Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Components of Food Notes: Everything You Need to Know
Uploaded by
Mohan Reddy KothapetaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Components of Food Notes: Everything You Need to Know
Uploaded by
Mohan Reddy KothapetaCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 2: Components of Food
Q1. List out the different components of food.
Ans. The different components of food are: Carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins,
minerals, roughage and water.
Q2. Discuss the two types of carbohydrates with examples. Also explain why our body
needs them.
Ans. The two different types of carbohydrates are ‘simple sugar’ and ‘complex sugar’
Simple carbohydrates (sugar) Complex carbohydrates (Sugar)
Sugar is called the simple carbohydrate. Starch is called the complex carbohydrate.
Fruits, honey and table sugar are some Plants store energy in the form of starch.
sources of simple carbohydrates Rice, water, corn, potato and bread are some
sources of complex carbohydrate.
Q3. Write the functions of proteins in our body. Give five good sources of protein.
Ans. Proteins are known as the body building food. Proteins are needed by our body
because it is required for muscle-building and repairing worn-out diseases. Proteins helps in
development and growth of the body. Our muscles, organs and even blood are made up of
mostly proteins.
Proteins in our diet come from both animal and plant sources. Meat, fish, eggs and milk are
some animal sources of proteins. Pulses, soybeans, grams and nuts are some plant sources
of protein.
Q4. Differentiate between saturated and unsaturated fats. Give examples.
Ans. Saturated fats are normally solid at room temperature. Generally derived from animal
products: Example: Meat, ghee, butter, cheese.
Unsaturated fats are mostly liquid at room temperature. Generally derived from plant
products. Example: Vegetable oil, nuts.
Q5. Differentiate between the two types of vitamins.
Ans. The two types of vitamins are fat-soluble vitamins and water- soluble vitamins.
Fat- soluble vitamins Water- soluble Vitamins
1. These vitamins are in the fat These are not stored in our body.
tissues of our body and are only
used when the body needs them.
2. Regular intake is not necessary Need to supplied to through food items.
Regular intake is necessary.
3. Vitamins A, D, E, K. Vitamins B complex and C.
Components of Food Notes: - P
Q6. Write the functions of minerals in our body. Name some good sources of minerals.
Ans. Minerals are micronutrients and are known as protective food. We need minerals in
our diet because they help our body to stay healthy. Minerals perform important functions
like formation of bones, teeth and blood cells helps in maintaining a normal heartbeat.
Food rich in minerals are: Dairy products, green leafy vegetables, fish, Citrus fruits.
Q7. Write short note on dietary fibers (Roughage).
Ans. The fibers that we eat are known ad dietary fibers or roughage. The portion of the
plant that remains undigested and do not provide any nutrients to our body is called
roughage or dietary fibers.
Roughage are of two types: Soluble and insoluble. Soluble roughage is soluble in water
whereas insoluble roughage is not.
Apple, strawberry, peach and rice are examples of food rich in soluble roughage.
Whole grain, carrot, cabbage, turnip and cauliflower are examples of food rich in insoluble
roughage.
Lack of insoluble roughage in the diet causes stool to become hard and difficult to pass.
This condition is called constipation.
Q8. Define a balanced diet.
Ans. A diet that contains adequate amount of different nutrients required for the heathy
functioning of our body is called a balanced diet. A balanced diet must include food items
like carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals along with roughage and water .Ex
food items like
Milk group: Milk and milk products.
Meat groups: Meat (Chicken, fish, lamb) and meat substitutes (beans, peas, nuts and seeds).
Fruit and vegetables: All edible fruits and vegetables.
Grain Group: Includes breads and cereals.
Q9. Why is water important for our body?
Ans. Water is needed by our body for good health. Almost 70% of our body weight is
water.
It helps to transport substances inside our body.
It helps our body to absorb nutrients.
It regulates the body temperature.
Components of Food Notes: - P
It is needed for various chemical reactions that take place inside our body during digestion,
excretion, etc.
Q10. What are deficiency diseases?
Ans. Diseases that are caused due to the lack of nutrients in the diet are called deficiency
diseases. They are different from other diseases as they cannot be transmitted from one
person to another.
Q11. What is dehydration? How can it be treated?
Ans. Excess loss of water from the body leads to a condition called dehydration.
Dehydration causes loss of salts and leads to weakness in the body. Oral Rehydration
Solution (ORS) can be given to the patient to recover from dehydration. It can be made by
mixing 8 spoons of sugar and 1 teaspoon of salt in 1litre of clean, drinking water.
