Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Macronutrients Fats and Lipids
Uploaded by
Jilliary Alexandra0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views3 pagesThe document discusses nutrition and diet therapy, focusing on macronutrients like fats and lipids. It provides details on the classification of lipids, including triglycerides, fatty acids, and phospholipids. Specific fatty acids like linoleic acid, linolenic acids, EPA, and DHA are examined for their roles in metabolism, brain development, and disease prevention. The document also touches on fats in foods, digestion of fats, and sources of healthy oils.
Original Description:
fdfdgr
Original Title
Macronutrients-Fats-and-Lipids
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses nutrition and diet therapy, focusing on macronutrients like fats and lipids. It provides details on the classification of lipids, including triglycerides, fatty acids, and phospholipids. Specific fatty acids like linoleic acid, linolenic acids, EPA, and DHA are examined for their roles in metabolism, brain development, and disease prevention. The document also touches on fats in foods, digestion of fats, and sources of healthy oils.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views3 pagesMacronutrients Fats and Lipids
Uploaded by
Jilliary AlexandraThe document discusses nutrition and diet therapy, focusing on macronutrients like fats and lipids. It provides details on the classification of lipids, including triglycerides, fatty acids, and phospholipids. Specific fatty acids like linoleic acid, linolenic acids, EPA, and DHA are examined for their roles in metabolism, brain development, and disease prevention. The document also touches on fats in foods, digestion of fats, and sources of healthy oils.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
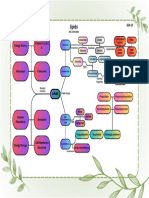
NUTRITION AND DIET THERAPY
MACRONUTRIENTS – FATS AND LIPIDS
PRELIM | Ma’am Aguirre
Transcribed by: Ochave, Daisy Rey C.
Topic Outline LINOLEIC ACID – OMEGA
6 FATTY ACIDS
(1) Classification of Lipids Found in the seeds of plants
(2) Fats in Foods and in the oils produced from the
seeds
(3) The Effects of Various Kinds of Fats on Blood Lipids Some food sources are
(4) Fats Digestion vegetable oils, seeds, nuts, whole
(5) Sources of Healthy Oil grain
LINOLENIC ACIDS –
OMEGA 3 FATTY ACIDS
FATS AND LIPIDS Belongs to a family of
Lipids are compounds PUFA
Contains EPA and DHA
that are founds primarily in fish
CLASSIFICACTION OF LIPIDS oil
EPA – Eicosapentaenoid
Acid
CLASSIFICATION OF LIPIDS DHA –
The fatty content of meat and fats in the body Docosahexaenoic Acid
TRIGLYCERIDE Impressive roles in
Predominate in the diet and in the body
S (FATS AND Composed of 3 Fatty Acids + Glycerol metabolism and disease
OILS) GLYCEROL AND FATTY ACIDS
prevention
Needed for normal brain
GLYCEROL A small water soluble compound development
Organic compounds with a chain Brain has a high content of
FATTY DHA
of C atoms with H attached and an
ACIDS acid group at one end differ in chain DHA is also especially
length and saturation active in the rods and cones of the
retina of the eye
CHAIN LENGTH Essential for normal growth
Refers to the number of C in FA and development
Play an important role in
SATURATON the prevention and treatment of
Refers to its chemical structure heart disease, diabetes,
Especially the number of H the C in the FA are holding hypertension, arthritis and cancer
The more hydrogen atoms attached to those C the more PHOSPHOLIPIDS Lecithin and cephalin
