Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1 PDF
1 PDF
Uploaded by
Rohit ShresthaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1 PDF
1 PDF
Uploaded by
Rohit ShresthaCopyright:
Available Formats
Terminology 285
Dual Path: A system in which the air flows through heating and
cooling coils essentially parallel to each other. The coils may be
side-by-side or stacked. Multizone and dual duct systems are
dual path. Some systems may not have a heating coil but instead
bypass return air or mixed air into the hot deck.
Dumping: The rapidly falling action of cold air caused by a vari-
able air volume box or other device reducing airflow velocity.
Economizer Control: A control system for the changeover be-
tween natural cooling with outside air instead of refrigerated
mechanical cooling.
Effective Area: The sum of the areas of all the vena contractas
existing at the outlet. Effective area is affected by the number of
orifices and the exact location of the vena contractas, and the size
and shape of the grille bars, diffuser rings, etc. Manufacturers
have conducted airflow tests and, based on their findings, they’ve
established flow factors, or area correction factors, for their prod-
ucts. Each flow factor, sometimes called “K-factor” or “AK,” ap-
plies to a specific type and size of grille, register or diffuser, a
specific air measuring instrument, and the correct positioning of
that instrument.
Efficiency: Useful energy output divided by the power input.
Energy: A measure of power consumed. The ability to do work.
Stored work. The units of energy are foot-pound, Btu, and kilo-
watt-hour.
Energy Management System: A system based on a microproces-
sor, microcomputer, or minicomputer whose primary function is
the controlling of energy using equipment so as to reduce the
amount of energy used. Also called Energy Management Control
System.
286 HVAC Fundamentals
Enthalpy: Total heat content. Thermodynamic property of a
working substance.
Evaporation Stage: Evaporation stage is the heating of a liquid
refrigerant to convert it to a vapor in the evaporator.
Evaporator Coil: A coil containing a refrigerant other than water
used for cooling the air.
Face Velocity: The average velocity of the air leaving a coil, sup-
ply air outlet, or entering a return air inlet, exhaust air inlet, or
fume hood.
Feet Per Minute: Air velocity (fpm)
Fluid: A liquid or a vapor. A vapor is a compressible fluid and a
liquid is a non-compressible fluid.
Grille: A wall, ceiling or floor mounted louvered or perforated
covering for an air opening. To control airflow pattern, some
grilles have a removable louver. Reversing or rotating the louver
changes the air direction. Grilles are also available with adjustable
horizontal or vertical bars so the direction, throw, and spread of
the supply air stream can be controlled.
Heat: Heat is form of energy transferred by a difference in tem-
perature. Heat always flows from a higher temperature to a lower
temperature. In HVAC systems fluids such as air, water, and re-
frigerants are used to carry or transfer heat from one place to an-
other.
Heat Exchanger: A heat exchanger is a device such as a water or
refrigerant coil that is designed to allow the transfer of heat be-
tween two physically separated fluids.
High Pressure Systems: Static pressures above 6 in. wg. (6"wg.),
with velocities above 2000 feet per minute.