Q12. Why do growing children need more proteins.
Ans. Growing children need more proteins in their diet. The growing children need proteins
in the diet to fulfil the requirement of body development and growth. Lack of proteins in the
diet can cause weakness in muscles. Deficiency of proteins leads to a disease called
Kwashiorkor.
Deficiency of proteins along with carbohydrates deficiency is called ‘Protein Energy
Malnutrition’ (PEM). It leads to marasmus.
Q13. Differentiate between constipation and dehydration.
Ans.
Constipation Dehydration
Constipation is the condition in which Dehydration is the condition of excess
lack of insoluble roughage in the diet loss of water from the body.
causes the stool to become hard and
difficult to pass.
Q14. Mention the different kinds of vitamins with their sources, functions and
deficiency disease.
Ans.
Vitamins and sources Function Deficiency Disease and
symptoms.
A Keeps eyes, hair and skin Night Blindness
Source: Green leafy healthy Symptoms: Dryness of eyes,
vegetables, fruits, butter, improper vision.
egg yolk, carrots and fish.
Components of Food Notes: - P
B1 Aids in digestion; Beriberi
Sources: Eggs, whole maintains nervous system. Symptoms: Inflammation of
grains and sprouts nerves; digestive problems and
heart abnormalities.
B2 Keeps skin and mouth Skin disorders
Sources: Eggs, milk and healthy.
green leafy vegetables.
C Helps to resist infectionsScurvy
Sources: Citrus fruits, and keeps teeth, gums and Symptoms: Loosening of teeth;
tomatoes and sprouts. joints healthy spongy and bleeding gums;
increased susceptibility to
disease; slow healing of wounds;
weakness; pain in the limbs.
D Aids in the normal growth Rickets
Sources: Milk, fish and of bones in children Symptoms: Weak bones
eggs:
Sunlight
K Helps in blood clotting Hemorrhage (excessive
Sources: Spinach, cabbage, bleeding)
green leafy vegetables. Symptoms: Affects clotting of
blood.
E Protects the cell from Chronic Liver Disorder
Sources: Avocado, damage Symptoms: Poor eating habits
spinach, ground nuts, and loss of weight.
coconut oil.
Q15. Mention the different kinds of vitamins with their sources, functions and
deficiency disease.
Ans.
Minerals sources Symptoms Deficiency
disorders
Calcium Milk, green Brittle bones, Osteoporosis,
vegetables stunted growth, rickets
Function:
Strengthens bones Weak teeth and
and teeth and helps bones.
in blood clotting.
Components of Food Notes: - P
Phosphorus Cereals, pulses, Weakening of Rickets in children
milk bones, poor
Function:
development
Strengthens bones
and teeth.
Iron Dates, jaggery, Pale colouration of Anaemia
pulses, spinach, skin, fatigue, brittle
Function: Helps in
leafy vegetables etc and white nails.
formation of
haemoglobin and red
blood cells.
Iodine Fish and salt Enlargement of Goitre
thyroid gland,
Function: Required
mental retardation,
for proper working
growth stunted
of thyroid gland.
Magnesium Green vegetables, Loss of appetite, Weak muscles and
cereals, fish, chicken nerves.
Function: Protein Sleeplessness, upset
synthesis, muscle stomach
and nerve
function.
Calcium Milk and milk Weakness in bones, Weak bones, teeth
products, ragi muscles, tooth decay decay
Function: Regulates
the functioning of
muscles and nerves.
Bone , teeth
formation
Q16. How will the test for protein, starch, sugar and fats in the food?
Ans.
Starch Sugar Proteins Fats
The food is tested The food is tested The food is first The food is placed
with iodine with Benedicts added with copper on a paper and
solution. solution and kept in sulphate solution smashed.
hot water followed with
sodium hydroxide
Components of Food Notes: - P
A color change to Color change from A color change Oily translucent
blue black indicates Blue from blue to shades stain on the paper
the presence of to green: low of purple indicates indicates the
starch. sugar the presence of presence of fats.
Blue to yellow: proteins.
medium sugar.
