Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Risk-Informed Integrity Management of Marine Structures Subject To Fatigue Deterioration
Risk-Informed Integrity Management of Marine Structures Subject To Fatigue Deterioration
Uploaded by
Arturo GonzalezOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Risk-Informed Integrity Management of Marine Structures Subject To Fatigue Deterioration
Risk-Informed Integrity Management of Marine Structures Subject To Fatigue Deterioration
Uploaded by
Arturo GonzalezCopyright:
Available Formats
Workshop on Structural Safety and
Infrastructure Management
Lloyd’s Register, London, 24th May 2017
Risk-informed Integrity Management of marine Structures
subject to Fatigue Deterioration
G. Zou1,2 *, K. Banisoleiman 1, A. González2 and M. H. Faber3
1Lloyd’s Register, 2UCD School of Civil Engineering , 3 AAU Department of Civil Engineering
*guang.zou@lr.org
Motivation
Mitigate failure risk and reduce inspection and maintenance costs
Significant uncertainties associated with wave loads and fatigue deterioration
Design assumptions usually cannot be fully satisfied during operation.
Risk-based inspection/monitoring provide actual structural performance and
support optimal decisions on operation and maintenance (Fig 1).
Fig 4 Decision-making model for inspection planning
Highlights
Hierarchical characteristics for different marine structures are identified and
generic requirements for risk-informed integrity management are concluded
(Fig 5).
Fig 1 Integrity management of ship structures
Ideas Fig 5 System representation for fatigue risk assessment
Stochastic modelling of fatigue deterioration is based on dynamic Bayesian Uncertainty associated with initial damage state a(0) is reduced by updating
networks (DBN) (Fig 2). prior distribution with a likelihood (Fig 7). A model is developed to construct
Probabilistic risk assessment facilitates consistent treatment of information the likelihood based on available S-N curves or test data (Fig 6).
collected through inspection/monitoring. 𝑎𝑐
1 𝑑𝑎
Bayesian decision theory facilitates quantification of the value of information 𝑁𝑆𝑁 = 𝑁𝐼 + 𝑁𝑃 =
𝜋𝑚 2 𝐶∆𝜎 𝑚 𝑚 2𝑌 𝑎 𝑚
𝑎𝐸𝐼𝐹𝑆 𝑎
which has not yet been collected (Fig 3).
Influence diagram serves as a strong tool for cost-optimal decision making on
inspection/monitoring and maintenance in face of uncertainty (Fig 4).
Fig 6 Model for 𝒂𝑬𝑰𝑭𝑺 Fig 7 Bayesian updating of a(0)
The benefit of sampling inspection on structural systems are evaluated with
Bayesian networks. The potential harm of inspection results on decision are
studied with Bayesian decision theory.
Fig 2 Stochastic modelling of fatigue crack growth based on DBN Sequential optimal decisions and lifetime globally-optimal decisions are
investigated by use of DBN and optimization techniques (Fig 8).
Fig 3 Maximization the value of inspection Fig 8 Sequential decisions and global decisions (inspection number n=3)
Follow TRUSS ITN on
The TRUSS project has received funding from the European Union’s
Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under the Marie
Skłodowska-Curie grant agreement No. 642453
www.trussitn.eu
You might also like
- Musical Theatre Revision Guide - Rodgers and HammersteinDocument3 pagesMusical Theatre Revision Guide - Rodgers and HammersteinChris Powell0% (1)
- Handbook of Mathematical Induction Theory and Applications (David S. Gunderson)Document923 pagesHandbook of Mathematical Induction Theory and Applications (David S. Gunderson)ulises150293No ratings yet
- Algebra 1. (Electronic Resource) Concepts and SkillsDocument244 pagesAlgebra 1. (Electronic Resource) Concepts and SkillsginotrucheliNo ratings yet
- An Insight Into Predictive Analytics TechniquesDocument6 pagesAn Insight Into Predictive Analytics TechniquesIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- SQL Technical INterview PDFDocument13 pagesSQL Technical INterview PDFGuru100% (1)
