Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ehambutol Inhibits Mycobacterial Arabinosyltransferase Streptomcin Binds To 16s rRNA of Bacteria
Uploaded by
kamil malikOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ehambutol Inhibits Mycobacterial Arabinosyltransferase Streptomcin Binds To 16s rRNA of Bacteria
Uploaded by
kamil malikCopyright:
Available Formats
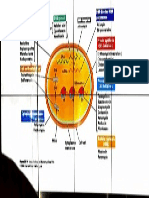
Drug for Tuberculosis
Isoniazid Rifampicin Pyrazinamide Ethambutol Streptomycin
General ~ Bactericidal – fast-dividing ~ Bactericidal – extra & intracellular ~ largely bacteriostatic ~ bacteriostatic on MTB ~ broad-spectrum
~ Bacteriostatic – slow-dividing bacilli ~ bacteriostatic on actively ~ poor penetration (extracellular
~ Penetrates cell wall – extra & intracellular ~ Broad-spectrum – gram +, gram - , replicating MTB bacilli only)
bacilli clamydiae
Pharmaco-kinetics ~ Oral or parenteral route ~ Oral ~ Oral ~ Oral ~ IM only
~ excreted in urine in 24h ~ excreted in feces ~ excreted in urine ~ excreted in urine ~ excreted in urine
Mode of Action Cell wall systhesis DNA transcription Synthesis of fatty acid Cell wall systhesis Protein synthesis
Major adverse ~ Neurotoxicity (pyridoxine deficiency) – ~ harmless – orange urine sweat ~ joint pain (arthralgia) ~ Retrobulbar neuritis (loss of ~ ototoxicity (hearing loss)
reactions paraesthesia, convulsion, ataxia ~ rash, fever, vomiting ~ hepatitis visual acuity & red-green clor ~ nephrotoxicity
~ Induced hepatitis (build up toxic ~ hepatitis ~ skin rash blindness)
acetylisoniazid) ~ nausea, vomiting, anorexia ~skin rash, pleuritis, joint pain
~ allergy: skin rash
Precaution Hepatic deficiency: ↓ dose
Ethanol: isoniazid hepatotoxicity
Ehambutol inhibits
X Mycobacterial
polymerization of
(encoded by pncA gene)
arabinosyltransferase
arqabinogalactan
X formation
(cell wall
of cell wall
component)
Streptomcin binds
X transcription to RNA & X to 16s rRNA of
X protein
synthesis
bacteria
You might also like
- Chapter 7 Neoplasia 1 2 Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of DiseaseDocument9 pagesChapter 7 Neoplasia 1 2 Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of DiseaseArun Nayak100% (11)
- SketchyMicro ChartDocument14 pagesSketchyMicro ChartSonia100% (8)
- 2011 Diagnosis and Treatment in ProsthodonticsDocument353 pages2011 Diagnosis and Treatment in ProsthodonticsAnonymous 0pg1qSpO100% (1)
- Gram Positive Bacteria: Antibacterial DrugsDocument4 pagesGram Positive Bacteria: Antibacterial DrugsMOHAMAD HASSOUNANo ratings yet
- Southern Blot Lab ReportDocument10 pagesSouthern Blot Lab ReportPeter Ickes0% (1)
- Unseen Trends in Biotechnology-Part1Document100 pagesUnseen Trends in Biotechnology-Part1Shourya17No ratings yet
- Environmental Microbiology: Second EditionDocument22 pagesEnvironmental Microbiology: Second EditionLa Ode Muhammad ErifNo ratings yet
- Target AB Ke BakteriDocument1 pageTarget AB Ke Bakterimazz.rianNo ratings yet
- Carbapenems Monobactam Glycopeptide Lipopeptide Tetracycline Penicillins CephalosporinsDocument8 pagesCarbapenems Monobactam Glycopeptide Lipopeptide Tetracycline Penicillins CephalosporinsBrandon Georges (Scribblemeascript)No ratings yet
- Reviewer PcolDocument3 pagesReviewer PcolMycaela Archivido De AlvaNo ratings yet
