Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Objectives
Objectives
Uploaded by
Janelyn GarinOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Objectives
Objectives
Uploaded by
Janelyn GarinCopyright:
Available Formats
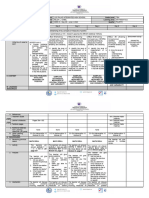
OBJECTIVES SESSION 1 SESSION 2 SESSION 3 SESSION 4
The learners demonstrate an The learners demonstrate an understanding of… The learners demonstrate The learners
understanding of… 1. Accuracy versus precision an understanding of… demonstrate an
1. The effect of instruments on 2. Uncertainty of derived quantities Graphical analysis: linear understanding of…
D. Content Standards measurements 2. 3. Error bars fitting and transformation 1. Vectors and vector
Uncertainties and deviations in of functional dependence addition
measurement to linear form 2. Components of vectors
3. Sources and types of error 3. Unit vectors
The learners shall be able to solve using experimental and theoretical approaches, multi-concept and rich-context problems involving motions in one
E. Performance Standards
dimension.
1. Solve measurement problems 1. Differentiate vector
Estimate intercepts and
involving conversion of units, and scalar quantities
1. Differentiate accuracy from precision slopes—and their
expression of measurements in 2. Perform addition of
2. Estimate errors from multiple measurements of a uncertainties—in
scientific notation vectors
physical quantity using variance experimental data with
F. Learning Competencies 2. Differentiate random errors from 3.Rewrite a vector in
3. Estimate the uncertainty of a derived quantity from the linear dependence using
systematic errors component form
estimated values and uncertainties of directly measured the “eyeball method”
3. Use the least count concept to 4. Calculate directions
quantities and/or linear regression
estimate errors associated with single and magnitudes of
formulae
measurements vectors
The effect of instruments on Graphical analysis: linear
Vectors and vector
measurements, uncertainties and Accuracy versus precision, uncertainty of derived quantities fitting and transformation
VI. CONTENT addition, components of
deviations in measurement, and and error bars of functional dependence
vectors and unit vectors
sources and types of error. to linear form
General Physics 1 (Teacher's
VII. LEARNING Manual)
RESOURCES Caintic Helen E. PhD., 2018 Quezon
City, City Phoenix Publishing House www.real-world-physics-
www.brighthubengineering.com problems.com
VIII. LEARNING PROCESS
Introduction (10 mins) (10 mins)
(Motivation) Have the student share their Pictures of showing accuracy and precision will be shown to
experiences in doing measurements. the students. The following questions may be asked:
They may share the challenges they 1. Compare the three darts.
have encounter when doing
measurements. Ask the students to 2. What similarities do they have?
perform the following activity in 3. From the image shown can you define and differentiate
group of four. Prepare measuring accuracy and precision?
tools that can be used to measure
length, time, and mass. Assign each Do Activity 6: Accuracy and Precision
group of objects that can be Objective: Identify the factors that affect accuracy and
measured in terms of length, mass, precision.
and time. Each member of the group
will measure each of objects. Have Procedure:
them compare the measurements 1. Lay the paper target on the floor and have each group
they have obtained. member choose a color dot marker.
2. Take turns holding the marker 1 meter above the target
and releasing the marker.
3. Try to hit the bullseye. Measure the distance in
centimeters from the target center to the dot made by the
marker when it lands.
4. Round to the nearest tenth. Record the measurements in
the data table and calculate the value for mean
5. Repeat so that each group member has two attempts.
Use the wipes or paper towels to clean up any marks that
got on the floor
Instruction/ Delivery (25 mins) (30 mins)
Process what they have observed 1. Explain the difference between the accuracy and
from the data they have gained form precision
the activity. Ask them what are the 2. Give examples of accuracy and precision
limits and difficulties they have
observed while measuring. Explain 3. What do you call the difference between the measured
uncertainties and errors in result and the target value/accepted value?
measurement. 4. What is the importance of accuracy and precision on real
life?
* In P.E, like playing basketball, If the player shoots with
accuracy, his aim will always take the ball close to or into
the basket. If the player shoots with precision, his aim will
always take the ball to the same location which may or may
not be close to the basket. A good player will be both
accurate and precise by shooting the ball the same way
each time and each time making it in the basket.
