Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Newton'S Laws of Motion: Nuevo Colegio Del Prado
Uploaded by
nubiaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Newton'S Laws of Motion: Nuevo Colegio Del Prado
Uploaded by
nubiaCopyright:
Available Formats
Name_______________________________ Period__________ Date________________
NUEVO COLEGIO DEL PRADO
NEWTON’S LAWS
Res. Nº 00819 OF
de 17 de Abril de 2007 MOTION
Licencia de Funcionamiento Res. Nº 305 de Diciembre 02 de 1994.
Name: ______________________________ 7 A B C D
If I am anything, which I highly doubt,
Teacher: Mr. LuisIÁvila
have made myself so by hard work.
Due date: March 27th/2020– Isaac Newton
Goals:
1. Students will use conceptual and mathematical models to predict and
understand patterns in motion. (3.1.10.B-C)
2. Students will be able to apply Newton’s laws of motion to solve
problems related to forces and mass. (3.4.10.C, 3.1.10.E)
3. Students will integrate new information into existing theories and
explain implied results. (3.2.10.A)
Information
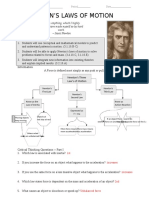
A Force is defined most simply as any push or pull.
Newton’s Three
Law’s of Motion
Newton’s Newton’s
First Law Third Law
Newton’s
Second Law
Know as the Know as
Law of Inertia Action-Reaction
Expressed as
F = ma
Moving objects Objects at
rest stay at If an object The 2nd exerts an
keep moving
rest exerts a force on equal & opposite
another object force on the 1st
More force means More mass means
more acceleration less acceleration
Unless acted
on by an
unbalanced
force.
Critical Thinking Questions – Part I
1. Which law is associated with inertia?
2. If you increase the force on an object what happens to the acceleration?
3. If you use the same force on a less massive object what happens to the acceleration?
4. Which law states force is dependent on the mass and acceleration of an object?
5. What causes an object to slowdown or speed-up?
6. What law is known as the law of action-reaction?
7. Which law explains why when you bump into something you fall backwards?
8. If you double the force of an object what happens to the acceleration?
9. If you double the mass of an object what happens to the acceleration?
10. Force is measured in newtons (N). A newton is based on base units in the metric system.
What is a newton equal to in terms of units of mass and acceleration?
Exercises
1. When Jane drives to work, she always places her purse on the passenger’s seat. By the time
she gets to work, her purse has fallen on the floor in front of the passenger seat. One day, she
asks you to explain why this happens in terms of physics. What do you say?
2. You are waiting in line to use the diving board at your local pool. While watching people dive
into the pool from the board, you realize that using a diving board to spring into the air before a
dive is a good example of Newton’s third law of motion. Explain how a diving board illustrates
Newton’s third law of motion.
3. You know the mass of an object and the force applied to the object to make it move. Which of
Newton’s laws of motion will help you calculate the acceleration of the object?
4. How many newtons of force are represented by the following amount: 3 kg·m/sec2? Justify
your answer.
5. Your shopping cart has a mass of 65 kilograms. In order to accelerate the shopping cart down
an aisle at 0.3 m/sec2, what force would you need to use or apply to the cart?
6. A small child has a wagon with a mass of 10 kilograms. The child pulls on the wagon with a
force of 2 newtons. What is the acceleration of the wagon?
7. You dribble a basketball while walking on a basketball court. List and describe at least 3 pairs
of action-reaction forces in this situation.
