Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Heat Flow 15
Uploaded by
rohit0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesDiagrama de GIVONI
Original Title
1 (34)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDiagrama de GIVONI
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesHeat Flow 15
Uploaded by
rohitDiagrama de GIVONI
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Heat Flow 15
Chapter 2
Heat Flow
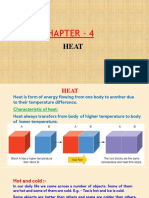
eat is energy in the form of molecules in motion. Heat flows from
H a warmer substance to a cooler substance. Heat energy flows
downhill! Heat does not rise, heated air rises!
Temperature is the level of heat (energy).
The lowest temperature is minus 460°F.
The sun’s temperature is approximately 27,000,000°F.
The temperatures associated with most HVAC systems range from 0°F
to 250°F.
Most people feel comfortable if the indoor air temperature is between
68°F and 78°F.
HEAT AND TEMPERATURE
Heat is energy in the form of molecules in motion. As a
substance becomes warmer, its molecular motion and energy
level (temperature) increases. Temperature describes the level of
heat (energy) with reference to no heat. Heat is a positive value
relative to no heat. Because all heat is a positive value in relation
to no heat, cold is not a true value. It is really an expression of
comparison. Cold has no number value and is used by most
people as a basis of comparison only. Therefore, warm and hot are
comparative terms used to describe higher temperature levels.
Cool and cold are comparative terms used to describe lower tem-
perature levels. The Fahrenheit scale is the standard system of
temperature measurement used in the United States. However,
the U.S. is one of the few countries in the world still using this
system. Most countries use the metric temperature measurement
15
16 HVAC Fundamentals
system, which is the Celsius scale. The Fahrenheit and Celsius
scales are currently used interchangeably in the U.S. to describe
equipment and fundamentals in the heating, ventilating and air
conditioning industry.
STANDARD TEMPERATURES
ON THE FAHRENHEIT AND CELSIUS SCALES
Freezing point of (pure) water is:
32 degrees Fahrenheit (32°F) and zero degrees Celsius (0°C).
Boiling point of (pure) water is:
212 degrees Fahrenheit (212°F) and 100 degrees Celsius
(100°C).
Temperature Conversions for Fahrenheit and Celsius
°C = (°F - 32) ÷ 1.8
°F = 1.8 (°C) + 32
The following is a quick reference for estimating and con-
verting everyday temperatures from Celsius to Fahrenheit:
0°C is 32°F
16°C is approximately 61°F
28°C is approximately 82°F
37°C is 98.6°F
100°C is 212°F
Absolute Temperatures
The Fahrenheit absolute scale is the Rankine (°R) scale.
The Celsius absolute scale is the Kelvin (°K) scale.
Absolute zero is minus 460°F and 0°R, or minus 273°C and
0°K.
The Fahrenheit/Celsius and the Rankine/Kelvin scales are
used interchangeably to describe equipment and fundamentals of
the heating and air conditioning industry.
You might also like
- Mechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesFrom EverandMechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics: Heat & Temperature: Chapter OutlineDocument27 pagesThermodynamics: Heat & Temperature: Chapter OutlineMD OHiNo ratings yet
- TemperatureDocument26 pagesTemperatureAbdelkader Faklani DouNo ratings yet
- Lecture-02 - PHY101 (BBA) - 51KA+52KB - PHY101.KC-22-05-2021Document39 pagesLecture-02 - PHY101 (BBA) - 51KA+52KB - PHY101.KC-22-05-2021KRZ. Arpon Root HackerNo ratings yet
- TemperatureDocument26 pagesTemperatureTanya WhiteNo ratings yet
- BME-Temperature Measurement - NOTESDocument5 pagesBME-Temperature Measurement - NOTESAisha JainNo ratings yet
- TEMPERATUREDocument4 pagesTEMPERATUREsergeantstaff597No ratings yet
- Basic Principles of RefrigerationDocument16 pagesBasic Principles of Refrigerationgenas7265No ratings yet
- HeatDocument12 pagesHeatJyoti ShresthaNo ratings yet
- TemperatureDocument3 pagesTemperaturePark Wei WeiNo ratings yet
- RefrigerationDocument84 pagesRefrigerationGeorge AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Process Variables-TemperatureDocument5 pagesProcess Variables-TemperatureFarouk BassaNo ratings yet
- HEAT SRGDocument67 pagesHEAT SRGBharat JadhavNo ratings yet