saturated the FA Found in brain, bile and nerve tissues
Formed in all cells of the body
Some are circulated in the blood to combine with fatty
CLASSIFICATION OF FATTY metabolites make phospholipids more H20 soluble
ACIDS Act as emulsifier
Help to keep other fats in solution in the watery blood and
ACCORDING SATURATED FATTY ACIDS
body fluids
SFA
TO more H atoms attached to Lecithin used to build well membranes are made from starch
by the liver
SATURATION those C atoms
Soluble in both water and fats
Fully loaded with hydrogen
and has only single bonds with STEROLS Precursor of Vitamin D
the C KINDS OF STEROLS
CHOLESTEROL Most familiar word
UNSATURATED FATTY
ACIDS FOOD SOURCES OF
H atoms are missing in the FA CHOLESTEROL
chains Only animal derived foods
The degree of unsaturation of contain significant amount of
the FA in a fat, influences the cholesterol
health of the body Richest sources are liver,
kidneys and eggs
MONOUNSATURATED Eggs source are cheeses and
FATTY ACIDS (MUFA) meats
1 point of unsaturation Shellfish has more sterol but
less in cholesterol
POLYUNSATURATED Fish liver oils
FATTY ACIDS (PUFA) Organic compounds with a
More points of unsaturation FATTY ACIDS
chain of C atoms with H attached
ACCORDING HARD AND SOFT FATS and an acid group at one end
Unsaturated FA differ in chain length and
TO PHYSICAL Soft at room temperature saturation
CHARACTER and melt more easily
chicken fats less saturated
and soft WAYS USED BY MANUFACTURER TO PROTECT FAT –
vegetable oil most CONTIANING PRODUCTS FROM SANCIDITY
unsaturated, liquids at room (1) Sealed airtight and refrigeration – an expensive and inconvenient storage system
temperature
(2) Add antioxidants to complete for the O and also to protect the oil
STABILITY (3) Use the process called hydrogenation
Saturated fats are more
resistant to oxidation and lesser HYDROGENATION
chance for rancidity Saturate some or all of the points of unsaturation by adding hydrogen atoms
PUFA spoil most readily ADVANTAGES OF HYDROGENATION
because their double bonds (1) Prolonging shelf life
(2) Increasing the solidity of fats
ACCORDING EFA
(3) When partially hydrogenated vegetable oil will become spreadable
cannot be made from other
TO substances in the body, must be margarines
ESSENTIALITY obtained from the food or from (4) Make piecrust flaky and puddings creamy
the diet
DISADVANTAGES OF HYDROGENATION Seeds (pumpkin, sunflower)
(1) Make PUFA more saturated OMEGA 3 – POLYUNSATURATED
(2) Health advantages are lost in hydrogenation fatty fish (herring, mackerel, salmon, tuna)
(3) Change FA from Cis to Trans FA Flaxseed
Nuts
SYNTHESIS AND ESSENTIALITY OF CHOLESTEROL
(1) Can be made by the boy
HARMFUL FATTY ACIDS
(2) Synthesized mainly in the liver “endogenous”
SATURATED
(3) Raw materials used by the liver to make cholesterol are glucose and FA
Bacon, butter, cheese
ROUTES OF CHOLESTEROL IN THE BODY Chocolate, coconut cream
(1) Made into bile, stored in the gallbladder, and delivered into the SI to digest fats Milk fat (whole milk products)
(2) Travel via the bloodstream and to all the body cells or membranes of the cell to perform Oils (coconut, palm, palm kernel)
vital structural and metabolic functions Shortening, sour cream
TRANS FATS
EXCRETION OF CHOLESTEROL
Commercial baked goods made with margarine and Shortening
(1) Bile is release into the SI to aid in the digestion and absorption of fats
(2) After digestion, it is reabsorbed into the body and recycled, the rest are excreted in the (cookies, cake pies, etc.)
