Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Title Aim To Investigate If Potassium Permanganate Crystal Will Diffuse in Water. Material
Title Aim To Investigate If Potassium Permanganate Crystal Will Diffuse in Water. Material
Uploaded by
Sherida GibbsOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Title Aim To Investigate If Potassium Permanganate Crystal Will Diffuse in Water. Material
Title Aim To Investigate If Potassium Permanganate Crystal Will Diffuse in Water. Material
Uploaded by
Sherida GibbsCopyright:
Available Formats
Title
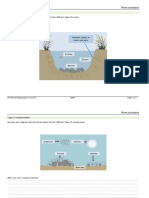
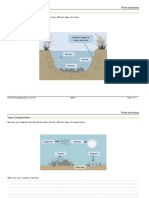
Aim To investigate if Potassium permanganate crystal will diffuse in water.
Material;
white sheet of paper
pencil
a pair of compasses
petri dish
Potassium permanganate crystals
water
timer
ruler
method
In preparing for experiment all materials and apparatus were collected for use throughout the
experiment
Subsequently the radii of 1,2,3,4 and 5cm was measured on a ruler using a pair of compasses for
accuracy
When the radii of the circles were measured five circles with same Centre of radii 1,2,3,4 and 5cm were
drawn using pencil and a pair of compasses on white sheet paper
Then the container was filled with tap water
Place the container with water on the directly on the outer circle on the white sheet of paper
Left the beaker for a minute so water can settle
Choose a single crystal of Potassium permanganate and drop it in the container of water so that it lands
in the 1cm circle that has been drawn on the sheet of paper
Immediately after the timer start buton was pressed to detect the time the Potassium permanganate
crystals took to diffuse to 1,2,3,4 and 5cm individually
Observe what happens in each case, record time and details
Discussion
Diffusion occurs when particles spread and move from a region where they are in high concentration to
a region where they are in low concentration that results in distribution of the chemicals particles to
become more uniform in space as time passes. The driving force for diffusion is the thermal motion of
molecules. At temperatures above absolute zero, molecules are never at rest. Them having kinetic
energy means that they are always in motion, and when molecules collide with each other frequently,
the direction of the motion becomes randomized but in most cases, these collisions are common. The
average kinetic energy of different types of molecules of different masses are the same but their
average velocities are different. Their average diffusion rate depends upon that average velocity, which
gives a relative diffusion rate. Diffusion proceeds at a maximum rate in gases, at a lower rate in liquids,
and at a still lower rate in solids. These differences are determined by the nature of thermal motion in
them. Diffusion is evident in gases and for particles dissolved in solutions. An experiment was conducted
to investigate what happens when Potassium permanganate when it comes in contact with water.
Potassium permanganate is a purplish colored crystalline solid. As the crystal of Potassium
permanganate is placed in the water, the water molecules begins the react with the potassium cation
and the permanganate anions held in the crystal to break the ionic bonds that hold the crystal together.
Eventually the random motion of potassium permanganate particles results in the purple color being
equally dispersed throughout the water. However when observing, the diffusion process would appear
slow because the dissolved particles of Potassium permanganate collide with the water molecules and
each other, slowing their progress. After the diffusion process is complete when the crystal is dissolved
in solution it can be observed that the solution will finally take on a uniform purple color which is simply
a homogeneous solution of Potassium permanganate in water.
Conclusion
When soild crystals of potassium permanganate IS add or comes in contact with the water at room
temperature diffusion takes place
The driving force for diffusion is the thermal motion of molecules. At temperatures above absolute zero,
molecules are never at rest. Their kinetic energy means that they are always in motion, and when
molecules collide with each other frequently, the direction of the motion becomes randomized but In
most cases, these collisions are common;.
