Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Elastic and Plastic Section Modulus
Uploaded by
Satha IyathuraiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Elastic and Plastic Section Modulus
Uploaded by
Satha IyathuraiCopyright:
Available Formats
Plastic section modulus
The plastic section modulus is used for materials where elastic yielding is acceptable and
plastic behavior is assumed to be an acceptable limit. Designs generally strive to ultimately
remain below the plastic limit to avoid permanent deformations, often comparing the plastic
capacity against amplified forces or stresses.
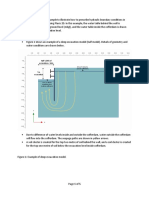
The plastic section modulus depends on the location of the plastic neutral axis (PNA). The
PNA is defined as the axis that splits the cross section such that the compression force from
the area in compression equals the tension force from the area in tension. So, for sections
with constant yielding stress, the area above and below the PNA will be equal, but for
composite sections, this is not necessarily the case.
The plastic section modulus is the sum of the areas of the cross section on each side of the
PNA (which may or may not be equal) multiplied by the distance from the local centroids of
the two areas to the PNA:
You might also like
- Stress and StrainDocument60 pagesStress and StrainMuhammad Shafie100% (1)
- Stress-Strain Diagram (Curve)Document4 pagesStress-Strain Diagram (Curve)kevinNo ratings yet
- Plastic Analysis NotesDocument26 pagesPlastic Analysis NotesTatiana Espinoza Eusebio100% (1)
- 6 BeamsDocument116 pages6 BeamsIrish TambisNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties PDFDocument57 pagesMechanical Properties PDFvardhaNo ratings yet
- Mackenzie PVP2017 Stress Linearization Concepts and Restrictions in Elastic Design by AnalysisDocument8 pagesMackenzie PVP2017 Stress Linearization Concepts and Restrictions in Elastic Design by Analysissvk_ntNo ratings yet
- On Shrink Fit Analysis and DesignDocument10 pagesOn Shrink Fit Analysis and DesignParag NaikNo ratings yet
- Mechanical PropertiesDocument57 pagesMechanical PropertiesElmedin Gluhic100% (1)
- Compre 1Document4 pagesCompre 1Marco Ramos JacobNo ratings yet
- FLAC Basics by MeDocument3 pagesFLAC Basics by Mesujan95No ratings yet
- Plastic BendingDocument1 pagePlastic BendingmajmjudNo ratings yet
- Imot 2176 Tensile PropertiesDocument4 pagesImot 2176 Tensile PropertiesEry KuswantoroNo ratings yet
- What Are The Differences Between Implicit and Explicit?: Weak SpringDocument2 pagesWhat Are The Differences Between Implicit and Explicit?: Weak SpringKoral ToptopNo ratings yet
- Plastic Section ModulusDocument1 pagePlastic Section ModulusHina MuslimNo ratings yet
- Garland AUC2008Document16 pagesGarland AUC2008klomps_jrNo ratings yet
- Tensile PropertiesDocument4 pagesTensile Propertiesjontylee87No ratings yet
- Fixed Supports: Boundary Conditions Section For A Listing of All Remote Boundary Conditions and TheirDocument5 pagesFixed Supports: Boundary Conditions Section For A Listing of All Remote Boundary Conditions and TheirFairnandobgspNo ratings yet
- CtpzsDocument4 pagesCtpzsMohamed SamehNo ratings yet
- Bending: Dr. Kamaran S. IsmailDocument11 pagesBending: Dr. Kamaran S. IsmailWael ImadNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of Dental MaterialsDocument7 pagesMechanical Properties of Dental Materialsshubhe08No ratings yet
- Stress ConcentrationDocument22 pagesStress Concentrationbomeje5457No ratings yet
- Basic Properties of Dental MaterialsDocument17 pagesBasic Properties of Dental MaterialsUmut ASLANNo ratings yet
- Stress Strain DiagramDocument4 pagesStress Strain DiagramMartine CastroNo ratings yet
- StrengthDocument2 pagesStrengthBello JaneNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metal FormingDocument7 pagesSheet Metal FormingHussien EbrhimNo ratings yet
- ME501 L3 Stress-Strain Relations Oct 2017Document8 pagesME501 L3 Stress-Strain Relations Oct 2017Firas RocktNo ratings yet
- Module 07 - Plastic Analysis of BeamsDocument8 pagesModule 07 - Plastic Analysis of BeamsSameera Jayaratne100% (1)
- Secant ModulusDocument1 pageSecant ModulushudpalNo ratings yet
- Ahmed H. Zubydan - Inelastic Large Deflection Analysis of Space Steel Frames Including H-Shaped Cross Sectional MembersDocument11 pagesAhmed H. Zubydan - Inelastic Large Deflection Analysis of Space Steel Frames Including H-Shaped Cross Sectional MemberscosminducaNo ratings yet