You might also like
- HVAC TerminologyDocument4 pagesHVAC Terminologyhuy luongNo ratings yet
- Conduction Convection Radiation WsDocument2 pagesConduction Convection Radiation Wsapi-27272903069% (35)
- Istilah Istilah Yang Sering Di Temukan Dalam Kamus PendinginDocument9 pagesIstilah Istilah Yang Sering Di Temukan Dalam Kamus PendinginFriget RusiantoNo ratings yet
- 1 HVAC IntroductionDocument41 pages1 HVAC IntroductionAbdullah SendiNo ratings yet
- Heating And/or Cooling Elements: Heat Exchanger HVAC Air CoilsDocument3 pagesHeating And/or Cooling Elements: Heat Exchanger HVAC Air CoilsAshiqNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document12 pagesChapter 2Mohammad Muawya Nouri HijaziNo ratings yet
- Hvac Def of TermsDocument3 pagesHvac Def of Terms88ncd4y4r7No ratings yet
- Air ConditioningDocument22 pagesAir ConditioningEmmanuel BuhwaNo ratings yet
- Architectural Science (HVAC) Lecture 6 & 7Document32 pagesArchitectural Science (HVAC) Lecture 6 & 7ezakbelachewNo ratings yet
- Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning Systems: Dr. Suraj JOSHIDocument67 pagesHeating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning Systems: Dr. Suraj JOSHISidd SalNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning SystemsDocument3 pagesAir Conditioning SystemsArman Ul NasarNo ratings yet
- Air Handling Units: Report by Vaishnavi Chandrakant Kamble B (Voc) - Int Sem IIIDocument7 pagesAir Handling Units: Report by Vaishnavi Chandrakant Kamble B (Voc) - Int Sem IIIVaishnavi KambleNo ratings yet
- Building Assignment - Ii: ServicesDocument53 pagesBuilding Assignment - Ii: ServicesVivek SinghNo ratings yet
- Air Handling Unit (AHU)Document6 pagesAir Handling Unit (AHU)bibombioNo ratings yet
- Class-1-HVAC GLOSSARYDocument7 pagesClass-1-HVAC GLOSSARYAmrit BaniyaNo ratings yet
- Air Handler: Navigation SearchDocument5 pagesAir Handler: Navigation SearchNikhil KallaNo ratings yet
- Me 451 - 1Document35 pagesMe 451 - 1Edrees AldreesNo ratings yet
- Air Handling UnitDocument27 pagesAir Handling Unitobaidur_rehman_3100% (1)
- Operating: A Cleanroom Which Is Complete and Operating: Terminology 283Document2 pagesOperating: A Cleanroom Which Is Complete and Operating: Terminology 283Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Operating: A Cleanroom Which Is Complete and Operating: Terminology 283Document2 pagesOperating: A Cleanroom Which Is Complete and Operating: Terminology 283rohitNo ratings yet
- Hvac 160820181216Document33 pagesHvac 160820181216mani aroraNo ratings yet
- HVAC System in VehiclesDocument14 pagesHVAC System in Vehiclespmu2273100% (1)
- Oel HvacDocument21 pagesOel HvacFurqan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Choosing An HVAC System 223Document2 pagesChoosing An HVAC System 223Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Central AcDocument39 pagesCentral Acmonica singh100% (1)
- Terminology 287Document2 pagesTerminology 287rohitNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Basics: Air-Source, Split SystemsDocument4 pagesAir Conditioning Basics: Air-Source, Split SystemsAhmad MujahidNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Central Air-Conditioning System With Air Cooled Chiller of Multi-Storey Office BuildingDocument16 pagesDesign and Analysis of Central Air-Conditioning System With Air Cooled Chiller of Multi-Storey Office BuildingSajjad HasanNo ratings yet
- Performance and Efficiency Test of Refrigeration Sysytem: (Mel Lab 3 Report)Document14 pagesPerformance and Efficiency Test of Refrigeration Sysytem: (Mel Lab 3 Report)Yhan SombilonNo ratings yet
- Air-Distribution SystemsDocument18 pagesAir-Distribution SystemsHarjo Wiyono100% (1)
