Professional Documents
Culture Documents
All Climatology Seminar - 498
Uploaded by
Rohit ShresthaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
All Climatology Seminar - 498
Uploaded by
Rohit ShresthaCopyright:
Available Formats
BALANCING BUILT ENVIRONMENT: A HYBRID DESIGN APPROACH
Other air pollutants, such as lead-based compounds, can lead to serious health effects like
cancer, or other types of reproductive effects and birth defects.
1.1.3. Change in Climate
Climate change is the variation in regional and global weather or climatic pattern studied for
the extended period typically decades or longer. In present context, the climate change is
global concerned since the range of its effect on environment is considerable. Earth's climate
has fluctuated for millions of years but the rate of changes verified since industrial revolution
is very alarming. These changes are linked to some natural phenomenon and human activities
such as the combustion of fossil fuels, large scale industrial pollution, deforestation and land-
use change connected to urbanization and human settlement around the world. (Ede, et al.,
2013).
The world is heading towards rapid urbanization which has directly aided the emission of green
house gases. The plants and equipments required for infrastructural project consume huge
amount of fuel and energy for their operation which seems to be large emitter giving negative
impact to the environment.
1.2. Urban Heat Island Effects
Urban heat island (UHI) effect is widely recognized as a heat accumulation phenomenon,
which is the most obvious characteristic of urban climate caused by urban construction and
human being activities. (Yang Li, 2016)
Urban Heat Island is classified into two types, namely, Surface Urban Heat Island and
Atmospheric Urban Heat Island. Surface Urban Heat Island is a phenomenon where surfaces
like roofs, pavements are heated on day time. When urban air gets warmer than the adjacent
rural air temperature, it defines as Atmospheric Urban Heat Island which is further divided in
two subdivisions in the form of Canopy Layer Urban Heat Island and Boundary Layer Urban
Heat Island. Canopy Layer Urban Heat Island Heat Island forms from the ground to below the
tops of trees or roofs whereas Boundary Layer Urban Heat Island start from the roof top or
tree top level and extend up to the point where urban landscape no longer influence the
atmosphere. (Bhargava A, 2017)
One of the vital reasons for the formation of UHI is the large amount of built up surfaces like
concrete, asphalt which has a high heat capacity (Akbari et al. 2001). Low albedo materials
are further contributing to worsening the phenomenon.
The urbanization causes an increased need for mobility in conjunction with the expansion of
trade and the improvement of accessibility to different parts of the globe which then leads to
congestion in traffic. Urban centers are often developed according to specific natural settings
and thus in singular conditions. Thus, the transport will concentrate mainly in the urban areas
and its impact will therefore appear dramatically on the environment and the atmosphere that
lead to climate change. (Haddad Louiza, 2015)
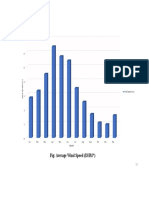
GROUP-5 3
You might also like
- The Impact of Green Areas On Mitigating Urban Heat Island Effect: A Review by Nastaran ShishegarDocument8 pagesThe Impact of Green Areas On Mitigating Urban Heat Island Effect: A Review by Nastaran ShishegarNastaran ShishegarNo ratings yet
- Urban Heat Island EffectDocument2 pagesUrban Heat Island EffectpopeyethesailormanNo ratings yet
- EJCC 2019 004 V1i1Document8 pagesEJCC 2019 004 V1i1Basit SaeedNo ratings yet
- Adapting Cities For Climate Change The Role of TheDocument20 pagesAdapting Cities For Climate Change The Role of TheAnastasiia Sin'kovaNo ratings yet
- Climate Change Impacts On and Actions From The Construction IndustryDocument10 pagesClimate Change Impacts On and Actions From The Construction IndustryBraylon RobinsonNo ratings yet
- General Summary of Climate Change and The Probable Consequences Resulting From It - EditedDocument9 pagesGeneral Summary of Climate Change and The Probable Consequences Resulting From It - EditedTonny MokayaNo ratings yet
- Urbanization & Modernization Effects on WeatherDocument2 pagesUrbanization & Modernization Effects on WeatherFried ChickenNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 502Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 502Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 500Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 500Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Applying Cool Pavements to Improve Urban EnvironmentsDocument2 pagesApplying Cool Pavements to Improve Urban EnvironmentsArmarniel Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument12 pagesClimate ChangeNyagudi Arucho KeithNo ratings yet
