Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chart Antibiotics I
Uploaded by
RedOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chart Antibiotics I
Uploaded by
RedCopyright:
Available Formats
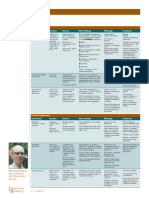
Mechanism Adverse effects Uses
Sulfonamides Inhibits dihydropteroate (a step in folate Involve skin Hypersensitivity reactions; rash/itch Can be used as monotherapy for UTI (reaches
metabolism) —(true anaphylaxis is rare) high conc. in urine bc excreted by urine)
Stevens-Johnson syndrome occurs rarely
(widespread death of skin and mucosa with Often used in combo with trimethoprim (synergistic
desquamation) — due to hemolysis with G6PD bc inhibit separate step in single pathway of
tetrahydrofolate)
Combo = broad spectrum (many Gram + and -)
Combo use: GI infections,
enterobacteriaceae
S. aureus (including most MRSA)
DHFR Inhibit dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) Trimethoprim: rare suppressive effect on bone Trimethoprim is a selective inhibitor of bacterial
inhibitors production of tetrafolate marrow cells, reducing production of RBC, WBC DHRF, it is rarely used as monotherapy
and platelets (occurs in patients with low folate) =
anemia, granulocytopenia, thrombocytopenia Often used in combo with sulfonamides (see
above) combo = broad spectrum
Several DHFR inhibitors, have different targets
Quinolones Block activity of gyrase and Connective tissue: in animal models = weakened Naladixic acid (used to treat UTIs)
topoisomerase IV at the step where cartilage in juveniles Fluroquinolones (F atom blood levels, tissue
DNA has a double stranded break — Adults = rare tendintis and tendon rupture penetration and half-life) — many kinds with
Presence of a break in DNA leads to May predispose to cardiac arrythmias different spectrum (Gram +, Gram -, anaerobic,
bacterial death mycobacterium)
Fluroquin has good activity against urinary and
resp pathogens = can be used as empiric therapy
for these
- Enterobacteria, P. arginosa, N. gonorrhea,
Streptococcus, Staphylococcus,
Mycobacteria, Anaerobic
Rifamycins Block RNA synthesis by binding B- Discoloration of secretions (orange tears, urine, Broad spectrum of activity but resistance quickly
subunit of RNA pol (binding within saliva) develops if used alone (so when rifamycins used
DNA/RNA channel of pol stops nucleic Can injury liver in presence of other sources of for serious infections they are used in combo with
acid form progressing through channel) hepatic injury other antibiotics)
Can induce expression of hepatic metabolic
enzymes leading to increased metabolism of Lipid soluble (excellent penetration into tissues
other drugs and secretion)
Used in combo for treatment of mycobacterium TB
and staphylococcal endocarditis/arthritis
Used as monotherapy to eradicate colonizing N.