- RAC H3 Spring2019Document24 pagesRAC H3 Spring2019mfnzk1980No ratings yet
- Energy Recovery VentilationDocument3 pagesEnergy Recovery VentilationPrabhat KumarNo ratings yet
- Acu GlossaryDocument7 pagesAcu GlossaryErika RafaelNo ratings yet
- Heating Coil in The Main Air Handling UnitDocument13 pagesHeating Coil in The Main Air Handling UnitApurv GoyalNo ratings yet
- Water Dispenser System Using Air ConditionerDocument12 pagesWater Dispenser System Using Air ConditionerinventionjournalsNo ratings yet
- Literature AdDocument7 pagesLiterature AdSINDU ANUMALANo ratings yet
- Siez Assignment2 ME413Document5 pagesSiez Assignment2 ME413Yehosuah RanoaNo ratings yet
- Presentation On: Heating Ventilation and Air CondtioningDocument52 pagesPresentation On: Heating Ventilation and Air CondtioningEDUARD VI DANDANo ratings yet
- Construction: Air FilterDocument10 pagesConstruction: Air FilterSreekanth MadakaNo ratings yet
- Course Content: Fundamentals of HVAC ControlsDocument39 pagesCourse Content: Fundamentals of HVAC ControlsMuhammad AfzalNo ratings yet
- Heat Pipe ApplicationDocument3 pagesHeat Pipe ApplicationAnonymous mRBbdopMKfNo ratings yet
- Presentation On: Heating Ventilation and Air CondtioningDocument36 pagesPresentation On: Heating Ventilation and Air Condtioningaishwarya903100% (2)
- ARCHABArch65021rBUIrAP - AIR HANDLING UNIT AND ITS COMPONENTSDocument28 pagesARCHABArch65021rBUIrAP - AIR HANDLING UNIT AND ITS COMPONENTSAditiNo ratings yet
- Types of HVAC SystemsDocument6 pagesTypes of HVAC Systemsm2110100% (1)
- Building Services II,,Group 2a - Ventilation and Air Conditioning SystemsDocument10 pagesBuilding Services II,,Group 2a - Ventilation and Air Conditioning SystemsnkosentshaNo ratings yet
- Lec-10 MECHANICAL SERVICES IN BUILDINGSDocument31 pagesLec-10 MECHANICAL SERVICES IN BUILDINGSZain ZulfiqarNo ratings yet
- Building Utilities 2 Air ConditioningDocument4 pagesBuilding Utilities 2 Air ConditioningianyanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Hvac SystemDocument16 pagesIntroduction To Hvac SystemJohn ApeladoNo ratings yet
- Hvac EquipmentsDocument16 pagesHvac EquipmentsRahul Prajapati100% (1)
- 1707 SIDDHARTH BHITALE 2nd Ques SetDocument16 pages1707 SIDDHARTH BHITALE 2nd Ques Set1707 Bhitale SiddharthNo ratings yet
- Portable Air ConditonerDocument4 pagesPortable Air ConditonerAmit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Centralised20ac20system 190120171416Document23 pagesCentralised20ac20system 190120171416Saba ArifNo ratings yet
- Recuperator - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument3 pagesRecuperator - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaAvijit DasNo ratings yet
- 502 CAC-Unit IIIDocument22 pages502 CAC-Unit IIIGauri ShindeNo ratings yet
- A Z GlossaryDocument47 pagesA Z Glossaryhijasdayamahal hijasNo ratings yet
- Hvac System & Test For Hvac QualificationDocument9 pagesHvac System & Test For Hvac Qualificationlaap85100% (1)
- Unit-3 - Energy Efficiency in BuildingsDocument39 pagesUnit-3 - Energy Efficiency in BuildingsNmg KumarNo ratings yet
- Draft Basic AirconDocument37 pagesDraft Basic AirconcspolaNo ratings yet
- Air Water Heat ExchangerDocument2 pagesAir Water Heat ExchangerZain Ul AbideenNo ratings yet
- Terminologies of HVACDocument9 pagesTerminologies of HVACDaryl Gomez TimatimNo ratings yet
- Temperature and Humidity Independent Control (THIC) of Air-conditioning SystemFrom EverandTemperature and Humidity Independent Control (THIC) of Air-conditioning SystemNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 35Document2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 35rohitNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 33Document2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 33rohitNo ratings yet
