Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Actual Biology Notes
Uploaded by
Nadji Gadji-BaxisOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Actual Biology Notes
Uploaded by
Nadji Gadji-BaxisCopyright:
Available Formats
Biology notes:
Introduction to cells:
Cell- The smallest, basic unit if life that is responsible for all of life’s
processes. Often referred as the living organisms’ building block. The cell is also
referenced as a room, compartment.
How does a cell look like a room?
1. For example, furniture in a room can be the organelles of cells.
2. The walls and the roof of the room can be cell wall.
3. The space in the room can be the cytoplasm.
If something is made of cells, then it is a living thing.
Bacteria is a living thing but, viruses are not living things.
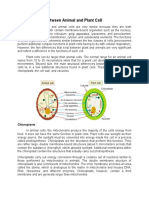
The main difference between plant and animal cells is that the animal cells
don’t have cell walls.
There are 2 types of cells (so far):
1. Eukaryotic cells
2. Prokaryotic cells
Prokaryotic cells- Unicellular cells that don’t have organelles or other
membrane-bound structure. These types of cells do not have a nucleus, but
instead have a nucleoid. Prokaryotic cells can’t be multicellular.
Unicellular- Consisting of only one cell. (bacteria, yeast, paramecium,
amoeba)
Eukaryotic cells- Multicellular organisms whose cells have a nucleus
enclosed within a nuclear envelope.
Multicellular- Consisting more than one cell. (animals, plants)
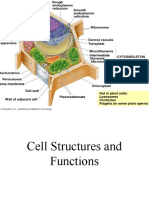
Organelles- Membrane enclosed structure inside a cell with a particular
function.
Compartments= organelles.
Cytoplasm- It is a jellylike substance that makes up inside of a cell. The
organelles of eukaryotic cells are contained in the cytoplasm.
Cell wall- A structural layer surrounding plant cells that is made of cellulose. It
provides cells with structural support and protection. It doesn’t count as an
organelle because it’s just outside of the cell membrane and it’s not a
subcellular structure.
Vacuole- A space in a cell, surrounded by a membrane that is containing a
solution and a cell sap.
Animal cells have a smaller membrane-bound space called vesicles. These
vesicles contain food or water.
Chloroplast- a plastid in green plant cells which contains chlorophyll and in
which photosynthesis takes place. There aren’t any chloroplasts in animal cells.
Chloroplasts contain starch grains, which animal cells don’t. Instead they have
a similar substance called glycogen.
Chlorophyll- A green pigment inside a chloroplast that absorbs energy from
sunlight and makes it food for the plant. This process is called photosynthesis.
Nucleus- A part of the eukaryotic cell where genetic information is stored.
They contain chromosomes in which the information is kept, and they are
made from DNA.
Mitochondria- Mitochondria is the powerhouse of a cell. They are found in
all cells except prokaryotic cells. Inside them the process of aerobic respiration
happens. This is when oxygen is used to release energy from glucose.
Ribosome- A sphere shaped structure in the cytoplasm that is composed of
RNA and protein.
Differences of plant and animal cells:
1. Plant cells have cell wall when the animal cells don’t.
2. Plant cells often have chloroplasts containing chlorophyll, but animal cell
don’t.
3. Plant cells often have large vacuoles containing cell sap, but animal cells
only have small vacuoles and don’t have cell sap.
4. Plant cells have starch grains when animal cells only have glycogen.
5. Plant cells are often in a regular shape when animal cells are in an
irregular shape.
Micro- Means small. (milli, micro, nano, pico, femto)
Macro- Means big. (kilo, mega, giga, tera)
Milli= 10-3 (1000 times less)
Micro= 10-6 (1,000,000 times less)
We also use this mark for micro (µ)
Nano= 10-9 (a billion times less)
Kilo= 103 (1000 times more)
Mega= 106 (1,000,000 times more)
Giga= 109 (a billion times more)
Red blood cell= 7.5µm
White blood cell= 12µm
Human egg cell= 140µm
Smooth muscle cell= 200µm
Virus cell= approx. 150µm
Levels of organization:
Cell< Tissue< Organ< System< Organism
Tissue- A group of cells that specialize in the same activity.
