Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 10: Automotive Industries
Uploaded by
dangthanhhd79Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 10: Automotive Industries
Uploaded by
dangthanhhd79Copyright:
Available Formats
Automotive Industries Unit 10
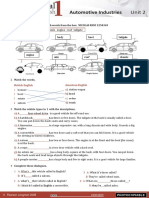
1 Read the descriptions of the electrical components and complete the table.
Conductors
A component which allows the flow of an electrical current through it is called a conductor. A conductor can be a
wire or a bar. Some materials have properties that allow electricity to pass very freely through them. These materials
are said to be ‘good conductors’ with ‘low resistance’. Examples of good conductors are: copper, platinum, gold
and silver.
Several factors affect the resistance of a conductor, for example. the material, length and temperature of the
conductor. Some conductors become more resistant as the temperature rises; other conductors become less resistant
as the temperature rises.
Insulators
A component which resists the flow of an electrical current through it is called an insulator. Good insulating materials
include glass, plastic, rubber and porcelain.
Electrical cables are covered in an insulation material, like PVC or rubber. The current runs along the wire inside the
cable.
Semiconductors
A component that allows some electricity to flow through it, but which offers some resistance, is called a
semiconductor. Semiconductors are materials which have a resistance value higher than a good conductor, but lower
than an insulator.
Silicon and germanium are two materials used in semiconductors. By themselves, they do not conduct electricity,
but when mixed with other materials they do.
The resistance of semiconductors can change when the temperature rises or falls, or when exposed to light. An
example of a semiconductor is the temperature sensor. When the temperature rises, this affects the electrical current
in a circuit, and indicates a change in temperature.
Component Property Example Material
conductor
resists the flow
of an electrical
current
silicon, germanium
2 Complete the sentences with words from 1.
1 A component is a part of a machine.
2 The qualities that a material has (e.g. electrical) are called .
3 are materials like copper that allow electricity to pass through
them easily.
4 An prevents electricity from passing from a wire to a metal object
next to it.
5 A material which has a high is not a good conductor.
6 Sensors notice a difference in the strength of the in a circuit.
7 Light and heat can the performance of a semiconductor.
© Pearson Longman 2008 www.pearsonlongman.com/technicalenglish
Automotive Industries Unit 10
3 Complete the text with words or phrases from the box and the diagrams.
blade connectors / blown fuse / conductor / current / fuses / higher / lower / overheat /
plastic housing / resistance / signals
conductor blown fuse
plastic
housing
blade
connectors
Wire: Some wires in a car carry very little (1) current . They carry (2) from
switches and sensors. Other wires carry a lot of current, for example, to power the starter motor. Each
type of wire has a certain amount of (3) per metre. The longer the wire, the
(4) the resistance. Automotive wire is made from strands of copper. The finer the
strands, the (5) the resistance.
Fuses: If too much current goes through a wire, it can (6) and melt. Then the wire has
to be replaced, which is a difficult job. To prevent this from happening, (7) are included
in an electrical circuit. Automotive fuses have two (8) which complete the circuit. Inside
the (9) is the (10) , which carries the current. The conductor has a lower
melting point than the wire of the circuit. If the wire carries too much current, the heat of the current
melts the conductor and ‘blows’ the fuse. A (11) must be replaced with a good one. Then
the electrical circuit will work again.
4 Replace the word(s) in italics with the word(s) in brackets. Make any necessary changes in J7276
punctuation and word order. Use your notebook. PEARSON Technical English
Automotive Industries
Example: 1 The driver left the headlights on, so the car had a flat battery. aw_10_01
