Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Calcium
Uploaded by
Noah Kent Mojica0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesCalcium supplements are used to treat and prevent low blood calcium levels. Calcium is commonly taken to support bone and muscle health. Common side effects include constipation and gastrointestinal upset. Nurses should monitor patients for signs of constipation and check serum calcium levels regularly in those on long-term therapy or with kidney problems. Calcium supplementation is contraindicated in patients with hypercalcemia, kidney disease, or cardiac issues.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCalcium supplements are used to treat and prevent low blood calcium levels. Calcium is commonly taken to support bone and muscle health. Common side effects include constipation and gastrointestinal upset. Nurses should monitor patients for signs of constipation and check serum calcium levels regularly in those on long-term therapy or with kidney problems. Calcium supplementation is contraindicated in patients with hypercalcemia, kidney disease, or cardiac issues.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesCalcium
Uploaded by
Noah Kent MojicaCalcium supplements are used to treat and prevent low blood calcium levels. Calcium is commonly taken to support bone and muscle health. Common side effects include constipation and gastrointestinal upset. Nurses should monitor patients for signs of constipation and check serum calcium levels regularly in those on long-term therapy or with kidney problems. Calcium supplementation is contraindicated in patients with hypercalcemia, kidney disease, or cardiac issues.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
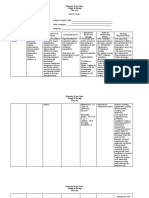
Calcium
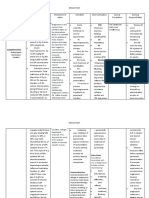
GENERIC NAME: DOSAGE/FREQUENCY/ROUT SIDE NURSING
Calcium Gluconate E: EFFECTS/ADV RESPONSIBILITY
All doses are in terms of elemental ERSE
calcium: 1 g calcium carbonate = 400 mg REACTION
(20 mEq, 40%) elemental calcium; 1 g Note number and
calcium acetate = 250 mg (12.6 mEq, consistency of
25%) elemental calcium; 1 g calcium GI: Constipation or stools. If
citrate = 210 mg (12 mEq, 21%) laxative effect, acid constipation is a
elemental calcium; 1g tricalcium rebound, nausea, problem,
phosphate = 390 mg (19.3 mEq, 39%) eructation, flatulence, physician may
elemental calcium vomiting, fecal prescribe alternate
concretions. or combination
Supplement for Osteoporosis Adult: PO
1–2 g b.i.d. or t.i.d. Metabolic: Hyperc therapy with a
magnesium
alcemia with
Antacid Adult: PO 0.5–2 g 4–6 times/d antacid or advise
alkalosis, metastatic
patient to take a
Hyperphosphatemia Adult: PO calcium calcinosis,
laxative or stool
acetate 2–4 tablets with each meal hypercalciuria,
softener as
hypomagnesemia,
necessary.
hypophosphatemia
(when phosphate Lab tests:
BRAND NAME: INDICATION:
intake is low). Determine serum
Calgonate This medication is used to prevent or treat
and urine calcium
low blood calcium levels in people who
do not get enough calcium from their CNS: Mood and weekly in patients
DRUG mental changes. receiving
diets. It may be used to treat conditions
ILLUSTRATION: prolonged therapy
caused by low calcium levels such as Urogenital: Polyuri and in patients
bone loss (osteoporosis), weak bones a, renal calculi. with renal
(osteocalcin/rickets), decreased activity of
dysfunction.
the parathyroid gland
Record
(hypoparathyroidism), and a certain
amelioration of
muscle disease (latent tetany). It may also
symptoms of
be used in certain patients to make sure
hypocalcemia (see
they are getting enough calcium (e.g.,
Signs &
women who are pregnant, nursing, or
Symptoms,
postmenopausal, people taking certain
Appendix F).
medications such as phenytoin,
phenobarbital, or prednisone). Observe for S&S
of hypercalcemia
CLASSIFICATION: CONTRAINDICATION: in patients
FLUID AND ELECTROLYTIC Hypercalcemia and hypercalciuria (e.g., receiving frequent
BALANCE AGENT; hyperparathyroidism, vitamin D or high doses, or
REPLACEMENT SOLUTION; who have
overdosage, decalcifying tumors, bone
ANTACID
MECHANISM OF ACTION: metastases), calcium loss due to impaired renal
Rapid-acting antacid with high immobilization, severe renal disease, function (see
neutralizing capacity and renal calculi, GI hemorrhage or Appendix F).
relatively prolonged duration of obstruction, dehydration, hypochloremic
action. Decreases gastric acidity,
alkalosis, ventricular fibrillation, cardiac
thereby inhibiting proteolytic
action of pepsin on gastric disease, pregnancy (category C).
mucosa. Also increases lower
esophageal sphincter tone.
