Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Analogue Output Modules of A 0-5V To - 5V - +5V Signal Converter
Uploaded by
Ardhy IskandarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Analogue Output Modules of A 0-5V To - 5V - +5V Signal Converter
Uploaded by
Ardhy IskandarCopyright:
Available Formats
Column: Analogue I/O modules
Analogue output modules of a 0-5V to
-5V - +5V signal converter
T
By Dr. Murat Uzam, Academic and Technical Author, Turkey
his series of columns is dedicated to a project of thirteen A ferrite bead is connected in series with the output path to add isolation
analogue input modules and seven analogue output and decoupling from high-frequency transients. A TVS (Transient Voltage
modules for a 5V microcontroller, which connect to its Suppressor) filters and suppresses any VOUT transients.
ADC and DAC channels. This circuit can supply up to 20mA output current.
This month's column covers the third and forth Table 1 shows input and output voltages for this module, assuming
analogue output modules, or analogue output modules 0.00V ≤ VIN ≤ 5.00V. Its prototype circuit board is shown in Figure 4.
1 and 2 for a 0-5V to -5V - +5V signal converter. These provide voltages Circuit calibration when S1 is closed: By adjusting P1, ensure that when
from -5V to +5V; module 2 requires three DC power supplies (+5V, -12V VIN = 0.00V, VOUT = -5.00V and, also, when VIN = +5.00V, VOUT = +5.00V.
and +12V) and module 1 two DC power supplies (-12V and +12V). When S1 is open there’s no need for calibration.
Output module 1 Analogue output module 2
Figure 1 shows module 1’s circuit, with its connections shown in Figure 5 shows the circuit diagram of analogue output module 2 for
Figure 2. We’ve assumed that VIN comes from the DAC output of the 5V a 0-5V to -5V - +5V signal converter, with its connections to the 5V
microcontroller with 0.00V ≤ VIN ≤ 5.00V. When 0.00V ≤ VIN ≤ 5.00V, microcontroller shown in Figure 6.
VOUT = 2VIN ≤ 5. Input voltage range VIN = 0.00-5.00V and therefore the As in the previous module, we assume VIN comes from the MCU’s
output voltage range VOUT is -5.00V to +5.00V. The relationship between DAC, with 0.00V ≤ VIN ≤ 5.00V. When 0.00V ≤ VIN ≤ 5.00V, VOUT = 2VIN
VOUT and VIN is shown in Figure 3. ≤ 5. The input voltage range VIN = 0.00V to 5.00V and therefore the output
Jumper S1 (shown as a switch) is used to select either 0-5V operation voltage range VOUT = -5.00V to +5.00V; see VOUT and VIN’s relationship in
mode (S1 open) or 0-5V to -5V - +5V mode (S1 closed). The design is Figure 3.
used to level-shift the unipolar 0-5V input voltage signal to a bipolar -5V The bottom part of Figure 5 is identical to that of module 1, whereas
to +5V output voltage signal. When 0.00V ≤ VIN ≤ 5.00V, the operational the top part produces the +5.00V reference voltage. R3, D3 (a 10V Zener
amplifier LM358P-A, with bipolar supply voltages, acts with the transfer diode) and C3, together with the buffer amplifier LM358P-1A, provide
function: a 10.00V reference voltage from a +12V power supply. This 10.00V
reference voltage is then divided by resistors R4 and R5 to obtain a +5.00V
reference voltage. Next, the +5.00V reference voltage is connected to the
non-inverting input of the buffer amplifier LM358P-1B, whose output is
By adjusting P1 we obtain R1 + P1 = R2, hence: fixed as a +5.00V reference, capable of sourcing up to 20mA.
Table 1 shows voltages for this module, with its prototype circuit board
VOUT= 2VIN - 5 shown in Figure 7.
For proper operation make sure that R4 = R5.
The buffer amplifier (a voltage follower) LM358P-B is used on the Circuit calibration with S1 closed: By adjusting P1, ensure that when VIN
output of LM358P-A. Two series Schottky barrier diodes D1 and D2 = 0.00V, VOUT = -5.00V and, also, when VIN = +5.00V, VOUT = +5.00V. When
divert any VOUT overcurrent to the positive or negative power supply. S1 is open, there’s no need for calibration.