- Temperature FinalDocument5 pagesTemperature FinalAkmad ManabilangNo ratings yet
- Temperature FundamentalsDocument39 pagesTemperature Fundamentalsartup3l0nNo ratings yet
- Temperature Conversion FormulasDocument7 pagesTemperature Conversion FormulasamyNo ratings yet
- Science 8: Most Essential Learning CompetenciesDocument24 pagesScience 8: Most Essential Learning CompetenciesVeronica KimNo ratings yet
- TemperatureDocument14 pagesTemperatureFajar SanjayaNo ratings yet
- Hat and Its EffectsDocument45 pagesHat and Its EffectsFurious GamingNo ratings yet
- Non-Contact ThermometerDocument8 pagesNon-Contact ThermometerSino Ba ToNo ratings yet
- Absolute Temperatrure ScaleDocument20 pagesAbsolute Temperatrure ScaleKhaqan AminNo ratings yet
- TODocument3 pagesTOMelkamu AkumaNo ratings yet
- GROUP 2 - Adverse Effects of Temperature On Human Body - PHY162 - BIO3ADocument5 pagesGROUP 2 - Adverse Effects of Temperature On Human Body - PHY162 - BIO3AIvan Jay DomingoNo ratings yet
- Class 7 PPT - Heat and TemperatureDocument45 pagesClass 7 PPT - Heat and TemperatureNAMAN SRIVASTAVA100% (1)
- 05 Ley Cero Escalas TemperaturaDocument32 pages05 Ley Cero Escalas TemperaturaMichelle SerranoNo ratings yet
- Conversie TempDocument1 pageConversie TempemiljuchiacNo ratings yet
- Thermometer and Its Lower and Upper Fixed PointsDocument1 pageThermometer and Its Lower and Upper Fixed PointsshaheerNo ratings yet
- Instituto Episcopal San Cristóbal Workshop # - Temperature Teacher: Elva de Clarke Level: 9°Document4 pagesInstituto Episcopal San Cristóbal Workshop # - Temperature Teacher: Elva de Clarke Level: 9°IcecreamchuserNo ratings yet
- Zeroth Law Clariss ReportDocument34 pagesZeroth Law Clariss ReportangelamaevillonNo ratings yet
- Temperature, Heat & Thermal: Physics Thermodynamics Energy System Thermal Contact WorkDocument12 pagesTemperature, Heat & Thermal: Physics Thermodynamics Energy System Thermal Contact WorkAmirul ZahariNo ratings yet
- Physics I-21-22Document50 pagesPhysics I-21-22Ahmed BagradNo ratings yet
- Please Remember To Photocopy 4 Pages Onto One Sheet by Going A3 A4 and Using Back To Back On The PhotocopierDocument10 pagesPlease Remember To Photocopy 4 Pages Onto One Sheet by Going A3 A4 and Using Back To Back On The PhotocopierChrise RajNo ratings yet
- TemperatureDocument8 pagesTemperatureEdward Joseph ResocoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 HeatDocument38 pagesChapter 4 Heatsmi_santhoshNo ratings yet
- Thermal Physics PDFDocument87 pagesThermal Physics PDFPriyanshu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Heat and ThermometryDocument8 pagesHeat and ThermometryElizabeth AnyegaNo ratings yet
- 06082021024459am - S.1 Physics Heat IiDocument41 pages06082021024459am - S.1 Physics Heat Iimarionmbambu9No ratings yet
- HVAC For BeginnersDocument695 pagesHVAC For BeginnerssandeshlikesNo ratings yet
- Ch. 17 Biomedical Phy.Document9 pagesCh. 17 Biomedical Phy.Mahmoud Abu MayalehNo ratings yet
- c8 PhysicsDocument14 pagesc8 PhysicsMomina NaveedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 FisikaDocument17 pagesChapter 1 FisikaDea NirmalaNo ratings yet
- Temperature Conversion - Formula, Examples, ConversionsDocument1 pageTemperature Conversion - Formula, Examples, Conversionspanida SukkasemNo ratings yet
- Batang GuroDocument2 pagesBatang GuroMerida BravoNo ratings yet
- CH 11Document11 pagesCH 11vikram11032008No ratings yet
- Open in Browser PRO Version: Are You A Developer? Try Out TheDocument4 pagesOpen in Browser PRO Version: Are You A Developer? Try Out TheparashargunjanNo ratings yet
- Digital ThermometerDocument34 pagesDigital ThermometerVincent Korie100% (1)
- Refrigeration Part 5 TemperatureDocument3 pagesRefrigeration Part 5 TemperaturemaloyNo ratings yet
- SUMMARY - ThermodynamicsDocument18 pagesSUMMARY - Thermodynamicssethupanic macanic gamedzeNo ratings yet
- IFE4Document22 pagesIFE4n295w769vjNo ratings yet
- Copeland Refrigeration Manual - Part 1 - Fundamentals of RefrigerationDocument40 pagesCopeland Refrigeration Manual - Part 1 - Fundamentals of RefrigerationMohammad Amer100% (1)
- Ch.11 Heat and ThermoDocument10 pagesCh.11 Heat and ThermoJoanne Aga EslavaNo ratings yet