You might also like
- Lab#3 DiffusionDocument5 pagesLab#3 DiffusionTabitha Darrell100% (2)
- Investigatory ProjectDocument14 pagesInvestigatory Project8796d83% (6)
- Particles Mastery BookletDocument25 pagesParticles Mastery Bookletapi-42242870050% (2)
- Grade 9-Chem-Ch-1-Notes-1Document14 pagesGrade 9-Chem-Ch-1-Notes-1Aarushi 8741No ratings yet
- DiffusionDocument16 pagesDiffusionAbhinandan Sanduja100% (1)
- Chemistry Investigatory ProjectDocument12 pagesChemistry Investigatory ProjectMax gamingNo ratings yet
- Index: Acknowledgement Aim Objective Experiment 1 Experiment 2 Experiment 3 Result BibliographyDocument14 pagesIndex: Acknowledgement Aim Objective Experiment 1 Experiment 2 Experiment 3 Result BibliographyKunal MhatreNo ratings yet
- Aim:-To Study of Diffusion of Solids in LiquidsDocument11 pagesAim:-To Study of Diffusion of Solids in LiquidskaranNo ratings yet
- To Study The Diffusion of Solids in LiquidsDocument18 pagesTo Study The Diffusion of Solids in Liquidsdeepak876No ratings yet
- Diffusion of Solids in LiquidsDocument4 pagesDiffusion of Solids in LiquidssamyukthaNo ratings yet
- My Chemistry Sba: Name: Camaya Rumble Grade: 11 School: Tarrant High School Teacher: MR HiltonDocument7 pagesMy Chemistry Sba: Name: Camaya Rumble Grade: 11 School: Tarrant High School Teacher: MR HiltonCamaya RumbleNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes (Chapter 1)Document14 pagesChemistry Notes (Chapter 1)NiranjanNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our Surroundings Notes: Matter Is Made of ParticlesDocument7 pagesMatter in Our Surroundings Notes: Matter Is Made of ParticlesVedha SinghNo ratings yet
- CHM ProjectDocument14 pagesCHM ProjectShobhitNo ratings yet
- Sodapdf MergedDocument18 pagesSodapdf Mergedharshitgarg808No ratings yet
- Investigatory Project 16 PDF FreeDocument14 pagesInvestigatory Project 16 PDF FreeShobhitNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our Surroundings: Session 1Document11 pagesMatter in Our Surroundings: Session 1swarup.kadam17No ratings yet
- Study of Diffusion of Solids in LiquidsDocument8 pagesStudy of Diffusion of Solids in LiquidsRajesh NakotiNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry Principles of ChemistryDocument7 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Principles of Chemistrydanielmahsa100% (1)
- Diffusion of Solids in LiquidsDocument13 pagesDiffusion of Solids in LiquidsdhanapriyaNo ratings yet
- My Chemistry SbaDocument9 pagesMy Chemistry SbaCamaya RumbleNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Sba LabDocument5 pagesChemistry Sba LabTawayna HemmingsNo ratings yet
- MatterDocument4 pagesMatterJacinta MartinNo ratings yet
- Study of Diffusion of Solids in Liquids PDFDocument11 pagesStudy of Diffusion of Solids in Liquids PDFSumit AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Gas LawsDocument12 pagesGas LawsPadmaDevNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project On Study of Diffusion of Solids in LiquidsDocument3 pagesChemistry Project On Study of Diffusion of Solids in LiquidsAbhijith TharunNo ratings yet
- 1 Principles of Chemistry 1: 1.1 Evidence For Particles SolidDocument12 pages1 Principles of Chemistry 1: 1.1 Evidence For Particles SolidThu ReinNo ratings yet
- Document (5) Chemistry Project Class 12Document23 pagesDocument (5) Chemistry Project Class 12Deepak AroraNo ratings yet