Figure 1: Circuit diagram of the analogue output module 1 for a 0-5V to Figure 2: Connections of the analogue output module 1 for a
-5V - +5V signal converter 0-5V to -5V - +5V signal converter
08 July/August 2019 www.electronicsworld.com
Column: Analogue I/O modules
Figure 3: VOUT vs. VIN for
analogue output modules Figure 4: Analogue output module 1 for a 0-5V to
1 and 2 for a 0-5V to -5V - -5V - +5V signal converter
+5V signal converter
Figure 5: Circuit diagram of
VIN(V) VOUT(V) the analogue output module 2
5.00 +5.00 for a 0-5V to -5V - +5V signal
.. .. converter
4.50 +4.00
.. ..
4.00 +3.00
.. ..
3.75 +2.50
.. ..
Figure 7: Analogue
3.50 +2.00
output module 2’s
.. .. prototype circuit
3.00 +1.00 board, top and
.. .. bottom views
2.50 0.00
.. ..
2.00 -1.00
.. ..
1.50 -2.00
.. ..
1.25 -2.50
.. ..
1.00 -3.00
.. ..
0.50 -4.00
.. ..
0.00 -5.00
Table 1: Input and output
voltages for analogue
output modules 1 and
2 for a 0-5V to -5V -
+5V signal converter,
assuming 0.00V ≤ VIN ≤ Figure 6: Analogue output module 2’s connections
5.00V to a 5V microcontroller
www.electronicsworld.com July/August 2019 09
You might also like
- Lab 6Document7 pagesLab 6Augusta AverenceNo ratings yet
- Scalable Regulated Three Phase Power Rectifier: ECE 481 Senior Design Final PresentationDocument35 pagesScalable Regulated Three Phase Power Rectifier: ECE 481 Senior Design Final Presentationibs434No ratings yet
- Sensor Lab Report: Op-AmpDocument6 pagesSensor Lab Report: Op-AmpAyamGolek05No ratings yet
- Reference Variable Generator 734 02: Instruction Sheet BB 06/99Document2 pagesReference Variable Generator 734 02: Instruction Sheet BB 06/99Billel TalbiNo ratings yet
- 34 Saurav Bista Assignment 5Document7 pages34 Saurav Bista Assignment 5Anil PoudelNo ratings yet
- D-A Converter (Weighted Resistor Method)Document3 pagesD-A Converter (Weighted Resistor Method)neha yarrapothuNo ratings yet
- Learning Objectives:: Topic 5.2.2 - Digital To Analogue ConvertersDocument19 pagesLearning Objectives:: Topic 5.2.2 - Digital To Analogue Convertersquami3quartsNo ratings yet
- Pre Lab 6Document3 pagesPre Lab 6Ami ShahNo ratings yet
- ANALOG CIRCUITS 18EC42 (Module - 5)Document27 pagesANALOG CIRCUITS 18EC42 (Module - 5)mahendra naik82% (11)
- Slla 166Document8 pagesSlla 166Pablo Alexis García de la CruzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Opamp & Its ApplicationsDocument367 pagesChapter 13 Opamp & Its Applicationsshubhankar pal100% (1)
- Problems On Operational AmplifiersDocument84 pagesProblems On Operational Amplifiersvivekroy2991No ratings yet
- ConverterDocument17 pagesConverterJimmy TanNo ratings yet
- Opamp Applications: Session 10: Prakash Biswagar Asst. Professor E&C Engg. Dept RV College of Engineering, BangaloreDocument35 pagesOpamp Applications: Session 10: Prakash Biswagar Asst. Professor E&C Engg. Dept RV College of Engineering, BangaloreSatya Prasad AkkinaNo ratings yet
- The Operational AmplifierDocument35 pagesThe Operational Amplifierbbwx4114No ratings yet
- 371 Lab2Document13 pages371 Lab2Eugene ToNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1 Logic Inverter I. ObjectiveDocument6 pagesExperiment No. 1 Logic Inverter I. Objectivexoxoxoxox11No ratings yet
- AB-30 V-I and I-V Converter: An ISO 9001: 2000 CompanyDocument23 pagesAB-30 V-I and I-V Converter: An ISO 9001: 2000 CompanyWandi WandaniNo ratings yet
- AD 20flash 20converterDocument7 pagesAD 20flash 20converterChú Cá ConNo ratings yet