feces Fried foods particularly restaurants and fast foods such French
(3) While the bile is in the SI, some of it maybe trapped by soluble fibers or by some fires and chicken
medications, which carry it out of the body in feces
(4) The excretion of bile reduces the total amount remaining in the body Many fried or processed snack foods (microwave popcorn, chips
and crackers)
TRANSPORT OF CHOLESTEROL Margarine (hydrogenated or partially hydrogenated)
(1) Cholesterol packaged with other lipids and Proteins leaves the liver via the arteries and Non dairy creamer and shortening
is transported to the body Tissues by the blood
(2) Packaged between lipid and Proteins is called lipoproteins
THE EFFECTS OF VARIOUS KINDS OF FATS ON
(3) As it travels through the body it can extract lipids and it may form deposits that can
contribute to BLOOD LIPIDS
ATHEROSCLEROSIS – a disease that cause the heart attacks and strokes
KINDS OF CHOLESTEROL THE EFFECTS OF VARIOUS KINDS OF FATS ON
LDL LOW density lipoprotein BLOOD LIPIDS
Bad
For deposits of cholesterol
SATURATED DIETARY SOURCES
All animal meats, beef tallow, butter, butter cheese, chocolate,
HDL High density lipoprotein FATS cream, cocoa butter, coconut oil, palm oil, lard, hydrogenated oils,
Good stick margarine, shortening oils, stick margarine, shortening, and
will trap and deliver cholesterol out from the body whole milk
ERGOSTEROL Cholesterol from plant
FFECTS ON BLOOD LIPIDS
CALCIFEROL Cholesterol from fish liver oils
Increase total cholesterol
Increase LDL-Cholesterol
FUNCTION OF FATS MONO- DIETARY SOURCES
(1) PROVODE ENERGY Avocadoes, canola oil, cashews, olive oil, olives, peanut butter,
Triglycerides breakdown UNSATURATED peanut oil, peanuts, poultry
The body’s capacity in storing fat is unlimited FATTY ACID
Due to an enzyme LPL (lipoprotein lipase) that promotes fat storage in fat cells EFFECTS ON BLOOD LIPIDS
and muscles cells If used to replace saturated fats in the diet, monounsaturated fats
Due to hormone Ghrelin; produced by the stomach cells that will stimulate appetite may
ADIPOSE TISSUE – the body’s fat which consists of masses of fat storing cells, Decrease total cholesterol
when there are surplus of energy, new fat cells are readily produced Decrease LDL-cholesterol without decreasing HDL-cholesterol
(2) NATURAL OILS PROVIDE A RADIANT COMPLEXION, HELP NOURISH OMEGA 3 DIETARY SOURCES
THE HAIR AND MAKE IT GLOSSY Wheat germ canola oil, flaxseed, ocean fish (salmon, mackerel,
(3) INSULATE THE BODY AGAINST EXTREME TEMPERATURE FATTY ACID tuna), shellfish, some vegetables (spinach, broccoli, lettuce) soy
foods, walnuts
(4) PROTECT THE BODY’S VITAL ORGANS FROM SHOCK
Hard fat beneath each kidney
Soft fat in woman’s breast, protects mammary glands EFFECTS ON BLOOD LIPIDS
Cushions against shock form head and cold If used to replace saturated fats in the diet, omega-3 fatty acid may
Decrease total LDL-cholesterol
increase HDL-cholesterol
FATS IN FOODS Decrease triglycerides
HEALTHFUL FATTY ACIDS TRANS FATS DIETARY SOURCES
Margarine (hard stick), cake, cookies, doughnuts, crackers, chips,
MUFA meat and dairy products, peanut butter, (hydrogenated), shortening
Avocado
EFFECTS ON BLOOD LIPIDS
Nuts (almonds, cashew, filberts, hazelnuts, pecans; macademia Increases total cholesterol
nuts, peanuts, pistachos) crease LDL-cholesterol
Oils (Canola, peanut, seasame)
Olives
Peanut butter (old fashioned)