Although classified as a no
systemic antacid, a slight to
moderate alkalosis usually
develops with prolonged
therapy. Acid rebound, which
may follow even low doses, is
thought to be caused by release
of gastrin triggered by action of
calcium in small intestines.
You might also like
- Playing With Pop-Ups - The Art of Dimensional, Moving Paper DesignsDocument147 pagesPlaying With Pop-Ups - The Art of Dimensional, Moving Paper DesignsSara100% (4)
- National Football League FRC 2000 Sol SRGBDocument33 pagesNational Football League FRC 2000 Sol SRGBMick StukesNo ratings yet
- Top Activist Stories - 5 - A Review of Financial Activism by Geneva PartnersDocument8 pagesTop Activist Stories - 5 - A Review of Financial Activism by Geneva PartnersBassignotNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument18 pagesDrug StudyAngelou Joefred CongresoNo ratings yet
- Project Formulation and Appraisalpdf PDFDocument12 pagesProject Formulation and Appraisalpdf PDFabhijeet varadeNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Potassium ChlorideDocument5 pagesDrug Study Potassium ChlorideKenneth Mark B. TevesNo ratings yet
- CotrimoxazoleDocument3 pagesCotrimoxazolecsy123No ratings yet
- AcetazolamideDocument2 pagesAcetazolamideLIEZEL GRACE VELAYONo ratings yet
- Valproic Acid Drug StudyDocument4 pagesValproic Acid Drug StudyJeyser T. Gamutia100% (1)
- DMIT - Midbrain - DMIT SoftwareDocument16 pagesDMIT - Midbrain - DMIT SoftwarevinNo ratings yet
- CaCO3 Drug StudDocument2 pagesCaCO3 Drug StudAubrey SungaNo ratings yet
- Drugstudy PotassiumchlorideDocument3 pagesDrugstudy Potassiumchloridetrina412No ratings yet
- Case Study Scenario # 1 Congestive Heart Failure (Mojica)Document10 pagesCase Study Scenario # 1 Congestive Heart Failure (Mojica)Noah Kent MojicaNo ratings yet
- Calcium CarbonateDocument1 pageCalcium CarbonateMikko EnocNo ratings yet
- DFo 2 1Document15 pagesDFo 2 1Donna HernandezNo ratings yet
- Magnesium Sulfate 250 500 MG Metoclopramide Drug StudyDocument4 pagesMagnesium Sulfate 250 500 MG Metoclopramide Drug Studyprog.ecleo.swuNo ratings yet
- PHRM TemplateDocument4 pagesPHRM TemplateRichard SakyiamahNo ratings yet
- Final Magnesium SulfateDocument3 pagesFinal Magnesium SulfateGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Case Study - DrugsDocument4 pagesCase Study - DrugsYza DizaNo ratings yet
- AcetazolamideDocument3 pagesAcetazolamideGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument1 pageDrug Studyjasper pachingelNo ratings yet
- Kayexalate Drug StudyDocument3 pagesKayexalate Drug StudyAngelou Joefred Congreso100% (1)
- Antihypertension DrugsDocument2 pagesAntihypertension DrugsMarieCrisNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Marissa LugtuDocument6 pagesDrug Study Marissa LugtuMarzie LugtuNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic Name: BeforeDocument5 pagesName of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic Name: BeforeWestley RubinoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyAkira Poscablo PiranteNo ratings yet
- Drugs Study Drugs Classification Adverse Effect Mechanism of Action Contrandication Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument6 pagesDrugs Study Drugs Classification Adverse Effect Mechanism of Action Contrandication Nursing ResponsibilitiesRachel BotonNo ratings yet
- StudyDocument5 pagesStudyWestley RubinoNo ratings yet
- DS (Calcium + Vit. D)Document6 pagesDS (Calcium + Vit. D)Mary April MendezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - OmeprazoleDocument5 pagesDrug Study - OmeprazoleRonel ResurricionNo ratings yet
- Furosemide 1Document1 pageFurosemide 1Marck A. AlcedoNo ratings yet
- Drug SDocument2 pagesDrug SJane CasiquinNo ratings yet
- Pelagio-Drug StudyDocument45 pagesPelagio-Drug StudyShiena Mae PelagioNo ratings yet
- Potassium GluconateDocument2 pagesPotassium GluconateFika AmaliaNo ratings yet
- Potassiumchlorideoral PDFDocument2 pagesPotassiumchlorideoral PDFShaira TanNo ratings yet
- Sodium BicarbonateDocument20 pagesSodium BicarbonateChristian Dave EndinoNo ratings yet
- Diuretic Therapy and Drugs For Renal Failure: DiureticsDocument7 pagesDiuretic Therapy and Drugs For Renal Failure: DiureticsApple MaeNo ratings yet