- Microbiome - The Genomes of MicrobesDocument3 pagesMicrobiome - The Genomes of Microbes6wcdwfcfydNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic ATB For ExternDocument64 pagesAntibiotic ATB For ExternKarn AuerkarnnNo ratings yet
- Kerja ABDocument72 pagesKerja ABFarmasi RSUD Kramat JatiNo ratings yet
- Bacteria Summary TableDocument10 pagesBacteria Summary TableNur Alia YasminNo ratings yet
- Drug Worksheet - Answers-4Document3 pagesDrug Worksheet - Answers-4sirnNo ratings yet
- Pakistan Kidney and Liver Institute & Research Centre (PKLI)Document1 pagePakistan Kidney and Liver Institute & Research Centre (PKLI)Waqas SaleemNo ratings yet
- Classification of Antibiotics For PrintingDocument4 pagesClassification of Antibiotics For PrintingMuthu Kumar100% (2)
- Antibiotics ListDocument14 pagesAntibiotics ListBrenda LiawNo ratings yet
- Resistance To: Antibacterial AgentsDocument15 pagesResistance To: Antibacterial AgentsZeth MoturiNo ratings yet
- PDF Antibiotic Prescribing - CompressDocument1 pagePDF Antibiotic Prescribing - CompressMaximilian BezzeghNo ratings yet
- Monash PHA2022 Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesMonash PHA2022 Cheat Sheetdesna.ramjeeNo ratings yet
- Drugs For TuberculosisDocument3 pagesDrugs For TuberculosisJeanneRoseBlancaflorNo ratings yet
- Drug Interactions Results - MICROMEDEXDocument5 pagesDrug Interactions Results - MICROMEDEXAna SibajaNo ratings yet
- Hemostasis Substituition and Mixing StudiesDocument13 pagesHemostasis Substituition and Mixing StudiesjosereyescclNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics by Class: Escherichia ColiDocument8 pagesAntibiotics by Class: Escherichia ColiCremona ElenaNo ratings yet
- Malaria Primer FiguresDocument8 pagesMalaria Primer FiguresbacabacabacaNo ratings yet
- Active Ingredients Drug Classification EgyptDocument61 pagesActive Ingredients Drug Classification EgyptBassem WolselyNo ratings yet
- Chart Antibiotics IDocument1 pageChart Antibiotics IRedNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics - Classification & Mode of Action PDFDocument8 pagesAntibiotics - Classification & Mode of Action PDFtarun paulNo ratings yet
- Drug Study in PharmaDocument69 pagesDrug Study in PharmaPau-pau BasiNo ratings yet
- Pharm Chemo Drugs SauldDocument6 pagesPharm Chemo Drugs Sauldneal100% (1)
- AntibioticsDocument1 pageAntibioticsinst0015No ratings yet
- Leik AGNP Review PDFDocument8 pagesLeik AGNP Review PDFJhouleen Angelika Tam100% (4)
- In Et Ic S: To Xi Ci TyDocument63 pagesIn Et Ic S: To Xi Ci TyTsalitsa Nurramadhani MarjokoNo ratings yet
- Parathyroid DrugsDocument2 pagesParathyroid DrugsAmber LeJeuneNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobal Drugs #Dental 1Document30 pagesAntimicrobal Drugs #Dental 1ggNo ratings yet
- Drug Summary Table MEDSCI 202Document4 pagesDrug Summary Table MEDSCI 202Praveen WimalasenaNo ratings yet
- From Gene To Protein: How Genes WorkDocument58 pagesFrom Gene To Protein: How Genes WorkGabe GallagherNo ratings yet
- Dna Vs Rna and Protein Synthesis Updated Recap by Amoeba SistersDocument2 pagesDna Vs Rna and Protein Synthesis Updated Recap by Amoeba SistersJaneNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Chart FinalDocument1 pageAntibiotic Chart FinalJosh GardnerNo ratings yet