- SFG 3023 Chapter 1Document67 pagesSFG 3023 Chapter 1Nik AshrafNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four Heat and ThermodynamicsDocument44 pagesChapter Four Heat and ThermodynamicsmesfinNo ratings yet
- Temperature and HeatDocument26 pagesTemperature and HeatAlessandro YumangNo ratings yet
- Heat and TemperatureDocument26 pagesHeat and TemperatureWanMardziyyahNo ratings yet
- KobyDocument1 pageKobyJeanette Bonifacio CorpuzNo ratings yet
- The Home Owner's Guide to HVAC: The Envelope and Green TechnologiesFrom EverandThe Home Owner's Guide to HVAC: The Envelope and Green TechnologiesNo ratings yet
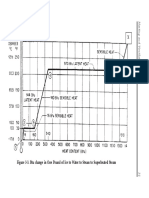
- Figure 3-3. Btu Change in One Pound of Ice To Water To Steam To Superheated SteamDocument2 pagesFigure 3-3. Btu Change in One Pound of Ice To Water To Steam To Superheated SteamrohitNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 35Document2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 35rohitNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Systems 63: Evaporators (Heat Picked Up From The Conditioned Space)Document2 pagesAir Conditioning Systems 63: Evaporators (Heat Picked Up From The Conditioned Space)rohitNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 27Document2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 27rohitNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 29: Figure 3-2. Steam BoilerDocument2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 29: Figure 3-2. Steam BoilerrohitNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 37: Figure 3-6. Combustion Chamber and Fire Tubes. Two-Pass BoilerDocument2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 37: Figure 3-6. Combustion Chamber and Fire Tubes. Two-Pass BoilerrohitNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 33Document2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 33rohitNo ratings yet
- 1 PDFDocument2 pages1 PDFrohitNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 25Document2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 25rohitNo ratings yet
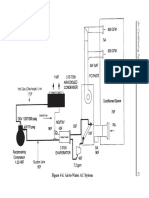
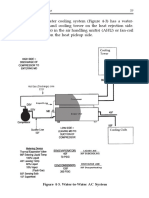
- Figure 4-4. Air-to-Water AC SystemDocument2 pagesFigure 4-4. Air-to-Water AC SystemrohitNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Systems 57Document2 pagesAir Conditioning Systems 57rohitNo ratings yet
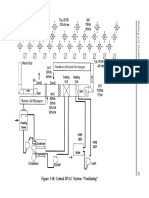
- Figure 3-10. Central HVAC System "Ventilating"Document2 pagesFigure 3-10. Central HVAC System "Ventilating"rohitNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Systems 59: Figure 4-3. Water-to-Water AC SystemDocument2 pagesAir Conditioning Systems 59: Figure 4-3. Water-to-Water AC SystemrohitNo ratings yet
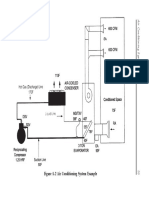
- Figure 4-.2 Air Conditioning System ExampleDocument2 pagesFigure 4-.2 Air Conditioning System ExamplerohitNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Systems 55Document2 pagesAir Conditioning Systems 55rohitNo ratings yet
- Btuh GPM ×: Heat Flow 23Document2 pagesBtuh GPM ×: Heat Flow 23rohitNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 43: MAT (%OA ×Document2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 43: MAT (%OA ×rohitNo ratings yet
- HVAC Systems 1Document2 pagesHVAC Systems 1rohitNo ratings yet
- Samuel C. Sugarman - HVAC Fundamentals-Fairmont Press - Distributed by Marcell Dekker - CRC Press (2005) - 4Document2 pagesSamuel C. Sugarman - HVAC Fundamentals-Fairmont Press - Distributed by Marcell Dekker - CRC Press (2005) - 4rohitNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Systems 47Document2 pagesAir Conditioning Systems 47rohitNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Systems 51Document2 pagesAir Conditioning Systems 51rohitNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 41: Figure 3-8. Oil BurnerDocument2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 41: Figure 3-8. Oil BurnerrohitNo ratings yet
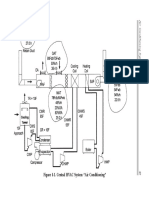
- Figure 4-1. Central HVAC System "Air Conditioning"Document2 pagesFigure 4-1. Central HVAC System "Air Conditioning"rohitNo ratings yet
- This Page Intentionally Left BlankDocument2 pagesThis Page Intentionally Left BlankrohitNo ratings yet
- HVAC Systems 13: VentilatingDocument2 pagesHVAC Systems 13: VentilatingrohitNo ratings yet