Organ- A part of a system that has a specific job which is made of a group
of tissues.
Organ system- A group of organs that work together to perform a specific
function.
Stem cells- Stem cells- the kind of cells that have the potential to become
anything like brain cells, nerve cells, muscle cells and sometimes they can
recover damaged tissues. Stem cells do not specialize.
Specialization- The structural adaptation of some body part for a particular
function.
There are 3 domains of life:
1. Eukarya (Plants, animals, fungi, Protista)
2. Prokaryotes (Bacteria)
3. Archaea
You might also like
- Animal and Plant CellsDocument14 pagesAnimal and Plant Cellslea a delgadoNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology NotesDocument18 pagesCell Biology NotesZara100% (2)
- Nutrition, Metabolism, and Body Temperature RegulationDocument11 pagesNutrition, Metabolism, and Body Temperature RegulationSNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Their FunctionsDocument9 pagesCell Parts and Their FunctionsMlshin LaoNo ratings yet
- Test Yourself On Enzymes Scoring GuidelinesDocument15 pagesTest Yourself On Enzymes Scoring GuidelinesDheepikha ShivakumarNo ratings yet
- MITOCHONDRIADocument3 pagesMITOCHONDRIAAbid RazaNo ratings yet
- The Difference Between Animal and Plant Cell: ChloroplastsDocument6 pagesThe Difference Between Animal and Plant Cell: ChloroplastsYukiNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument25 pagesUntitledlgNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellsDocument3 pagesAnimal and Plant CellsBeth AlcontinNo ratings yet
- The Cell: Eukaryotic Cells and Prokaryotic CellsDocument13 pagesThe Cell: Eukaryotic Cells and Prokaryotic CellsDiane CastroNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument31 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsKomalesh TheeranNo ratings yet
- DNA Extraction and Gel ElectrophoresisDocument31 pagesDNA Extraction and Gel Electrophoresisanimathz0% (1)
- Earth & Life ScienceDocument14 pagesEarth & Life ScienceYhazmeen Lily LibrodoNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument29 pagesCell Structure and Functionapi-217439283No ratings yet
- What Is A Cell? Describe The Functions of OrganellesDocument18 pagesWhat Is A Cell? Describe The Functions of Organellestdukes546No ratings yet
- 10 CMH Human and Social Biology: CellsDocument28 pages10 CMH Human and Social Biology: CellsScience,Physical Education And Sports VideosNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts & Functions PRSNTTN 20Document136 pagesCell Parts & Functions PRSNTTN 20Scar ShadowNo ratings yet
- O Level Bio - Chapter 1 - CellsDocument10 pagesO Level Bio - Chapter 1 - CellsTakudzwa ZvidzaNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument7 pagesAnimal CellLezircYojDapmalNo ratings yet
- CellDocument23 pagesCellridabatool151214No ratings yet
- Cell (Biology) : Structures Outside The Cell WallDocument5 pagesCell (Biology) : Structures Outside The Cell WallAsad MasoodNo ratings yet
- CellDocument5 pagesCellapi-267979304No ratings yet
- Gen Bio w1 SummaryDocument5 pagesGen Bio w1 Summaryyxcz.rzNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument26 pagesCellsNairita LetipoNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Science Page 1 NotesDocument3 pagesGrade 10 Science Page 1 Notessrossor6No ratings yet