- Kagaw Notes 100Document33 pagesKagaw Notes 100Stephany PolinarNo ratings yet
- ELE - PID Treatment To Lower Respiratory Tract InfectionsDocument12 pagesELE - PID Treatment To Lower Respiratory Tract InfectionsJane DoeNo ratings yet
- G11 DR BiologyDocument170 pagesG11 DR BiologyImran OryaNo ratings yet
- Tri Widyawat & Sit Syarifah: Dep. Farmakologi & TerapeutikDocument52 pagesTri Widyawat & Sit Syarifah: Dep. Farmakologi & TerapeutikAmie Tahir RajagukgukNo ratings yet
- Drugs Inhibiting Cell Wall Synthesis - 2Document6 pagesDrugs Inhibiting Cell Wall Synthesis - 2NeelabhNo ratings yet
- Pharma Notes 3Document10 pagesPharma Notes 3Mayya FirdousNo ratings yet
- AntibioticsDocument5 pagesAntibioticsgitama9904No ratings yet
- AntibioticsDocument6 pagesAntibioticsyezan27100% (8)
- Alevel Biology 16 Cell Structure NoteDocument10 pagesAlevel Biology 16 Cell Structure NoteAvidan ShahNo ratings yet
- PHARMACOLOGYDocument44 pagesPHARMACOLOGYshruti sangwan100% (1)
- Drug Mechanism Clincal Use Side Effects Antifungal: Amphote Ricin BDocument30 pagesDrug Mechanism Clincal Use Side Effects Antifungal: Amphote Ricin BCess Lagera Ybanez0% (1)
- Onc ChartDocument1 pageOnc Chartchelsea garzaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Concise Notes NEET-PGDocument30 pagesPharmacology Concise Notes NEET-PGMohamed TayyabNo ratings yet
- Bio Lec 3Document2 pagesBio Lec 3lilliaNo ratings yet
- Pharm All in OneDocument50 pagesPharm All in OneActeen MyoseenNo ratings yet
- TB Treatment RegimenDocument2 pagesTB Treatment RegimenTshiamo TekeNo ratings yet
- TB DRUGS 2023-2024 SummaryDocument4 pagesTB DRUGS 2023-2024 SummaryMark Lorenz NaldozaNo ratings yet
- Chenqi Liu - 11 - DNA Vs RNA and Protein Synthesis - Amoeba Sisters - SHODocument2 pagesChenqi Liu - 11 - DNA Vs RNA and Protein Synthesis - Amoeba Sisters - SHOthomasmarteauhNo ratings yet
- Daniel - Assignment On AntibioticsDocument6 pagesDaniel - Assignment On AntibioticsArun Roa DanielNo ratings yet
- Salicylates Propionic Acid Derivatives Indole Acetic Acid Phenylacet Ic Acid Derivatives Oxicam Acetaminoph enDocument4 pagesSalicylates Propionic Acid Derivatives Indole Acetic Acid Phenylacet Ic Acid Derivatives Oxicam Acetaminoph enLana AmerieNo ratings yet
- Daftar Antibiotik Dan Kerjanya YudistraDocument13 pagesDaftar Antibiotik Dan Kerjanya YudistraYudistra R ShafarlyNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument1 pageProtein SynthesisChristopher TalaveraNo ratings yet
- MICRO Master ListDocument63 pagesMICRO Master ListDaniel Del RiscoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory 05 - COPD: Definition: Types For EmphysemaDocument3 pagesRespiratory 05 - COPD: Definition: Types For Emphysemakamil malikNo ratings yet
- Respiratory 03 - Bronchiogenic CA: 1) Smoking/industrial Hazards/air Pollution 2) Molecular Genetic MutationDocument2 pagesRespiratory 03 - Bronchiogenic CA: 1) Smoking/industrial Hazards/air Pollution 2) Molecular Genetic Mutationkamil malikNo ratings yet
- Respiratory 02 - Pulmonary Tuberculosis: PathogenesisDocument3 pagesRespiratory 02 - Pulmonary Tuberculosis: Pathogenesiskamil malikNo ratings yet
- Drugs For AsthmaDocument1 pageDrugs For Asthmakamil malikNo ratings yet