- Latent HeatDocument2 pagesLatent HeatrohitNo ratings yet
- This Page Intentionally Left BlankDocument2 pagesThis Page Intentionally Left BlankrohitNo ratings yet
- Samuel C. Sugarman - HVAC Fundamentals-Fairmont Press - Distributed by Marcell Dekker - CRC Press (2005) - 3Document2 pagesSamuel C. Sugarman - HVAC Fundamentals-Fairmont Press - Distributed by Marcell Dekker - CRC Press (2005) - 3rohitNo ratings yet
- Heat Flow 17: ConductionDocument2 pagesHeat Flow 17: ConductionrohitNo ratings yet
- Heat Flow 19Document2 pagesHeat Flow 19rohitNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Department Institute of Technology Nirma UniversityDocument8 pagesChemical Engineering Department Institute of Technology Nirma UniversityJAY BHARATBHAI LAKHANINo ratings yet
- Know Your Cooling SystemDocument103 pagesKnow Your Cooling SystemgustavoNo ratings yet
- Unit One Formulae and Definitions Module 1: Mechanics D: Base Quantity Base Unit ImensionsDocument27 pagesUnit One Formulae and Definitions Module 1: Mechanics D: Base Quantity Base Unit ImensionsUnexpected TheoryNo ratings yet
- Example 8: Cantilever Wingwall Design Loads: Problem StatementDocument7 pagesExample 8: Cantilever Wingwall Design Loads: Problem StatementMaseeha GonowreeNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal CompressorDocument18 pagesCentrifugal CompressornisasoberiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 04 Machine DesignDocument34 pagesLecture 04 Machine DesignMuhammad NaeemNo ratings yet
- Brochure Catalog Genvac VacuumDocument8 pagesBrochure Catalog Genvac VacuumFrancisco BelloNo ratings yet
- R05220104-Hydraulics and Hydraulic MachineryDocument8 pagesR05220104-Hydraulics and Hydraulic MachinerySRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Design of Steel StructuresDocument129 pagesDesign of Steel StructuresFinney Wilson100% (3)
- Eotvos NumberDocument13 pagesEotvos NumberFoamboom SatjaritanunNo ratings yet
- Inverse Square Law of HeatDocument10 pagesInverse Square Law of HeatBoomday100% (1)
- Methodology To Predict Fatigue LifeDocument4 pagesMethodology To Predict Fatigue Lifeahmetsadry1No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Air System Design I-P, 2nd Ed.Document378 pagesFundamentals of Air System Design I-P, 2nd Ed.Mahmoud Gwaily100% (16)
- Bond Performance of Polystyrene Aggregate Concrete (PAC) Reinforced With Glass-Fibre-Reinforced Polymer (GFRP) BarsDocument10 pagesBond Performance of Polystyrene Aggregate Concrete (PAC) Reinforced With Glass-Fibre-Reinforced Polymer (GFRP) Barsandri.kusbiantoro9761No ratings yet
- IPLV NPLV Explained ComparisonDocument2 pagesIPLV NPLV Explained ComparisonKeerthi Krishnan0% (1)
- Reynolds Transport TheoremDocument21 pagesReynolds Transport TheoremMae BacurioNo ratings yet
- Ae 6504 Propulsion Long QuestionsDocument5 pagesAe 6504 Propulsion Long QuestionsVictor D. VickieNo ratings yet
- Assignments 0 XDocument6 pagesAssignments 0 XJoker AzzamNo ratings yet
- RMTUTORIALSDocument10 pagesRMTUTORIALSAnyasi UcheNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7-Control Effectiveness: AAE 556 AeroelasticityDocument17 pagesLecture 7-Control Effectiveness: AAE 556 AeroelasticityMichael BeasleyNo ratings yet
- Triplex Pump Capacity - Gallons Per StrokeDocument2 pagesTriplex Pump Capacity - Gallons Per Strokeozguncrl1No ratings yet
- Determination of Settlement For Beam On Elastic Foundation by ETABS SoftwareDocument8 pagesDetermination of Settlement For Beam On Elastic Foundation by ETABS SoftwareTabrez AhmedNo ratings yet
- Flowmeter DEMONSTRATIONDocument20 pagesFlowmeter DEMONSTRATIONAfiq IkhwanNo ratings yet
- Week Three Homework Problems: Fundamentals of ! Fluid PowerDocument2 pagesWeek Three Homework Problems: Fundamentals of ! Fluid PowerjtorerocNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Mixture of Ideal GasesDocument38 pagesCH 1 Mixture of Ideal GasesFasil GetachewNo ratings yet
- Science 7 - Module 6 - Version 3Document16 pagesScience 7 - Module 6 - Version 3Abegail Panang100% (2)
- Rotational ViscometerDocument3 pagesRotational ViscometerBhaskar Pratim DasNo ratings yet
- Arshad 2020Document13 pagesArshad 2020ramesh tNo ratings yet
- Solution To Exercise 7.4Document2 pagesSolution To Exercise 7.4priyankaNo ratings yet