1 The car had a flat battery because the driver left the headlights on. (so)
2 The driver tried the starter motor again and again, and as a result the battery became flat. (since)
3 Since the driver didn’t have a spare fuse, he couldn’t replace the blown fuse. (therefore)
4 The wrong fuse was used and therefore the wire in the circuit melted. (since)
5 The mechanic couldn’t repair the car as he didn’t have a wiring diagram for it. (and as a result)
6 The current in the circuit was too high and as a result the fuse blew. (because)
7 The rear windscreen heater was broken, so the driver couldn’t see out of the rear window. (as)
5 Match the car components with their properties.
1 electric cable a) flexible, durable, shock-absorbant
2 leaf-type springs b) fade-resistant, heat-resistant
3 fuel-tank c) flexible, inelastic
4 tyres d) impact-resistant
5 brake-drums e) flexible, fuel-resistant, water-resistant
6 diesel engine f) durable
7 seat belts g) flexible, skid-resistant
© Pearson Longman 2008 www.pearsonlongman.com/technicalenglish
Automotive Industries Unit 10
Word List
6 Write the meanings of these words and phrases in your own language.
NOUNS ADJECTIVES
conductor durable
copper fade-resistant
fuse fine
germanium impact-resistant
gold shock-absorbant
housing skid-resistant
insulator VERBS
platinum affect
porcelain blow / blew/ blown
PVC (polyvinyl chloride) expose
semiconductor melt
silicon overheat
silver power
strand
NOUN PHRASE
blade connector
leaf-type spring
resistance value
temperature sensor
© Pearson Longman 2008 www.pearsonlongman.com/technicalenglish
You might also like
- Get Ready For IELTS Listening Pre-Intermediate A2+ (RED)Document136 pagesGet Ready For IELTS Listening Pre-Intermediate A2+ (RED)ciobmary100% (11)
- Unit - 5 - The Interior Car PartsDocument13 pagesUnit - 5 - The Interior Car Partsdangthanhhd79100% (6)
- D&C Catalog Digest Index for Magnetic Contactors and StartersDocument148 pagesD&C Catalog Digest Index for Magnetic Contactors and StartersDhandang Wibowo100% (1)
- EKS83 Service Manual SkyAzulDocument30 pagesEKS83 Service Manual SkyAzulM Refai100% (2)
- VBCarCare PDFDocument24 pagesVBCarCare PDFbeesahNo ratings yet
- 5 HV Substation Design Feb 17 18Document254 pages5 HV Substation Design Feb 17 18HassenLNo ratings yet
- F1 GlossaryDocument13 pagesF1 Glossarypublicist100% (1)
- Te Automotive WorksheetsDocument36 pagesTe Automotive WorksheetsMarcio Noe0% (1)
- Technical English 3 (Course Book)Document52 pagesTechnical English 3 (Course Book)qawsedrfNo ratings yet
- Booklet Course 8 Chapter 4Document22 pagesBooklet Course 8 Chapter 4Mayis Monzón100% (1)
- Fuses and Circuit BrakersDocument43 pagesFuses and Circuit BrakersCristian Madalin GogoasaNo ratings yet
- Everything Easy SIRIUS SelectionDocument5 pagesEverything Easy SIRIUS SelectionVaibhav Thorat100% (2)
- Exercises Marine Engineer + Internal Combustion EnginesDocument3 pagesExercises Marine Engineer + Internal Combustion EnginesGeorge GaneaNo ratings yet
- Examen Reading B2 Con SolucionesDocument6 pagesExamen Reading B2 Con SolucionesigmarbarNo ratings yet
- Essay PollutionDocument3 pagesEssay PollutionRocío Romero HinojosaNo ratings yet
- Technical English 2 CBDocument128 pagesTechnical English 2 CBBulls VaiNo ratings yet
- Ingles TécnicoDocument5 pagesIngles TécnicoRigel OriónNo ratings yet
- Unit 01 PDFDocument3 pagesUnit 01 PDFEMYCEE2009No ratings yet
- Electrical SystemDocument94 pagesElectrical SystemCollins ManseloNo ratings yet
- Understanding Technical English-2Document91 pagesUnderstanding Technical English-2Ega Marga Putra100% (1)
- 503 504 OriginalesDocument175 pages503 504 OriginalesRicardo Felipe Cortes MenayNo ratings yet
