Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sit An
Uploaded by
babi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
68 views6 pagesOriginal Title
SIT AN.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
68 views6 pagesSit An
Uploaded by
babiCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
BREAKING THROUGH: MILLENIUM VILLAGES PROJECT MWANDAMA, MALAWI
_____________________
A Situational Analysis Presented to
the Faculty of the Nursing Department
Mrs. Portia P. Ituhat, RN,MN
____________________
In Partial Fulfillment of
the Requirements in NCM 213 RLE
COMMUNITY HEALTH NURSING ROTATION
Care of Population, Groups and Community
By:
Torres, Clarissa S.
BSN 3D Group 5 – Subgroup 1
September 24, 2020
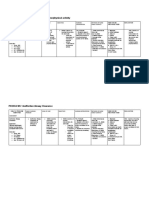
1. Community Problems and Community Diagnosis
Shuster and Goeppinger
Deficient community health among Mwandama, Malawi residents related to
insufficient access to healthcare provider as evidenced by program unavailable
to prevent health problems of a group or population.
Imbalanced Nutrition: less than body requirements among Mwandama, Malawi
residents related to insufficient dietary intake as evidenced by food and water
scarcity.
Risk for infection among the residents of Mwandama, Malawi related to
malnutrition and insufficient knowledge to avoid exposure to pathogens
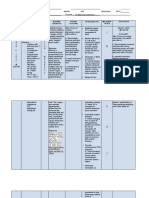
Omaha System
1. Domain: Environmental problems
Problem Classification Scheme: Residence
Modifiers: Community and Actual
Signs and Symptoms of Actual: Absence of houses after the calamity
Intervention Scheme:
Category - Case Management
o Residential homes (coordinate with local government officials in providing
materials for the building of their houses)
Problem Rating Scale
Knowledge – 3 Basic Knowledge
Behavior – 4 Usually Appropriate
Status – 1 Extreme signs and symptoms
2. Domain: Environmental problems
Problem Classification Scheme: Income
Modifiers: Community and Actual
Signs and Symptoms of Actual: Inadequate source of income;
inadequate community resources
Intervention Scheme:
Category - Case Management
o Businesses (coordinate with local government officials in supporting the
finances for trainings and programs)
Category – Teaching, Guidance and Counselling
o Teachings on importance of utilizing community resources for businesses
as a source of income
Problem Rating Scale
Knowledge – 2 Basic Knowledge
Behavior – 4 Usually Appropriate
Status – 2 Severe signs and symptoms
3. Domain: Environmental problems
Problem Classification Scheme: Sanitation
Modifiers: Community and Actual
Signs and Symptoms of Actual: Poor sanitation,
Intervention Scheme:
Category – Teaching, Guidance and Counselling
o Teachings on practices promoting good sanitation and hygiene.
Category – Surveillance
o Monitor the practices of the community with regards to good sanitation
and proper hygiene.
Problem Rating Scale
Knowledge – 2 Basic Knowledge
Behavior – 3 Inconsistently Appropriate
Status – 3 Moderate signs and symptoms
4. Domain: Psychosocial problems
Problem Classification Scheme: Growth and Development
Modifiers: Community and Actual
Signs and Symptoms of Actual:
Intervention Scheme:
Category – Teaching, Guidance and Counselling
Category – Treatments and Procedures
Problem Rating Scale
Knowledge – 2 Basic Knowledge
Behavior – 3 Inconsistently Appropriate
Status – 3 Moderate signs and symptoms
a. Domain 2: Psychosocial Problems
Growth and Development
Communication with community resources
b. Domain 3: Physiological Problems
Speech and language
Antepartum/Postpartum
Digestion/Hydration
c. Domain 4: Health-Related Behaviors
Nutrition
Family Planning
Healthcare Supervision
Personal Care
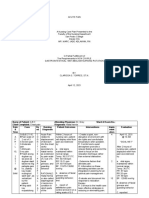
5. Activities that fall under each phase of Community Organizing
PHASES ACTIVITIES
1. Preparatory Phase Last 2000, the United Nations gathered
formulated 8 millennium development goals,
specifically to improve quality of life of those
under extreme poverty. The Millennium
Villages Project chose an area in Malawi
which is Mwandama, that is considered one
out of 14 millennium project sites in Africa.
They aim to help people in that specific
community with their basic needs that
include addressing issues on hunger,
education, healthcare, clean water,
sanitation.
