Professional Documents
Culture Documents
05 Oscillations and Waves
Uploaded by
Musharaf SwaliOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
05 Oscillations and Waves
Uploaded by
Musharaf SwaliCopyright:
Available Formats
5 Oscillations and waves
1. Oscillations
2012-4.
a. Define “oscillation”.
2010-6.
h.
(i) State any two factors which affect frequency of an oscillating pendulum. (2 marks)
(ii) Mention two characteristics of an oscillating system. (2 marks)
2008-2.
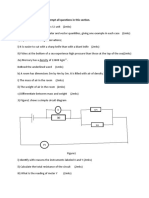
b. Figure 1 is a diagram showing a mass hanging on a spring. If the mass is pulled to point A and
released, it vibrates between points A and C through the rest position, B.
(i) Calculate the initial amplitude of the vibration. (2 marks)
(ii) At which point does the vibrating mass have the highest kinetic energy? (1 mark)
(iii) Describe how potential energy and kinetic energy change as the mass is vibrating from A to C.
(4 marks)
(iv) Give two reasons why the mass would eventually stop vibrating. (2 marks)
2004-5.
a. Define the term “oscillation” in relation to a swinging pendulum. (2 marks)
5 Oscillations and Waves - Questions
b. Figure 3 is a diagram of a simple pendulum. The mass vibrates between points A and C through B.
(i) What happens to the speed of the mass as it moves from positions:
(1) A to B? (1 mark)
(2) B to C? (1 mark)
(ii) What is the speed of the mass at C? (1 mark)
(iii) What happens to the frequency and amplitude of oscillation of a pendulum as time increases?
(2 marks)
(iv) State the energy changes of the mass as it changes from A to C. (2 marks)
(v) What happens to the frequency of vibration of a pendulum when the length of the string is
changed? (2 marks)
2. Waves
2012-4.
b.
(i) What type of wave is produced by a vibrating string? (1mark)
(ii) Calculate the frequency of a wave with a wavelength of 2m and speed of 6m/s. (3marks)
c. State the difference between “interference” and “diffraction” of waves. (2marks)
2012-8.
a. With the aid of a diagram, explain how destructive interference in water waves occurs. (4marks)
b. Explain why waves refract when travelling from one medium to another. (2marks)
2011-7.
a, State the difference between a ‘transverse’’ and a “longitudinal" wave. (2 marks)
2011-8.
b. With the aid of labeled diagrams, explain the difference between waves passing through narrow
and wide gaps. (6 marks)
5 Oscillations and Waves - Questions
2010-8.
a. Explain how constructive interference occurs in waves. (3 marks)
2009-2
b. Figure 3 is a diagram of a wave with a frequency of 2 Hz.
(i) Name the type of wave shown in figure 3. (1mark)
(ii) Give any two properties of the wave. (2marks)
(iii) What is the wavelength of the wave. (2marks)
2007-2.
a. Give two factors that affect the frequency of a vibrating spring. (2marks)
b. Figure 1 is a diagram of a wave.
(i) Name the part labeled A. (1mark)
(ii) Calculate the frequency of the wave. (2marks)
(iii) Calculate the velocity of the wave if its wavelength is 50m. (2marks
2006-6.
c. Figure 4 is a diagram showing waves n a rope xy.
5 Oscillations and Waves - Questions
(i) Calculate the wave length of this wave. (3marks)
(ii) If the rope xy is swung up and down 20 times in 2 seconds, calculate the average speed of the
wave. (4marks)
d. figure 5 is a diagram showing water wave approaching two slits, S1 and S2 in an obstacle.
(i) Complete the diagram to show waves emerging on the other side of the obstacle. (3marks)
(ii) State two properties of waves that are demonstrated in the completed diagram. (2marks)
(iii) What would happen to the waves emerging on the other side of the obstacle if the widths of S 1
and S2 were increased? (1mark)
2006-7.
b. explain with the help of diagrams, the difference between constructive interference and destructive
interference. (10marks)
2005-6.