- General Instructions for Centrifugal Fan Startup, Operation and MaintenanceDocument13 pagesGeneral Instructions for Centrifugal Fan Startup, Operation and MaintenanceEd FanunNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios Ingles 1ºesoDocument13 pagesEjercicios Ingles 1ºesocarminaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Management AccountingDocument37 pagesUnit 5 - Management Accountingdangthanhhd79100% (4)
- Gabinete Rectificador ELTEK FLATPACK 15KW OutdoorDocument20 pagesGabinete Rectificador ELTEK FLATPACK 15KW OutdoorEddie MuñozNo ratings yet
- Please Write Your Name and Period # On The Provided Scantron Form. 2 Pts Each / Graded Out of 50Document4 pagesPlease Write Your Name and Period # On The Provided Scantron Form. 2 Pts Each / Graded Out of 50Surya Kant KesariNo ratings yet
- Rinnai Service ManualDocument112 pagesRinnai Service Manualrlynch33100% (1)
- Technical English 1 - Unit-04Document3 pagesTechnical English 1 - Unit-04Thang TongNo ratings yet
- Unit 05 PDFDocument3 pagesUnit 05 PDFEMYCEE2009No ratings yet
- Basic Practice Unit 4 Test: Vocabulary 20 Points Grammar 20 PointsDocument1 pageBasic Practice Unit 4 Test: Vocabulary 20 Points Grammar 20 PointsFer PineiroNo ratings yet
- Technical English 1 - Unit-11Document3 pagesTechnical English 1 - Unit-11Thang TongNo ratings yet
- Unit 06 PDFDocument3 pagesUnit 06 PDFEMYCEE2009100% (1)
- Te 1 Answers AutomotiveDocument12 pagesTe 1 Answers AutomotivekiowacNo ratings yet
- Automotive Industries: Unit 2Document3 pagesAutomotive Industries: Unit 2Nicolas Rico100% (1)
- Unit 08 PDFDocument3 pagesUnit 08 PDFKin KevinNo ratings yet
- Practice Automotive Industries Tarea 2Document3 pagesPractice Automotive Industries Tarea 2Oscar FerNo ratings yet
- Technical English 1 Answer Key Workbook 1b PDFDocument6 pagesTechnical English 1 Answer Key Workbook 1b PDFZeem QaisiNo ratings yet
- SPECIAL ISE I Book PDFDocument24 pagesSPECIAL ISE I Book PDFRita BrestovskaNo ratings yet
- English in (Mechanical) EngineeringDocument9 pagesEnglish in (Mechanical) EngineeringJefri BaleNo ratings yet
- Technical English Level 4 Progress Test 5 (Units 9-10)Document5 pagesTechnical English Level 4 Progress Test 5 (Units 9-10)Chrząszcz SząbierajNo ratings yet
- Technical English Level 4 Progress Test 3 (Units 5-6) : Answer All The Questions. 1 Choose The Correct Option (A-D)Document5 pagesTechnical English Level 4 Progress Test 3 (Units 5-6) : Answer All The Questions. 1 Choose The Correct Option (A-D)fasdNo ratings yet
- Sample ISE III Portfolio With AnswersDocument6 pagesSample ISE III Portfolio With AnswersChristopher BrittNo ratings yet
- Datasheet Summary SAMSUNG LTN154U2-L05 15.4Document29 pagesDatasheet Summary SAMSUNG LTN154U2-L05 15.4Sergey DNo ratings yet
- Previous Op Notice To Shipping No. N-1-2013Document81 pagesPrevious Op Notice To Shipping No. N-1-2013Αγγελος ΠιλατηςNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: Automotive IndustriesDocument3 pagesUnit 3: Automotive IndustriesCp. Rengifo Manrique Yeison alexanderNo ratings yet
- ISE III TasksDocument2 pagesISE III TasksHoruhe PeresuNo ratings yet
- 02mindset1 Term1 Test WrittenComprehensionDocument2 pages02mindset1 Term1 Test WrittenComprehensionMari France Mayan BrocosNo ratings yet
- WorkbookDocument60 pagesWorkbookСлавик Сагайдак100% (1)
- Unit Test 2 PDFDocument1 pageUnit Test 2 PDFYONo ratings yet
- 3 PARTS 2 Technical EnglishDocument21 pages3 PARTS 2 Technical EnglishMirian Puma100% (1)
- Trinity Grade 5 - Means of Transports PDFDocument2 pagesTrinity Grade 5 - Means of Transports PDFcarnaibaNo ratings yet
- Unit2 A New Mechanic PDFDocument32 pagesUnit2 A New Mechanic PDFEdwar Santiago Buitrago AguirreNo ratings yet
- Install VulcanDocument3 pagesInstall VulcanAdoe LeddyNo ratings yet