- WEG CFW 11 plc11 Modulo Com Funcoes de CLP Guia de Instalacao Portugues BR PDFDocument24 pagesWEG CFW 11 plc11 Modulo Com Funcoes de CLP Guia de Instalacao Portugues BR PDFLeandro MartirNo ratings yet
- 10A45 SimerahDocument8 pages10A45 Simerahega nur aziesNo ratings yet
- Module 4 NewDocument27 pagesModule 4 Newsudeepbl123No ratings yet
- Position Control System: Transducer Amplifier Motor & Gearing Output Shaft Error + InputDocument6 pagesPosition Control System: Transducer Amplifier Motor & Gearing Output Shaft Error + InputZeeshan WaqasNo ratings yet
- 2014aaps274h Expt 5Document8 pages2014aaps274h Expt 5Praneeth KumarNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Diodes ReportDocument10 pagesExperiment 1 Diodes ReportTerry MazubaNo ratings yet
- 17 - Matlab-SIMULATION OF ELECTRICAL MACHINESDocument11 pages17 - Matlab-SIMULATION OF ELECTRICAL MACHINESأمجد هاتف منفي جفالNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - NotesDocument52 pagesUnit 2 - NotesJohnsi JNo ratings yet
- 74F280 9-Bit Parity Generator/Checker: General DescriptionDocument6 pages74F280 9-Bit Parity Generator/Checker: General DescriptionJavier LorensNo ratings yet
- Aic Unit 3Document96 pagesAic Unit 3SYETC156HARSHAL RAHENWALNo ratings yet
- Gain, Attenuation, and DecibelsDocument10 pagesGain, Attenuation, and DecibelsValentina NietoNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory - Solved Assignments - Spring 2005Document31 pagesCircuit Theory - Solved Assignments - Spring 2005Muhammad UmairNo ratings yet
- 7400 Series (TTL) : Symbol DescriptionDocument11 pages7400 Series (TTL) : Symbol DescriptionBobyNo ratings yet
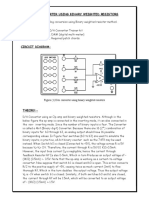
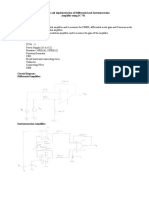
- Expt No: Design and Implementation of Differential and Instrumentation Amplifier Using IC 741 AimDocument2 pagesExpt No: Design and Implementation of Differential and Instrumentation Amplifier Using IC 741 AimaatityasriNo ratings yet
- STV9302BDocument15 pagesSTV9302BcocolisoteNo ratings yet
- IC Applications Lab ManualDocument42 pagesIC Applications Lab ManualRavikumar ImadabathuniNo ratings yet
- Zero Crossing Detector and Window DetectorDocument7 pagesZero Crossing Detector and Window DetectorTimoth Dev50% (2)
- HC SR08 3Document10 pagesHC SR08 3Juan PerezNo ratings yet
- Bjectives: OnvertersDocument9 pagesBjectives: OnvertersRiver hutabaratNo ratings yet
- LM211, LM311 Single Comparators: $15 V Split Supplies, As Commonly Used With Operational AmplifiersDocument10 pagesLM211, LM311 Single Comparators: $15 V Split Supplies, As Commonly Used With Operational AmplifiersShalini GuptaNo ratings yet
- Eim377 Ad9850 Signal Generator Module v01Document10 pagesEim377 Ad9850 Signal Generator Module v01Frederico Ribeiro BarnabéNo ratings yet
- Sbea 001Document18 pagesSbea 001firstbook1No ratings yet
- Non LinearDocument11 pagesNon LinearvineethrajuNo ratings yet
- Simulation PDFDocument4 pagesSimulation PDFKalimuthu KumarNo ratings yet
- Exp 1 OpAmp Appications LDIC LABDocument3 pagesExp 1 OpAmp Appications LDIC LABswathiNo ratings yet
- ISOCON 6 Product ManualDocument16 pagesISOCON 6 Product ManualAman Kumar MauryaNo ratings yet
- Analog Sensor InterfacingDocument5 pagesAnalog Sensor Interfacingkokolanski100% (1)
- DUALCON 6 Product ManualDocument16 pagesDUALCON 6 Product ManualSuryadiNo ratings yet
- Lab 1a - ME3000 Practical Op-Amp Circuits - v1.32Document7 pagesLab 1a - ME3000 Practical Op-Amp Circuits - v1.32MrmouzinhoNo ratings yet