Figure 6 is a diagram shooing crests of straight ripples on water surface produced in a ripple tank by
a wave generator.
a. What kind of waves is represented by the crests? (2marks)
b. What is the wavelength of the ripples if there are 5 complete waves in a distance of 60 cm?
(2marks)
c. What is the frequency of the ripples if four crests pass through point A in one second? (1mark)
d. Calculate the speed of the waves. (3marks)
e. What would happen to the wave length if the waves moved from deep water to shallow water?
f. explain the answer to (e). (5marks)
g. describe “constructive interference” in water waves. (2marks)
h. what is the difference between “longitudinal” and “transverse” waves? (2marks)
i. what type of waves are radio waves? (1mark)
5 Oscillations and Waves - Questions
2003-1.
c.
(i) What is the difference between a transverse wave and a longitudinal waves? (4marks)
(ii) Give any two characteristics of a wave. (2marks)
3. Light
2011-7.
b. Explain how the focal length of a convex lens can be determined using a distant object. (3 marks)
c. State any two differences between a “camera” and a “human eye”. (2 marks)
2010-6.
g.
(i) State any three differences between a real image and a virtual image. (3 marks)
(ii) An object 6 cm long is placed 30 cm in front of a converging lens of focal length 10 cm. Use the
lens formula to calculate;
(1) image distance (4 marks)
(2) magnification of the object (2 marks)
2010-7.
a. Explain how an image is formed by a convex lens. (4 marks)
2009-2
a. Figure 2 shows part of a ray diagram.
Figure 2
(i) Complete the ray diagram to show the position of the image. (3marks)
(ii) Calculate the magnification of the image. (4marks)
5 Oscillations and Waves - Questions
c. Figure 4 is diagram of a slide projector.
(i) State the function of each of the following:
Concave mirror: (1mark)
Condenser lens: (1mark)
(ii) Describe the nature of the image formed on the screen. (3marks)
2008-2.
a
(i) Define “focal length” of a convex lens. (2 marks)
(ii) State any two ways of determining the focal length of a convex lens. (2 marks)
(iii) An object 10 cm high is placed 25 cm from the centre of a convex lens of focal length 10 cm. Draw
a ray diagram to show the position of the image formed. (Scale: 1 cm to represent 5 cm) (6 marks)
2007-2.
c.
(i) State any three similarities between a camera and a human eye. (3marks)
(ii) What is the function of an aperture in a camera? (1mark)
d.
An object placed 15 cm away from a convex lens of focal length 10 cm.
(i) Using the lens formula, calculate the image distance. (4marks)
(ii) Calculate the magnification of the image. (2marks)
(iii) What is the nature of the image produced? (3marks)
2004-5.
c.
An object 2 cm high is placed 7.5 cm in front of a converging lens of focal length 5 cm.