- Bombay & Romero - AIL 2Document7 pagesBombay & Romero - AIL 2aira bombayNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument6 pagesThe CellshaniahNo ratings yet
- The Basic Unit of Life: ObjectiveDocument4 pagesThe Basic Unit of Life: ObjectiveHershell ContaNo ratings yet
- Hannah Belle Catharine M. Malinis Bsn1B: Assignment No. 1 - Cell OrganizationDocument5 pagesHannah Belle Catharine M. Malinis Bsn1B: Assignment No. 1 - Cell OrganizationAngelo AbulenciaNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument10 pagesBiologyalmahaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Bio NotesDocument5 pagesChapter 2 Bio NotesArabella ShepherdNo ratings yet
- Diagram of Plant CellDocument4 pagesDiagram of Plant CellekongNo ratings yet
- Why Is It Important To Learn About CellsDocument1 pageWhy Is It Important To Learn About Cellsrambo0% (1)
- What A Middle School 7 Grade Science Student Should Know: About ProtistsDocument3 pagesWhat A Middle School 7 Grade Science Student Should Know: About Protistsapi-300685908No ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Cell: - Powerpoint Presentation of Group 1Document20 pagesPlant and Animal Cell: - Powerpoint Presentation of Group 1Hanz Nujapa BalistoyNo ratings yet
- Science Notes: Plant and Animal CellDocument4 pagesScience Notes: Plant and Animal CellRosalinda LappayNo ratings yet
- Biology Handouton CellsDocument2 pagesBiology Handouton CellsAbigail JohnNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Their FunctionsDocument3 pagesCell Parts and Their FunctionsMark MagatNo ratings yet
- Biology Study GuideDocument35 pagesBiology Study GuideJuliana Gortaire EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Bio NotesDocument43 pagesBio NotesKyi ThitsarNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell - The Definitive Guide Biology DictiDocument8 pagesAnimal Cell - The Definitive Guide Biology DictiKolade YousuffNo ratings yet
- Byjus Com Biology Cell OrganellesDocument26 pagesByjus Com Biology Cell OrganellesᏗᏕᎥᎷ ᏗᏝᎥNo ratings yet
- Intro To Cells 2017Document38 pagesIntro To Cells 2017YHTAK1792No ratings yet
- 1C-Tabugoc - LA2 Plant CellDocument5 pages1C-Tabugoc - LA2 Plant CellClint Jhun TabugocNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Cell Parts and FunctionDocument60 pagesLecture 3 Cell Parts and FunctionEsther Suan-LancitaNo ratings yet
- Cell - Structure and FunctionsDocument6 pagesCell - Structure and Functionssidhantm823No ratings yet
- Introduction To Living OrganismsDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Living OrganismsSabita SinghNo ratings yet
- Student Booklet 8 Sci Student Activiry BookletDocument14 pagesStudent Booklet 8 Sci Student Activiry Bookletthe.efroNo ratings yet
- Plant Cell and Animal CellDocument12 pagesPlant Cell and Animal CellKimverheart Dennisse NavalNo ratings yet
- The CellsDocument4 pagesThe CellsSlaheddineNo ratings yet
- All About Animal Cells: Key TakeawaysDocument8 pagesAll About Animal Cells: Key TakeawaysRishikesh BhintadeNo ratings yet
- What Is Cytology? What Is Cell?Document3 pagesWhat Is Cytology? What Is Cell?Elcee QuindozaNo ratings yet
- The Cell: Types of CellsDocument4 pagesThe Cell: Types of CellsAllen MurilloNo ratings yet
- Cells - The Building Blocks of LifeDocument2 pagesCells - The Building Blocks of LifeMuhammad QasimNo ratings yet
- The Cell: An Internet Laboratory On The Cell, Created by Wendy M. Rounds 5/3/00Document24 pagesThe Cell: An Internet Laboratory On The Cell, Created by Wendy M. Rounds 5/3/00zalifah74No ratings yet
