalytic Activity of Zeolite Encapsulated Fe (III) Schiff Base Complexes For OxidativeDocument18 pagesBania Et Al 2012 Enhanced Catalytic Activity of Zeolite Encapsulated Fe (III) Schiff Base Complexes For OxidativeBuddha Shankar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Agarose Gel Electrophoresis, How It Works and Its UsesDocument17 pagesAgarose Gel Electrophoresis, How It Works and Its UsesSami RaiNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Chemistry Half Yearly VMCDocument7 pagesClass 12 Chemistry Half Yearly VMCno accountNo ratings yet
- Supercritical Fluid Extraction: by Nicole Adams and Morgan CampbellDocument27 pagesSupercritical Fluid Extraction: by Nicole Adams and Morgan CampbellAni KushwahaNo ratings yet
- ENERGY AND ENVIRONMENT - 18ME751 Module 4 - Dr. ShashikantDocument31 pagesENERGY AND ENVIRONMENT - 18ME751 Module 4 - Dr. Shashikant17druva MNo ratings yet
- Grade VIII Science Material With Worksheets 2022-23Document64 pagesGrade VIII Science Material With Worksheets 2022-23Ravi KiranNo ratings yet
- Biofuel An Environmental Friendly FuelDocument14 pagesBiofuel An Environmental Friendly FuelRoberticoZeaNo ratings yet