(i) Calculate the image distance. (4 marks)
(ii) Describe the image formed. (3 marks)
(iii) Calculate the magnification of the image. (2 marks)
5 Oscillations and Waves - Questions
You might also like
- Physics Seminar IIDocument9 pagesPhysics Seminar IImundu mustafaNo ratings yet
- CSEC Physics - Sound - SPQDocument20 pagesCSEC Physics - Sound - SPQA.BensonNo ratings yet
- End of Term 1 2023 Phy S.4Document5 pagesEnd of Term 1 2023 Phy S.4DENIS AKOLNo ratings yet
- 6.test Mix 2 (1h)Document4 pages6.test Mix 2 (1h)Duncan LinNo ratings yet
- Physics Chapter WaveDocument22 pagesPhysics Chapter Wavesaffiya imanNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 10 Physics Previous Year Question Paper 2018Document10 pagesICSE Class 10 Physics Previous Year Question Paper 2018Niyati AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Turkish Light Academy Uganda Advanced Certificate of EducationDocument6 pagesTurkish Light Academy Uganda Advanced Certificate of EducationMutsyaba Victor JuniorNo ratings yet
- Uce Physics Paper Two 2010Document4 pagesUce Physics Paper Two 2010DENIS MANDE UgandaNo ratings yet
- Waves and Sound WorksheetDocument11 pagesWaves and Sound WorksheetLailaNo ratings yet
- Physics FVDocument3 pagesPhysics FVsam2jbegNo ratings yet
- P510/2 Physics Paper 2Document6 pagesP510/2 Physics Paper 2Java JimmyNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Phy P510-2 (1993-2012) .Document102 pagesQuestion Bank Phy P510-2 (1993-2012) .Tumusiime osagyefo Johnbosco Adyeeri100% (1)
- Phy 2-2017Document4 pagesPhy 2-2017Eremu ThomasNo ratings yet
- 10 Icse Physics Practice QuestionsDocument3 pages10 Icse Physics Practice QuestionsKevin JosephNo ratings yet
- UACE KCB MOCK Phy2 PDFDocument8 pagesUACE KCB MOCK Phy2 PDFTRIPPLE KAYZ UGNo ratings yet
- UCE Physics 2013 Paper 2Document4 pagesUCE Physics 2013 Paper 2Shy DudeNo ratings yet
- Uace Physics Paper 2 2001Document6 pagesUace Physics Paper 2 2001Ainebyoona ChriscentNo ratings yet
- 2014 - 2015 1st Term Monthly Test of IG2Document12 pages2014 - 2015 1st Term Monthly Test of IG2rehanNo ratings yet
- IG2 PaperDocument12 pagesIG2 PaperrehanNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 2Document5 pagesWorksheet 2Devansh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- UACE Physics Paper 2 2019Document7 pagesUACE Physics Paper 2 2019Gadget TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Long AnswerDocument10 pagesLong AnswerAAYUSHNo ratings yet
- Uace Physics Paper 2 2002Document6 pagesUace Physics Paper 2 2002Ainebyoona ChriscentNo ratings yet
- SQP Hy 11 2022 23Document13 pagesSQP Hy 11 2022 23It's all About fitnessNo ratings yet
- Uce Physics Paper Two 3Document7 pagesUce Physics Paper Two 3Okiror GeorgeNo ratings yet
- 1999 AL Phy Paper 1Document9 pages1999 AL Phy Paper 1KelvinNgNo ratings yet
- Physics Set 8Document4 pagesPhysics Set 8bijayakumal819No ratings yet
- Entire Physics Numericals ICSE CLASS 10Document83 pagesEntire Physics Numericals ICSE CLASS 10snigdha varsha100% (2)
- KCET 2014 Previous Year Paper For PhysicsDocument58 pagesKCET 2014 Previous Year Paper For PhysicsVeeresh badigerNo ratings yet
- ExercisesDocument13 pagesExercisesAhmed Magdy Beshr100% (1)
- Inter Part One Physics Old PaperDocument72 pagesInter Part One Physics Old PaperMian EjazNo ratings yet
- Uce Physics Paper Two 2012Document5 pagesUce Physics Paper Two 2012DENIS MANDE UgandaNo ratings yet
