Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Part3 PDF
Uploaded by
Educational ReformsOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Part3 PDF
Uploaded by
Educational ReformsCopyright:
Available Formats
Philadelphia University
Faculty of Engineering
Communication and Electronics Engineering
MOBILE
COMMUNICATIONS
(650539)
Part 3
Dr. Omar R Daoud ١
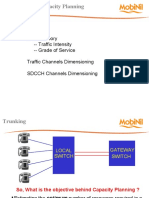
Trunking and Grade Services
The accommodation of larger number of
users in a limited radio spectrum denoted
by trunking
a large number of users share a pool of available channels
(relatively small number of channels)
Trade off between the number of available
telephone circuits (in the telephony system)
and the likelihood of a particular users
finding that no circuits on the peak time
Dr. Omar R Daoud ٢
Trunking and Grade Services
What will happen to the user if all
channels are in use ?? (in some systems a
queue may be used to solve the blocking or
denying process)
In the 19th century, Erlang (Danish
mathematician) study how a large number
of population could be accommodated
by a limited number of services (today its
known by the measure of traffic intensity)
Dr. Omar R Daoud ٣
Trunking and Grade Services
The Grade of Service (GOS) is a measure
of the ability of a user to access a trunked
system during the busiest hour
By specifying a desired likelihood of a user
obtaining channel access given a specific
number of channels available in the system
(It’s the benchmark used to design the performance of a
particular trunked system)
It’s the designer’s job to estimate the max
required capacity to allocate the proper
number of channels to meet the GOS
Dr. Omar R Daoud ٤
Trunking and Grade Services
GOS is typically given as the likelihood
that a call is blocked or experiencing a
delay greater than a certain queuing
delay time
Au is defined as a traffic intensity and
is given by
Au= λH where λ is the average number of
call requests per unit time for each user, H is the
average duration of a call
Dr. Omar R Daoud ٥
Trunking and Grade Services
The total offered traffic intensity for U
users is
A= AuU
In a C channel trucked system, the traffic
intensity per channel, Ac, is given by
Ac = A/C
The max possible carried traffic is the total
number of channels, C, in Erlangs
Dr. Omar R Daoud ٦
Trunking and Grade Services
Some needed definitions
- Set-up time: the time required to allocate a trunked radio channel to
a requesting user
- Holding time: call which cannot be completed at time of request,
due to congestion (lost calls)
- Traffic intensity: measure of channel time utilisation, which is the
average channel occupancy measured in Erlang. This is a
dimensionless quantity and may be used to measure the time
utilisation of single or multiple channels, A
- Load: traffic intensity across the entire trunked radio system,
measured in Erlang
- GOS: A measure of congestion which is specified as the probability
of a call blocked or a call being delayed beyond a certain amount of
time
- Request Rate: the average number of call requests per unit time
Dr. Omar R Daoud ٧
Trunking and Grade Services
AMPS system is designed for a GOS of
2% blocking
Tow types of trunked systems
- offers no queuing for call requests (no set up time and
given immediate access to a channel if one is available or blocked if
no available ones )
* assume infinite number of users
* memoryless arrivals of requests
* exponentially distributed probability of a user occupying a channel
(longer calls are less to happened)
* a finite number of channels are available in the pool
Dr. Omar R Daoud ٨
Trunking and Grade Services
Erlang B formula determine the probability
that a call is blocked and is a measure of
the GoS for a trunked system (which provides
no queuing for blocked call)
Pr( Blocking ) GoS
A / C! C
C 1
A / k!
k 0
k
where C is the number of trunked channels offered by a radio system
A is the total offered traffic
Dr. Omar R Daoud ٩
Trunking and Grade Services
Erlang B chart
Dr. Omar R Daoud ١٠
Trunking and Grade Services
Tow types of trunked systems
the second type is one in which a queue is
provided to hold calls which are blocked
(called by blocked calls delayed, Erlang C)
AC
Pr(delay 0)
C 1 k
AC C!1 A
A
C k 0 k!