2. Organizational Phase The Millennium Villages Project develop
programs that involve training of community
residents. They chose different individuals
that will somewhat lead a particular area like
in bakery, Martha Simoko was chosen to be
part of the training for baking thus, she has
the responsibility to teach other members of
the community to sustain the baking
businesses. On the other hand, trainings are
also given to those
3. Education and Training
Phase
4. Intersectoral
Collaboration Phase
5. Phase Out
6. Discuss the factors that may have served as opportunities/contributory factors to
success or threats/barriers to community development in terms of:
OPPORTUNITIES/CONT THREATS/ BARRIERS
RIBUTORY FACTORS
a. Personal -The people of -financial constraints
Mwandama are -poverty
determined and
motivated to strive hard in
any aspect in order to
survive and succeed in
life.
-The students are
inspired and eager to
learn and be part of the
people helping the
community.
b. Socio-cultural - -inadequate social or
community
organizations like
cooperatives due to
inadequate monetary
source
c. Economic -Training programs -No source of income
provided by the
Millennium Villages
Project that includes skills
on baking, agriculture,
livestock, and teaching.
-Mobile banks
d. Environmental
e. Political/Religiou
s factors
7. What community development programs/ projects were established to address
the identified problems/issues?
The Millennium Villages Project, upholding the United Nation’s 8 millennium
development goals of helping those from extreme poverty improve their quality of life.
With a ten-year program, they plan to achieve their goal by going through phases that
first includes providing the basic needs of the people. A number of programs or projects
were developed to address issues regarding hunger, education, healthcare, clean
water, sanitation which include the following:
Innovative, Low cost Programs for Agriculture particularly for the farmers in
2005
Farming Inputs and teaching farming methods (eg. teaching modern farming
methods and improvement of seeds and fertilizers)
Variety of women cooperative for promoting business, or other agricultural
cooperatives that encouraged farmers to expand business activities
Utilization of crops grown from the community into businesses
Training for business like bakery training (by Bakery Cooperative)
Schools have been built (Dindi Primary School); and providing teacher
training and learning materials
Opening of clinics and other primary health care facilities (maternity clinic,
out-patient department
Installation of electricity
Mobile phone networks were in place
Basic infrastructure like improvement of roads
Access for safe water, and good sanitation
Child survival and safe childbirth programs
Fighting Epidemic Diseases
Mobile bank that serves the community (once a week)
Operating of Grain Bank (2008)
World Food Programme (WFP) buys their maize every year for feeding
programs in Malawi’s schools
Rearing livestock programs
Teaching on how to cook nutritious food that can also give profit
Hygiene and Sanitation classes to help prevent the spread of disease
Formation of Parent-Teacher Association for relatives to be involved in pupils’
education
Regular home visits by community health workers (monitoring pregnant
mothers and malnutrition, gathering data of under-fives, educating about
hygiene and sanitation, conducting on the spot malaria test, distributing life-
saving drugs)
Introduction of bicycles for community health workers
Family Planning Services, antenatal clinic, under five clinic (immunizations)
Academic Scholarships for secondary education
You might also like
- San Luis, Trio - ActivityDocument4 pagesSan Luis, Trio - ActivityTrio San Luis100% (1)
- Activity Intolerance R/T Generalized WeaknessDocument3 pagesActivity Intolerance R/T Generalized Weaknesschanmin limNo ratings yet
- FNCPDocument62 pagesFNCPcathypolido100% (1)
- Withering Flowers: A Multiple Case Study About The Life of An Elderly Inside A Home Care FacilityDocument67 pagesWithering Flowers: A Multiple Case Study About The Life of An Elderly Inside A Home Care FacilityRuben Medina SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas Exchange NCPDocument3 pagesImpaired Gas Exchange NCPRomel BaliliNo ratings yet