- Physics Late Night Predictions 2023Document17 pagesPhysics Late Night Predictions 2023Mithilesh PandeyNo ratings yet
- S.6 Physics Paper 2 Set 1 FebDocument6 pagesS.6 Physics Paper 2 Set 1 FebAinebyoona ChriscentNo ratings yet
- Waves: 1. Nov 01-Q/6Document5 pagesWaves: 1. Nov 01-Q/6Coolman PoonNo ratings yet
- Uce Physics Paper Two 2007Document5 pagesUce Physics Paper Two 2007DENIS MANDE UgandaNo ratings yet
- Section C Physics Paper 1 Revision Questions For A LevelDocument24 pagesSection C Physics Paper 1 Revision Questions For A LevelzakNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- NAME .ADM CLASS : 2022 Form 3 Term 1 Opener Exam - (April 2022)Document6 pagesNAME .ADM CLASS : 2022 Form 3 Term 1 Opener Exam - (April 2022)Benjamin mwanikiNo ratings yet
- Paper2 Sept Mock OmegaDocument3 pagesPaper2 Sept Mock OmegaJonas OkaleNo ratings yet
- Physics 1 - F6 - 2016Document6 pagesPhysics 1 - F6 - 2016Suhaila MbaroukNo ratings yet
- Test Form Iv 1. (A) Write Down The Readings BelowDocument26 pagesTest Form Iv 1. (A) Write Down The Readings BelowMichael LeungNo ratings yet
- Mock 2019Document10 pagesMock 2019eric takyi atakoraNo ratings yet
- 5054 MJ 2023 P22Document16 pages5054 MJ 2023 P22Raahin RahimNo ratings yet
- Sph3u Exam ReviewDocument8 pagesSph3u Exam ReviewchelseaNo ratings yet
- SS3 1st Further MathsDocument14 pagesSS3 1st Further MathsoluwafemiabdulsemiuNo ratings yet
- Uce Physics Paper Two 2013Document6 pagesUce Physics Paper Two 2013DENIS MANDE UgandaNo ratings yet
- IX ICSE 1st Assessment Physics Paper 2018-19Document4 pagesIX ICSE 1st Assessment Physics Paper 2018-19Loganathan KandasamyNo ratings yet
- Holy Angels College Pre-Registration Exam Phy2 2023Document4 pagesHoly Angels College Pre-Registration Exam Phy2 2023DENIS AKOLNo ratings yet
- WA DOC 20230324 44dd412aDocument8 pagesWA DOC 20230324 44dd412aNadine MonkamNo ratings yet
- Class 9 PhysicsDocument3 pagesClass 9 PhysicsGreatAkbar1No ratings yet
- Cape 2003 Unit 1 Paper 2Document12 pagesCape 2003 Unit 1 Paper 2petey78No ratings yet
- Reasoning and Proving Representing Selecting Tools Problem Solving Connecting Reflecting CommunicatingDocument7 pagesReasoning and Proving Representing Selecting Tools Problem Solving Connecting Reflecting CommunicatingmyobNo ratings yet
- Uce Physics Paper Two 2009Document5 pagesUce Physics Paper Two 2009DENIS MANDE UgandaNo ratings yet
- Physics "O"Level Seminar 535 at Seeta High School Green Campus 6 JUL 2019Document7 pagesPhysics "O"Level Seminar 535 at Seeta High School Green Campus 6 JUL 2019Daniel MarkNo ratings yet
- ICSE Board Class X Physics Gold Series Sample Paper - 2: Time: 1 Hrs Total Marks: 80 General InstructionsDocument16 pagesICSE Board Class X Physics Gold Series Sample Paper - 2: Time: 1 Hrs Total Marks: 80 General InstructionsArijit Das GuptaNo ratings yet
- Past 10 Years Paper SortDocument16 pagesPast 10 Years Paper Sortdanyalhaider222333No ratings yet
- 5 Sets Model Questions of PhysicsDocument27 pages5 Sets Model Questions of Physicsdast DonNo ratings yet
- Mock Paper 1Document6 pagesMock Paper 1AAYUSHNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Matrix Grade 8Document27 pagesMatrix Grade 8Alain Sayson PresillasNo ratings yet
- 9702:13:1823Document224 pages9702:13:1823kathleen hoNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Second QuarterDocument10 pagesScience 10 Second QuarterElle Segovia SungaNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of MaterialsDocument323 pagesPhysical Properties of Materialstehtehteh100% (1)