- Worldofmatter 130724204531Document16 pagesWorldofmatter 130724204531patmadasdasNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument23 pagesMatter in Our SurroundingsDeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- 01 Structure of Matter 2009Document6 pages01 Structure of Matter 2009api-27085921No ratings yet
- Osmosis: Diffusion Is The Process Where Molecules of Two or More Substances Move AboutDocument3 pagesOsmosis: Diffusion Is The Process Where Molecules of Two or More Substances Move AboutizzahNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of ChemistryDocument92 pagesBasic Concepts of ChemistryNehaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 8 The Force: Diffusion and Osmosis Water Movement in Plants and SoilDocument26 pagesLaboratory 8 The Force: Diffusion and Osmosis Water Movement in Plants and Soilah maNo ratings yet
- Study of Diffusion of Solids in Liquids and Rate of DiffusionDocument6 pagesStudy of Diffusion of Solids in Liquids and Rate of DiffusionPiyush Agarwal0% (1)
- All Substances Are Made of AtomsDocument3 pagesAll Substances Are Made of AtomsNaomiNo ratings yet
- What Is DiffusionDocument4 pagesWhat Is DiffusionccffyNo ratings yet
- Avneesh Kumar Chemistry ProjectDocument16 pagesAvneesh Kumar Chemistry ProjectAvneesh RoyNo ratings yet
- Rough Employee DetailsDocument13 pagesRough Employee DetailskannianbuNo ratings yet
- Investigatory ProjectDocument17 pagesInvestigatory ProjectJeevikaaNo ratings yet
- Diffusion of Solids in LiquidsDocument8 pagesDiffusion of Solids in LiquidsAditya MishraNo ratings yet
- Journal Group #4Document13 pagesJournal Group #4Vincent A. Sunggayan-NiezNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Water On The Size of Gold Nanoparticles 1Document18 pagesThe Effects of Water On The Size of Gold Nanoparticles 1api-469291896No ratings yet
- Aim Objective Experiment 1 Experiment 2 Experiment 3 Result: IndexDocument15 pagesAim Objective Experiment 1 Experiment 2 Experiment 3 Result: IndexAbhijeet RautelaNo ratings yet
- General Physics2 ScriptDocument2 pagesGeneral Physics2 ScriptClaire DonilaNo ratings yet
- Particulate Theory of MatterDocument23 pagesParticulate Theory of MatterTyrell trimNo ratings yet
- Principles of ChemistryDocument14 pagesPrinciples of ChemistrydinuNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes 5070Document93 pagesChemistry Notes 5070yawerakNo ratings yet
- Determination of Rate of Evaporation of Different Liquids.Document22 pagesDetermination of Rate of Evaporation of Different Liquids.Jinesh Doshi33% (6)
- Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument9 pagesMatter in Our SurroundingsDilip Kumar KumawatNo ratings yet
- ChemicalDocument2 pagesChemicalMUHAMMAD AKRAMNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Exam RevisionDocument10 pagesChemistry Exam RevisionTriple D'JanNo ratings yet
- Ch-1, Cl-9, Matter in Our SurroundingDocument37 pagesCh-1, Cl-9, Matter in Our SurroundingSoumalyaNo ratings yet
- Study of Diffusion of Solids in LiquidsDocument11 pagesStudy of Diffusion of Solids in Liquidsshivyamishra75% (8)
- Chemistry Class 9 Chapter 1Document75 pagesChemistry Class 9 Chapter 1Dhruv SinghNo ratings yet
- 12th Chemistry ProjectDocument11 pages12th Chemistry Projectapi-369623577% (56)
- States of Matter: Solids Have Particles That Are Packed Closely Together. The Atoms Are Arranged in ADocument92 pagesStates of Matter: Solids Have Particles That Are Packed Closely Together. The Atoms Are Arranged in AAminah ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Chemistry Project Report On Diffusion of Solids in LiquidsDocument11 pagesClass 12 Chemistry Project Report On Diffusion of Solids in LiquidsASHWIN KUMAR KANNIYAPPANNo ratings yet