meningitides from people exposed during outbreak
Fidaxomicin Blocks RNA synthesis by binding RNA Well tolerated C. difficile infection
pol-DNA complex before DNA strands Narrow spectrum of activity (poor lipid solubility)
are separated to initiate RNA synthesis Poorly absorbed from GI tract so it is concentrated
at site of C. diff infection
As effective as vancomycin for treatment of C. diff
infection (fewer relapses with fidaxomicin)
You might also like
- Gram Positive Bacteria: Antibacterial DrugsDocument4 pagesGram Positive Bacteria: Antibacterial DrugsMOHAMAD HASSOUNANo ratings yet
- 7 Case ScenarioDocument3 pages7 Case ScenarioLucas JelmarNo ratings yet
- Tangina Mo BizarDocument1 pageTangina Mo BizarJhon eric EscultorNo ratings yet
- AAD BF PanniculitisDocument2 pagesAAD BF Panniculitiskahkashanahmed065No ratings yet
- TB DrugsDocument1 pageTB DrugsDiane LuiNo ratings yet
- Antihelminthic Drugs PDFDocument3 pagesAntihelminthic Drugs PDFCas BuNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid Synthesis InhibitorsDocument3 pagesNucleic Acid Synthesis InhibitorsMirna HusseinNo ratings yet
- Antifungal Agents: EchinocandinsDocument2 pagesAntifungal Agents: EchinocandinsCourtney TownsendNo ratings yet
- AntibioticsDocument1 pageAntibioticsinst0015No ratings yet
- Inhibitors of Protein SynthesisDocument2 pagesInhibitors of Protein Synthesiselsayed barhomeNo ratings yet
- Drug Study QIDocument8 pagesDrug Study QImaeDonitaNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial IIDocument11 pagesAntimicrobial IIFrances Lau Yee ChinNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyRenmen Rosito Hortelano100% (3)
- Antimycobacterial Drugs PDFDocument3 pagesAntimycobacterial Drugs PDFCas BuNo ratings yet
- Tablets - 100, 200 MG Side Effects: Drug StudyDocument2 pagesTablets - 100, 200 MG Side Effects: Drug StudyMae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study in PharmaDocument69 pagesDrug Study in PharmaPau-pau BasiNo ratings yet
- UAW Respiratory Antimicrobial Pharm Guide MedstuDocument19 pagesUAW Respiratory Antimicrobial Pharm Guide MedstuNabeel ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Catetan AntibioticDocument7 pagesCatetan Antibiotic067Safira AuliaNo ratings yet
- Abfghx Cfghheat Shfgheet Abx QNDocument6 pagesAbfghx Cfghheat Shfgheet Abx QNRăzvan RoșcaNo ratings yet
- L9 Drug Therapy of TuberculosisDocument3 pagesL9 Drug Therapy of TuberculosisNurul Izzati AsyiqinNo ratings yet
- M.06 MISCELLANEOUS ANTIMICROBIALS (Part 1)Document3 pagesM.06 MISCELLANEOUS ANTIMICROBIALS (Part 1)PAUL ALINGKAYONNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobials 2 PDFDocument5 pagesAntimicrobials 2 PDFCas BuNo ratings yet
- Drugstudy 20Document9 pagesDrugstudy 20MahledJoy EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Antiparasitic & Antifungal DrugsDocument30 pagesAntiparasitic & Antifungal DrugsAbdullah AlkharsNo ratings yet
- Lecture #1 - AntimetabolitesDocument4 pagesLecture #1 - AntimetabolitesIshraq AfifiNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics: Lecture 6: Antibiotics For Anaerobic InfectionsDocument12 pagesAntibiotics: Lecture 6: Antibiotics For Anaerobic InfectionsMuath AlqarniNo ratings yet
- Antimikroba Untuk Infeksi Gastrointestinal: Oleh: Evi Sovia Lab. Farmakologi FK UNJANIDocument86 pagesAntimikroba Untuk Infeksi Gastrointestinal: Oleh: Evi Sovia Lab. Farmakologi FK UNJANIKresna Denta ElygioNo ratings yet
- Metronidazole Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMetronidazole Drug StudyA.No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug Studyecasantos595No ratings yet
- 3rd 5th Gen CephalosporinDocument5 pages3rd 5th Gen CephalosporinJR BetonioNo ratings yet
- Farklin, AntivirusDocument47 pagesFarklin, AntivirusFilhaqqiNo ratings yet