Blue to
red/orange: high
sugar
Components of Food Notes: - P
You might also like
- Components of FoodDocument11 pagesComponents of Foodapi-246586162100% (1)
- First Council of NicaeaDocument18 pagesFirst Council of Nicaeamr_insiong100% (1)
- Intelligent Design or Non-Intelligent Design?: Searching for AnswersFrom EverandIntelligent Design or Non-Intelligent Design?: Searching for AnswersNo ratings yet
- 3.3 The Role of Hormones in HumansDocument35 pages3.3 The Role of Hormones in HumansIMELDANo ratings yet
- Bio Chapter 35 Nervous System: Notes 35.1 Human Body SystemsDocument11 pagesBio Chapter 35 Nervous System: Notes 35.1 Human Body SystemsLeah100% (1)
- Anatomy of The Urinary System: ExerciseDocument4 pagesAnatomy of The Urinary System: ExerciseKym Resuena0% (1)
- Bowel 1 EliminationDocument33 pagesBowel 1 EliminationKhumaeyraBundaSetiyaniWindratiNo ratings yet
- Phytoecdysteroids RkleinDocument11 pagesPhytoecdysteroids RkleintrungkunmingNo ratings yet
- Food: Where Does It Come From?: Chapter 1 Subject Science Class 6 by Neena MadamDocument12 pagesFood: Where Does It Come From?: Chapter 1 Subject Science Class 6 by Neena MadamNeena MadamNo ratings yet
- The Law in The Gospel Life: Galatians 3 Verses 15-25Document8 pagesThe Law in The Gospel Life: Galatians 3 Verses 15-25NIKKOLASINo ratings yet
- FolateDocument18 pagesFolateNauman ShakirNo ratings yet
- True Education and The Medical Missionary WorkDocument66 pagesTrue Education and The Medical Missionary WorkYewo Humphrey Mhango100% (1)
- 13 Surprising Benefits of Papaya (Pawpaw) - Organic FactsDocument10 pages13 Surprising Benefits of Papaya (Pawpaw) - Organic FactsStela GallarNo ratings yet
- Ghandi's Faith in Aloe Vera and its BenefitsDocument62 pagesGhandi's Faith in Aloe Vera and its BenefitsRuben HernandezNo ratings yet
- Resting and FastingDocument15 pagesResting and Fastingmark ignacioNo ratings yet
- FAQ - Deuteronomy 21:18-21 - Should We Stone Our Children?Document9 pagesFAQ - Deuteronomy 21:18-21 - Should We Stone Our Children?119 MinistriesNo ratings yet
- Food SupplimentsDocument7 pagesFood SupplimentsTania BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- 2-How Is The Bible Organized - Baker Handbook Pp.23-28Document6 pages2-How Is The Bible Organized - Baker Handbook Pp.23-28Efraim de Souza MoraesNo ratings yet
- Hindi ch-1 Q-ADocument9 pagesHindi ch-1 Q-AmahipalNo ratings yet
- CSO Olympiad Book For Class 6Document14 pagesCSO Olympiad Book For Class 6harnil trivediNo ratings yet
- 1.2 - Components of Our FoodDocument8 pages1.2 - Components of Our FoodSNo ratings yet
- ch-7 Nutretion in DietDocument7 pagesch-7 Nutretion in Dietxhtk3em03zNo ratings yet
- Week 2 & 3 - Overview of NutrientsDocument84 pagesWeek 2 & 3 - Overview of Nutrientsامل الهوسهNo ratings yet
- Nutrients in Food: Sources of Carbs, Proteins, Vitamins, Minerals and FatsDocument5 pagesNutrients in Food: Sources of Carbs, Proteins, Vitamins, Minerals and FatsPranav ShindeNo ratings yet
- Fitness and WellnessDocument6 pagesFitness and Wellnessaruba anwarNo ratings yet
- Unit-6 - Diet (Refer Textbook Topics: 7.1 TO 7.5, Page No: 92 - 101)Document5 pagesUnit-6 - Diet (Refer Textbook Topics: 7.1 TO 7.5, Page No: 92 - 101)Mr : NADe?RNo ratings yet
- Unit-6 - Diet (Refer Textbook Topics: 7.1 TO 7.5, Page No: 92 - 101)Document5 pagesUnit-6 - Diet (Refer Textbook Topics: 7.1 TO 7.5, Page No: 92 - 101)Mr : NADe?RNo ratings yet
- 6th Science Source of Food Notes PDFDocument2 pages6th Science Source of Food Notes PDFPankaj ARORANo ratings yet
- FiberDocument5 pagesFiberAsia Mae GuerraNo ratings yet
- Unit3 Physical Activity and NutritionDocument5 pagesUnit3 Physical Activity and NutritionJames Andrei LeonidaNo ratings yet