- Theory of The Tensile Strength ExperimentDocument18 pagesTheory of The Tensile Strength ExperimentKaty PerryNo ratings yet
- File 1567673653Document107 pagesFile 1567673653angeloNo ratings yet
- Design of Tension MembersDocument30 pagesDesign of Tension Memberssharer1No ratings yet
- Finite Element Method Analysis of Rectangular Plate With Circular Hole Using Ansys PDFDocument12 pagesFinite Element Method Analysis of Rectangular Plate With Circular Hole Using Ansys PDFVikashNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Method Analysis of Rectangular Plate With Circular Hole Using AnsysDocument12 pagesFinite Element Method Analysis of Rectangular Plate With Circular Hole Using AnsysNarayana Swamy GNo ratings yet
- True Stress Strain PDFDocument12 pagesTrue Stress Strain PDFBrian ForsmanNo ratings yet
- 152 1199 2 PB PDFDocument16 pages152 1199 2 PB PDFRohit GadekarNo ratings yet
- Fem SlabDocument22 pagesFem SlabEfren ElegadoNo ratings yet
- 3D CZM Ductile Crack Growth TriaxialityDocument23 pages3D CZM Ductile Crack Growth TriaxialityfrvdabeeNo ratings yet
- Module3 Design of Tension MembersDocument33 pagesModule3 Design of Tension MembersPrem KumarNo ratings yet
- LectureNo 16Document16 pagesLectureNo 16Dinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Tension Members DesignDocument30 pagesTension Members Designrameshbabu_1979No ratings yet
- Plastic Analysis1Document18 pagesPlastic Analysis1Varun Singh ChandelNo ratings yet
- Circular DiaphragmDocument4 pagesCircular DiaphragmHrushi KesanNo ratings yet
- 2006 Int Ansys Conf 134Document15 pages2006 Int Ansys Conf 134bamboolNo ratings yet
- Platic AnalysisDocument29 pagesPlatic AnalysisSiddhanth S NairNo ratings yet
- Designofbeams 160410151902 PDFDocument76 pagesDesignofbeams 160410151902 PDFsurendra bhattaNo ratings yet
- A Simplified Formula To Estimate The Size of The Cyclic Plastic Zone in Metals Containing Elastic ParticlesDocument33 pagesA Simplified Formula To Estimate The Size of The Cyclic Plastic Zone in Metals Containing Elastic Particlesstan TriNo ratings yet
- Harris ThesisDocument22 pagesHarris ThesisTanu RdNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Properties of EngineeringDocument11 pagesManufacturing Properties of EngineeringSanjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Cavity Expansion in SandsDocument21 pagesCavity Expansion in SandsszilvagyizsoltNo ratings yet
- On Shrink Fit Analysis and Design: OriginalarticleDocument2 pagesOn Shrink Fit Analysis and Design: OriginalarticleDedy SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Ce150 Steel 4.1 Tension Members Tensile Strength 01Document3 pagesCe150 Steel 4.1 Tension Members Tensile Strength 01Jhan SeenNo ratings yet
- Research On Crowning Profile To Obtain Maximum Load Carrying Capacity For Roller BearingsDocument6 pagesResearch On Crowning Profile To Obtain Maximum Load Carrying Capacity For Roller BearingskiranmittisilaNo ratings yet
- Plane Stress and Strain 2Document8 pagesPlane Stress and Strain 2Akash PrabhakaranNo ratings yet
- Definition - What Does Plastic Hinge Mean?Document1 pageDefinition - What Does Plastic Hinge Mean?Ishwarya SrikanthNo ratings yet
- Sandwich LaminateDocument43 pagesSandwich LaminateAnonymous wWOWz9UnWNo ratings yet
- Stress Strain RealtionshipDocument35 pagesStress Strain RealtionshipKhalid YousafNo ratings yet
- Geometry of Surfaces: A Practical Guide for Mechanical EngineersFrom EverandGeometry of Surfaces: A Practical Guide for Mechanical EngineersNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Boundary Conditions For ExcavationsDocument5 pagesHydraulic Boundary Conditions For ExcavationsSatha IyathuraiNo ratings yet
- 1stability AnalysisDocument93 pages1stability AnalysisSatha IyathuraiNo ratings yet
- Dimensions Used in Analysis: 0.60m 7.40m 0.90m 1.50mDocument4 pagesDimensions Used in Analysis: 0.60m 7.40m 0.90m 1.50mSatha IyathuraiNo ratings yet
- Stockwell June 1977 DCPDocument4 pagesStockwell June 1977 DCPSatha IyathuraiNo ratings yet
- Impact Assessment - 4-Storey Car ParkDocument4 pagesImpact Assessment - 4-Storey Car ParkSatha IyathuraiNo ratings yet
- Derivation of Burland's Chart For Assessing Category of Building DamageDocument5 pagesDerivation of Burland's Chart For Assessing Category of Building DamageSatha IyathuraiNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Risk of Damage To BuildingDocument11 pagesAssessment of Risk of Damage To BuildingSatha IyathuraiNo ratings yet