- Repairing Appliances: Instructions for Fixing Faulty Lamp WiringDocument4 pagesRepairing Appliances: Instructions for Fixing Faulty Lamp WiringMari MarianaNo ratings yet
- Topicos Orales EoiDocument7 pagesTopicos Orales Eoilouiseconn08No ratings yet
- Connectors and LinkersDocument9 pagesConnectors and LinkersALLISON VANESSA DIAZ GUERRERO100% (1)
- Transport English. Answer Key1Document48 pagesTransport English. Answer Key1Jogi Nero100% (1)
- Writing Tips and GuidelinesDocument25 pagesWriting Tips and GuidelinesFtyn NajihaNo ratings yet
- Cooking and Eating British English TeacherDocument4 pagesCooking and Eating British English TeacherEwa HelinskaNo ratings yet
- Opinion EssayDocument2 pagesOpinion EssayMay Phoo MonNo ratings yet
- C1 Advanced Sample Paper 2 Reading and Use of English 2022Document15 pagesC1 Advanced Sample Paper 2 Reading and Use of English 2022eNo ratings yet
- ISE III - Task 4 - Extended Writing - CA1 (Role Models in The Media)Document8 pagesISE III - Task 4 - Extended Writing - CA1 (Role Models in The Media)Ascension VillalbaNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesLesson PlanEnggar Pangesti WibowoNo ratings yet
- CBLM NhedzDocument23 pagesCBLM NhedzManny YapNo ratings yet
- Ferrules Ensure Safe ConnectionsDocument6 pagesFerrules Ensure Safe ConnectionstotovasiNo ratings yet
- Camesa TechBulletin-023Document2 pagesCamesa TechBulletin-023Dmz FreakzNo ratings yet
- Insulating and Conducting MaterialsDocument8 pagesInsulating and Conducting MaterialsRukayyahNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report On Aluminum-Electrolytic-CapacitorDocument19 pagesSeminar Report On Aluminum-Electrolytic-CapacitorChitranshu Srivastav0% (2)
- Overhead Conductors: ACAR (Aluminium Conductor, Aluminium Reinforce)Document21 pagesOverhead Conductors: ACAR (Aluminium Conductor, Aluminium Reinforce)Malik Shahzeb AliNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 Central Testing Lab (C.T.L.) : 1.1) IntroductionDocument41 pagesChapter-1 Central Testing Lab (C.T.L.) : 1.1) IntroductionNitesh SutharNo ratings yet
- Comparative Studies of The Susceptibility of Copper and Aluminum To Processing in Wire Drawing ProcessDocument7 pagesComparative Studies of The Susceptibility of Copper and Aluminum To Processing in Wire Drawing ProcessIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- What Is Polyvinyl ChlorideDocument21 pagesWhat Is Polyvinyl ChlorideAnonymous vcadX45TD7No ratings yet
- villanueva basic lecDocument43 pagesvillanueva basic lecKEVIN EDUARD VILLANUEVANo ratings yet
- Understanding Technical English-1Document67 pagesUnderstanding Technical English-1Ega Marga PutraNo ratings yet
- Unit 1. All Work and No PlayDocument48 pagesUnit 1. All Work and No Playdangthanhhd79No ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Makinng SenseDocument11 pagesUnit 2 - Makinng Sensedangthanhhd79No ratings yet
- Unit 3Document27 pagesUnit 3dangthanhhd79No ratings yet
- Công phá 8+ Môn tiếng anh đề tuyển sinh vào lớp 10Document234 pagesCông phá 8+ Môn tiếng anh đề tuyển sinh vào lớp 10Phuong HaNo ratings yet
- Gerundsandinfinitivesbaru 130316023713 Phpapp02Document18 pagesGerundsandinfinitivesbaru 130316023713 Phpapp02josiasNo ratings yet
- Unit 9: Automotive IndustriesDocument3 pagesUnit 9: Automotive Industriesdangthanhhd79No ratings yet
- Unit 11: Automotive IndustriesDocument3 pagesUnit 11: Automotive Industriesdangthanhhd79No ratings yet
- Sentence 1Document34 pagesSentence 1dangthanhhd79No ratings yet
- Tactics For Toeic - BookDocument24 pagesTactics For Toeic - Bookdangthanhhd79No ratings yet
- English Idioms - Sayings and SlangDocument1,569 pagesEnglish Idioms - Sayings and SlangMaaloum_1No ratings yet