- A Comparison Between Safe Life Damage Tolerance AnDocument13 pagesA Comparison Between Safe Life Damage Tolerance AnIqbal MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Xantrex Inverter ManualDocument90 pagesXantrex Inverter Manualpthakur234No ratings yet
- Philosophy of Space and TimeDocument9 pagesPhilosophy of Space and TimeThien Van TranNo ratings yet
- SiC-SiC Composites, A State of The Art ReviewDocument12 pagesSiC-SiC Composites, A State of The Art ReviewMaría Camila Belduque CorreaNo ratings yet
- Rasmussen TextbookDocument160 pagesRasmussen TextbookMohamad Ikhwan100% (1)
- Heating Belt Conveyor Design ReportDocument20 pagesHeating Belt Conveyor Design ReportamardeepsinghseeraNo ratings yet
- PreviewDocument26 pagesPreviewmanuel100% (1)
- Accident Data Analysis Using Machine LearningDocument6 pagesAccident Data Analysis Using Machine LearningIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Statistical Analysis of Cost-Effectiveness DataFrom EverandStatistical Analysis of Cost-Effectiveness DataRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Buildings 13 02918 With CoverDocument18 pagesBuildings 13 02918 With CoverTaufik SiregarNo ratings yet
- 22 - Di - 1200909 - PS - Wellbarrier Integrity Management - New BrandDocument3 pages22 - Di - 1200909 - PS - Wellbarrier Integrity Management - New Brandjahehe2000No ratings yet
- STR Safety 2015Document12 pagesSTR Safety 2015Jimmy PhoenixNo ratings yet
- Fuzzy Stochastic Cost and Schedule Risk Analysis: Mob Case StudyDocument10 pagesFuzzy Stochastic Cost and Schedule Risk Analysis: Mob Case StudyAhmed S. EldiebNo ratings yet
- Sustainability Analytics Toolkit For Practitioners Creating Value in The 21St Century 1St Edition Renard Siew Full ChapterDocument67 pagesSustainability Analytics Toolkit For Practitioners Creating Value in The 21St Century 1St Edition Renard Siew Full Chaptermelissa.maglori550100% (5)
- 06-04-2022-1649216751-6-.-1. Engg - Analysis and Research On Credit Card Fraud Detection Based On Machine LearningDocument10 pages06-04-2022-1649216751-6-.-1. Engg - Analysis and Research On Credit Card Fraud Detection Based On Machine LearningImpact JournalsNo ratings yet
- The Effectiveness of Using Biometric Based Attendance Monitoring SystemDocument12 pagesThe Effectiveness of Using Biometric Based Attendance Monitoring SystemDan NiezNo ratings yet
- Paper On Sensitivity Analysis of CPTs PDFDocument48 pagesPaper On Sensitivity Analysis of CPTs PDFGovind M.PNo ratings yet
- Visual Inspection and Condition Assessment of Structures (VICAS) : An Innovative Tool For Structural Condition AssessmentDocument10 pagesVisual Inspection and Condition Assessment of Structures (VICAS) : An Innovative Tool For Structural Condition AssessmentAlbert YesayaNo ratings yet
- Engineering StructuresDocument17 pagesEngineering StructuresThea Sofia Newton-JohnNo ratings yet
- Real Life Applications of Integration To Calculate Area and VolumeDocument15 pagesReal Life Applications of Integration To Calculate Area and VolumepaheldharodNo ratings yet
- An Approach For Maintenance Safety EvaluationDocument13 pagesAn Approach For Maintenance Safety EvaluationSally SandersNo ratings yet
- Retinal Vessel Centerline Extraction Using Multiscale Matched Filters, Confidence and Edge MeasuresDocument16 pagesRetinal Vessel Centerline Extraction Using Multiscale Matched Filters, Confidence and Edge Measureslilong10100% (7)
- Uncertainty and Sensitivity AnalysisDocument38 pagesUncertainty and Sensitivity Analysisxinyi tangNo ratings yet
- Deep Belief Network Based State Classification For Structural Health DiagnosisDocument11 pagesDeep Belief Network Based State Classification For Structural Health Diagnosisdasabhisek46No ratings yet
- Integration of Markov ChainsDocument19 pagesIntegration of Markov ChainsAlex PachecoNo ratings yet