Dr. Omar R Daoud ١١
Trunking and Grade Services
Erlang C chart
Dr. Omar R Daoud ١٢
Trunking and Grade Services
Tow types of trunked systems
The GoS of a trunked system where blocked calls are
delayed is given by
( ( C A) t )
0) e
H
Pr(delay t ) Pr(delay
The average delay D for all calls in a
queued system is given by
D = Pr(delay>0) [H/(C-A)]
Dr. Omar R Daoud ١٣
Trunking and Grade Services
Ex.1
Dr. Omar R Daoud ١٤
Trunking and Grade Services
Ex.1
Dr. Omar R Daoud ١٥
Trunking and Grade Services
Ex.1
Dr. Omar R Daoud ١٦
Trunking and Grade Services
Ex.1
Dr. Omar R Daoud ١٧
Trunking and Grade Services
Ex.1
Dr. Omar R Daoud ١٨
Trunking and Grade Services
Ex.2
Dr. Omar R Daoud ١٩
Trunking and Grade Services
Ex.2
Dr. Omar R Daoud ٢٠
You might also like
- Learning Morse Code As A LanguageDocument16 pagesLearning Morse Code As A LanguageAhmad Mostofa TaqyNo ratings yet
- 004Document61 pages004Илья НикульшинNo ratings yet
- Radio Control for Model Ships, Boats and AircraftFrom EverandRadio Control for Model Ships, Boats and AircraftRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Typical Radio ProblemsDocument97 pagesTypical Radio ProblemsBeedjoNo ratings yet
- Explorer 5 EX-528A ManualDocument78 pagesExplorer 5 EX-528A ManualWijang PrastowoNo ratings yet
- ECS455 - 2 - 4 - Erlang B Formula PDFDocument22 pagesECS455 - 2 - 4 - Erlang B Formula PDFArdiyanSatriyawanNo ratings yet
- Radar SpectrumDocument18 pagesRadar SpectrumSry SantosNo ratings yet
- Mobile Communications (650539) : Communication and Electronics EngineeringDocument20 pagesMobile Communications (650539) : Communication and Electronics EngineeringOrpheo NgadimanNo ratings yet
- Rohini 85782880952Document6 pagesRohini 85782880952PrathmeshNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8: Frequency Reuse Concepts Trunking and Grade of Service (Gos)Document5 pagesLecture 8: Frequency Reuse Concepts Trunking and Grade of Service (Gos)Orpheo NgadimanNo ratings yet
- CHP 2 Part 4: Trunking and Grade of Service (GOS)Document10 pagesCHP 2 Part 4: Trunking and Grade of Service (GOS)abdul wakeelNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Lecture: - Trunking Theory - Grade of Service - ExamplesDocument15 pagesOverview of The Lecture: - Trunking Theory - Grade of Service - ExamplesAli AL-KHAYYATNo ratings yet
- Design of Subscriber LoopDocument36 pagesDesign of Subscriber LoopKier Jexter BagunuNo ratings yet
- Maintenance of Communication SystemsDocument14 pagesMaintenance of Communication Systemsفاضل سجادNo ratings yet
- MOB3Document8 pagesMOB3Paterson NguepiNo ratings yet
- Expt 3 - Trunking Theory - StuDocument7 pagesExpt 3 - Trunking Theory - StuXavierNo ratings yet
- ECS455 - 2 - 4 - Erlang BDocument17 pagesECS455 - 2 - 4 - Erlang Bmahamd saiedNo ratings yet
- 5.cell Splitting, Sectoring, and MicrocellDocument21 pages5.cell Splitting, Sectoring, and MicrocellAnkit KumarNo ratings yet
- 6 Telecommunications TrafficDocument21 pages6 Telecommunications TrafficMitzOsorioNo ratings yet
- Wireless Chapter 2Document131 pagesWireless Chapter 2Babal YepaNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 9Document5 pagesChapter1 9Sompal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Telephone Losses: Net LossDocument47 pagesTelephone Losses: Net LossRaldge ANo ratings yet
- GSM Network Capacity Planning: TrunkingDocument41 pagesGSM Network Capacity Planning: TrunkingZoheir KacimiNo ratings yet
- Wireless Slides CH 03Document59 pagesWireless Slides CH 03Nishi ShahNo ratings yet
- Limitations of Conventional Mobile Systems Over Cellular Mobile SystemDocument17 pagesLimitations of Conventional Mobile Systems Over Cellular Mobile SystemSrinadh ShaikNo ratings yet
- Wireless Networks - CS718 Power Point Slides Lecture 14Document27 pagesWireless Networks - CS718 Power Point Slides Lecture 14asimnaqvi2003No ratings yet
- Lecture 5 6 7 Winter 2023 2024Document26 pagesLecture 5 6 7 Winter 2023 2024ritamonde4No ratings yet
- GSM Network Capacity Planning: TrunkingDocument50 pagesGSM Network Capacity Planning: TrunkingsaeedfsaeedNo ratings yet