- Global Warming Can Be Said As Extreme Changes in The Weather and Climate of The EarthDocument2 pagesGlobal Warming Can Be Said As Extreme Changes in The Weather and Climate of The Earthandreas ivan sNo ratings yet
- Climate Change Effects and CausesDocument16 pagesClimate Change Effects and CausesKidus FelekeNo ratings yet
- Adaptacijagradova CvejicTutundzicBobicRadulovicDocument19 pagesAdaptacijagradova CvejicTutundzicBobicRadulovicstratmen.sinisa8966No ratings yet
- Research Literature Sample CodingDocument4 pagesResearch Literature Sample CodingAngelo MalonzoNo ratings yet
- CLIMATE CHANGE PPTDocument25 pagesCLIMATE CHANGE PPTHershey MagsayoNo ratings yet
- Preparing For The Future: The Impact of Climate Change On The Civil Engineering ProfessionDocument7 pagesPreparing For The Future: The Impact of Climate Change On The Civil Engineering ProfessionMuhannad AbdulRaoufNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument10 pagesClimate ChangeGaniyuNo ratings yet
- Paper 5B 2759 PR PDFDocument8 pagesPaper 5B 2759 PR PDFCarolina MacielNo ratings yet
- 2010 Mok Et Al AN EVALUATION OF GREEN INFRASTRUCTURE FOR THE RESTORATION OF ECOSYSTEM IN HONG KONGDocument18 pages2010 Mok Et Al AN EVALUATION OF GREEN INFRASTRUCTURE FOR THE RESTORATION OF ECOSYSTEM IN HONG KONGAbid NadeemNo ratings yet
- Discussion Question. No 1Document3 pagesDiscussion Question. No 1TopeNo ratings yet
- RWS Assignment 1Document4 pagesRWS Assignment 1Aizan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Ass EthicsDocument5 pagesAss EthicsBertrand TuyishimeNo ratings yet
- Urban Heat Island Causes Effects and MitigationDocument8 pagesUrban Heat Island Causes Effects and MitigationTapiwanashe NyakabauNo ratings yet
- Shafique Et Al. 2017Document6 pagesShafique Et Al. 2017CarlosNo ratings yet
- An Assessment of Heatwave Impact in Enugu Metropol-1Document31 pagesAn Assessment of Heatwave Impact in Enugu Metropol-1israelamaxissNo ratings yet
- Urban Heat Island Causes Effectsand MitigationDocument8 pagesUrban Heat Island Causes Effectsand MitigationRashmi AradhyaNo ratings yet
- Causes and Effects of the Urban Heat Island EffectDocument7 pagesCauses and Effects of the Urban Heat Island EffectKesto LoriakNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument11 pagesDocumentNiveditha TGNo ratings yet
- Building ClimatologyDocument3 pagesBuilding ClimatologyTobilobaNo ratings yet
- What Is Climate ChangeDocument2 pagesWhat Is Climate ChangeKayla SyahnikaNo ratings yet
- Global Climate Change and Its Effects On Human Habitat and Environment in MalaysiaDocument16 pagesGlobal Climate Change and Its Effects On Human Habitat and Environment in MalaysiaJhonrioacong PaneNo ratings yet
- Jet 003 Edward Climate ChangeDocument12 pagesJet 003 Edward Climate ChangeAlessandro CrimaldiNo ratings yet
- Climate Change Indias Perception and Legal FrameworkDocument16 pagesClimate Change Indias Perception and Legal FrameworkShrey NirmalNo ratings yet
- Hydro Assign 1Document8 pagesHydro Assign 1AHR NICOLE PANGILINANNo ratings yet
- Impacts of Climate Change On Urban Areas and NatureDocument13 pagesImpacts of Climate Change On Urban Areas and NatureGourab MondalNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument6 pagesClimate ChangeShashi KantNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument4 pagesClimate Changejerilyn.jayNo ratings yet
- EMR Hazard Regarding GSM/LTE Networks: Harem Masroor-16122063 Kiran Maqsood-16122087Document14 pagesEMR Hazard Regarding GSM/LTE Networks: Harem Masroor-16122063 Kiran Maqsood-16122087Harem MasroorNo ratings yet
- Urban Environments and Ecosystem FunctionsDocument9 pagesUrban Environments and Ecosystem FunctionsvvaldiviaaedoNo ratings yet
- Carbon Sequestration in The Root, Stem and Leaf of Different PlantDocument27 pagesCarbon Sequestration in The Root, Stem and Leaf of Different PlantRichard RexNo ratings yet
- The Environmental ImmunityDocument12 pagesThe Environmental ImmunityDr.Safaa Fetouh GomaaNo ratings yet
- BALANCING BUILT ENVIRONMENTS WITH HYBRID DESIGNDocument1 pageBALANCING BUILT ENVIRONMENTS WITH HYBRID DESIGNRohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Sustainability 11 03182Document20 pagesSustainability 11 03182Vera FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Arghavani 2020Document20 pagesArghavani 2020Fajar TaqyNo ratings yet
- Climate Change and BuildingsDocument7 pagesClimate Change and BuildingsShikha AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument9 pagesClimate ChangeOzair AtalNo ratings yet
- Figure 1: Urban ClimateDocument9 pagesFigure 1: Urban Climateadeel raziNo ratings yet
- Healing Earth with Green SolutionsDocument8 pagesHealing Earth with Green SolutionsSue VenidaNo ratings yet
- Building and Environment: Udayasoorian Kaaviya Priya, Ramalingam SenthilDocument20 pagesBuilding and Environment: Udayasoorian Kaaviya Priya, Ramalingam Senthilmercyella prasetyaNo ratings yet
