0% found this document useful (0 votes)
442 views6 pagesEngine Power Calculation
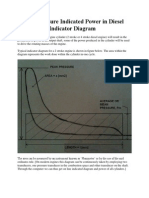
This document summarizes the calculation of main engine test bench values and fuel consumption for a DEUTZ TBD 645 L6 main engine. It calculates values like effective power, fuel consumption, torque, and thermal efficiency at 110%, 100%, 90%, 75%, 50%, and 25% loads using formulas involving parameters like piston bore, stroke, revolutions, and pressure. Carbon dioxide emissions in metric tons per hour and per 24 hours are also estimated for different fuel types and loads based on effective power and fuel consumption.
Uploaded by
gurcanogluCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
442 views6 pagesEngine Power Calculation
This document summarizes the calculation of main engine test bench values and fuel consumption for a DEUTZ TBD 645 L6 main engine. It calculates values like effective power, fuel consumption, torque, and thermal efficiency at 110%, 100%, 90%, 75%, 50%, and 25% loads using formulas involving parameters like piston bore, stroke, revolutions, and pressure. Carbon dioxide emissions in metric tons per hour and per 24 hours are also estimated for different fuel types and loads based on effective power and fuel consumption.
Uploaded by
gurcanogluCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Main Engine Test Bench and Fuel Consumption
- Lubrication Oil Calculation
- Effective Power and Fuel Consumption Analysis
- Energy Efficiency Operational Indicator (EEOI) Calculations
- CO2 Emissions and Load-specific Analysis