You might also like
- The Laws of Motion : Physics for Kids | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandThe Laws of Motion : Physics for Kids | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- Law of Interaction (Innovators Group)Document2 pagesLaw of Interaction (Innovators Group)Jheaz Zelle100% (4)
- Laws of Motion - NewtonDocument17 pagesLaws of Motion - NewtonpseudonimNo ratings yet
- Laws of MotionDocument18 pagesLaws of MotionJhen BonNo ratings yet
- Math8 - q1 - Mod5a - Multiplying and Dividing Rational Algebraic Expressions - 08092020Document34 pagesMath8 - q1 - Mod5a - Multiplying and Dividing Rational Algebraic Expressions - 08092020JaylanGalasi100% (4)
- Laws of MotionDocument17 pagesLaws of MotionClaudiu NicusorNo ratings yet
- Type Certificate Data Sheet No. 1E4Document12 pagesType Certificate Data Sheet No. 1E4flyingemuNo ratings yet
- Manual de Servicio Jac 5 InglésDocument375 pagesManual de Servicio Jac 5 InglésJT Pe100% (1)
- Using A Scientific Journal Article To Write A Critical ReviewDocument6 pagesUsing A Scientific Journal Article To Write A Critical ReviewJaime Martinez100% (1)
- Newton'S Laws of Motion: Name KeyDocument13 pagesNewton'S Laws of Motion: Name KeyMingNo ratings yet
- Lista de verbos irregulares en españolDocument5 pagesLista de verbos irregulares en españolMonserrath :p100% (1)
- Laws of MotionDocument17 pagesLaws of MotionGraceyxie GrasyaNo ratings yet
- DLL On Laws of MotionDocument12 pagesDLL On Laws of MotionCharo Nudo Pongasi100% (4)
- Nkdievid 2Document10 pagesNkdievid 2nik100% (2)
- Newtons Laws of Motion - Activity SheetDocument2 pagesNewtons Laws of Motion - Activity SheetJMDNo ratings yet
- Newtons 3rd LawDocument15 pagesNewtons 3rd LawcaitlyntreacyNo ratings yet
- Saint Mary's Academy Newton's Laws of MotionDocument1 pageSaint Mary's Academy Newton's Laws of MotionKristel Claire BalderasNo ratings yet
- Final Learning Activity SheetsDocument17 pagesFinal Learning Activity SheetsVergenia EspielNo ratings yet
- According To NewtonDocument19 pagesAccording To Newtonjaycey24No ratings yet
- NewtonDocument2 pagesNewtonglueckwunsch.liebtNo ratings yet
- Physics - Newton's Laws of MotionDocument1 pagePhysics - Newton's Laws of MotionCam MukaNo ratings yet
- Motion in One Dimension Unit 2: Unit Outcomes: After Completing This Unit You Should Be Able ToDocument16 pagesMotion in One Dimension Unit 2: Unit Outcomes: After Completing This Unit You Should Be Able ToMahamud elmogeNo ratings yet
- Verde Blanco Plantas Foto Ciencia FolletoDocument2 pagesVerde Blanco Plantas Foto Ciencia FolletoAndrea Carolina Ictech EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Laws of MotionDocument17 pagesLaws of MotionMechaella Marie Maste GallazaNo ratings yet
- 3 Law of MotionDocument1 page3 Law of MotionAlyssa Dianne Rodriguez DumoNo ratings yet
- Newtons Law's of MotionDocument19 pagesNewtons Law's of MotionAira YamuyamNo ratings yet
- Me Sci 8 q1 0202 SGDocument10 pagesMe Sci 8 q1 0202 SGZyro Jay MonteroNo ratings yet
- Newtons3rdlawofmotion 210202095340Document20 pagesNewtons3rdlawofmotion 210202095340Rocil ValdezNo ratings yet
- Name - Period - Date - Newton'S Laws WebquestDocument5 pagesName - Period - Date - Newton'S Laws WebquestsohiNo ratings yet
- Newton's Law of MotionDocument8 pagesNewton's Law of MotionLouigene QuiloNo ratings yet
- DLL Sci 8 Week 2 Q1Document9 pagesDLL Sci 8 Week 2 Q1Rhazel CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Science LESSON PLAN - Week 2Document4 pagesScience LESSON PLAN - Week 2Kathryn Decena CentinalesNo ratings yet