- Calcium Gluconate LasixDocument4 pagesCalcium Gluconate LasixChristian Dave EndinoNo ratings yet
- Pathopharm Drug Tables Nclex ReviewDocument65 pagesPathopharm Drug Tables Nclex ReviewRuiqi YangNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug Studyfaula rocamoraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Anti-AnemiaDocument3 pagesDrug Study - Anti-AnemiaChelsy Sky SacanNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Actions Side Effects Adverse Effects Indicati ONS Contraindic Ations Nursing Responsibil Ities Generic NameDocument5 pagesDrug Name Actions Side Effects Adverse Effects Indicati ONS Contraindic Ations Nursing Responsibil Ities Generic NameMae Abigail Mallonga BunaganNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Santiago, J. L. 243-D Dr. E. de Lunas Liver CirrhosisDocument2 pagesDrug Study: Santiago, J. L. 243-D Dr. E. de Lunas Liver CirrhosisNathalia CabalseNo ratings yet
- Fosrenol หรือ Lanthanum carbonateDocument5 pagesFosrenol หรือ Lanthanum carbonateอภิสิทธิ์อ้ายเป็งNo ratings yet
- GI: Gastric: Distention, Belching, FlatulenceDocument8 pagesGI: Gastric: Distention, Belching, FlatulenceAjie ZamNo ratings yet
- Drugs and NCPDocument4 pagesDrugs and NCPApril Anne CostalesNo ratings yet
- BisacodylDocument1 pageBisacodylJoover AquinoNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Trade Name Uses Adverse Reactions Dosage RangesDocument5 pagesGeneric Name Trade Name Uses Adverse Reactions Dosage Rangessticksam203No ratings yet
- Potassium Supplements ParenteralDocument3 pagesPotassium Supplements Parenteralcarl meiNo ratings yet
- Medications and Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument6 pagesMedications and Nursing ResponsibilitiesDarla JoyceNo ratings yet
- Generic NameDocument5 pagesGeneric NameJanika BecieraNo ratings yet
- 1magsu 2methergineDocument5 pages1magsu 2metherginelaiza_lumbaNo ratings yet
- Drug Studies and Health Teaching PlanDocument28 pagesDrug Studies and Health Teaching PlansfkjalkhsafgNo ratings yet
- AcetazolamideDocument2 pagesAcetazolamideAlexandra Antondy0% (1)
- Furosemide Drug StudyDocument4 pagesFurosemide Drug StudyAngelou Joefred CongresoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study WengelDocument3 pagesDrug Study WengelWen SilverNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Dosage/Frequency/Ti Ming/route Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument3 pagesName of Drug Dosage/Frequency/Ti Ming/route Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibilitieskyle100% (1)
- Sodium Bicarbonate: (Soe-Dee-Um Bye-Kar-Boe-Nate)Document3 pagesSodium Bicarbonate: (Soe-Dee-Um Bye-Kar-Boe-Nate)Chryst Louise SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Magnesium SulfateDocument2 pagesMagnesium SulfateGwyn Rosales100% (1)
- Drug Study Magnesium SulfateDocument3 pagesDrug Study Magnesium SulfateSchyna Marielle VitaleNo ratings yet
- Furosemide DSDocument5 pagesFurosemide DSArone SebastianNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Dosage, Route, Frequency Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument1 pageDrug Name Dosage, Route, Frequency Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesJonna Mae TurquezaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study..SynergyDocument3 pagesDrug Study..SynergyIris Coronel AdamosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Drug StudyDocument16 pagesChapter 5 Drug StudyRegee Rose LacsonNo ratings yet
- Generic Name:: ElectrolytesDocument9 pagesGeneric Name:: ElectrolytesEleazar Desillarico GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Optimización del tratamiento de las fluctuaciones motoras en la enfermedad de Parkinson: Adaptando el tratamiento al pacienteFrom EverandFast Facts: Optimización del tratamiento de las fluctuaciones motoras en la enfermedad de Parkinson: Adaptando el tratamiento al pacienteNo ratings yet
- Western Mindanao State University College of Nursing: Zamboanga CityDocument8 pagesWestern Mindanao State University College of Nursing: Zamboanga CityNoah Kent MojicaNo ratings yet
- Adult: PO 5-10 MG Once Daily Geriatric: Start With 2.5 MG, Adjust Dose at Intervals of Not Less Edema, Bradycardia, Chest PainDocument2 pagesAdult: PO 5-10 MG Once Daily Geriatric: Start With 2.5 MG, Adjust Dose at Intervals of Not Less Edema, Bradycardia, Chest PainNoah Kent MojicaNo ratings yet