Seeds (seasame)
OMEGA 6 POLYUNSATURATED
Margarine (nonhydrogenated)
Mayonnaise
Nuts (walnuts)
Oils (corn, cotton seed, safflower, soy beans)
Salad dressing
Transes by: Daisy Rey Ochave | Template by: camillexcar 2
FATS DIGESTION
MOUTH
GLANDS
In the base of the tongue-lingual-secretes fat digesting enzyme
ENZYME
Lingual lipase
ACTIONS
Some hard fats begin to melt as they reach body temperature
STOMACH
ENZYME
Acid stable lingual lipase
ACTIONS
Split one bond of Triglycerides to produce diglycerides and FA
the degree of hydrolysis is slight for most fats but appreciable for
milk fats
the stomach chumming action mixes fats with water and acids
GLAND
Gastric
ENZYME
Gastric Lipase
SMALL INTESTINE
Bile flows in from the liver and Gallbladder (via common bile duct)
Bilesalts and pancreatic lipase will emulsified fats to monoglycerides
for absorption in a form of
Glycerol and fatty acids
LARGE INTESTING
Some fats and cholesterol are trapped in fiber for excretion
SOURCES OF HEALTHY OIL
SOURCES OF HEALTHY OIL
(1) Flaxseed Oil
(2) Avocado Oil
(3) Olive Oil
(4) Peanut Oil
(5) Canola Oil
(6) Coconut Oil
(7) Walnut Oil
(8) Sesame Oil
Transes by: Daisy Rey Ochave | Template by: camillexcar 3
You might also like
- Biochem Post Lab 5aDocument12 pagesBiochem Post Lab 5aJessica Lorenz PablicoNo ratings yet
- Lipids: Lipids Known As Fats Provide A MajorDocument82 pagesLipids: Lipids Known As Fats Provide A MajorYoshiNo ratings yet
- 1 Notes Basic NutrientsDocument8 pages1 Notes Basic Nutrientsclear kNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2 - Macronutrient (FATS Slash LIPIDS)Document6 pagesMODULE 2 - Macronutrient (FATS Slash LIPIDS)Donna MarieNo ratings yet
- J. B. Brown, Department of Physiological Chemistry, Ohio State UniversityDocument13 pagesJ. B. Brown, Department of Physiological Chemistry, Ohio State UniversityJohn JoseNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument14 pagesLipidsBeverlyNo ratings yet
- 3 LipidsDocument42 pages3 LipidsSyifaAnandaNo ratings yet
- Lipids: Mục tiêu học tậpDocument56 pagesLipids: Mục tiêu học tậpÁnh NaNo ratings yet
- Lipids Chemistry Revision NursingDocument40 pagesLipids Chemistry Revision NursingJohn Matthew100% (1)
- Biochemistry - Chemistry of LipidsDocument42 pagesBiochemistry - Chemistry of LipidsSyifaAnandaNo ratings yet
- Lipids PresentationDocument38 pagesLipids Presentationbmuzammil236No ratings yet
- LipidsDocument17 pagesLipids2m2f2k99y6No ratings yet
- LIPIDSDocument30 pagesLIPIDSMary Ann OgoyNo ratings yet
- Bio 2Document14 pagesBio 2Maria Jeorgia SalinasNo ratings yet
- Concept Map - Dietary FatDocument1 pageConcept Map - Dietary FatGyra Marie AgraNo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument5 pagesLipidsChandanaNo ratings yet
- Fatty AcidsDocument9 pagesFatty AcidsQOTRUNNADA AIDANo ratings yet
- LipidsDocument4 pagesLipidsshane.surigaoNo ratings yet
- The Lipids What Are Lipids?Document16 pagesThe Lipids What Are Lipids?Sire100% (1)
- LFS 233:module 5 Fats: College of Health Sciences Integrated Sciences DepartmentDocument65 pagesLFS 233:module 5 Fats: College of Health Sciences Integrated Sciences DepartmentHussain Ali100% (1)
- MAcronutrients - LipidsDocument40 pagesMAcronutrients - LipidsNurten Ayça AktaşNo ratings yet
- Specialty Lipids in Health and Disease: Fayez HamamDocument8 pagesSpecialty Lipids in Health and Disease: Fayez HamamRetno PurwaningsihNo ratings yet