- Usain Bolt Peregrine Falcon Cheetah: Illustration 1. Sir Isaac NewtonDocument7 pagesUsain Bolt Peregrine Falcon Cheetah: Illustration 1. Sir Isaac NewtonNeema RelucioNo ratings yet
- Newton Third LawDocument15 pagesNewton Third Lawapi-260547045No ratings yet
- Newton's Laws: Al-Basra University College of Engineering Department of MechanicsDocument12 pagesNewton's Laws: Al-Basra University College of Engineering Department of MechanicsZahra 9oNo ratings yet
- Chap3 Newton LawsDocument65 pagesChap3 Newton LawsAnwar Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 ConceptDocument15 pagesChapter 1 ConceptSiti KhalijahNo ratings yet
- 3rd Law of MotionDocument16 pages3rd Law of MotionØᎶ •тzυNo ratings yet
- G8-LESSON1-LAWSOFMOTIONDocument21 pagesG8-LESSON1-LAWSOFMOTIONVincent AbucayNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of Motion Glenn Research Center NASADocument1 pageNewton's Laws of Motion Glenn Research Center NASAelenekalandadzeeeNo ratings yet
- LM5b - Newton - S Laws of Motion - GPHYS1Document40 pagesLM5b - Newton - S Laws of Motion - GPHYS1burner accNo ratings yet
- Pythagorean TheoremDocument2 pagesPythagorean TheoremGuNo ratings yet
- Chap. 5: Three Forces Gravity Wind Force Water ForceDocument32 pagesChap. 5: Three Forces Gravity Wind Force Water ForceFranco FrecheroNo ratings yet
- 3.4 Force, Mass and AccelerationDocument9 pages3.4 Force, Mass and Acceleration42h47n5zvrNo ratings yet
- Dhruv Bhardwaj Physics 11 Law of Motion ProjectDocument30 pagesDhruv Bhardwaj Physics 11 Law of Motion ProjectComrade YTNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of Motion Explained for RocketsDocument2 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion Explained for RocketsAhsah AshhadNo ratings yet
- The E Tutor - Laws of MotionDocument11 pagesThe E Tutor - Laws of Motioninfo5963No ratings yet
- Scientific Review of NewtonDocument8 pagesScientific Review of NewtonAnwesh SarkarNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of Motion GuideDocument37 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion GuideAj TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Newtons Laws PPTDocument29 pagesNewtons Laws PPTchris estradaNo ratings yet
- Q1 Wk4 WPLPDocument11 pagesQ1 Wk4 WPLPKris JoyNo ratings yet
- CPO Science Foundations of Physics: Unit 2, Chapter 5Document29 pagesCPO Science Foundations of Physics: Unit 2, Chapter 5farismohNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of Motion ExplainedDocument6 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion Explainedrizki siwiNo ratings yet
- Lec03-Newton's Laws of MotionDocument19 pagesLec03-Newton's Laws of MotionpvriiscNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document3 pagesWeek 2benjamin.saranilloNo ratings yet
- Adv. Physics Revised1st QDocument33 pagesAdv. Physics Revised1st QYlena AllejeNo ratings yet
- f5 Physics Newtons LawsDocument3 pagesf5 Physics Newtons LawsDesmond simpsonNo ratings yet
- Newton LawsDocument3 pagesNewton LawsA BarrettNo ratings yet
- 2 G8 Science Q1-Week 1 of 1law of InertiaDocument16 pages2 G8 Science Q1-Week 1 of 1law of InertiaAn BautistaNo ratings yet
- Dynamics: CausesDocument20 pagesDynamics: CausesperwinsharmaNo ratings yet
- Newton's First Law Explains His Second LawDocument5 pagesNewton's First Law Explains His Second Lawdva222No ratings yet
- Physics Project - Drishti Modi 1Document5 pagesPhysics Project - Drishti Modi 1api-317134398No ratings yet
- Newton Laws - Angel and AshleyDocument4 pagesNewton Laws - Angel and Ashleyapi-438888114No ratings yet