- High Speed Underwater Accoustic CommunicationDocument4 pagesHigh Speed Underwater Accoustic CommunicationShagunChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Simulation of The Aeronautical Radio Channel For Telemetry ApplicationsDocument10 pagesSimulation of The Aeronautical Radio Channel For Telemetry ApplicationsgoliatcarroNo ratings yet
- Intersection Analysis PDFDocument64 pagesIntersection Analysis PDFAmar Al ChaabanNo ratings yet
- Homework 3Document2 pagesHomework 3Miew KookkookNo ratings yet
- ECS455 Chapter 2: Cellular SystemsDocument24 pagesECS455 Chapter 2: Cellular SystemsIftikhar JavedNo ratings yet
- COMunicacion InalambricaDocument6 pagesCOMunicacion InalambricaJc xDNo ratings yet
- Medium Access: Basics of Cellular CommunicationDocument21 pagesMedium Access: Basics of Cellular Communicationਮ੍ਰਿਦੁਲਾ ਬਾਂਸਲNo ratings yet
- WC MP Mod1Document80 pagesWC MP Mod1Arham SyedNo ratings yet
- Lec 4Document24 pagesLec 4Dhruv WaliaNo ratings yet
- Cellular ConceptDocument27 pagesCellular ConceptAsit Panda100% (2)
- Dr.M.sushanth Babu - Cellular and Mobile CommunicationsDocument133 pagesDr.M.sushanth Babu - Cellular and Mobile CommunicationsSushanth Babu100% (1)
- Capacity Planning 00'1Document3 pagesCapacity Planning 00'1kkmNo ratings yet
- Planning For Radio Coverage & Capacity: Security LevelDocument18 pagesPlanning For Radio Coverage & Capacity: Security LevelRasyidi UsmanNo ratings yet
- HW 2Document2 pagesHW 2PankajNo ratings yet
- Switching System:: Give The Classification of Switching Systems?Document54 pagesSwitching System:: Give The Classification of Switching Systems?Jeet BarmanNo ratings yet
- Cellular Mobile System FundamentalDocument17 pagesCellular Mobile System Fundamentalmahfuz.jkkniu13No ratings yet
- Module 3 Digital Switching SystemDocument76 pagesModule 3 Digital Switching Systemface D&DNo ratings yet
- Mobile Communication Systems: Part III-Traffic EngineeringDocument50 pagesMobile Communication Systems: Part III-Traffic EngineeringmuralitejasNo ratings yet
- Coverage Session SlidesDocument29 pagesCoverage Session SlidesJayakrishnan MarangattNo ratings yet
- Green Wireless Communications: A Time-Reversal ParadigmDocument13 pagesGreen Wireless Communications: A Time-Reversal ParadigmyoumnizNo ratings yet
- Influence of Velocity On The Handover Delay Associated With A Radio-Signal-Measurement-based Handover DecisionDocument5 pagesInfluence of Velocity On The Handover Delay Associated With A Radio-Signal-Measurement-based Handover DecisionBui ThanhThanhNo ratings yet
- AWSN MaterialsDocument61 pagesAWSN MaterialsMadhavan SamNo ratings yet
- Telecom Principles GOSDocument30 pagesTelecom Principles GOSmoshesas100% (1)
- WC Assignment 3 RahmatDocument10 pagesWC Assignment 3 RahmatRahmatullah MuhammadiNo ratings yet
- Wireless Communication Assignment - 2022Document5 pagesWireless Communication Assignment - 2022Yakob Yeme LijNo ratings yet
- Telephony 3Document120 pagesTelephony 3mc chesterNo ratings yet
- 8.carried Traffic Is The Volume of Traffic ActuallyDocument2 pages8.carried Traffic Is The Volume of Traffic ActuallyAgung HaryantoNo ratings yet
- 2 Wireless Communications RFDocument79 pages2 Wireless Communications RFCherukuri BharaniNo ratings yet
- Determination of Traffic Load and Traffic Performance Parameters in Mobile Communication in NigeriaDocument6 pagesDetermination of Traffic Load and Traffic Performance Parameters in Mobile Communication in NigeriaYashika choudharyNo ratings yet
- Final Ofdm PPT 3Document36 pagesFinal Ofdm PPT 3Pankaj AroteNo ratings yet
- Multiple AccessDocument5 pagesMultiple AccessJyotiSenguptaNo ratings yet
- MIcrocell Zone OnceptDocument6 pagesMIcrocell Zone OnceptNaveed Ali100% (1)
- Software Radio: Sampling Rate Selection, Design and SynchronizationFrom EverandSoftware Radio: Sampling Rate Selection, Design and SynchronizationNo ratings yet
- Research Proposal: Bakhtiar AliDocument1 pageResearch Proposal: Bakhtiar AliEducational ReformsNo ratings yet
- Comsats: Institute of Information Technology Principle Seat IslamabadDocument2 pagesComsats: Institute of Information Technology Principle Seat IslamabadEducational ReformsNo ratings yet