- Diode CircuitsDocument23 pagesDiode CircuitsSurendra BachinaNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory - Solved Assignments - Semester Fall 2005Document18 pagesCircuit Theory - Solved Assignments - Semester Fall 2005Muhammad Umair50% (2)
- Tiara Ning Tias 20063099 Praktek Elektronika 6Document9 pagesTiara Ning Tias 20063099 Praktek Elektronika 6Tiara Ning TiasNo ratings yet
- TAREA 2.6 Ejercicios Con AMP. Operacionales NRC 3417-ComprimidoDocument26 pagesTAREA 2.6 Ejercicios Con AMP. Operacionales NRC 3417-ComprimidoLuis MontesNo ratings yet
- MTE 3105 - Lecture-01Document46 pagesMTE 3105 - Lecture-01shafin2031010No ratings yet
- EGR240 D3.1 Op AmpsDocument20 pagesEGR240 D3.1 Op AmpsErnesto Vergara Jr.No ratings yet
- Analogue EEC436Document46 pagesAnalogue EEC436Akachi OkoroNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- TMS320F28335 DSP Programming Using MATLAB Simulink Embedded Coder: Techniques and AdvancementsDocument8 pagesTMS320F28335 DSP Programming Using MATLAB Simulink Embedded Coder: Techniques and AdvancementsSaid MerengueNo ratings yet
- AT27C512 ATMELCorporationDocument7 pagesAT27C512 ATMELCorporationArdhy IskandarNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Manual: Centrifugal ChillersDocument12 pagesMaintenance Manual: Centrifugal ChillersSugito De solehNo ratings yet
- Introduction To TMS320F28335Document33 pagesIntroduction To TMS320F28335Arthi Sahaya RonesNo ratings yet
- BukaDocument1 pageBukaArdhy IskandarNo ratings yet
- Convert 1V To 5V Signal To 4ma To 20ma Output: by Thomas Mosteller, Field Applications Engineer Linear Technology CorpDocument2 pagesConvert 1V To 5V Signal To 4ma To 20ma Output: by Thomas Mosteller, Field Applications Engineer Linear Technology CorpArdhy IskandarNo ratings yet
- 512K (64K X 8) One-Time Programmable, Read-Only Memory: FeaturesDocument14 pages512K (64K X 8) One-Time Programmable, Read-Only Memory: FeaturesArdhy IskandarNo ratings yet
- BoussoleDocument3 pagesBoussoleBacem ElhouimliNo ratings yet
- 4 Mbit (512Kb X 8) UV EPROM and OTP EPROM: DescriptionDocument18 pages4 Mbit (512Kb X 8) UV EPROM and OTP EPROM: DescriptionArdhy IskandarNo ratings yet
- Bank Detail SSIDocument1 pageBank Detail SSIArdhy IskandarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial1 7 PDFDocument7 pagesTutorial1 7 PDFArdhy IskandarNo ratings yet
- SchematicDocument1 pageSchematicArdhy Iskandar100% (2)
- Physics Workbook Answers P5H EDITED Sl2Document5 pagesPhysics Workbook Answers P5H EDITED Sl2Ardhy IskandarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial1 7 PDFDocument7 pagesTutorial1 7 PDFArdhy IskandarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial1 7 PDFDocument7 pagesTutorial1 7 PDFArdhy IskandarNo ratings yet
- Faq 052Document2 pagesFaq 052sallongjoeNo ratings yet
- Tutorial1 7 PDFDocument7 pagesTutorial1 7 PDFArdhy IskandarNo ratings yet
- Faq 052Document2 pagesFaq 052sallongjoeNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuit Unit 1Document10 pagesElectric Circuit Unit 1Ardhy IskandarNo ratings yet
- The Mean of The Sample MeanDocument31 pagesThe Mean of The Sample MeanAngelie Limbago CagasNo ratings yet
- Graduate Trainee 2023 - Asia Pulp & Paper (Sinar Mas)Document4 pagesGraduate Trainee 2023 - Asia Pulp & Paper (Sinar Mas)Gege MarhaendraNo ratings yet
- FutureofDocumentation OurToolsServicesDocument1 pageFutureofDocumentation OurToolsServicesDemandeur AsileNo ratings yet
- Infineon SAA - XC866 DS v01 - 05 enDocument114 pagesInfineon SAA - XC866 DS v01 - 05 enpatricio andradeNo ratings yet