- NewtonsDocument3 pagesNewtonsapi-260817414No ratings yet
- Present Perfect Simple Vs Present Perfect ContinuousDocument14 pagesPresent Perfect Simple Vs Present Perfect ContinuousnubiaNo ratings yet
- Roleplay Activity: Andrea: ? SebastianDocument3 pagesRoleplay Activity: Andrea: ? SebastiannubiaNo ratings yet
- Second Term - Vocabulary #1 - 1st Part (Entertainment)Document2 pagesSecond Term - Vocabulary #1 - 1st Part (Entertainment)nubiaNo ratings yet
- Sayings and Proverbs Presentation: Andrea Rodríguez 7°CDocument6 pagesSayings and Proverbs Presentation: Andrea Rodríguez 7°CnubiaNo ratings yet
- A1 English Test TitleDocument3 pagesA1 English Test TitlenubiaNo ratings yet
- Simple Machine 4Document24 pagesSimple Machine 4nubiaNo ratings yet
- Social Taller PDFDocument1 pageSocial Taller PDFnubiaNo ratings yet
- Activity English 16 Junio 2020Document19 pagesActivity English 16 Junio 2020nubiaNo ratings yet
- End Sem - Solution & Marking SchemeDocument41 pagesEnd Sem - Solution & Marking SchemeHaryanvi ChhoraNo ratings yet
- AEE 211-Chapter 01-Rev 1Document66 pagesAEE 211-Chapter 01-Rev 1AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Ayangpallii1 PDFDocument1 pageAyangpallii1 PDFHemam PrasantaNo ratings yet
- Ev 3 Solar StationDocument52 pagesEv 3 Solar Stationavira0002No ratings yet
- Summed Area TablesDocument29 pagesSummed Area TablesDhillonvNo ratings yet
- Changelog User en PDFDocument136 pagesChangelog User en PDFgrufNo ratings yet
- Phy QBDocument25 pagesPhy QBManav MehtaNo ratings yet
- NSXT 30 AdminDocument1,028 pagesNSXT 30 AdminAlessandroNo ratings yet
- XPS Insulation ASTM - C578 - Types PDFDocument1 pageXPS Insulation ASTM - C578 - Types PDFSushil KumarNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Using FlowchartsDocument14 pagesBenefits of Using FlowchartsDave FlautaNo ratings yet
- Cadence LN ADocument68 pagesCadence LN AfocclasNo ratings yet
- Wave Motion on a StringDocument17 pagesWave Motion on a StringAnkit JhaNo ratings yet
- 03 - Reactions Between CaO and SO2 in Carbonating and No Carbonating ConditionsDocument9 pages03 - Reactions Between CaO and SO2 in Carbonating and No Carbonating ConditionsNishantNo ratings yet
- Android: Uni-Stroke Touch Gesture Recognition Using $1 Gesture ReconigizerDocument13 pagesAndroid: Uni-Stroke Touch Gesture Recognition Using $1 Gesture Reconigizerpi194043No ratings yet
- Manual Del Usuario MCI-WIR-00787 (ENG)Document23 pagesManual Del Usuario MCI-WIR-00787 (ENG)Helio CoragemNo ratings yet
- Comparison of methods for determining the plateau modulus and entanglement molecular weightDocument19 pagesComparison of methods for determining the plateau modulus and entanglement molecular weightfaezehNo ratings yet
- Raynoise Manual Rn31Document377 pagesRaynoise Manual Rn31Jay JayNo ratings yet
- CH-2 Relational ModelDocument51 pagesCH-2 Relational ModelhkNo ratings yet
- HeatDocument31 pagesHeatnicky1213a100% (1)
- Dynamics - Rotational Motion Lab ReportDocument16 pagesDynamics - Rotational Motion Lab ReportTim Ghent100% (1)
- Geeks For Geeks - ArrayDocument33 pagesGeeks For Geeks - ArrayLove MehtaNo ratings yet
- Clutch DynamicsDocument6 pagesClutch DynamicsKen SmithNo ratings yet
- Configure NTP Server on Cisco WLC via CLIDocument3 pagesConfigure NTP Server on Cisco WLC via CLImbayeNo ratings yet
- K-Gamma and K-Beta FunctionDocument5 pagesK-Gamma and K-Beta FunctionketashiNo ratings yet
- E06 - CONSTANTINACHE PompiliuDocument4 pagesE06 - CONSTANTINACHE PompiliuNgô Hải ĐăngNo ratings yet