- Poseter ConferenceDocument1 pagePoseter Conference张伟恒No ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document98 pagesChapter 8Tegegn TeloNo ratings yet
- Course Title: Project Management, Course Code: 603: Assignment On Measures of Project RiskDocument5 pagesCourse Title: Project Management, Course Code: 603: Assignment On Measures of Project Riskfaisal gaziNo ratings yet
- MEAL Handbook Table2Document1 pageMEAL Handbook Table2aymenalshaeNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Effectiveness Particle Swarm Optimization in Improving The Performance of Naïve Bayes AlgorithmDocument5 pagesAnalysis of Effectiveness Particle Swarm Optimization in Improving The Performance of Naïve Bayes Algorithmikhsan romliNo ratings yet
- 10082-Article Text-40794-1-10-20230326Document9 pages10082-Article Text-40794-1-10-20230326Yonvi SatriaNo ratings yet
- Deep Learning Corrosion Detection With Con Fidence: ArticleDocument13 pagesDeep Learning Corrosion Detection With Con Fidence: ArticleManh Hoang VanNo ratings yet
- Exploring The Types of Construction Cost Modelling For Industrialised Building System (Ibs) Projects in MalaysiaDocument21 pagesExploring The Types of Construction Cost Modelling For Industrialised Building System (Ibs) Projects in MalaysiaTharaka KodippilyNo ratings yet
- Using RRC Algorithm Classify The Proteins and Visualize in Biological DatabasesDocument6 pagesUsing RRC Algorithm Classify The Proteins and Visualize in Biological DatabasesRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- DCDS2009 - Medina - Weber - Simon - Iung Review HALDocument6 pagesDCDS2009 - Medina - Weber - Simon - Iung Review HALgabs521No ratings yet
- Sandoval - 2023 - Internal Consistency and Diversity Scenario Development A ComparativeDocument12 pagesSandoval - 2023 - Internal Consistency and Diversity Scenario Development A Comparativecends.gptNo ratings yet
- Deep Feature Based Cross-Slide RegistrationDocument19 pagesDeep Feature Based Cross-Slide Registrationedfewf3No ratings yet
- CDA DamSafety 2013revDocument10 pagesCDA DamSafety 2013revAliNo ratings yet
- Evaluating Risk in Construction-Schedule Model Eric-S: Construction Schedule Risk ModelDocument10 pagesEvaluating Risk in Construction-Schedule Model Eric-S: Construction Schedule Risk ModelSteeltonNo ratings yet
- Cost and Benefit Analysis of Supplier RiskDocument8 pagesCost and Benefit Analysis of Supplier Risksimeonkasumu74No ratings yet
- Modeling of Uncertainties in Reliability CenteredDocument3 pagesModeling of Uncertainties in Reliability CenteredFilipe CarneiroNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0951832000000880 MainDocument6 pages1 s2.0 S0951832000000880 Maintomo tomoNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0021967317304909 MainDocument5 pages1 s2.0 S0021967317304909 MaineducobainNo ratings yet
- Journal of Sound and Vibration: Buddhi L. Wahalathantri, David P. Thambiratnam, Tommy H.T. Chan, Sabrina FawziaDocument19 pagesJournal of Sound and Vibration: Buddhi L. Wahalathantri, David P. Thambiratnam, Tommy H.T. Chan, Sabrina Fawziaikhsan febriyanNo ratings yet
- Article 1 PDFDocument13 pagesArticle 1 PDFRawad YaredNo ratings yet
- Infrastructures 07 00005Document24 pagesInfrastructures 07 00005BigkiandiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 IntroductionDocument5 pagesUnit 1 Introductionmoneyheistberlin09No ratings yet
- Improved Visual Final Version NewDocument9 pagesImproved Visual Final Version NewAmanda CarterNo ratings yet
- Imposing Consistency For Optical Flow EstimationDocument14 pagesImposing Consistency For Optical Flow Estimation948261817No ratings yet
- Koraz2017 PDFDocument5 pagesKoraz2017 PDFrarepersonNo ratings yet
- Fault Detection in Complex Mechatronic Systems by A Hi - 2024 - Reliability EngiDocument11 pagesFault Detection in Complex Mechatronic Systems by A Hi - 2024 - Reliability EngibihailantianmyNo ratings yet