- Plasma Membrane: Hydro PhilicDocument8 pagesPlasma Membrane: Hydro PhilicAlthea Junsan BernabeNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal CellDocument7 pagesPlant and Animal CellHera Lopez100% (1)
- CellsDocument4 pagesCellsKristelle Dae PagunsanNo ratings yet
- Science RevisionDocument38 pagesScience Revisiongamerboy1234567890000No ratings yet
- Plant Cells PDFDocument7 pagesPlant Cells PDFMarcus Ben AlgerreNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures and FunctionsDocument18 pagesCell Structures and FunctionsAleia Trixie100% (1)
- Cell and TissueDocument10 pagesCell and TissueCarl SantosNo ratings yet
- Bio and PhysicsDocument25 pagesBio and Physicsyasser yousriNo ratings yet
- Note-Taking StrategiesDocument1 pageNote-Taking StrategiesNadji Gadji-BaxisNo ratings yet
- HW1Document2 pagesHW1Nadji Gadji-BaxisNo ratings yet
- HomeworkDocument1 pageHomeworkNadji Gadji-BaxisNo ratings yet
- Eng HW 23Document1 pageEng HW 23Nadji Gadji-BaxisNo ratings yet
- FPSMonitorDocument10 pagesFPSMonitorStoian ValentinNo ratings yet
- Snipping Tool On Windows or Shift, Command, and 4 Keyboard Shortcut On MacDocument5 pagesSnipping Tool On Windows or Shift, Command, and 4 Keyboard Shortcut On MacNadji Gadji-BaxisNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: Sevinj AhmadovaDocument16 pagesEnzymes: Sevinj AhmadovaNadji Gadji-BaxisNo ratings yet
- Instructor: Telman Askeraliyev DATA: 07 Sept-14 Sept Lesson: W1-L1 Topic: Introductory CourseDocument2 pagesInstructor: Telman Askeraliyev DATA: 07 Sept-14 Sept Lesson: W1-L1 Topic: Introductory CourseNadji Gadji-BaxisNo ratings yet
- Instructor: Ruhiyya Gafarli Level Grade: 10th Topic Name: The Law of SinesDocument10 pagesInstructor: Ruhiyya Gafarli Level Grade: 10th Topic Name: The Law of SinesNadji Gadji-BaxisNo ratings yet
- 10 B3 Teachers' List: Kamran Mammadli (Chemistry)Document1 page10 B3 Teachers' List: Kamran Mammadli (Chemistry)Nadji Gadji-BaxisNo ratings yet
- 1.the Graph of A Function Is Given - Decide Whether It Is Even, Odd, or NeitherDocument3 pages1.the Graph of A Function Is Given - Decide Whether It Is Even, Odd, or NeitherNadji Gadji-BaxisNo ratings yet
- ответыDocument5 pagesответыNadji Gadji-BaxisNo ratings yet
- Cartographic Projection and DistortionsDocument18 pagesCartographic Projection and DistortionsNadji Gadji-BaxisNo ratings yet
- Animation Practice Document Aiza Malik TransitionsDocument6 pagesAnimation Practice Document Aiza Malik Transitionshuma mirzaNo ratings yet
- Physics - Porocity Measure - Nijat Najafov 10B3Document17 pagesPhysics - Porocity Measure - Nijat Najafov 10B3Nadji Gadji-BaxisNo ratings yet
- Reading Materials (L02 - L08)Document40 pagesReading Materials (L02 - L08)Nadji Gadji-BaxisNo ratings yet
- Category of GeograhpyDocument2 pagesCategory of GeograhpyNadji Gadji-BaxisNo ratings yet
- Covalent BondingDocument20 pagesCovalent BondingNadji Gadji-BaxisNo ratings yet
- Geo History Nadjmeddin BakhishDocument10 pagesGeo History Nadjmeddin BakhishNadji Gadji-BaxisNo ratings yet
- Physics NotesDocument5 pagesPhysics NotesNadji Gadji-BaxisNo ratings yet
- Receptor TypesDocument3 pagesReceptor TypesPardeep SonyNo ratings yet
- 1.porphyrin & Bile Pigment 2014Document94 pages1.porphyrin & Bile Pigment 2014Henyta TsuNo ratings yet