- 1 PDFDocument2 pages1 PDFrohitNo ratings yet
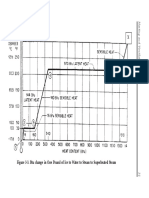
- Figure 3-3. Btu Change in One Pound of Ice To Water To Steam To Superheated SteamDocument2 pagesFigure 3-3. Btu Change in One Pound of Ice To Water To Steam To Superheated SteamrohitNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 29: Figure 3-2. Steam BoilerDocument2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 29: Figure 3-2. Steam BoilerrohitNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 37: Figure 3-6. Combustion Chamber and Fire Tubes. Two-Pass BoilerDocument2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 37: Figure 3-6. Combustion Chamber and Fire Tubes. Two-Pass BoilerrohitNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 27Document2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 27rohitNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 25Document2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 25rohitNo ratings yet
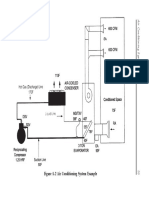
- Figure 4-.2 Air Conditioning System ExampleDocument2 pagesFigure 4-.2 Air Conditioning System ExamplerohitNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Systems 63: Evaporators (Heat Picked Up From The Conditioned Space)Document2 pagesAir Conditioning Systems 63: Evaporators (Heat Picked Up From The Conditioned Space)rohitNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Systems 57Document2 pagesAir Conditioning Systems 57rohitNo ratings yet
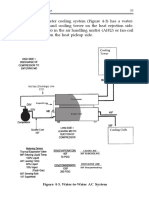
- Air Conditioning Systems 59: Figure 4-3. Water-to-Water AC SystemDocument2 pagesAir Conditioning Systems 59: Figure 4-3. Water-to-Water AC SystemrohitNo ratings yet
- Btuh GPM ×: Heat Flow 23Document2 pagesBtuh GPM ×: Heat Flow 23rohitNo ratings yet
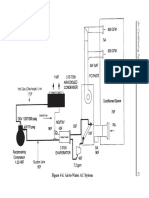
- Figure 4-4. Air-to-Water AC SystemDocument2 pagesFigure 4-4. Air-to-Water AC SystemrohitNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Systems 47Document2 pagesAir Conditioning Systems 47rohitNo ratings yet
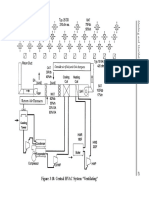
- Figure 4-1. Central HVAC System "Air Conditioning"Document2 pagesFigure 4-1. Central HVAC System "Air Conditioning"rohitNo ratings yet
- Figure 3-10. Central HVAC System "Ventilating"Document2 pagesFigure 3-10. Central HVAC System "Ventilating"rohitNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Systems 51Document2 pagesAir Conditioning Systems 51rohitNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Systems 55Document2 pagesAir Conditioning Systems 55rohitNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 43: MAT (%OA ×Document2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 43: MAT (%OA ×rohitNo ratings yet
- This Page Intentionally Left BlankDocument2 pagesThis Page Intentionally Left BlankrohitNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 41: Figure 3-8. Oil BurnerDocument2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 41: Figure 3-8. Oil BurnerrohitNo ratings yet
- HVAC Systems 13: VentilatingDocument2 pagesHVAC Systems 13: VentilatingrohitNo ratings yet
- HVAC Systems 1Document2 pagesHVAC Systems 1rohitNo ratings yet
- This Page Intentionally Left BlankDocument2 pagesThis Page Intentionally Left BlankrohitNo ratings yet
- Heat Flow 17: ConductionDocument2 pagesHeat Flow 17: ConductionrohitNo ratings yet
- Heat Flow 19Document2 pagesHeat Flow 19rohitNo ratings yet
- Latent HeatDocument2 pagesLatent HeatrohitNo ratings yet
- Heat Flow 15Document2 pagesHeat Flow 15rohitNo ratings yet
- Air Volume: HVAC Systems 11Document2 pagesAir Volume: HVAC Systems 11rohitNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power Plant - BEE PDFDocument232 pagesThermal Power Plant - BEE PDFSUTIRTHA DAS100% (3)