- Statement of Loan AccountDocument2 pagesStatement of Loan Accountdangthanhhd79No ratings yet
- Tactics For Toeic - BookDocument2 pagesTactics For Toeic - Bookdangthanhhd79100% (1)
- Tactics For Toeic - BookDocument34 pagesTactics For Toeic - Bookdangthanhhd79100% (2)
- Tactics For Toeic - BookDocument11 pagesTactics For Toeic - Bookdangthanhhd79100% (1)
- Tactics For Toeic - BookDocument35 pagesTactics For Toeic - Bookdangthanhhd79No ratings yet
- Real Life Elementary WorkbookDocument110 pagesReal Life Elementary Workbookdangthanhhd7963% (16)
- Unit 1. All Work and No PlayDocument48 pagesUnit 1. All Work and No Playdangthanhhd79No ratings yet
- Unit4 AuditingDocument37 pagesUnit4 Auditingdangthanhhd79100% (8)
- Unit 3 Urban LifeDocument37 pagesUnit 3 Urban Lifedangthanhhd79100% (1)
- Unit 2 Your DayDocument23 pagesUnit 2 Your Daydangthanhhd79No ratings yet
- Real Life Elementary Teacher's HandbookDocument146 pagesReal Life Elementary Teacher's Handbookdangthanhhd7975% (8)
- Unit 5 - EAT WELLDocument38 pagesUnit 5 - EAT WELLdangthanhhd79No ratings yet
- Real Life Elementary Student's BookDocument138 pagesReal Life Elementary Student's Bookdangthanhhd7968% (22)
- Challenges for ESP Teachers and Learners in Teaching Legal EnglishDocument8 pagesChallenges for ESP Teachers and Learners in Teaching Legal Englishdangthanhhd79No ratings yet
- Ms. Nguyen Thi Le NguyenDocument12 pagesMs. Nguyen Thi Le Nguyendangthanhhd79No ratings yet
- Golf ASV EDC15 121pin - ElsaDocument14 pagesGolf ASV EDC15 121pin - ElsagrzegorzNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme For Oxford AQA IGCSE Physics Paper 2 June 19Document21 pagesMark Scheme For Oxford AQA IGCSE Physics Paper 2 June 19Pop VNo ratings yet
- Electrical Safety Devices at Home: Science 8Document5 pagesElectrical Safety Devices at Home: Science 8John Mark PrestozaNo ratings yet
- Grid and System Protection Relay Users GuideDocument201 pagesGrid and System Protection Relay Users GuideNemanja BgdNo ratings yet
- Control Ad or Temperatura Shimaden - SR73Document8 pagesControl Ad or Temperatura Shimaden - SR73Alexis Daniel Rosas MachadoNo ratings yet
- Dometic RM4185 6405 PDFDocument20 pagesDometic RM4185 6405 PDFcarlosrei2No ratings yet
- Power Electronics NomenclatureDocument109 pagesPower Electronics NomenclatureTeo BreviNo ratings yet
- Instructions Manual: Unit Control Vk-30CDocument8 pagesInstructions Manual: Unit Control Vk-30Ccristino_djNo ratings yet
- LG MS-194HDocument36 pagesLG MS-194HGabriela Ferencik SiveriNo ratings yet
- CTRL-70 Ui ConDocument20 pagesCTRL-70 Ui Conسکریپ بوائےNo ratings yet
- EEC 233 TheoryDocument75 pagesEEC 233 TheoryAdeniji Olusegun100% (8)
- SCAK200 - AK300 BookDocument28 pagesSCAK200 - AK300 BookStavre SorinNo ratings yet
- Selecting Low Voltage Wiring SystemsDocument96 pagesSelecting Low Voltage Wiring SystemsGetahunNo ratings yet
- Chapter-8 Distribution BoardsDocument27 pagesChapter-8 Distribution BoardsabdullahNo ratings yet
- Dynacraft Fire Dampers - CBRI TestedDocument40 pagesDynacraft Fire Dampers - CBRI Testedprabhanshu241991No ratings yet
- Allegato 11.2 - Service Manual New Askir 30 (RE 310100-02)Document26 pagesAllegato 11.2 - Service Manual New Askir 30 (RE 310100-02)Roger0% (1)
- Moeller ManualDocument12 pagesMoeller ManualAlexandre DiasNo ratings yet
- Alphasonik: Owner's ManualDocument8 pagesAlphasonik: Owner's Manualapi-290101261No ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering - Practical English Medium - 20.5.18 PDFDocument72 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering - Practical English Medium - 20.5.18 PDFjillNo ratings yet
- 22kV Kiosk Distribution Substation - Scope of WorksDocument82 pages22kV Kiosk Distribution Substation - Scope of WorksMauricio SaulNo ratings yet