- Impaired Skin Integrity For NCP Oct. 212020Document2 pagesImpaired Skin Integrity For NCP Oct. 212020Benjie DimayacyacNo ratings yet
- Exercise No.009Document2 pagesExercise No.009bea pegadNo ratings yet
- NCP DiarrheaDocument2 pagesNCP DiarrheaPrincess Xzmae RamirezNo ratings yet
- NCP LeprosyDocument3 pagesNCP LeprosyJane MinNo ratings yet
- Jose Rizal University: College of NursingDocument11 pagesJose Rizal University: College of NursingDhan Mark Trinidad100% (3)
- Salaknib Portfolio Final1-NSTPDocument39 pagesSalaknib Portfolio Final1-NSTPEmmanuel Jimenez-Bacud, CSE-Professional,BA-MA Pol SciNo ratings yet
- Biopsy: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesBiopsy: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDan HizonNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument11 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Intervention Rationale EvaluationBenjie DimayacyacNo ratings yet
- CHOLElithiasisDocument93 pagesCHOLElithiasisfranciscomaricris13No ratings yet
- NCP - ConstipationDocument2 pagesNCP - Constipationgringo1388No ratings yet
- NCP Nutrition1Document4 pagesNCP Nutrition1java_biscocho1229100% (1)
- Now, Try Some Big Leap.: Keep GoingDocument2 pagesNow, Try Some Big Leap.: Keep GoingShyla ManguiatNo ratings yet
- Problem IdentificationDocument3 pagesProblem IdentificationkgxviiNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN - Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitDocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN - Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitDaniel Andre S. SomorayNo ratings yet
- NCP For Parent and Child PDFDocument3 pagesNCP For Parent and Child PDFMariana Mikaela AlagarNo ratings yet
- St. Paul University Philippines: School of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences College of NursingDocument5 pagesSt. Paul University Philippines: School of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences College of NursingChristian UmosoNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument6 pagesNCPSarah Younes AtawnehNo ratings yet
- Ecologic Model NRMFDocument4 pagesEcologic Model NRMFgreyzelNo ratings yet
- NCP 6-10Document4 pagesNCP 6-10Junabel EmNo ratings yet
- Case Scenario:: 6. Make A Pain and Comforting Cycle For Your Patient Using This Diagram: See The Diagram in Your ModuleDocument1 pageCase Scenario:: 6. Make A Pain and Comforting Cycle For Your Patient Using This Diagram: See The Diagram in Your ModulewokorowNo ratings yet
- NCP-Ineffective Breathing Pattern-ManaoisDocument2 pagesNCP-Ineffective Breathing Pattern-ManaoisDan Dan ManaoisNo ratings yet
- Imbalanced Nutrition NCPDocument2 pagesImbalanced Nutrition NCPTINAYNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Breast Cancer NCP PDFDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Breast Cancer NCP PDFMaina Barman100% (1)
- Oks Na To Thank U Aubs!!: Okiii!!! Wuv U All!Document10 pagesOks Na To Thank U Aubs!!: Okiii!!! Wuv U All!CiaraNo ratings yet
- IDBDocument2 pagesIDBPaulo PolinagNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment FHP - Nutrition and MetabolismDocument25 pagesHealth Assessment FHP - Nutrition and MetabolismKim DajaoNo ratings yet
- Case Study NCPDocument4 pagesCase Study NCPKelly OstolNo ratings yet
- Laryngeal Cancer Concept MapDocument1 pageLaryngeal Cancer Concept MapTessa Claire JaranowskiNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Cardiopulmonary PerfusionDocument3 pagesNCP Ineffective Cardiopulmonary PerfusionjamiemapanaoNo ratings yet
- Fam Care PlanDocument3 pagesFam Care PlanGraiLe Joy Palbusa Ngina-BadayNo ratings yet
- Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument3 pagesImpaired Skin IntegrityAubrey SungaNo ratings yet
- CHN FNCPDocument6 pagesCHN FNCPKit LaraNo ratings yet
- PrioritizationDocument2 pagesPrioritizationJamil Lorca100% (1)
- Ursing ARE LAN: Short Term Goal: Independent Intervention: Independent InterventionDocument2 pagesUrsing ARE LAN: Short Term Goal: Independent Intervention: Independent InterventionGiselle EstoquiaNo ratings yet
- NCP PainDocument4 pagesNCP PainMark Allison BuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- NLE Practice Test 3aDocument17 pagesNLE Practice Test 3amikoy_tikoyNo ratings yet