5. How will you able to improve accuracy and precision?
6. Coin diameter
A gold coin has an ‘accepted’ diameter of 28.054 mm.
Two students are asked to measure the diameter of four
gold coins. Student A uses a simple plastic ruler. Student B
uses a precision measuring tool called a micrometer.
Student A – Student B – micrometer
plastic ruler
27.9 mm 28.246 mm
28.0 mm 28.244 mm
27.8 mm 28.246 mm
28.1 mm 28.248 mm
1. Calculate the average value for each set of
measurements
Student A – plastic Student B – micrometer
ruler
2. Calculate the % error for each set of measurements.
Student A – plastic Student B – micrometer
ruler
3. Compare the average value for each set with the
accepted value:
• Which student’s data is more accurate?
• Which student’s data is more precise?
4. Compare the percentage error for each set:
• Which student’s data is more accurate?
• Which student’s data is more precise?
5. Explain any odd findings:
(15 mins)Perform the activity of
Practice Estimating the Uncertainty of a
Derived Quantity
Enrichment/ Evaluation
Assignment
You might also like
- Ideal Gas Law (Part 4)Document5 pagesIdeal Gas Law (Part 4)asapamore100% (1)
- Free Surface EffectDocument12 pagesFree Surface EffectBharatiyulam100% (2)
- Electromagentic SpectrumDocument24 pagesElectromagentic SpectrumJanelyn Garin100% (1)
- 2021MATHADVHO2.6 - Selected Session 2 PPT SlidesDocument31 pages2021MATHADVHO2.6 - Selected Session 2 PPT SlidesChang CarelNo ratings yet
- The Scope and Delimitation and The Significance of The StudyDocument59 pagesThe Scope and Delimitation and The Significance of The StudyJanelyn Garin100% (1)
- Stem-Gen. Physics1 - q1Document13 pagesStem-Gen. Physics1 - q1Meldren TorrevillasNo ratings yet
- The Statement of The ProblemDocument37 pagesThe Statement of The ProblemJanelyn Garin100% (1)
- Measuring Road Roughness by Static Level Method: Standard Test Method ForDocument6 pagesMeasuring Road Roughness by Static Level Method: Standard Test Method ForDannyChaconNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1: Graphical Analysis, and Basic Calculus. Mechanics, Fluids, Motion and ThermodynamicsDocument29 pagesGeneral Physics 1: Graphical Analysis, and Basic Calculus. Mechanics, Fluids, Motion and ThermodynamicsEisle Keith Tapia100% (1)
- Determination of Tap Density of Metallic Powders and CompoundsDocument2 pagesDetermination of Tap Density of Metallic Powders and CompoundsLuigi HernándezNo ratings yet
- Tanauan City College: Republic of The Philippines Province of Batangas City of TanauanDocument23 pagesTanauan City College: Republic of The Philippines Province of Batangas City of TanauanQueenie Gonzales-AguloNo ratings yet
- Physics I SyllabusDocument21 pagesPhysics I SyllabusRonnel Ladac UseroNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Physics Annual PlanDocument14 pagesGrade 11 Physics Annual PlanKeol Akuma100% (2)
- DLL Gen-Phys. (July Week1)Document4 pagesDLL Gen-Phys. (July Week1)Jesse Gabriel0% (1)
- STEM - Physics 1 CG - With Tagged Sci EquipmentDocument15 pagesSTEM - Physics 1 CG - With Tagged Sci EquipmentAndres Kalikasan Sara100% (8)
- StatisticsDocument29 pagesStatisticsseenubarman12No ratings yet
- The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding Of... The Learners Are Able To... The Learners..Document24 pagesThe Learners Demonstrate An Understanding Of... The Learners Are Able To... The Learners..Mark Francis HernandezNo ratings yet
- DLL Gen-Phys. (July Week2)Document4 pagesDLL Gen-Phys. (July Week2)Jesse GabrielNo ratings yet
- Annex III-Course Specifications For ChEDocument94 pagesAnnex III-Course Specifications For ChETheresa TuliaoNo ratings yet