- The Phases of Matter - Chemistry Book Grade 1 | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandThe Phases of Matter - Chemistry Book Grade 1 | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Social Psychology: Lecture 3.3: Group Pressure and Conformity (Part 1)Document1 pageSocial Psychology: Lecture 3.3: Group Pressure and Conformity (Part 1)Sherida GibbsNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System Organization: Jennifer Carbrey Ph.D. Department of Cell BiologyDocument8 pagesThe Nervous System Organization: Jennifer Carbrey Ph.D. Department of Cell BiologySherida GibbsNo ratings yet
- DiscussionDocument3 pagesDiscussionSherida GibbsNo ratings yet
- Doing Together What We Would Not Do Alone: Social PsychologyDocument8 pagesDoing Together What We Would Not Do Alone: Social PsychologySherida GibbsNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System Action Potentials: Jennifer Carbrey Ph.D. Department of Cell BiologyDocument9 pagesThe Nervous System Action Potentials: Jennifer Carbrey Ph.D. Department of Cell BiologySherida GibbsNo ratings yet
- H-P Axis-Thyroid: Learning ObjectivesDocument9 pagesH-P Axis-Thyroid: Learning ObjectivesSherida GibbsNo ratings yet
- Week2-4pptphysiology Nervous System Organisation 2Document9 pagesWeek2-4pptphysiology Nervous System Organisation 2Sherida GibbsNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Risk Rate Measures Cohort Studies PDFDocument3 pages3.2 Risk Rate Measures Cohort Studies PDFSherida GibbsNo ratings yet
- The Female Reproductive System - 1Document9 pagesThe Female Reproductive System - 1Sherida GibbsNo ratings yet
- Jennifer Carbrey Ph.D. Department of Cell Biology: Image by OCAL,, Public DomainDocument11 pagesJennifer Carbrey Ph.D. Department of Cell Biology: Image by OCAL,, Public DomainSherida GibbsNo ratings yet
- Types of Erosion:: River ProcessesDocument3 pagesTypes of Erosion:: River ProcessesSherida GibbsNo ratings yet
- Jennifer Carbrey Ph.D. Department of Cell BiologyDocument13 pagesJennifer Carbrey Ph.D. Department of Cell BiologySherida GibbsNo ratings yet
- Digestive System - 4: Learning ObjectivesDocument4 pagesDigestive System - 4: Learning ObjectivesSherida GibbsNo ratings yet
- Reading4-3-Plous The Psy of Prejudice, Stereotyping and DiscriminationDocument49 pagesReading4-3-Plous The Psy of Prejudice, Stereotyping and DiscriminationSherida GibbsNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Function Tests and Alveolar Ventilation: Introductory Human PhysiologyDocument3 pagesPulmonary Function Tests and Alveolar Ventilation: Introductory Human PhysiologySherida GibbsNo ratings yet
- Social Psychology: Lecture 2.8: The Ins and Outs of Social InfluenceDocument2 pagesSocial Psychology: Lecture 2.8: The Ins and Outs of Social InfluenceSherida GibbsNo ratings yet
- Week3-6pptcaridac MuscleDocument7 pagesWeek3-6pptcaridac MuscleSherida GibbsNo ratings yet
- Types of Erosion:: River ProcessesDocument3 pagesTypes of Erosion:: River ProcessesSherida GibbsNo ratings yet
- Social Psychology: Lecture 6.1: Bystander Intervention in EmergenciesDocument2 pagesSocial Psychology: Lecture 6.1: Bystander Intervention in EmergenciesSherida GibbsNo ratings yet
