Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1 PDF
1 PDF
Uploaded by
Rohit Shrestha0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesOriginal Title
1 (28).pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pages1 PDF
1 PDF
Uploaded by
Rohit ShresthaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
HVAC Systems 3
7. A filter section to remove dirt and dust particles from the
air.
8. Heat exchangers such as a refrigerant evaporator and con-
denser coil for cooling, and a furnace for heating.
9. A compressor to compress the refrigerant vapor and pump
the refrigerant around the refrigeration system.
10. An outdoor fan (blower) to circulate outside air across the
condenser coil.
11. Controls to start, stop or regulate the flow of air, refrigerant,
and electricity.
HVAC COMPONENTS
H is for Heating
Boilers (Figure 1-2)
• Types of Boilers
— Steam
— Water
• Boiler Pressures
— Low
— High
• Boiler Fuels
— Natural Gas
— Oil
— Coal
— Electricity
• Boiler Configurations
— Fire Tube
— Water Tube
Furnaces (Figure 1-3)
• Furnace Fuels
— Natural Gas
— Oil
— Coal
— LPG (Liquid Petroleum Gas)
— Electricity
4 HVAC Fundamentals
Heating Coils (Figure 1-4)
• Types of Heating Coils
— Steam
— Water
— Electrical
V is for Ventilation for each of the following:
1) Approximately 20 cfm (cubic feet per minute) of air volume
per person of outside air (OA) for ventilation for non-smok-
ing areas.
2) Make-up air (MUA) for exhaust systems such as:
— Kitchen hoods
— Fume hoods
— Toilets
3) Room (conditioned space) pressurization
— +0.03 to +0.05 inches of water gage for commercial build-
ings.
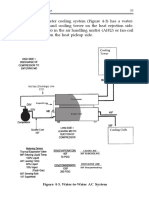
Figure 1-2. Fire Tube Boiler
You might also like
- Boiler Case StudyDocument17 pagesBoiler Case StudyAbu Faiz100% (1)
- Heat Losses in BoilersDocument5 pagesHeat Losses in Boilersgad480100% (1)
- Waste Heat RecoveryDocument11 pagesWaste Heat RecoveryKashifKhan100% (1)
- FURNACE Operations Rev2Document41 pagesFURNACE Operations Rev2Lakhvinder Singh100% (9)
- Components of HVAC Systems: Indoor Fan (Blower)Document17 pagesComponents of HVAC Systems: Indoor Fan (Blower)monoj5859No ratings yet
- HVAC Systems in Buildings: The ComponentsDocument27 pagesHVAC Systems in Buildings: The ComponentsHimani NagarNo ratings yet
- Waste Heat Recovery BoilerDocument28 pagesWaste Heat Recovery BoilerNath Boyapati100% (2)
- HVAC Basics - ADocument39 pagesHVAC Basics - AAbhik Bhattacharjee100% (1)
- 19 - Heating and Ventilating Systems - HVACDocument6 pages19 - Heating and Ventilating Systems - HVACJoshua EvansNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Heating, Ventilation & Air Conditioning (Hvac)Document42 pagesChapter 14 Heating, Ventilation & Air Conditioning (Hvac)MunirKhanNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Heating, Ventilation and Air ConditioningDocument96 pagesThe Basics of Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioningsakshi1405No ratings yet
- Waste Heat RecoveryDocument32 pagesWaste Heat RecoveryManish Tiwari100% (1)
- Heating Ventilation and Air Condtioning: Mahatma Gandhi Mission's College of Engineering and TechnologyDocument39 pagesHeating Ventilation and Air Condtioning: Mahatma Gandhi Mission's College of Engineering and Technologyyinkaakins2001No ratings yet
- HVAC Basics Lunch & LearnDocument64 pagesHVAC Basics Lunch & Learnreyes500100% (2)
- Circulation Ratio by HTSDocument9 pagesCirculation Ratio by HTSHiteshSandhal100% (1)
- Furnace OperationsDocument53 pagesFurnace OperationsRana Shahid Raza100% (1)
- Waste Heat RecoveryDocument32 pagesWaste Heat RecoveryRavi DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Primary Air in A BoilerDocument8 pagesPrimary Air in A BoilerDanielEMNo ratings yet
- TSEE NoteDocument12 pagesTSEE NoteYogesh ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Week 3Document24 pagesWeek 3Aaron LisboaNo ratings yet
- Presentation BoilerDocument24 pagesPresentation BoilerRanjanaWaje100% (1)