- Sphere: These DiarrheaDocument3 pagesSphere: These Diarrheamed testNo ratings yet
- Anti Leprosy Drug SeminarDocument76 pagesAnti Leprosy Drug SeminarSiddharth DashNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyJhaztene Mae BaniquedNo ratings yet
- Carlos D. Achondo JR 2MD-1 March 19, 2020Document6 pagesCarlos D. Achondo JR 2MD-1 March 19, 2020Carlos NiñoNo ratings yet
- IE - Antibiotic TableDocument5 pagesIE - Antibiotic TablemeganNo ratings yet
- Antiprotozoal Drugs: DR Manik GhadlingeDocument63 pagesAntiprotozoal Drugs: DR Manik GhadlingeEscitalopram 5mgNo ratings yet
- Daniel - Assignment On AntibioticsDocument6 pagesDaniel - Assignment On AntibioticsArun Roa DanielNo ratings yet
- 408 Antifungal Stu 1 07Document6 pages408 Antifungal Stu 1 07Hassan.shehriNo ratings yet
- ANTIFUNGALDocument5 pagesANTIFUNGALMarioli Rodríguez CoronaNo ratings yet
- Treatments and Preventive Methods of MSDocument11 pagesTreatments and Preventive Methods of MSvisiniNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Indications Actions Contraindications and Cautions Adverse Effects Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities BeforeDocument2 pagesDrug Name Indications Actions Contraindications and Cautions Adverse Effects Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities BeforeArdel LabadaNo ratings yet
- BenadrylDocument2 pagesBenadrylsamfandood10No ratings yet
- Drugs For Coagulation Disorders: Coagulant DrugDocument6 pagesDrugs For Coagulation Disorders: Coagulant DrugApple MaeNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - AmpicillinDocument1 pageDrug Study - AmpicillinsebbyenolaNo ratings yet
- Sulphonamides 4 1Document3 pagesSulphonamides 4 1Aymen BekirNo ratings yet
- 06 - Tetracyclines and Other AntimicrobialsDocument6 pages06 - Tetracyclines and Other Antimicrobialsjulinka beyla yansonNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Pharmacological ManagementDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing: Pharmacological ManagementAnika PleñosNo ratings yet
- ChemotherapyDocument66 pagesChemotherapyElias HaimanotNo ratings yet
- Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole-Bactim-DSDocument4 pagesTrimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole-Bactim-DSAnika Pleños100% (1)
- Katzung Pharmacology Semester 5 TablesDocument29 pagesKatzung Pharmacology Semester 5 TablesfatimaNo ratings yet
- FTX Infeksi JamurDocument64 pagesFTX Infeksi JamurNafisah SofiaNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime GonzagaDocument3 pagesCefuroxime GonzagaSheryl Anne GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Notes Diagnostic MicrobiologyDocument7 pagesNotes Diagnostic MicrobiologyTae KimNo ratings yet
- Erythromycins PDFDocument3 pagesErythromycins PDFMariaNo ratings yet
- AAD BF Systemic Antifungal AgentsDocument2 pagesAAD BF Systemic Antifungal Agentskahkashanahmed065No ratings yet
- FRAC CODE LIST 1: Fungicides Sorted by FRAC CodeDocument8 pagesFRAC CODE LIST 1: Fungicides Sorted by FRAC CodeJosé Inés Bazán MotaNo ratings yet
- Frac Code List 1: Fungicides Sorted by FRAC CodeDocument8 pagesFrac Code List 1: Fungicides Sorted by FRAC CodeGeorgette MuñozNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Classification: Indication:: Candida InfectionsDocument1 pageGeneric Name: Classification: Indication:: Candida Infectionscen janber cabrillos0% (1)
- Adult Infectious Disease Bulletpoints HandbookFrom EverandAdult Infectious Disease Bulletpoints HandbookRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)
- New Scientist-3255 2019Document61 pagesNew Scientist-3255 2019SIXTO GUTIERREZ75% (4)
- Scharlab S.L. Certificate of Analysis: Sabouraud Dextrose AgarDocument1 pageScharlab S.L. Certificate of Analysis: Sabouraud Dextrose AgarAndres BenavidesNo ratings yet