- New possible mathematical developments concerning ζ (2), ?, the Rogers- Ramanujan identity: Mathematical connections with some sectors of Particles Physics and the Black Hole physical parameters.Document197 pagesNew possible mathematical developments concerning ζ (2), ?, the Rogers- Ramanujan identity: Mathematical connections with some sectors of Particles Physics and the Black Hole physical parameters.Michele NardelliNo ratings yet
- Ocean Wave Measurement Techniques: R.H. StewartDocument24 pagesOcean Wave Measurement Techniques: R.H. StewartvalynoNo ratings yet
- Effective Index Exercise MSCDocument2 pagesEffective Index Exercise MSCTruthera AndalusiaNo ratings yet
- Assignment Interference 2016Document4 pagesAssignment Interference 2016Ritesh MeelNo ratings yet
- Final Neet Revision Test-09Document19 pagesFinal Neet Revision Test-09FᏞ么MES々ʀᴇʙᴇʟ GamingNo ratings yet
- Bisat Bansal MockDocument30 pagesBisat Bansal MockNihar KajlaNo ratings yet
- Soil Stiffness For Shallow Foundation Design in The Perth CBDDocument30 pagesSoil Stiffness For Shallow Foundation Design in The Perth CBDKen LiewNo ratings yet
- 030 Degree 1 Nos 1-3 1011Document32 pages030 Degree 1 Nos 1-3 1011vinny kilondaNo ratings yet
- IB Physics Review-WavesDocument21 pagesIB Physics Review-WavesTheEinsteinofTomorrow100% (1)
- 3) Diffraction - Final 23 Sep 2021Document38 pages3) Diffraction - Final 23 Sep 2021Game 1No ratings yet
- Prism OpticsDocument32 pagesPrism OpticsFredNo ratings yet
- Whitepaper NIR Spectrometer Technology Comparison PDFDocument14 pagesWhitepaper NIR Spectrometer Technology Comparison PDFMostafa Medhat Mostafa HassanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Electronic Structure of Atoms: WavesDocument17 pagesChapter 6: Electronic Structure of Atoms: WavesGerald AlbasinNo ratings yet
- Superposition Summary NotesDocument6 pagesSuperposition Summary Notesxwenhan100% (2)
- LS300 Series Manual Ver 1.14Document12 pagesLS300 Series Manual Ver 1.14Lys Vola Dollar RabessonNo ratings yet
- COMSOL Scatterer On Substrate TutorialDocument28 pagesCOMSOL Scatterer On Substrate TutorialDyingUmbrellaNo ratings yet
- Proceedings of The Institute of AcousticsDocument11 pagesProceedings of The Institute of AcousticsdanielcristobalNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - Wave Optics PDFDocument2 pagesTutorial - Wave Optics PDFRavi NasitNo ratings yet
- Light WaveDocument28 pagesLight WaveKomalFatimaNo ratings yet
- 15 Interference, of Waves Question PaperDocument5 pages15 Interference, of Waves Question PaperFatima RahmanNo ratings yet
- LP4 EMSpectrumDocument2 pagesLP4 EMSpectrumMarco GNo ratings yet
- Design and Simulation of A Compact All-Optical Differentiator Based On Silicon Microring ResonatorDocument5 pagesDesign and Simulation of A Compact All-Optical Differentiator Based On Silicon Microring ResonatortheijesNo ratings yet
- Single Slit DiffDocument2 pagesSingle Slit DiffDR.P.V.Kanaka RaoNo ratings yet
- Science8 Q1 Module5 Colorsoflight v2-1Document25 pagesScience8 Q1 Module5 Colorsoflight v2-1Twela Dea Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Scattering Theory: Johns APL TechnicalDocument15 pagesElectromagnetic Scattering Theory: Johns APL TechnicalValerie LaneNo ratings yet
- Skema Jawapan (Gelombang)Document4 pagesSkema Jawapan (Gelombang)ChewLee TanNo ratings yet