- 2 BoilersDocument58 pages2 BoilersParameswararao BillaNo ratings yet
- Optimize Fired Heater Operations To Save MoneyDocument8 pagesOptimize Fired Heater Operations To Save Moneyyogitadoda100% (2)
- 2.8 Waste Heat Recovery-LibreDocument18 pages2.8 Waste Heat Recovery-Libredivyank3dNo ratings yet
- WASTE HEAT RECOVERY (HRSG) PerformanceDocument17 pagesWASTE HEAT RECOVERY (HRSG) PerformanceEjaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis of Separating and Throttling Calorimeter To DetermineDocument5 pagesPerformance Analysis of Separating and Throttling Calorimeter To DetermineDaniel LauNo ratings yet
- HVAC 101: The Basics of Heating, Ventilation and Air ConditioningDocument33 pagesHVAC 101: The Basics of Heating, Ventilation and Air ConditioningChan SeanNo ratings yet
- Waste Heat Recovery NDocument28 pagesWaste Heat Recovery NranveerNo ratings yet
- Fired Heater Design and CalcDocument35 pagesFired Heater Design and CalcDavidMBBSNo ratings yet
- Process Heaters Furnaces and Fired Heaters PDFDocument12 pagesProcess Heaters Furnaces and Fired Heaters PDFHaris Nu'man Aulia100% (1)
- Boiler DesignJuly 2010Document44 pagesBoiler DesignJuly 2010dheerumgiNo ratings yet
- Furnace and BoilerDocument91 pagesFurnace and Boilermujeebmehar100% (1)
- HVACDocument58 pagesHVACAnonymous 6V5QyM1M3LNo ratings yet
- Steam & Combustion Technology Inc. - Boiler Room Air SupplyDocument3 pagesSteam & Combustion Technology Inc. - Boiler Room Air SupplyAstri NgentNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Boiler Accessories, Super HeaterDocument74 pagesModule 4 - Boiler Accessories, Super Heaterkngkng100% (1)
- Introduction To Vapor Compression Refrigeration SystemDocument51 pagesIntroduction To Vapor Compression Refrigeration SystemNaveen Prakash Noronha50% (2)
- Burners Test RigDocument4 pagesBurners Test RigTian JinayonNo ratings yet
- Hydronic SystemsDocument5 pagesHydronic SystemsValentinNo ratings yet
- 2.8 Waste Heat BasicsDocument9 pages2.8 Waste Heat BasicsRajwardhan PawarNo ratings yet
- Waste Heat RecoveryDocument37 pagesWaste Heat Recoveryommech2020No ratings yet
- Boiler Fundamental & Water Circulation SystemDocument30 pagesBoiler Fundamental & Water Circulation SystemSamNo ratings yet
- Steam PropertiesDocument72 pagesSteam Propertieskidseismic100% (1)
- ME Lab 2 Module No. 1Document12 pagesME Lab 2 Module No. 1Ismaeli KielNo ratings yet
- Boiler Fuel Firing SystemDocument44 pagesBoiler Fuel Firing Systemrashm006ranjanNo ratings yet
- OptimizationDocument22 pagesOptimizationNirban KhaundNo ratings yet
- Ch3 Steam Boiler - Sub-Critical PDFDocument57 pagesCh3 Steam Boiler - Sub-Critical PDFأمير حارث100% (1)
- NOTES 5 - RefrigerationDocument20 pagesNOTES 5 - RefrigerationMakoya_malumeNo ratings yet
- 9 - HVAC - Heat Recovery Ventilation - (Slide 3 and Slide 10 - Slide 15)Document24 pages9 - HVAC - Heat Recovery Ventilation - (Slide 3 and Slide 10 - Slide 15)Zhori DuberryNo ratings yet
- Energy Performance Assessment of Cogenration Systems: DHILIP.P BTG-10-006Document25 pagesEnergy Performance Assessment of Cogenration Systems: DHILIP.P BTG-10-006HANIF AKBARNo ratings yet
- Chapter TwoDocument80 pagesChapter TwobroNo ratings yet
- Boiler TypesDocument9 pagesBoiler TypesDevidutta PandaNo ratings yet
- Boilers and Thermic Fluid HeatersDocument54 pagesBoilers and Thermic Fluid HeatersAmit ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Energy Conservation: Topic "Boiler"Document38 pagesEnergy Conservation: Topic "Boiler"Ghazanfar GulNo ratings yet
- Waste Heat RecoveryDocument19 pagesWaste Heat RecoveryAnjanKumarMahanta100% (2)
- Heating Systems Troubleshooting & Repair: Maintenance Tips and Forensic ObservationsFrom EverandHeating Systems Troubleshooting & Repair: Maintenance Tips and Forensic ObservationsNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesFrom EverandMechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesNo ratings yet