- AI-assistance For Predictive Maintenance 2021Document12 pagesAI-assistance For Predictive Maintenance 2021r.demchakNo ratings yet
- Biomedical Research PaperDocument7 pagesBiomedical Research PaperSathvik ShenoyNo ratings yet
- Information Fusion: SciencedirectDocument55 pagesInformation Fusion: SciencedirectJunjie LeeNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer Prediction Using Machine LearningDocument9 pagesBreast Cancer Prediction Using Machine LearningIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Model Selection Issue in Calibrating Reliability-Based Resistance Factors Based On In-Situ Test DataDocument9 pagesModel Selection Issue in Calibrating Reliability-Based Resistance Factors Based On In-Situ Test Datadj_taipeiNo ratings yet
- Well-Calibrated Prediction Intervals For Regression ProblemsDocument33 pagesWell-Calibrated Prediction Intervals For Regression ProblemsЮрий ЗемсковNo ratings yet
- Reducing Subjectivity Qualitative Risk Assessments 2014Document13 pagesReducing Subjectivity Qualitative Risk Assessments 2014AbhiNo ratings yet
- Optimization Approach Under Uncertainty inDocument4 pagesOptimization Approach Under Uncertainty inAbdelmajid AittalebNo ratings yet
- Qualitative-Quantitative Bayesian Belief Networks For ReliabilityDocument5 pagesQualitative-Quantitative Bayesian Belief Networks For Reliabilitymeercat_alexNo ratings yet
- tmp4BC6 TMPDocument35 pagestmp4BC6 TMPFrontiersNo ratings yet
- The Catapult Project An Innovative Approach For Learning StatistDocument5 pagesThe Catapult Project An Innovative Approach For Learning Statistegor.mfgNo ratings yet
- Risk Management of Pile Foundation Work PDFDocument10 pagesRisk Management of Pile Foundation Work PDFArdewi TesalonikaNo ratings yet
- 2021 CVEN40770 1 Stiffness Method Part1 OldDocument84 pages2021 CVEN40770 1 Stiffness Method Part1 OldArturo GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Lasker: Move by MoveDocument26 pagesLasker: Move by MoveArturo GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Updating Bridge Safety Based On Damage Indicators: B. Heitner, E.J. Obrien, T. Yalamas and F. SchoefsDocument1 pageUpdating Bridge Safety Based On Damage Indicators: B. Heitner, E.J. Obrien, T. Yalamas and F. SchoefsArturo GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Types of Failure Failure Theories For Ductile Materials Failure Theories For Brittle MaterialsDocument6 pagesTypes of Failure Failure Theories For Ductile Materials Failure Theories For Brittle MaterialsArturo GonzalezNo ratings yet
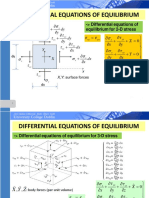
- Differential Equations of Equilibrium: Dy y Dy y DX X Y XDocument42 pagesDifferential Equations of Equilibrium: Dy y Dy y DX X Y XArturo GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Residual Life Assessment and Management of Ship Unloaders: G. Milana, K. Banisoleiman and A. GonzalezDocument1 pageResidual Life Assessment and Management of Ship Unloaders: G. Milana, K. Banisoleiman and A. GonzalezArturo GonzalezNo ratings yet
- ESR7 Poster Lloyd'sDocument1 pageESR7 Poster Lloyd'sArturo GonzalezNo ratings yet
- ESR9 Poster Lloyd'sDocument1 pageESR9 Poster Lloyd'sArturo GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Training in Reducing Uncertainty in Structural Safety: WWW - Trussitn.euDocument4 pagesTraining in Reducing Uncertainty in Structural Safety: WWW - Trussitn.euArturo GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Reduction of Uncertainty in The Assessment of Concrete Strength in Existing StructuresDocument1 pageReduction of Uncertainty in The Assessment of Concrete Strength in Existing StructuresArturo GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Reliability of Offshore Wind Turbine Towers Based On Kriging Surrogate ModelsDocument1 pageReliability of Offshore Wind Turbine Towers Based On Kriging Surrogate ModelsArturo GonzalezNo ratings yet