- Physics ReviewerDocument8 pagesPhysics ReviewerSOLIS, John Ernest S.No ratings yet
- Civl ENGG SyllabusDocument45 pagesCivl ENGG SyllabusKenneth Joy SorianoNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log: The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding ofDocument5 pagesDaily Lesson Log: The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding ofJay MellizaNo ratings yet
- Pacing Guide Curriculum Map Lesson PlansDocument17 pagesPacing Guide Curriculum Map Lesson Plansapi-437527252No ratings yet
- The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding Of... The Learners Are Able To... The Learners..Document15 pagesThe Learners Demonstrate An Understanding Of... The Learners Are Able To... The Learners..Shendy AcostaNo ratings yet
- Fisika Kelas X Semester I: With Both Analogue and Digital DisplaysDocument69 pagesFisika Kelas X Semester I: With Both Analogue and Digital DisplaysSilka AbyadatiNo ratings yet
- Physics XIDocument12 pagesPhysics XIAshish UpretiNo ratings yet
- Genaral Physics 1Document5 pagesGenaral Physics 1Nicole LagumbayNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1: Overview of Multivariate Techniques: Meena NotesDocument9 pagesLecture 1: Overview of Multivariate Techniques: Meena Notesmgmt6008No ratings yet
- Senior High School - Year 1: Section 1 Introductory Physics and Properties of MatterDocument46 pagesSenior High School - Year 1: Section 1 Introductory Physics and Properties of MatterSharifNo ratings yet
- BOW-Physics 1 FinalDocument11 pagesBOW-Physics 1 Finaljoshann251No ratings yet
- Mathematics Syllabus: Subjects Topic To Be CoveredDocument1 pageMathematics Syllabus: Subjects Topic To Be CoveredAnanya NNo ratings yet
- 4.september 12-16Document3 pages4.september 12-16Lyka BugarinNo ratings yet
- DCSBME604Document5 pagesDCSBME604bariNo ratings yet
- August 29 - August 31,2023Document8 pagesAugust 29 - August 31,2023Arlene GaculaNo ratings yet
- 2023 Level II Key Facts and Formula Sheet (KFFS)Document14 pages2023 Level II Key Facts and Formula Sheet (KFFS)xsiaoNo ratings yet
- Course Plan PDFDocument6 pagesCourse Plan PDFhamidNo ratings yet
- NDA Syllabus and BooklistDocument7 pagesNDA Syllabus and BooklistPriyanshu UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- NDA Syllabus and BooklistDocument7 pagesNDA Syllabus and BooklistPriyanshu UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Quality of Analytical Measurements: Statistical Methods For Internal ValidationDocument60 pagesQuality of Analytical Measurements: Statistical Methods For Internal ValidationCalidad LassNo ratings yet
- Contextualized DLL Oct. 2, 2023Document6 pagesContextualized DLL Oct. 2, 2023ianNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 Classroom Instruction Delivery Alignment PlanDocument1 pageGeneral Physics 1 Classroom Instruction Delivery Alignment PlanIsrael Morta Garzon100% (1)
- CMO 13 S. 2008 Annex III COURSE SPECIFICATIONS FOR THE BSCpE PROGRAMDocument52 pagesCMO 13 S. 2008 Annex III COURSE SPECIFICATIONS FOR THE BSCpE PROGRAMMichellePascualPullonNo ratings yet
- Abbe 637 640Document4 pagesAbbe 637 640Rahul ChavanNo ratings yet
- Annex III - BSCE Course Specs (Jan. 25, 2007) - ApprovedPDFDocument73 pagesAnnex III - BSCE Course Specs (Jan. 25, 2007) - ApprovedPDFcimpstazNo ratings yet
- COMEDK UGET Syllabus 2021 (Out) - Check Subject and Topic Wise SyllabusDocument27 pagesCOMEDK UGET Syllabus 2021 (Out) - Check Subject and Topic Wise SyllabusRudra VashistaNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Skills - SyllabusDocument2 pagesQuantitative Skills - SyllabusUsha ThakurNo ratings yet