- Job Description-Piping EngineerDocument1 pageJob Description-Piping EngineerThirukkumaranBalasubramanianNo ratings yet
- AI Based ProctoringDocument4 pagesAI Based ProctoringmedhaNo ratings yet
- Lead2Pass Latest Free Oracle 1Z0 060 Dumps (81 90) Download!Document5 pagesLead2Pass Latest Free Oracle 1Z0 060 Dumps (81 90) Download!aaNo ratings yet
- Brochure Linea Ego Chorus Tecnica - en - LDocument77 pagesBrochure Linea Ego Chorus Tecnica - en - LStefan IorgaNo ratings yet
- BCSL056Document25 pagesBCSL056r06677624No ratings yet
- Pvi-Aec-Evo: ABB Monitoring and CommunicationsDocument4 pagesPvi-Aec-Evo: ABB Monitoring and CommunicationsroscribNo ratings yet
- Ec Case Study (22,44)Document11 pagesEc Case Study (22,44)Aditya KanojiyaNo ratings yet
- Seminar "Functional Safety - Basic Knowledge For Users"Document4 pagesSeminar "Functional Safety - Basic Knowledge For Users"Angie AmadoNo ratings yet
- The Operations FunctionDocument35 pagesThe Operations FunctionrajNo ratings yet
- Production Scheduling Board With PP - DS For SAP S - 4HANA (Advanced Planning) On SAP S - 4HANA 1709 FPS1 - SAP BlogsDocument16 pagesProduction Scheduling Board With PP - DS For SAP S - 4HANA (Advanced Planning) On SAP S - 4HANA 1709 FPS1 - SAP BlogsDipak Banerjee100% (3)
- Matlab Assignment: Submitted By:-Siddhant Raut (6464)Document3 pagesMatlab Assignment: Submitted By:-Siddhant Raut (6464)Prem Swaroop KadavakuduruNo ratings yet
- AST3300 Hmi Proface PDFDocument11 pagesAST3300 Hmi Proface PDFDuc LeNo ratings yet
- 5 - Big Data Dimensions, Evolution, Impacts, and Challenges PDFDocument11 pages5 - Big Data Dimensions, Evolution, Impacts, and Challenges PDFPushpendra Kumar RaiNo ratings yet
- Data Mining Chapter 1Document12 pagesData Mining Chapter 1Rony saha0% (1)
- 403 Quick Guide 403 v2 PDFDocument2 pages403 Quick Guide 403 v2 PDFJoaquin Alberto Flores CastroNo ratings yet
- CT002-3-2 AI Methods: Swarm Intelligence, Technique and application-IIDocument29 pagesCT002-3-2 AI Methods: Swarm Intelligence, Technique and application-IIChester ChongNo ratings yet
- Juno Lighting Vector Track Lights Brochure 1995Document12 pagesJuno Lighting Vector Track Lights Brochure 1995Alan MastersNo ratings yet
- ADD DeletePlaceAPIsDocument4 pagesADD DeletePlaceAPIsRahul GehlotNo ratings yet
- Contract Title Contract No. Contractor Name and Address Original Contract Value (KWD) RFP No. Duration (Days) S. NoDocument2 pagesContract Title Contract No. Contractor Name and Address Original Contract Value (KWD) RFP No. Duration (Days) S. NoKoteswar MandavaNo ratings yet
- Group 5 Detailed-Level-Dimensional-Modeling-Workbook-Group5Document48 pagesGroup 5 Detailed-Level-Dimensional-Modeling-Workbook-Group5Hai Do VietNo ratings yet
- tNavReleaseNotesEnglish PDFDocument220 pagestNavReleaseNotesEnglish PDFstbernardjNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Guide To HL Global Politics PresentationsDocument17 pagesThe Ultimate Guide To HL Global Politics Presentationsayah sadiehNo ratings yet
- Habit 2 One Hour TrainingDocument23 pagesHabit 2 One Hour TrainingVincent BautistaNo ratings yet
- Limitorque Actuation Systems MX Actuators: Technical SpecificationsDocument4 pagesLimitorque Actuation Systems MX Actuators: Technical SpecificationsJP EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Enterprise Information Systems Project Implementation: A Case Study of ERP in Rolls-RoyceDocument22 pagesEnterprise Information Systems Project Implementation: A Case Study of ERP in Rolls-Roycesandyjbs100% (1)
- Lecture 7Document70 pagesLecture 7M ShookNo ratings yet