- Furosemide Drug StudyDocument2 pagesFurosemide Drug StudyNoah Kent MojicaNo ratings yet
- Drugstudy Buscopan & d5lrDocument8 pagesDrugstudy Buscopan & d5lrNoah Kent MojicaNo ratings yet
- Name: Mojica, Noah Kent Date: September 19, 2020Document6 pagesName: Mojica, Noah Kent Date: September 19, 2020Noah Kent MojicaNo ratings yet
- NAME: Mojica, Noah Kent - : Date: September 11, 2020Document2 pagesNAME: Mojica, Noah Kent - : Date: September 11, 2020Noah Kent MojicaNo ratings yet
- Activity-3 (Juksin)Document5 pagesActivity-3 (Juksin)Noah Kent MojicaNo ratings yet
- Gerontology Act 1 (Mojica)Document1 pageGerontology Act 1 (Mojica)Noah Kent MojicaNo ratings yet
- Name: Date: Lesson 1. Activity #2Document2 pagesName: Date: Lesson 1. Activity #2Noah Kent MojicaNo ratings yet
- Gerontology Act 1 (Mojica)Document1 pageGerontology Act 1 (Mojica)Noah Kent MojicaNo ratings yet
- Mojica, Noah Kent BSN 3-D Barangay Sta. CatalinaDocument1 pageMojica, Noah Kent BSN 3-D Barangay Sta. CatalinaNoah Kent MojicaNo ratings yet
- Anti Tetanus SerumDocument3 pagesAnti Tetanus SerumNoah Kent MojicaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of RabiesDocument13 pagesPathophysiology of RabiesNoah Kent Mojica100% (1)
- Siemens Rapidlab 248, 348, 840, 845, 850, 855, 860, 865: Reagents & ControlsDocument2 pagesSiemens Rapidlab 248, 348, 840, 845, 850, 855, 860, 865: Reagents & ControlsJuan Carlos CrespoNo ratings yet
- Ilocos Norte Youth Development Office Accomplishment Report 2Document17 pagesIlocos Norte Youth Development Office Accomplishment Report 2Solsona Natl HS MaanantengNo ratings yet
- Predator U7135 ManualDocument36 pagesPredator U7135 Manualr17g100% (1)
- 2016 W-2 Gross Wages CityDocument16 pages2016 W-2 Gross Wages CityportsmouthheraldNo ratings yet
- Numerical Modelling and Design of Electrical DevicesDocument69 pagesNumerical Modelling and Design of Electrical Devicesfabrice mellantNo ratings yet
- Csu Cep Professional Dispositions 1Document6 pagesCsu Cep Professional Dispositions 1api-502440235No ratings yet
- 1.SDH Basics PDFDocument37 pages1.SDH Basics PDFsafder wahabNo ratings yet
- Brigade Product Catalogue Edition 20 EnglishDocument88 pagesBrigade Product Catalogue Edition 20 EnglishPelotudoPeloteroNo ratings yet
- Upes School of Law Lac & Adr Association: PresentsDocument7 pagesUpes School of Law Lac & Adr Association: PresentsSuvedhya ReddyNo ratings yet
- Basic Econometrics Questions and AnswersDocument3 pagesBasic Econometrics Questions and AnswersRutendo TarabukuNo ratings yet
- Architectural ConcreteDocument24 pagesArchitectural ConcreteSaud PathiranaNo ratings yet
- Project Management TY BSC ITDocument57 pagesProject Management TY BSC ITdarshan130275% (12)
- Notes On Antibodies PropertiesDocument3 pagesNotes On Antibodies PropertiesBidur Acharya100% (1)
- A Review of Service Quality ModelsDocument8 pagesA Review of Service Quality ModelsJimmiJini100% (1)
- PP Master Data Version 002Document34 pagesPP Master Data Version 002pranitNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 Q1 Lesson 5 Endothermic and Exotheric Reaction and Heating and Cooling CurveDocument19 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 Q1 Lesson 5 Endothermic and Exotheric Reaction and Heating and Cooling CurveJolo Allexice R. PinedaNo ratings yet
- Ring and Johnson CounterDocument5 pagesRing and Johnson CounterkrsekarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Retail LoansDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Retail LoansSameer ShahNo ratings yet
- Guardcam InstructionsDocument12 pagesGuardcam InstructionsCompuFix RepairsNo ratings yet
- Modern and Nonlinear OpticsDocument181 pagesModern and Nonlinear Opticssoma_venuNo ratings yet
- Form Expense ClaimDocument2 pagesForm Expense Claimviedelamonde_3868443No ratings yet
- Bba VDocument2 pagesBba VkunalbrabbitNo ratings yet
- Production of Bioethanol From Empty Fruit Bunch (Efb) of Oil PalmDocument26 pagesProduction of Bioethanol From Empty Fruit Bunch (Efb) of Oil PalmcelestavionaNo ratings yet
- 07 GDL Web-Site 04 (2021-2022) For 15284Document2 pages07 GDL Web-Site 04 (2021-2022) For 15284ABCDNo ratings yet