- Uncertainties and CFD Code Validation: H. W. ColemanDocument9 pagesUncertainties and CFD Code Validation: H. W. ColemanLuis Felipe Gutierrez MarcantoniNo ratings yet
- Annex III - BSCE Course Specs (Jan. 25, 2007) - ApprovedPDFDocument73 pagesAnnex III - BSCE Course Specs (Jan. 25, 2007) - ApprovedPDFDelmar GicaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus XI PhysicsDocument10 pagesSyllabus XI PhysicsNasimaNo ratings yet
- Course Number Course Title Credit/s Semester/Term/School Year Schedule College or DepartmentDocument8 pagesCourse Number Course Title Credit/s Semester/Term/School Year Schedule College or DepartmentHarvey RatunilNo ratings yet
- Plans IB HL AA Unit 08 VectorsDocument6 pagesPlans IB HL AA Unit 08 VectorsHui ZhengNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Unit QuestionDocument6 pagesMathematics: Unit QuestionLorraine SabbaghNo ratings yet
- ELEC2LPPTDocument12 pagesELEC2LPPTCLAUDINE INFANTENo ratings yet
- MAC-Artigo OriginalDocument7 pagesMAC-Artigo OriginalrompnadegasNo ratings yet
- RPT Math f1 2023 2024 DLPDocument17 pagesRPT Math f1 2023 2024 DLPSarina ShariffNo ratings yet
- Econ f241 Econometric Methods1Document3 pagesEcon f241 Econometric Methods1Bareddy Vamsidhar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Metodo Tres VoltmetrosDocument5 pagesMetodo Tres VoltmetrosSalvador PérezNo ratings yet
- Ijrdet 0314 09 PDFDocument9 pagesIjrdet 0314 09 PDFAnonymous P8Bt46mk5INo ratings yet
- 3 Mathematics Number and Algebra Levels 7-10ADocument2 pages3 Mathematics Number and Algebra Levels 7-10ADamon KeyNo ratings yet
- Quality of Analytical Measurements: Univariate Regression: 2009 Elsevier B.V. All Rights ReservedDocument43 pagesQuality of Analytical Measurements: Univariate Regression: 2009 Elsevier B.V. All Rights ReservedCalidad LassNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics II: Course DescriptionDocument3 pagesEngineering Mathematics II: Course DescriptionSubas ShresthaNo ratings yet
- 02 BiostatDocument4 pages02 BiostatDavid MangawilNo ratings yet
- DLL Math10 4Q W5Document3 pagesDLL Math10 4Q W5Nelda OabelNo ratings yet
- GED 109 Lesson2Document6 pagesGED 109 Lesson2Mitzi. SumaderoNo ratings yet
- O5 BmsiDocument2 pagesO5 BmsiAbbi CoolNo ratings yet
- As ContentDocument21 pagesAs Contentsanjana shettyNo ratings yet
- Valence Electrons, Ions, and The Periodic Table12789Document34 pagesValence Electrons, Ions, and The Periodic Table12789Janelyn GarinNo ratings yet
- Total Sales Per Month: MonthsDocument13 pagesTotal Sales Per Month: MonthsJanelyn GarinNo ratings yet
- Phase Change Calculation Worksheet: Specific Heat Values (C) Substance Specific HeatDocument2 pagesPhase Change Calculation Worksheet: Specific Heat Values (C) Substance Specific HeatJanelyn GarinNo ratings yet
- Light WorksheetDocument2 pagesLight WorksheetJanelyn GarinNo ratings yet
- Name Age Gender Mother: Educ. BackgroundDocument3 pagesName Age Gender Mother: Educ. BackgroundJanelyn GarinNo ratings yet
- Kings CoffersDocument7 pagesKings CoffersJanelyn GarinNo ratings yet
- The Aufbau PrincipleDocument2 pagesThe Aufbau PrincipleJanelyn GarinNo ratings yet
- San Antonio de Padua College Foundation of Pila, Laguna IncDocument2 pagesSan Antonio de Padua College Foundation of Pila, Laguna IncJanelyn Garin100% (1)
- BVP Order Form - Google - 16042021Document1 pageBVP Order Form - Google - 16042021Janelyn GarinNo ratings yet
- San Antonio de Padua College Foundation of Pila, Laguna IncDocument1 pageSan Antonio de Padua College Foundation of Pila, Laguna IncJanelyn GarinNo ratings yet
- Light Properties WorksheetDocument2 pagesLight Properties WorksheetJanelyn GarinNo ratings yet