- Title: Plan and Design AimDocument9 pagesTitle: Plan and Design AimSherida GibbsNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Quarter 1 Module 1 V7Document41 pagesEarth Science Quarter 1 Module 1 V7Angela RiegoNo ratings yet
- Wind Tunnel DataDocument4 pagesWind Tunnel DataNdumiso DlaminiNo ratings yet
- Cambridge-English-Proficiency-Sample-Paper-2-Reading-And-Use-Of-English v2 PDFDocument17 pagesCambridge-English-Proficiency-Sample-Paper-2-Reading-And-Use-Of-English v2 PDFMonseGarcíaEstrada0% (1)
- Mod 2 2 Protection ExternalDocument41 pagesMod 2 2 Protection ExternaldcsamaraweeraNo ratings yet
- Ki Chankim2009Document4 pagesKi Chankim2009reddy venkata krishnaNo ratings yet
- Gas Reservoir EngineeringDocument41 pagesGas Reservoir Engineeringxion_mew2100% (2)
- Periodic Exam 1Document7 pagesPeriodic Exam 1Inah RamosNo ratings yet
- Violin Modes in The S1 DataDocument5 pagesViolin Modes in The S1 DataChema MruaNo ratings yet
- Course Planner Pratham XIDocument2 pagesCourse Planner Pratham XIShivang 10FNo ratings yet
- Project MphilDocument64 pagesProject Mphilrameshmaths_aplNo ratings yet
- Physics 133: Tutorial Week 4 Ohm's Law, Electrical Power, Emf and Internal ResistanceDocument5 pagesPhysics 133: Tutorial Week 4 Ohm's Law, Electrical Power, Emf and Internal ResistanceAmrendra KumarNo ratings yet
- AlternatorsDocument43 pagesAlternatorsPauline SilvaNo ratings yet
- 1 - 7-PDF - Thermodynamics (Red Book) 2Document1 page1 - 7-PDF - Thermodynamics (Red Book) 2PranayNo ratings yet
- CT Science BJU Chapter 8 and 9Document3 pagesCT Science BJU Chapter 8 and 9Chelsea Sharon Miranda SiregarNo ratings yet
- A Level Applied Paper 3B Mechanics M16Document7 pagesA Level Applied Paper 3B Mechanics M16Stefan AlbertNo ratings yet
- UEET Assignment #3: I LT F WDocument13 pagesUEET Assignment #3: I LT F Wsophro syneNo ratings yet
- Science: Construction of The Gravito-Magnetic Device (GMD)Document3 pagesScience: Construction of The Gravito-Magnetic Device (GMD)rooNo ratings yet
- FT8260 1x AN Rev0.81Document15 pagesFT8260 1x AN Rev0.81Enéas BaroneNo ratings yet
- Determination of The Optic Sign of Biaxial MineralsDocument2 pagesDetermination of The Optic Sign of Biaxial MineralsAlexander Simatupang GeoNo ratings yet
- D7012 19774Document9 pagesD7012 19774christian moncayoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - IntroductionDocument33 pagesUnit 1 - IntroductionRavi KantNo ratings yet
- Phase Analysis: Making Vibration Analysis Easier: Tony DematteoDocument11 pagesPhase Analysis: Making Vibration Analysis Easier: Tony DematteoSrinivas BudatiNo ratings yet
- May 18 Physics English Markscheme PDFDocument15 pagesMay 18 Physics English Markscheme PDFuwuNo ratings yet
- Conduction Convection RadiationDocument24 pagesConduction Convection RadiationFlorinel BaietelNo ratings yet
- B9 - High Power Contactors (Ref) enDocument44 pagesB9 - High Power Contactors (Ref) enPablo Andres Jara GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Solid State Sintering 2009 Balakrishna PalankiDocument21 pagesSolid State Sintering 2009 Balakrishna PalankiBalakrishna PalankiNo ratings yet
- Elasticity and FlextureDocument37 pagesElasticity and FlextureArif SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Online Class - XII/2077Document9 pagesOnline Class - XII/2077zoomNo ratings yet
- Ikoku Ch1 Eng 01 52 EstimReservDocument37 pagesIkoku Ch1 Eng 01 52 EstimReservVictor Gomez100% (1)
- June 2012 Edexcel Chemistry Unit 1Document24 pagesJune 2012 Edexcel Chemistry Unit 1EzioAudi77No ratings yet