- Chem 1A Midterm 3 Practice SetDocument33 pagesChem 1A Midterm 3 Practice SetStephen Kok100% (3)
- Selection of Reboilers For DistillationDocument25 pagesSelection of Reboilers For DistillationYris RosarioNo ratings yet
- Metal Scrap Preheating Using Flue Gas Waste HeatDocument8 pagesMetal Scrap Preheating Using Flue Gas Waste HeatDiptoNo ratings yet
- 01 16transmission of Heat 273-284Document7 pages01 16transmission of Heat 273-284nellai kumarNo ratings yet
- Physics XI DAVCAEDocument4 pagesPhysics XI DAVCAEParth SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Irjet V3i4441 PDFDocument5 pagesIrjet V3i4441 PDFnisaNo ratings yet
- (Download PDF) Energy and Entropy A Dynamic Duo 1St Edition Harvey S Leff Online Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument42 pages(Download PDF) Energy and Entropy A Dynamic Duo 1St Edition Harvey S Leff Online Ebook All Chapter PDFamy.sorrentino869100% (11)
- Construction and Building Materials: Miloš Jerman, Martin Keppert, Jaroslav Vy Borny, Robert C ErnyDocument8 pagesConstruction and Building Materials: Miloš Jerman, Martin Keppert, Jaroslav Vy Borny, Robert C ErnyVijayNo ratings yet
- Specific Heat of A Metal Using The Mixture Method ExperimentDocument5 pagesSpecific Heat of A Metal Using The Mixture Method ExperimentAwny HabibNo ratings yet
- (TDB) ERV For Europe (Nasa, 50Hz - 60Hz) - Ver.1.4Document17 pages(TDB) ERV For Europe (Nasa, 50Hz - 60Hz) - Ver.1.4carlo jose cortez montanoNo ratings yet
- Lesson No. & Name-1: Matter in Our Surroundings: Chapter NotesDocument10 pagesLesson No. & Name-1: Matter in Our Surroundings: Chapter NotesおっぱいNo ratings yet
- Stable Versus Thermal Minimum Continuous Flow For Centrifugal PumpsDocument3 pagesStable Versus Thermal Minimum Continuous Flow For Centrifugal PumpssatstarNo ratings yet
- Convection Heat TransferDocument60 pagesConvection Heat TransferPradyumna DhamangaonkarNo ratings yet
- Transformative Potential of Thermal Storage Applications in Advancing Energy Efficiency and SustainabilityDocument14 pagesTransformative Potential of Thermal Storage Applications in Advancing Energy Efficiency and SustainabilityKIU PUBLICATION AND EXTENSIONNo ratings yet
- Black Body RadiationDocument46 pagesBlack Body RadiationKryptosNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Lab 1Document12 pagesHeat Transfer Lab 1SAMARTH TIWARINo ratings yet
- Law of Conservation of Energy: ActivityDocument3 pagesLaw of Conservation of Energy: ActivityZac McGillNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Thermal Properties of MatterDocument88 pages3.2 Thermal Properties of MattertarunNo ratings yet
- Physics: Crash Course For JEE Main 2020Document15 pagesPhysics: Crash Course For JEE Main 2020Ayush SharmaNo ratings yet
- Avs 2 2012 Question PapersDocument76 pagesAvs 2 2012 Question Papersprk74No ratings yet
- Zhang2014 PDFDocument7 pagesZhang2014 PDFStefanNo ratings yet
- Cooling Methods ComparisonDocument9 pagesCooling Methods Comparisonvinay shimpiNo ratings yet
- Jntuk - Pre PHD 2011 Result 16-07-2011Document46 pagesJntuk - Pre PHD 2011 Result 16-07-2011satisheeeNo ratings yet
- Design, Fabrication and Inspection of Welded JointsDocument58 pagesDesign, Fabrication and Inspection of Welded Jointsbaca88No ratings yet
- Application of Transfer Matrix Method in AcousticsDocument7 pagesApplication of Transfer Matrix Method in AcousticsaruatscribdNo ratings yet
- PHY 131 2023 Study GuideDocument20 pagesPHY 131 2023 Study GuideTNo ratings yet
- 2011 PaperA Elec-Mech enDocument19 pages2011 PaperA Elec-Mech enMohammed AbdalrhmanNo ratings yet
- Tut 6Document3 pagesTut 6Jesús Alejandro SantillánNo ratings yet