- Coulomb LawDocument2 pagesCoulomb LawJanelyn GarinNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Laguna State Polytechnic University Main Campus Santa Cruz, LagunaDocument2 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Laguna State Polytechnic University Main Campus Santa Cruz, LagunaJanelyn GarinNo ratings yet
- San Antonio de Padua College Foundation of Pila, Laguna IncDocument1 pageSan Antonio de Padua College Foundation of Pila, Laguna IncJanelyn GarinNo ratings yet
- San Antonio de Padua College Foundation of Pila, Laguna IncDocument1 pageSan Antonio de Padua College Foundation of Pila, Laguna IncJanelyn GarinNo ratings yet
- Physics Test OSCillations & Waves With SolDocument7 pagesPhysics Test OSCillations & Waves With SolManishNo ratings yet
- Power Oroject Z&FDocument24 pagesPower Oroject Z&FzigijuNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Lab ManualDocument46 pagesFluid Mechanics Lab ManualphrqdurhNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Pressure: Static and Dynamic PressureDocument10 pagesMeasurement of Pressure: Static and Dynamic PressureTarun VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Genius by Pradeep Kshetrapal: Roblems Based On PressureDocument10 pagesGenius by Pradeep Kshetrapal: Roblems Based On PressureBanty SamantasingharNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Question Bank - 2021-22Document35 pagesEngineering Mechanics Question Bank - 2021-22Naman JainNo ratings yet
- Ee 6 FinalsDocument3 pagesEe 6 FinalsSantos, Jewella C.No ratings yet
- E 617 Â " 97 - RTYXNY05NWDocument7 pagesE 617 Â " 97 - RTYXNY05NWhans ccNo ratings yet
- Technical Specifications & Proposed Solution: A - Automatic Weather Station (Aws)Document67 pagesTechnical Specifications & Proposed Solution: A - Automatic Weather Station (Aws)Hamza AliNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism 2 Study Exit Exam - 2023Document10 pagesElectromagnetism 2 Study Exit Exam - 2023Esubalew Molla100% (1)
- Model SK 6150 6155Document14 pagesModel SK 6150 6155Abdalhakeem AlturkyNo ratings yet
- Hexagon MI GLOBALS Datasheet APAC Rel3 MinDocument16 pagesHexagon MI GLOBALS Datasheet APAC Rel3 MinPablo FreyNo ratings yet
- Shrink Disc MAV 2208 Heavy Duty: FeaturesDocument4 pagesShrink Disc MAV 2208 Heavy Duty: Featuresemrah nalbantNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY #1 SymbolsDocument5 pagesACTIVITY #1 Symbolskenneth jade orocayNo ratings yet
- ECT Inspection Technique: Theory and General ConceptsDocument9 pagesECT Inspection Technique: Theory and General ConceptsKvanan78No ratings yet
- Surveying Prelim ReviewerDocument4 pagesSurveying Prelim ReviewerBanana QNo ratings yet
- Suvat PrepDocument2 pagesSuvat Prepalicia.milligan1107No ratings yet
- DefinitionsDocument9 pagesDefinitionsshirley wangNo ratings yet
- David 2105 PrelimExamsDocument10 pagesDavid 2105 PrelimExamsJAZPER DAVIDNo ratings yet
- Euroloop Calibrations B.VDocument3 pagesEuroloop Calibrations B.VmohamedNo ratings yet
- SOLUTION NumericalsDocument2 pagesSOLUTION NumericalsThorNo ratings yet
- Design of Rogowski Coil With IntegratorDocument32 pagesDesign of Rogowski Coil With IntegratorrichatNo ratings yet
- Triaxial Accelerometer With Integral Magnet (A0643TX)Document2 pagesTriaxial Accelerometer With Integral Magnet (A0643TX)ORAMAYNo ratings yet
- Metrology Lab Viva Voce QuestionsDocument6 pagesMetrology Lab Viva Voce Questionsmrbalaji88No ratings yet
- Physics Project Based LearningDocument17 pagesPhysics Project Based Learningphanindra vulliNo ratings yet
- Minggu 5. TIME STUDY - Stopwatch (Rev)Document47 pagesMinggu 5. TIME STUDY - Stopwatch (Rev)RONI AJI SILALANGITNo ratings yet