- FNCP - FinalDocument6 pagesFNCP - FinalmarkyabresNo ratings yet
- Amoebiasis Case StudyDocument13 pagesAmoebiasis Case StudymelvinpasionaNo ratings yet
- Gordon'S Functional Health Patterns Illness Scientific Rationale Before CurrentDocument3 pagesGordon'S Functional Health Patterns Illness Scientific Rationale Before CurrentGen Rodriguez100% (1)
- FNCP Figueroa and de GuzmanDocument3 pagesFNCP Figueroa and de GuzmanDANIELA DE GUZMANNo ratings yet
- Prenatal Care NCPDocument10 pagesPrenatal Care NCPAlex AntipordaNo ratings yet
- 3 NCP AsthmaDocument6 pages3 NCP AsthmajaninenicoleNo ratings yet
- Cu 4Document3 pagesCu 4Paul SahagunNo ratings yet
- Ranking and Scoring of Health ProblemsDocument2 pagesRanking and Scoring of Health ProblemsMonmon BagarinaoNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Tissue Perfusion - NCPDocument7 pagesIneffective Tissue Perfusion - NCPVianah Eve EscobidoNo ratings yet
- Risk For AspirationDocument1 pageRisk For Aspirationmmcgee01No ratings yet
- NCP CSDocument7 pagesNCP CSTwobee Kriz LeghidNo ratings yet
- NCP PainDocument5 pagesNCP PainChloe Crystal DorojaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationMeena KoushalNo ratings yet
- Prodoc - Youth Volunteer Rebuilding Darfur Project - Final1Document55 pagesProdoc - Youth Volunteer Rebuilding Darfur Project - Final1Anh ĐặngNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Rural Community DevelopmentDocument32 pagesIntroduction To Rural Community DevelopmentS.Rengasamy100% (6)
- Community Organizing Participatory & ActionDocument49 pagesCommunity Organizing Participatory & Actionrhenier_ilado100% (3)
- Day 1 Thursday Attendance Check OrientationDocument16 pagesDay 1 Thursday Attendance Check OrientationDummy AccountNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8:: Community Engagement, Solidarity and CitizenshipDocument4 pagesLesson 8:: Community Engagement, Solidarity and CitizenshipRouiz Jopert A. FerrerNo ratings yet
- Community Engagement, Solidarity and Citizenship: Group 4 (12 HUMSS-D)Document17 pagesCommunity Engagement, Solidarity and Citizenship: Group 4 (12 HUMSS-D)jeonghan aegiNo ratings yet
- Huling PaalamDocument1 pageHuling PaalambabiNo ratings yet
- Torres Clarissa ChartingDocument2 pagesTorres Clarissa Chartingbabi100% (1)
- 4 Primary Immune AberrationsDocument5 pages4 Primary Immune AberrationsbabiNo ratings yet
- Intravenous Fluid: A Lecturette OnDocument16 pagesIntravenous Fluid: A Lecturette OnbabiNo ratings yet
- 4 Primary Immune AberrationsDocument5 pages4 Primary Immune AberrationsbabiNo ratings yet
- Hiatal HerniaDocument60 pagesHiatal Herniababi100% (1)
- Torres Clarissa ChartingDocument2 pagesTorres Clarissa Chartingbabi100% (1)
- Reading CompilationDocument30 pagesReading CompilationbabiNo ratings yet
- 30a2131 Complete Blood Count Normal Pediatric Values PDFDocument1 page30a2131 Complete Blood Count Normal Pediatric Values PDFReziel Basilan Manalo100% (2)
- Donning A Sterile Gown and Close GlovingDocument2 pagesDonning A Sterile Gown and Close Glovingbabi100% (4)
- Torres ProcedureDocument3 pagesTorres Procedurebabi100% (1)
- Torres, Clarissa - RABIESDocument9 pagesTorres, Clarissa - RABIESbabiNo ratings yet
- Esophageal CA DrugsDocument7 pagesEsophageal CA DrugsbabiNo ratings yet
- Hypercalcemia: Etiology and Management: Amanda Demauro Renaghan and Mitchell H. RosnerDocument3 pagesHypercalcemia: Etiology and Management: Amanda Demauro Renaghan and Mitchell H. RosnerbabiNo ratings yet
- Journal Ortho RequirementDocument13 pagesJournal Ortho RequirementKenn yahweexNo ratings yet
- TORRES READING - IntussusceptionDocument8 pagesTORRES READING - IntussusceptionbabiNo ratings yet
- Dissociative Identity DisorderDocument24 pagesDissociative Identity DisorderbabiNo ratings yet
- Hiatal Hernia FinalDocument7 pagesHiatal Hernia FinalbabiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Lidocaine HCL) - TorresDocument6 pagesDrug Study (Lidocaine HCL) - TorresbabiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - ERDocument10 pagesDrug Study - ERbabiNo ratings yet
- Torres-Reading On PTSDDocument15 pagesTorres-Reading On PTSDbabiNo ratings yet
- Acute PainDocument5 pagesAcute PainbabiNo ratings yet
- TORRES - SybilDocument10 pagesTORRES - SybilbabiNo ratings yet