- Dietary HabitsDocument19 pagesDietary Habitsfypbz6dncsNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Fitness and WellnessDocument6 pagesAssignment 1 Fitness and WellnessKashanAkmalNo ratings yet
- You Are What You EatDocument17 pagesYou Are What You EatShambhvi PathakNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Chapter 3 NutritionDocument68 pagesForm 2 Chapter 3 NutritionAmer MalekNo ratings yet
- The Six Basic NutrientsDocument28 pagesThe Six Basic Nutrientsrewadrian100% (1)
- Exp SC 5 - Chapter 07Document9 pagesExp SC 5 - Chapter 07megamind publicationNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9 - Nutritional GuidelinesDocument14 pagesLesson 9 - Nutritional Guidelines문유나No ratings yet
- Nutritional GuidelinesDocument29 pagesNutritional GuidelinesHazel Joie Alcaide NavarroNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Chapter 3 NutritionDocument83 pagesForm 2 Chapter 3 Nutritionsiti latifahNo ratings yet
- HakdogDocument10 pagesHakdogcotaabdulnabelNo ratings yet
- Minerals, Vitamins and WaterDocument8 pagesMinerals, Vitamins and WatermaxwelndemNo ratings yet
- Component of FoodDocument9 pagesComponent of FoodnidhiNo ratings yet
- Vitamins and Minerals READINGDocument5 pagesVitamins and Minerals READINGXimena Lucia Grandez BreñaNo ratings yet
- Biokeme: Minerals: Asia Pacific College of Advanced StudiesDocument5 pagesBiokeme: Minerals: Asia Pacific College of Advanced StudiesTrisha Anne MariNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 6Document1 pageWorksheet 6Computer DoctorsNo ratings yet
- Food NutritionDocument21 pagesFood NutritionLaine AcainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Nutrition: 2.1 Classes of FoodDocument11 pagesChapter 2: Nutrition: 2.1 Classes of Foodpclim2010No ratings yet
- Science Folio Form 2 (Nutrition)Document15 pagesScience Folio Form 2 (Nutrition)Larry Song93% (14)
- Lesson Plan For Demo Teaching 5 PDF FreeDocument11 pagesLesson Plan For Demo Teaching 5 PDF FreeDen Angelica DungoNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Notes Science Form 2Document9 pagesNutrition Notes Science Form 2Yi YingNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1.Balance Food Major Food GroupsDocument30 pagesLecture 1.Balance Food Major Food Groupsshani9976614No ratings yet
- Vitamin & MineralDocument19 pagesVitamin & MineralyanasrieNo ratings yet
- Kwashiorkor: The Function of Fat IncludeDocument3 pagesKwashiorkor: The Function of Fat IncludeJASHINEE A/P BASKARAN MoeNo ratings yet
- NUTRITION_FORM_1_NOTESDocument4 pagesNUTRITION_FORM_1_NOTEStatendachimbandi1No ratings yet
- Vitamins and MineralsDocument26 pagesVitamins and MineralsAisha Doll100% (1)
- NUTRITION - Micronutrients and Revision OfficialDocument25 pagesNUTRITION - Micronutrients and Revision OfficialAsawni McDowellNo ratings yet
- NutritionDocument11 pagesNutritionMrittika WadderNo ratings yet
- 2.food and Its Components-Notes-2Document2 pages2.food and Its Components-Notes-2mohaddisaNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Animal Nutrition B5.01 DietDocument4 pagesGrade 8 Animal Nutrition B5.01 DietAmy BeacherNo ratings yet
- L PDFDocument51 pagesL PDFMs RawatNo ratings yet
- Samsidh Mount Litera Zee School - HSR Grade 5 - Worksheet L1 Simple MachineDocument1 pageSamsidh Mount Litera Zee School - HSR Grade 5 - Worksheet L1 Simple MachineMohan Reddy KothapetaNo ratings yet
- GRADE 5 - DieasesDocument4 pagesGRADE 5 - DieasesMohan Reddy KothapetaNo ratings yet
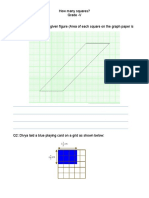
- How Many SquaresDocument4 pagesHow Many SquaresMohan Reddy KothapetaNo ratings yet
- Super Senses of AnimalsDocument4 pagesSuper Senses of AnimalsMohan Reddy KothapetaNo ratings yet