- Reference AkhlaqalikhanDocument1 pageReference AkhlaqalikhanEducational ReformsNo ratings yet
- To Whom It May Concern: With Warm RegardsDocument1 pageTo Whom It May Concern: With Warm RegardsEducational ReformsNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Raza Ahmad KhanDocument5 pagesMuhammad Raza Ahmad KhanEducational ReformsNo ratings yet
- Abdul Rauf Khan: ObjectiveDocument2 pagesAbdul Rauf Khan: ObjectiveEducational ReformsNo ratings yet
- Context Clues Multiple Choice ExerciseDocument14 pagesContext Clues Multiple Choice ExerciseCharlyn GanzonNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: Vhf/Uhf FM TransceiverDocument52 pagesService Manual: Vhf/Uhf FM TransceivercarlosNo ratings yet
- Basic Knowledge About Radio Network: Viettel Networks Corporation - O0oDocument34 pagesBasic Knowledge About Radio Network: Viettel Networks Corporation - O0ovilaphong vongphachithNo ratings yet
- Reflector Antenna Group Simulation ReportDocument13 pagesReflector Antenna Group Simulation ReportNaman BairagiNo ratings yet
- User'S Manual: UHF/VHF Dual Band RadioDocument19 pagesUser'S Manual: UHF/VHF Dual Band Radiofreddy6188No ratings yet
- Cell Phone Jammer: By:-Ganesh Pathak Pallavi Mantri Rohit Patil Pawan KumarDocument16 pagesCell Phone Jammer: By:-Ganesh Pathak Pallavi Mantri Rohit Patil Pawan KumarvishalsinghvivekNo ratings yet
- Application VT1005 PW8001 Solar E1 220829Document3 pagesApplication VT1005 PW8001 Solar E1 220829Joel DsouzaNo ratings yet
- VFD-EMI ProblemsDocument5 pagesVFD-EMI ProblemsBelal AmeenNo ratings yet
- Ic 2730a ManualDocument53 pagesIc 2730a ManualFrancisco GomesNo ratings yet
- Optimizer® Panel Dual Polarized Antenna, 790-960, 65deg, 17.8dbi, 2.6M, Vet, 0-10degDocument2 pagesOptimizer® Panel Dual Polarized Antenna, 790-960, 65deg, 17.8dbi, 2.6M, Vet, 0-10degCarlos Limonchi CoronelNo ratings yet
- Garmin GFC 500 Pa28rt-201t Flight Supplement 190-02291-50 - 03Document44 pagesGarmin GFC 500 Pa28rt-201t Flight Supplement 190-02291-50 - 03ttNo ratings yet
- ChinaSat 10 at 110.5°E - LyngSatDocument1 pageChinaSat 10 at 110.5°E - LyngSatRusdi AbdullahNo ratings yet
- On The Machine Learning-Based Smart Beamforming For Wireless Virtualization With Large-Scale MIMO SystemDocument11 pagesOn The Machine Learning-Based Smart Beamforming For Wireless Virtualization With Large-Scale MIMO Systemdtvt2006No ratings yet
- USER Manual enDocument15 pagesUSER Manual enGuljar AliNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: Colour TelevisionDocument32 pagesService Manual: Colour Televisionsegundo rodrigo barrera lopezNo ratings yet
- GRADE XII - 2023-24 - Holiday Assignment PDFDocument1 pageGRADE XII - 2023-24 - Holiday Assignment PDFSumretha SrihariNo ratings yet
- Archer Semiconductor Reference Guide 1988Document134 pagesArcher Semiconductor Reference Guide 1988xigajoj513No ratings yet
- Non Orthogonal Multiple Access For VLCDocument4 pagesNon Orthogonal Multiple Access For VLCcharu dattaNo ratings yet
- Service Center Repairs We Buy Used Equipment: InstraDocument5 pagesService Center Repairs We Buy Used Equipment: InstranorbertscribdNo ratings yet
- Sukkur - Data AIPDocument6 pagesSukkur - Data AIPWorld VideosNo ratings yet
- Design Wideband RF Imp TransformersDocument16 pagesDesign Wideband RF Imp TransformersdwisselNo ratings yet
- DUAL B - Product Catalogue 2021Document49 pagesDUAL B - Product Catalogue 2021Hậu NguyễnNo ratings yet
- DX-790-960-65-16.5i-M Model: A79451600v02: Antenna SpecificationsDocument2 pagesDX-790-960-65-16.5i-M Model: A79451600v02: Antenna SpecificationsakiselNo ratings yet
- Unit4 WCDocument53 pagesUnit4 WCManimegalaiNo ratings yet
- 4 - Digital ModulationDocument30 pages4 - Digital ModulationJin MacaranasNo ratings yet
- Multichannel IR Remote Control For Home OfficeDocument7 pagesMultichannel IR Remote Control For Home OfficeKamlesh Motghare100% (1)
- 3G2080 TL2803G Reference-Manual-Extended R001 enDocument52 pages3G2080 TL2803G Reference-Manual-Extended R001 enDragus IonelNo ratings yet