- Introduction To LipidsDocument29 pagesIntroduction To LipidsBharaniDeepan50% (2)
- Lipids Structure IDocument45 pagesLipids Structure Ijffernando1994No ratings yet
- Lipids: o Dehydration Synthesis Is When TheDocument3 pagesLipids: o Dehydration Synthesis Is When TheKheza SuravillaNo ratings yet
- LIPIDS Graphic OrganizerDocument1 pageLIPIDS Graphic OrganizerJuancho OsorioNo ratings yet
- Lipid Metabolism - I: Chemistry, Digestion and Absorption of LipidsDocument38 pagesLipid Metabolism - I: Chemistry, Digestion and Absorption of LipidscheckmateNo ratings yet
- DMK 5022 Chapter 1Document12 pagesDMK 5022 Chapter 1nityaNo ratings yet
- Beige Minimal Professional Business Project PresentationDocument47 pagesBeige Minimal Professional Business Project PresentationBhagwat KaurNo ratings yet
- Oleo JadiDocument9 pagesOleo JadiputriNo ratings yet
- Jaim 5 85 PDFDocument4 pagesJaim 5 85 PDFAnonymous IPmHmtQNkKNo ratings yet
- 2013EC Source-Extraction-And-Constituents-Of-Fats-And-OilsDocument8 pages2013EC Source-Extraction-And-Constituents-Of-Fats-And-OilsĜĭdęŷ KîřöşNo ratings yet
- Structure and Classification of Lipids: PresentDocument4 pagesStructure and Classification of Lipids: Presentsamantha laurenthNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Biochemtry Lecture LipidsDocument6 pages5.1 Biochemtry Lecture LipidsMika SaldañaNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules: Prepared By: Mrs. Eden C. SanchezDocument62 pagesBiological Molecules: Prepared By: Mrs. Eden C. SanchezBernard D. Fajardo Jr.No ratings yet
- Genbio LipidsDocument3 pagesGenbio LipidsAssasin KillerNo ratings yet
- TVP 2016 0910 NN FattyAcidsDocument7 pagesTVP 2016 0910 NN FattyAcidsAmandaNo ratings yet
- Hemp Oil ReportDocument20 pagesHemp Oil Reportapi-431234431No ratings yet
- Caractristica Fisicoquimica Aceite de Coco InglesDocument12 pagesCaractristica Fisicoquimica Aceite de Coco InglesanibalNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acids: Akshatha NaikDocument12 pagesFatty Acids: Akshatha NaikBig ZeroNo ratings yet
- Owodunni SodeeqDocument59 pagesOwodunni SodeeqOgunyemi VictorNo ratings yet
- C5 Chem For User N IndustryDocument78 pagesC5 Chem For User N Industrynory msNo ratings yet
- Introduction in Organic Chemistry: LipidsDocument6 pagesIntroduction in Organic Chemistry: LipidsMariellaIsabelCasuyonNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: Ihrevale LIPID META Bolism 1Document92 pagesBiochemistry: Ihrevale LIPID META Bolism 1Roy BelenNo ratings yet
- 3 - LipidsDocument106 pages3 - LipidsBea BalungayaNo ratings yet
- Preventive Effect of Cinnamon Essential Oil On Lipid Oxidation of Vegetable OilDocument7 pagesPreventive Effect of Cinnamon Essential Oil On Lipid Oxidation of Vegetable OilDaniel MarţuneacNo ratings yet
- Ewb AYU.. - 3-DikonversiDocument1 pageEwb AYU.. - 3-DikonversiAlvyolianNo ratings yet
- WWW Britannica Com Science Human Nutrition LipidsDocument6 pagesWWW Britannica Com Science Human Nutrition LipidsJd DiazNo ratings yet
- Nutrients: Uncommon Fatty Acids and Cardiometabolic HealthDocument14 pagesNutrients: Uncommon Fatty Acids and Cardiometabolic Healthjoshua80No ratings yet
- Lysitunaoilbrochure 2019 Online 1Document4 pagesLysitunaoilbrochure 2019 Online 1walkrogNo ratings yet
- Oils and Fats: Induction Training (Technical-1/2)Document27 pagesOils and Fats: Induction Training (Technical-1/2)Umesha shankra ShettyNo ratings yet