- Subject: Lesson: Date:: Compassion-Humility-HappinessDocument2 pagesSubject: Lesson: Date:: Compassion-Humility-HappinessMohan Reddy KothapetaNo ratings yet
- Samsidh Mount Litera Zee School - HSR Grade 5 - Worksheet L1 Dignity of LabourDocument1 pageSamsidh Mount Litera Zee School - HSR Grade 5 - Worksheet L1 Dignity of LabourMohan Reddy KothapetaNo ratings yet
- Samsidh Mount Litera Zee School - HSR Grade 5 - Worksheet L1 Dignity of LabourDocument1 pageSamsidh Mount Litera Zee School - HSR Grade 5 - Worksheet L1 Dignity of LabourMohan Reddy KothapetaNo ratings yet
- Section 1:: How Big How Heavy Grade - V Q1: The Shapes Are Made of 1 Cubes - What Are Ther Volumes?Document4 pagesSection 1:: How Big How Heavy Grade - V Q1: The Shapes Are Made of 1 Cubes - What Are Ther Volumes?Mohan Reddy KothapetaNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document19 pagesPresentation 1Mohan Reddy KothapetaNo ratings yet
- Area and Its BoundaryDocument5 pagesArea and Its BoundaryMohan Reddy KothapetaNo ratings yet
- Preethika PPT On Freedom FightersDocument7 pagesPreethika PPT On Freedom FightersMohan Reddy KothapetaNo ratings yet
- MathsDocument40 pagesMathsMohan Reddy KothapetaNo ratings yet
- Smart ChartsDocument7 pagesSmart ChartsMohan Reddy KothapetaNo ratings yet
- How Many SquaresDocument4 pagesHow Many SquaresMohan Reddy KothapetaNo ratings yet
- Gr-6 Food and Diet (Booklet Answers) PDFDocument5 pagesGr-6 Food and Diet (Booklet Answers) PDFMohan Reddy KothapetaNo ratings yet
- Section 1:: Can You See The Pattern? Worksheet - 1 Grade - VDocument5 pagesSection 1:: Can You See The Pattern? Worksheet - 1 Grade - VMohan Reddy KothapetaNo ratings yet
- Light and Shadow FundamentalsDocument4 pagesLight and Shadow FundamentalsMohan Reddy Kothapeta0% (1)
- Ch-3 - Separating Substances - Worksheet Answers PDFDocument7 pagesCh-3 - Separating Substances - Worksheet Answers PDFMohan Reddy KothapetaNo ratings yet
- Separating Substances Methods PDocument7 pagesSeparating Substances Methods PMohan Reddy KothapetaNo ratings yet
- Gr-6 Light, Shadow (Booklet Answers)Document7 pagesGr-6 Light, Shadow (Booklet Answers)Mohan Reddy KothapetaNo ratings yet
- Fibre To Fabric Notes 1Document3 pagesFibre To Fabric Notes 1Mohan Reddy KothapetaNo ratings yet
- Ch-3 - Separating Substances - Worksheet AnswersDocument7 pagesCh-3 - Separating Substances - Worksheet AnswersMohan Reddy KothapetaNo ratings yet
- Gr-6 Food and Diet (Booklet Answers)Document5 pagesGr-6 Food and Diet (Booklet Answers)Mohan Reddy KothapetaNo ratings yet
- Separating Substances Methods PDocument7 pagesSeparating Substances Methods PMohan Reddy KothapetaNo ratings yet
- Fibre To Fabric Notes 1Document3 pagesFibre To Fabric Notes 1Mohan Reddy KothapetaNo ratings yet
- Completed Letter Intro-9Document6 pagesCompleted Letter Intro-9Mohan Reddy KothapetaNo ratings yet
- Components of Food Notes: Everything You Need to KnowDocument6 pagesComponents of Food Notes: Everything You Need to KnowMohan Reddy KothapetaNo ratings yet
- R12 Oracle PaymentsDocument3 pagesR12 Oracle PaymentsMohan Reddy KothapetaNo ratings yet
- What Is A Legal EntityDocument1 pageWhat Is A Legal EntityMohan Reddy KothapetaNo ratings yet
- Health Impact of Fast Food On TeensDocument2 pagesHealth Impact of Fast Food On TeensBianka RigóNo ratings yet
- SBFP Form 4 2019 Pupils Attendance WDocument12 pagesSBFP Form 4 2019 Pupils Attendance WJeela VincoNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Science QP Set 1Document5 pagesClass 7 Science QP Set 1Kalpna RaniNo ratings yet
- Exam Unit 3 Sciences 3º by MeDocument3 pagesExam Unit 3 Sciences 3º by MeesperanzaNo ratings yet