- ESR 14: Reduction of Uncertainty Through Regularized, Automated Road InspectionDocument1 pageESR 14: Reduction of Uncertainty Through Regularized, Automated Road InspectionArturo GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Using Truck Sensors For Road Pavement Performance InvestigationDocument1 pageUsing Truck Sensors For Road Pavement Performance InvestigationArturo GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Drive-By Monitoring Bridge Damage Detection Using Velocity Instantaneous CurvatureDocument1 pageDrive-By Monitoring Bridge Damage Detection Using Velocity Instantaneous CurvatureArturo GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Development of Optical Fibre Distributed Sensing For SHM of Bridges and Large Scale StructuresDocument1 pageDevelopment of Optical Fibre Distributed Sensing For SHM of Bridges and Large Scale StructuresArturo GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Bridge Condition and Safety Based On Measured Vibration LevelDocument1 pageAssessment of Bridge Condition and Safety Based On Measured Vibration LevelArturo GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Notes - PSOCDocument24 pagesModule 2 Notes - PSOCpriyaNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 - 3 - Implementation of Genetic AlgorithmsDocument73 pagesTopic 2 - 3 - Implementation of Genetic AlgorithmsAlyssa AnnNo ratings yet
- Jenkins LabDocument41 pagesJenkins LabYash SinghalNo ratings yet
- Eval-Matrix ShortGuide FinalDocument2 pagesEval-Matrix ShortGuide FinalAngele Hema MarajNo ratings yet
- G6 S4Document34 pagesG6 S4Vincent TeoNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Grade 4 - Activity Sheet - Multiply Numbers PDFDocument9 pagesMathematics Grade 4 - Activity Sheet - Multiply Numbers PDFJoanna Mae ArmasNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 Electrical InstallationDocument41 pagesMODULE 1 Electrical InstallationhmnzkonNo ratings yet
- Seperation of A Mixture - ScienceDocument2 pagesSeperation of A Mixture - ScienceShaheer HashmiNo ratings yet
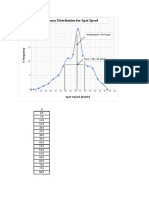
- Frequency Distribution For Spot SpeedDocument1 pageFrequency Distribution For Spot Speeddil afroza karim LinaNo ratings yet
- 3014 Top1Document26 pages3014 Top1DavidNo ratings yet
- CE5601-CE5010-Lecture 1Document34 pagesCE5601-CE5010-Lecture 1OmaidTanhaNo ratings yet
- Lab. 1 Two Component SystemsDocument4 pagesLab. 1 Two Component Systemssultan100% (1)
- I C Serial EEPROM Family Data Sheet: Features: DescriptionDocument42 pagesI C Serial EEPROM Family Data Sheet: Features: DescriptionSebastiao RochaNo ratings yet
- PDF Download by Creating Spool Request - ABAP Development - SCN WikiDocument7 pagesPDF Download by Creating Spool Request - ABAP Development - SCN WikipietersonNo ratings yet
- For Final Defense2Document39 pagesFor Final Defense2PJ PoliranNo ratings yet
- DeltaV SIS With Electronic Marshalling Hardware Reference GuideDocument115 pagesDeltaV SIS With Electronic Marshalling Hardware Reference GuideRobby NoviantoNo ratings yet
- X 25 UsrgdDocument364 pagesX 25 UsrgdALsandeepNo ratings yet
- Depositional Sequences and Microfacies of Lower Carboniferous Strata in The Marsel Block of The Chu Sarysu Basin, Southern KazakhstanDocument18 pagesDepositional Sequences and Microfacies of Lower Carboniferous Strata in The Marsel Block of The Chu Sarysu Basin, Southern KazakhstanMakhabbatNo ratings yet
- LTE OFDMA SimulationDocument9 pagesLTE OFDMA Simulationrajendra4343No ratings yet
- Emissary v2.0.0 User Manual PDFDocument12 pagesEmissary v2.0.0 User Manual PDFCaloy CabreraNo ratings yet
- 195 RMO 2015 Paper Solution AhmedabadDocument8 pages195 RMO 2015 Paper Solution AhmedabadRayan SinghNo ratings yet
- CSCE 411H Design and Analysis of Algorithms: Set 8: Greedy Algorithms Prof. Evdokia Nikolova Spring 2013Document61 pagesCSCE 411H Design and Analysis of Algorithms: Set 8: Greedy Algorithms Prof. Evdokia Nikolova Spring 2013Tanvi SharmaNo ratings yet