- Scott'S Bale Emulsion Scott'S Bale Emulsion: Isi:100 ML Netto:100 MLDocument1 pageScott'S Bale Emulsion Scott'S Bale Emulsion: Isi:100 ML Netto:100 MLAlvyolianNo ratings yet
- Lipids: MIDTERM ExaminationDocument4 pagesLipids: MIDTERM ExaminationKUZONo ratings yet
- Blending of Soybean Oil With Selected Vegetable Oils: Impact On Oxidative Stability and Radical Scavenging ActivityDocument7 pagesBlending of Soybean Oil With Selected Vegetable Oils: Impact On Oxidative Stability and Radical Scavenging ActivitySuresh GuluwadiNo ratings yet
- CH 5Document11 pagesCH 5ransinghNo ratings yet
- Lipids Basics: Fats, Oils, in Foods and Health: Socorro Milagros C. Alcancia, RND, PHDDocument9 pagesLipids Basics: Fats, Oils, in Foods and Health: Socorro Milagros C. Alcancia, RND, PHDCriszel SucgangNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument33 pagesCarbohydratesPadmanaaban PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Blue Illustrated Heart Health Fair FlyerDocument7 pagesBlue Illustrated Heart Health Fair FlyerFelipeMorenoNo ratings yet
- HBFS&T 9Document18 pagesHBFS&T 9M SNo ratings yet
- 1o - Romano Murcia LodoviceDocument4 pages1o - Romano Murcia LodoviceJilliary AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology MergedDocument18 pagesPharmacology MergedJilliary AlexandraNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument3 pagesIntroductionJilliary AlexandraNo ratings yet
- CHN MergedDocument16 pagesCHN MergedJilliary AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Macronutrients CarbohydratesDocument3 pagesMacronutrients CarbohydratesJilliary AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Macronutrients ChoDocument13 pagesMacronutrients ChoJilliary AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Micronutrients Water and ElectrolytesDocument3 pagesMicronutrients Water and ElectrolytesJilliary AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Pink Lined Illustration Communication Training Talking PresentationDocument9 pagesPink Lined Illustration Communication Training Talking PresentationJilliary AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Macronutrients Protein and Amino AcidsDocument2 pagesMacronutrients Protein and Amino AcidsJilliary AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument21 pagesChemical Reactions and EquationsShubham ShawNo ratings yet
- 22-Dr. Md. Jahangir Alam5f1f07d9bce4fDocument14 pages22-Dr. Md. Jahangir Alam5f1f07d9bce4fShakil MahmodNo ratings yet
- On Algae FuelDocument16 pagesOn Algae FuelKritika Joshi100% (4)
- Radiation Processing For Dry Sewage Sludge Hygienisation - Ahmedabad Municipal CorporationDocument24 pagesRadiation Processing For Dry Sewage Sludge Hygienisation - Ahmedabad Municipal CorporationVaghasiyaBipinNo ratings yet
- Food Microbiology IGNOU Unit 6Document21 pagesFood Microbiology IGNOU Unit 6Nawin at82No ratings yet
- Formulasi Krim Ekstrak Etanol Herba Krokot (Portulacca Oleracea L.) Sebagai Tabir SuryaDocument5 pagesFormulasi Krim Ekstrak Etanol Herba Krokot (Portulacca Oleracea L.) Sebagai Tabir SuryaTeguh Hidayat PanjaitanNo ratings yet
- Miscellaneous Food Products: Delicatessen and Related FoodsDocument17 pagesMiscellaneous Food Products: Delicatessen and Related FoodsEdwar JpNo ratings yet
- Fermented Foods and Gastrointestinal Health: Underlying MechanismsDocument19 pagesFermented Foods and Gastrointestinal Health: Underlying MechanismsFederica C.No ratings yet