- Should Fast Food Be Banned in School CanteensDocument7 pagesShould Fast Food Be Banned in School CanteensAbdullah al MamunNo ratings yet
- BBuds CreamBuds Descriptor 7.17Document2 pagesBBuds CreamBuds Descriptor 7.17sambhavjoshiNo ratings yet
- An Investigatory Project: Homemade Tomato JamDocument11 pagesAn Investigatory Project: Homemade Tomato JamDavid Carl LaddaranNo ratings yet
- Tomato Mozzarella Pasta Salad With Balsamic Vinaigrette - Budget BytesDocument26 pagesTomato Mozzarella Pasta Salad With Balsamic Vinaigrette - Budget BytesJimmy GillNo ratings yet
- Food and Nutrition Economics Fundamentals For Health Sciences by Davis, George Carroll Serrano, Elena LidiaDocument289 pagesFood and Nutrition Economics Fundamentals For Health Sciences by Davis, George Carroll Serrano, Elena LidiaNurhaeratiNo ratings yet
- Spiritual Weight Loss Viana StibalDocument59 pagesSpiritual Weight Loss Viana StibaltinadjamesNo ratings yet
- Food AllergensDocument49 pagesFood AllergensBareera MunirNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of Digestive SystemDocument211 pagesBiochemistry of Digestive Systemraynhard b. fandresNo ratings yet
- Product Description - PD 45000-7en Material No. 104414 Natamax®Document2 pagesProduct Description - PD 45000-7en Material No. 104414 Natamax®Mohamed BayomyNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Protein PDFDocument24 pagesAnalysis of Protein PDFpiagiopersempreNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesLesson PlanhendersonmusicNo ratings yet
- RRL Water SpinachDocument3 pagesRRL Water SpinachJozel Anne DoñasalesNo ratings yet
- I. Write Your Name, Roll No, Class& Section On Top of Answerscript. Write Page No.s On All PagesDocument4 pagesI. Write Your Name, Roll No, Class& Section On Top of Answerscript. Write Page No.s On All PagesewrNo ratings yet
- Assignment P58875Document11 pagesAssignment P58875om dairyNo ratings yet
- 2019 SREE Final Report Cassandra Jones Kansas State UniversityDocument5 pages2019 SREE Final Report Cassandra Jones Kansas State UniversityAlbert RiveroNo ratings yet
- Government Should Fund Both Professional and School SportsDocument23 pagesGovernment Should Fund Both Professional and School SportsZewana ZenanNo ratings yet
- Anti-Inflammatory DietDocument2 pagesAnti-Inflammatory DietGisna GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Human Nutrition Question BankDocument11 pagesHuman Nutrition Question BankA RahmanNo ratings yet
- Food Fortification Strategic Plan Final Press Signed - Aug 2018Document75 pagesFood Fortification Strategic Plan Final Press Signed - Aug 2018Abdul OmarNo ratings yet
- PDF Nilai Semangat Sumpah Pemuda Masa Sekarang CompressDocument44 pagesPDF Nilai Semangat Sumpah Pemuda Masa Sekarang CompressAzizNo ratings yet
- MarmaladeDocument16 pagesMarmaladeRA Na Si RCNo ratings yet
- Occipital Neuralgia - Symptoms, Causes, and TreatmentsDocument11 pagesOccipital Neuralgia - Symptoms, Causes, and Treatmentsthe conquerorNo ratings yet
- Sehatmand Zindagi Ke Raaz With Jawaano Ki ProblemsDocument300 pagesSehatmand Zindagi Ke Raaz With Jawaano Ki ProblemsrmdirfantvNo ratings yet
- Managing High-Output Stomas: Module 1 of 3: DR Simon Gabe and Rebecca SlaterDocument5 pagesManaging High-Output Stomas: Module 1 of 3: DR Simon Gabe and Rebecca SlaterAFH12No ratings yet
- Guidelines On Reg and Granting of Permit and Recog To Publ and Pte CDCs LCs Offering Early Childhood Prog For 0-4 Years Old CHNDocument85 pagesGuidelines On Reg and Granting of Permit and Recog To Publ and Pte CDCs LCs Offering Early Childhood Prog For 0-4 Years Old CHNMelona Barrientos100% (2)
- LEC. 2 Food Allergies and IntolerancesDocument61 pagesLEC. 2 Food Allergies and IntolerancesQueenie LatinaNo ratings yet