- Prevention of Hospital-Acquired Infections: A Practical Guide 2nd EditionDocument72 pagesPrevention of Hospital-Acquired Infections: A Practical Guide 2nd EditionHussein AhmedNo ratings yet
- Micro LectureDocument4 pagesMicro LectureJewel OlaezNo ratings yet
- Funding Vaccines For Emerging Infectious DiseasesDocument4 pagesFunding Vaccines For Emerging Infectious Diseasesfadfdafade uohdajufadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance NotesDocument3 pagesChapter 16: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance NotesJackie100% (1)
- اسئلة الهيئه 2010Document6 pagesاسئلة الهيئه 2010Mohsen HaleemNo ratings yet
- CAPE Unit 2 Biology P2 2019Document17 pagesCAPE Unit 2 Biology P2 2019Ellie100% (1)
- Bioterrorism and Biowarfare BTH 1Document6 pagesBioterrorism and Biowarfare BTH 1Akshita JainNo ratings yet
- Ppt.x.reproduction 10 23Document83 pagesPpt.x.reproduction 10 23ammara hyderNo ratings yet
- Genetic EngineeringDocument3 pagesGenetic EngineeringseshatcallingNo ratings yet
- Pseudomonas AeruginosaDocument2 pagesPseudomonas AeruginosaALYA ADRIANA ABDUL RAHMANNo ratings yet
- EndometritisDocument6 pagesEndometritisandriansyah2110% (1)
- Human Genome ProjectDocument5 pagesHuman Genome ProjectKyle Ambis SyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PharmacologyDocument119 pagesIntroduction To PharmacologyYzel Vasquez AdavanNo ratings yet
- Gardnerella VaginalisDocument12 pagesGardnerella VaginalisChristian John DelaCruz MolinoNo ratings yet
- PATH-365 Objective @agrounderDocument13 pagesPATH-365 Objective @agrounderNalini PathakeNo ratings yet
- Uses of Carbohydrate Fermentation Test: EnterobacteriaceaeDocument12 pagesUses of Carbohydrate Fermentation Test: EnterobacteriaceaeChristyl JoNo ratings yet
- Para Lec ReviewerDocument18 pagesPara Lec ReviewerRudolph MendozaNo ratings yet
- CELL CYCLE-WPS OfficeDocument40 pagesCELL CYCLE-WPS OfficeShubhendu ChattopadhyayNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology: Essentials ofDocument69 pagesAnatomy & Physiology: Essentials ofclyde i am100% (1)
- Treatment and Prevention of Meningococcal InfectionDocument18 pagesTreatment and Prevention of Meningococcal InfectionMárcius SilvaNo ratings yet
- Structure, Types and Various Methods For Estimation of HaemoglobinDocument49 pagesStructure, Types and Various Methods For Estimation of HaemoglobinChandra ShekharNo ratings yet
- Doripenem Vs Meropenem For CIAI (Lucasti Clin Ther 2008)Document16 pagesDoripenem Vs Meropenem For CIAI (Lucasti Clin Ther 2008)coffee muffinNo ratings yet
- D.S.S Aiims Prepration Test Series: Com M Un Ic Ab Le An D N On - Co M M Un Ic Ab Le Di Se AsDocument7 pagesD.S.S Aiims Prepration Test Series: Com M Un Ic Ab Le An D N On - Co M M Un Ic Ab Le Di Se AsDr-Sanjay SinghaniaNo ratings yet
- Binaxnow Covid-19 Antigen Self Test: For Use Under An Emergency Use Authorization (Eua) OnlyDocument20 pagesBinaxnow Covid-19 Antigen Self Test: For Use Under An Emergency Use Authorization (Eua) OnlyLUIS ALEJANDRO MURGASNo ratings yet
- Bioteknologi Dalam Bidang Perlindungan TanamanDocument38 pagesBioteknologi Dalam Bidang Perlindungan TanamanAlexizz AizenNo ratings yet
- The Isolation and Characterisation of Jacalin Artocarpus Heterophyllus Jackfruit Lectin Based On Its Charge Properties 1995 The International JournalDocument10 pagesThe Isolation and Characterisation of Jacalin Artocarpus Heterophyllus Jackfruit Lectin Based On Its Charge Properties 1995 The International JournalsfsmNo ratings yet
- Myelodysplastic Syndromes (2009) PDFDocument570 pagesMyelodysplastic Syndromes (2009) PDFNeli MihaelaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pathology MCQDocument14 pagesClinical Pathology MCQhshshhsjsjsbxxhNo ratings yet