- Vels Vidyashram Senior Secondary School: Investigatory Project in BiologyDocument20 pagesVels Vidyashram Senior Secondary School: Investigatory Project in BiologyAbhishek GautamNo ratings yet
- Approach To The Child With Acute Diarrhea in Resource-Limited Countries - UpToDateDocument17 pagesApproach To The Child With Acute Diarrhea in Resource-Limited Countries - UpToDateNedelcu MirunaNo ratings yet
- Mid-Term Review Practice QuestionsDocument2 pagesMid-Term Review Practice QuestionsYifei HeNo ratings yet
- From Gene To Protein - WorksheetDocument4 pagesFrom Gene To Protein - WorksheetpinkNo ratings yet
- Biofire FilmArray Full Panel Menu Info SheetDocument3 pagesBiofire FilmArray Full Panel Menu Info SheetAnne Jillian Castillo100% (1)
- Bet Question Paper 2008Document24 pagesBet Question Paper 2008Vasu MathuraNo ratings yet
- Alterations in Nutrition and Gastrointestinal, Metabolism and EndocrineDocument105 pagesAlterations in Nutrition and Gastrointestinal, Metabolism and EndocrineJanmichael FeliscuzoNo ratings yet
- USMLE Step 2CK Notes With AdditionsDocument103 pagesUSMLE Step 2CK Notes With AdditionsLuong Anh100% (1)
- Adenoviridae: Family: Adenoviridae Common Name: Adenovirus Virus: AdenovirusDocument3 pagesAdenoviridae: Family: Adenoviridae Common Name: Adenovirus Virus: AdenovirusTel LyNo ratings yet
- 9 Penyakit-Penyakit Pada BabiDocument77 pages9 Penyakit-Penyakit Pada BabiIrene SembiringNo ratings yet
- Gut Microbiota and Its Modulation For Healthy Farming of Pacific White Shrimp Litopenaeus VannameiDocument20 pagesGut Microbiota and Its Modulation For Healthy Farming of Pacific White Shrimp Litopenaeus VannameislothwonNo ratings yet
- An Introduction: Marx P. Catalan, RMTDocument48 pagesAn Introduction: Marx P. Catalan, RMTstoopiidgurl91% (11)
- Corneal Collagen Cross-Linking For Infectious Keratitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisDocument10 pagesCorneal Collagen Cross-Linking For Infectious Keratitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisJoseph Chipana GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Nihms 1779961Document28 pagesNihms 1779961Lynda Inesse KermiNo ratings yet
- Bio302 Final Term-1Document8 pagesBio302 Final Term-1Sanaya RaajputNo ratings yet
- Hair Sheep Blood, Citrated or Defibrinated, Fulfills All Requirements of Blood Agar For Diganostics Microbiology Laboratory Test PDFDocument8 pagesHair Sheep Blood, Citrated or Defibrinated, Fulfills All Requirements of Blood Agar For Diganostics Microbiology Laboratory Test PDFMaive Patricia Montaño VillarroelNo ratings yet
- 2 - Organisation of The OrganismDocument6 pages2 - Organisation of The OrganismAvyay TopraniNo ratings yet
- Passmedicine 2020 Keynotes MRCP Part1Document66 pagesPassmedicine 2020 Keynotes MRCP Part1saravanan100% (2)
- HemtDocument42 pagesHemtSaily JaquezNo ratings yet
- Bioplex BrochureDocument6 pagesBioplex BrochureRaul ReyesNo ratings yet
- P3118.1.08.E.1.Coglavax SPCDocument5 pagesP3118.1.08.E.1.Coglavax SPCJelena Terzic100% (1)
- Blood and Its ComponentsDocument30 pagesBlood and Its ComponentskushalNo ratings yet
- HEMA Lec 03 Bone Marrow Collection Lymphoid Organs 1Document9 pagesHEMA Lec 03 Bone Marrow Collection Lymphoid Organs 1Patrick AbellaNo ratings yet