- Model Answers: Chapter 3 Movement of Substances Across A Plasma MembraneDocument4 pagesModel Answers: Chapter 3 Movement of Substances Across A Plasma MembraneimanNo ratings yet
- Oxo ABioQ 08uu xs01 XxaannDocument2 pagesOxo ABioQ 08uu xs01 XxaannajaelupNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Used in Industry - DetergentsDocument8 pagesEnzymes Used in Industry - DetergentsdivakarabhadravathiNo ratings yet
- De Leon ExperimentNo.4 Hershey and ChaseDocument8 pagesDe Leon ExperimentNo.4 Hershey and ChasePang ChixxNo ratings yet
- A Peek Inside A CellDocument2 pagesA Peek Inside A CellJohn Carl Angelo EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Protein Synthesis Differs From Prokaryotic Protein Synthesis Primarily in Translation InitiationDocument4 pagesEukaryotic Protein Synthesis Differs From Prokaryotic Protein Synthesis Primarily in Translation InitiationJoyce DometitaNo ratings yet
- Q3 Week 5 Stem G11 General Biology 1Document23 pagesQ3 Week 5 Stem G11 General Biology 1John Benedict MaurilloNo ratings yet
- Ap Biology Vocabulary ListDocument6 pagesAp Biology Vocabulary Listapi-415920554No ratings yet
- CIFA TechnologyDocument8 pagesCIFA Technology1stabhishekNo ratings yet
- The Radial Path of Ion Movement Through RootsDocument2 pagesThe Radial Path of Ion Movement Through RootsAtika AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- Castes and Tribes in Hazara Division, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, PakistanDocument11 pagesCastes and Tribes in Hazara Division, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, PakistanScribd UploadsNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Bacteriology: David K. NgunjiriDocument69 pagesIntroduction To Bacteriology: David K. NgunjiriFrancis ChegeNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Genetic Regulation Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Plants PDFDocument17 pagesUnderstanding The Genetic Regulation Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Plants PDFfernanda0% (1)
- RetinoblastomaDocument42 pagesRetinoblastomaSrm GeneticsNo ratings yet
- Cells 11 03250Document18 pagesCells 11 03250Dhyana BuchNo ratings yet
- By: Herdianty Kusuma H, SST., FTR., M.KesDocument3 pagesBy: Herdianty Kusuma H, SST., FTR., M.KesTaufik Dwi KurniawanNo ratings yet
- 2007 A Level H2 Biology P2 AnsDocument6 pages2007 A Level H2 Biology P2 AnsjoannetzyNo ratings yet
- Brooker2014 COHESINAS PDFDocument38 pagesBrooker2014 COHESINAS PDFMary MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Primers Sry 2Document9 pagesPrimers Sry 2Josue BarralNo ratings yet
- Mega Script T7 KitDocument33 pagesMega Script T7 KitkitamandaNo ratings yet
- Molecular Diagnostics Fundamentals Methods and Clinical Applications 2Nd Edition Buckingham Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument21 pagesMolecular Diagnostics Fundamentals Methods and Clinical Applications 2Nd Edition Buckingham Test Bank Full Chapter PDFKatherineJohnsonDVMinwp100% (8)
- Nyctotherus Ovalis and Its RelativesDocument12 pagesNyctotherus Ovalis and Its RelativesSandy VasquezNo ratings yet
- 9th - Biology - 01 - Fundamental Unit of Life - 02 - Tissue - & - 03 - Improvement in Food ResourcesDocument124 pages9th - Biology - 01 - Fundamental Unit of Life - 02 - Tissue - & - 03 - Improvement in Food ResourcesMadhu SatapathyNo ratings yet
- Rahmat Nur Ainun - TranslateDocument2 pagesRahmat Nur Ainun - TranslateGAKUEN GAMING100% (1)