- Molecules: Black Chokeberry Aronia Melanocarpa L.-A Qualitative Composition, Phenolic Profile and Antioxidant PotentialDocument57 pagesMolecules: Black Chokeberry Aronia Melanocarpa L.-A Qualitative Composition, Phenolic Profile and Antioxidant PotentialDanaNo ratings yet
- 1999 John M Deman Principles of Food Chemistry Springer DikompresiDocument34 pages1999 John M Deman Principles of Food Chemistry Springer DikompresiansanyNo ratings yet
- CCA Eligible Processes 2014Document9 pagesCCA Eligible Processes 2014Carlos LouçãoNo ratings yet
- Study On Manures and FertilizersDocument7 pagesStudy On Manures and Fertilizersgenerlacc21No ratings yet
- Rice-Traditional Medicinal Plant in India: Journal of Pharmacognosy and PhytochemistryDocument7 pagesRice-Traditional Medicinal Plant in India: Journal of Pharmacognosy and PhytochemistrySyed Iftekhar AlamNo ratings yet
- Food Science and TechnologyDocument4 pagesFood Science and TechnologyChoi JunNo ratings yet
- SAI Global - Food Fraud The Basic, 2019 (7p)Document7 pagesSAI Global - Food Fraud The Basic, 2019 (7p)Mark KwanNo ratings yet
- Avichal Chemistry ProjectDocument19 pagesAvichal Chemistry Projectbiswanath.bhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- Basic Dispensing Theory For Pharmacy TechnicianDocument18 pagesBasic Dispensing Theory For Pharmacy TechnicianIfeanyichukwu HenryNo ratings yet
- Organic Agriculture Gr12 Module8.Final For StudentDocument25 pagesOrganic Agriculture Gr12 Module8.Final For StudentApril Jean Cahoy100% (1)
- Hortsci Article p472Document9 pagesHortsci Article p472GalinaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No: Immobilization of Enzyme Using Sodium AlginateDocument3 pagesExperiment No: Immobilization of Enzyme Using Sodium AlginateVijayasarathy Sampath KumarNo ratings yet
- Pembuatan Bioplastik Berbasis Komposit Pati Sagu-CarboxymethylDocument7 pagesPembuatan Bioplastik Berbasis Komposit Pati Sagu-CarboxymethylMuh. Ma'arifNo ratings yet
- Instead of Utilizing Soil To Produce Plants, A Method Called Hydroponics Uses A Water Based Nutritional SolutionDocument6 pagesInstead of Utilizing Soil To Produce Plants, A Method Called Hydroponics Uses A Water Based Nutritional SolutionTricia Elaine MitraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Bio F4Document51 pagesChapter 9 Bio F4Vinieysha LoganathanNo ratings yet
- Use of Coffee Waste For The Production of BiofuelsDocument9 pagesUse of Coffee Waste For The Production of BiofuelsRuth Noemy Ruiz MangandiNo ratings yet
- 2420 Microbial Nutrition and Growth 1 Population 090810Document30 pages2420 Microbial Nutrition and Growth 1 Population 090810jessicaNo ratings yet
- Pirlak 2007Document12 pagesPirlak 2007Lucas Antonio GallaratoNo ratings yet
- Vieira, Et All. 2018. Chayote (Sechium Edule) A Review of Nutritional Composition, Bioactivities and Potential Applications. Food ChemistryDocument50 pagesVieira, Et All. 2018. Chayote (Sechium Edule) A Review of Nutritional Composition, Bioactivities and Potential Applications. Food ChemistryKiki Nur AzizahNo ratings yet
- Indian Acetyls Market OverviewDocument24 pagesIndian Acetyls Market OverviewPrakrutiShahNo ratings yet
- Morgavi 2012Document18 pagesMorgavi 2012uusNo ratings yet
- Science Investigatory ProjectDocument28 pagesScience Investigatory ProjectHannah ۦۦNo ratings yet