- Zoledronic AcidDocument7 pagesZoledronic AcidbabiNo ratings yet
- PA TorresDocument4 pagesPA TorresbabiNo ratings yet
- Biographic and IllnessDocument2 pagesBiographic and IllnessbabiNo ratings yet
- Correlates To Work-Related Stress of Newly-Graduated Nurses in Critical-Care UnitsDocument11 pagesCorrelates To Work-Related Stress of Newly-Graduated Nurses in Critical-Care UnitsbabiNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis - Subgroup 2 Esophageal CADocument74 pagesCase Analysis - Subgroup 2 Esophageal CAbabiNo ratings yet
- NVS Written ReportDocument20 pagesNVS Written ReportbabiNo ratings yet
- Wuffda Rabbit RadnaDocument36 pagesWuffda Rabbit Radnaaleks3No ratings yet
- l2 Quarter 2 Week 1 - Prepare Mise en PlaceDocument38 pagesl2 Quarter 2 Week 1 - Prepare Mise en PlaceGwyneth VicenteNo ratings yet
- Year 13 LTP 2023 FinalDocument25 pagesYear 13 LTP 2023 FinalNimisha PrasadNo ratings yet
- Health Consciousness AND Lifestyle of Grade 12-Abm StudentsDocument21 pagesHealth Consciousness AND Lifestyle of Grade 12-Abm Studentschristine senajononNo ratings yet
- 4 Year Report in Ethio - California Flour FactoryDocument37 pages4 Year Report in Ethio - California Flour FactoryAmanual Shimekach100% (1)
- Current ResumeDocument1 pageCurrent Resumeapi-650480818No ratings yet
- Week 8: Personal Goal Setting (Smart)Document23 pagesWeek 8: Personal Goal Setting (Smart)Kathleen LunaNo ratings yet
- Refer To Problem 15 22 After Some Detailed Polling Among The 60Document1 pageRefer To Problem 15 22 After Some Detailed Polling Among The 60Amit PandeyNo ratings yet
- GDAs - Guideline Daily AmountsDocument10 pagesGDAs - Guideline Daily AmountssylvisionNo ratings yet
- English LDocument9 pagesEnglish LPlutoNo ratings yet
- Fasting vs. Eating Less - What's The Difference - (Science of Fasting)Document3 pagesFasting vs. Eating Less - What's The Difference - (Science of Fasting)WEMBE RAOULNo ratings yet
- Why Do People Take Vitamin K?Document27 pagesWhy Do People Take Vitamin K?JamesBuensalidoDellavaNo ratings yet
- Ellen Hill: Master of Public Health in Nutritional SciencesDocument2 pagesEllen Hill: Master of Public Health in Nutritional Sciencesapi-434483502No ratings yet
- FYP Final PresentationDocument27 pagesFYP Final PresentationLee MingjinNo ratings yet
- Development of Kangkong BreadDocument14 pagesDevelopment of Kangkong BreadJohnMichaelAnol100% (1)
- HEALTH MELCs Grade 7Document4 pagesHEALTH MELCs Grade 7Gisela CapiliNo ratings yet
- DSWD: Policies and Programs That Impact EducationDocument2 pagesDSWD: Policies and Programs That Impact EducationShaNe BesaresNo ratings yet
- UTS Bahasa Inggris Kelas X (Jawaban)Document35 pagesUTS Bahasa Inggris Kelas X (Jawaban)Yanuar Rizal Putra UtamaNo ratings yet
- Visualizing The Ratio of 2 Given NumbersDocument56 pagesVisualizing The Ratio of 2 Given NumbersMARIA KATHRINA ANACAY100% (1)
- 2006 - Utilization of Pumpkin Powder in Bakery ProductsDocument9 pages2006 - Utilization of Pumpkin Powder in Bakery ProductsDanaNo ratings yet
- Bakers Delight HandbookDocument12 pagesBakers Delight HandbookserenafcfNo ratings yet
- Salazar NDT - CHN Midterm Part 1Document4 pagesSalazar NDT - CHN Midterm Part 1Wincy SalazarNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0021925818760493 MainDocument7 pages1 s2.0 S0021925818760493 MainMarko Sanja StikovicNo ratings yet
- Infant Nutrition: of For Optimum andDocument35 pagesInfant Nutrition: of For Optimum andm mNo ratings yet
- Color Guide For Food SupplementsDocument2 pagesColor Guide For Food SupplementsNabla ciencia en movimientoNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Critical CareDocument6 pagesNutrition in Critical CareSusanita RamirezNo ratings yet
- FOND 121.aswerdDocument8 pagesFOND 121.aswerdBrian NyakundiNo ratings yet
- Pws Balita BGM Puskesmas Alalak Tengah Bulan: Desember 2021Document14 pagesPws Balita BGM Puskesmas Alalak Tengah Bulan: Desember 2021Novi ErwiNo ratings yet
- 10 Secrets To Growing Black Hair Long and Fast - Natural Hair Care (PDFDrive)Document62 pages10 Secrets To Growing Black Hair Long and Fast - Natural Hair Care (PDFDrive)la laNo ratings yet
- Ayushi Verma Practice SchoolDocument20 pagesAyushi Verma Practice SchoolAkash YadavNo ratings yet