- Process Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersFrom EverandProcess Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic analysis of geothermal heat pumps for civil air-conditioningFrom EverandThermodynamic analysis of geothermal heat pumps for civil air-conditioningRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 37: Figure 3-6. Combustion Chamber and Fire Tubes. Two-Pass BoilerDocument2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 37: Figure 3-6. Combustion Chamber and Fire Tubes. Two-Pass BoilerrohitNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 33Document2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 33rohitNo ratings yet
- 1 PDFDocument2 pages1 PDFrohitNo ratings yet
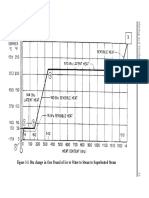
- Figure 3-3. Btu Change in One Pound of Ice To Water To Steam To Superheated SteamDocument2 pagesFigure 3-3. Btu Change in One Pound of Ice To Water To Steam To Superheated SteamrohitNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 25Document2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 25rohitNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 27Document2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 27rohitNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Systems 57Document2 pagesAir Conditioning Systems 57rohitNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 29: Figure 3-2. Steam BoilerDocument2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 29: Figure 3-2. Steam BoilerrohitNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 35Document2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 35rohitNo ratings yet
- Figure 4-4. Air-to-Water AC SystemDocument2 pagesFigure 4-4. Air-to-Water AC SystemrohitNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Systems 63: Evaporators (Heat Picked Up From The Conditioned Space)Document2 pagesAir Conditioning Systems 63: Evaporators (Heat Picked Up From The Conditioned Space)rohitNo ratings yet
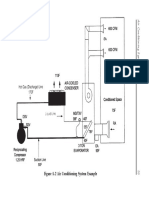
- Figure 4-.2 Air Conditioning System ExampleDocument2 pagesFigure 4-.2 Air Conditioning System ExamplerohitNo ratings yet
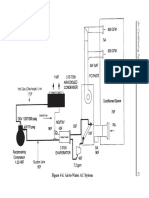
- Air Conditioning Systems 59: Figure 4-3. Water-to-Water AC SystemDocument2 pagesAir Conditioning Systems 59: Figure 4-3. Water-to-Water AC SystemrohitNo ratings yet
- Figure 4-1. Central HVAC System "Air Conditioning"Document2 pagesFigure 4-1. Central HVAC System "Air Conditioning"rohitNo ratings yet
- Btuh GPM ×: Heat Flow 23Document2 pagesBtuh GPM ×: Heat Flow 23rohitNo ratings yet
- This Page Intentionally Left BlankDocument2 pagesThis Page Intentionally Left BlankrohitNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Systems 55Document2 pagesAir Conditioning Systems 55rohitNo ratings yet
- Figure 3-10. Central HVAC System "Ventilating"Document2 pagesFigure 3-10. Central HVAC System "Ventilating"rohitNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Systems 51Document2 pagesAir Conditioning Systems 51rohitNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Systems 47Document2 pagesAir Conditioning Systems 47rohitNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 43: MAT (%OA ×Document2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 43: MAT (%OA ×rohitNo ratings yet
- This Page Intentionally Left BlankDocument2 pagesThis Page Intentionally Left BlankrohitNo ratings yet
- Heating and Ventilating Systems 41: Figure 3-8. Oil BurnerDocument2 pagesHeating and Ventilating Systems 41: Figure 3-8. Oil BurnerrohitNo ratings yet
- Latent HeatDocument2 pagesLatent HeatrohitNo ratings yet
- HVAC Systems 1Document2 pagesHVAC Systems 1rohitNo ratings yet
- Air Volume: HVAC Systems 11Document2 pagesAir Volume: HVAC Systems 11rohitNo ratings yet
- Heat Flow 19Document2 pagesHeat Flow 19rohitNo ratings yet
- Heat Flow 17: ConductionDocument2 pagesHeat Flow 17: ConductionrohitNo ratings yet
- HVAC Systems 13: VentilatingDocument2 pagesHVAC Systems 13: VentilatingrohitNo ratings yet
- Heat Flow 15Document2 pagesHeat Flow 15rohitNo ratings yet