- Urban Heat Island: A Presentation By: Madhumitha Sekar 2014701518 9 Semester Batch CDocument24 pagesUrban Heat Island: A Presentation By: Madhumitha Sekar 2014701518 9 Semester Batch CMadhu SekarNo ratings yet
- 2007 - GRIMMOND - Urbanization and Global Environmental Change Local Effects of Urban WarmingDocument6 pages2007 - GRIMMOND - Urbanization and Global Environmental Change Local Effects of Urban Warmingabraaolevi4009No ratings yet
- Ar 07Document7 pagesAr 07hndash100% (1)
- Rupa MergedDocument16 pagesRupa MergedSravya UpadrastaNo ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument11 pagesGlobal WarmingAmin BassitNo ratings yet
- The Role of Urban Trees and Greenspaces in Reducing Urban Air TemperaturesDocument12 pagesThe Role of Urban Trees and Greenspaces in Reducing Urban Air TemperaturesKalvin PratamaNo ratings yet
- Earth Science & Climatic Change: Building Energy Consumption and Carbon Dioxide Emissions: Threat To Climate ChangeDocument3 pagesEarth Science & Climatic Change: Building Energy Consumption and Carbon Dioxide Emissions: Threat To Climate ChangeKadiri OlanrewajuNo ratings yet
- Definition of Kyoto Protocol Principles of Kyoto ProtocalDocument16 pagesDefinition of Kyoto Protocol Principles of Kyoto ProtocalRavi MulimaniNo ratings yet
- Dincer - 2000 - and Sustainable Development A Crucial ReviewDocument19 pagesDincer - 2000 - and Sustainable Development A Crucial ReviewRen Eduardo Armenta CasalNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 67Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 67Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 43Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 43Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 42Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 42Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 55Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 55Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 45Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 45Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 56Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 56Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 51Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 51Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 47Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 47Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 46Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 46Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 52Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 52Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Literature Review Bioclimatic Charts Olgyay GivoniDocument1 pageLiterature Review Bioclimatic Charts Olgyay GivoniRohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Fig: Bioclimatic Chart of BiratnagarDocument1 pageFig: Bioclimatic Chart of BiratnagarRohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 49Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 49Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 54Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 54Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 38Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 38Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 53Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 53Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 50Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 50Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 40Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 40Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 29Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 29Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
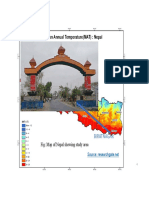
- Biratnagar: Fig: Map of Nepal Showing Study AreaDocument1 pageBiratnagar: Fig: Map of Nepal Showing Study AreaRohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 36Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 36Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 33Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 33Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 34Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 34Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 30Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 30Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 27Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 27Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 31Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 31Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 37Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 37Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 25Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 25Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- 9.4 Findings: Summary/checklist: Table 3 Check List of FindingsDocument1 page9.4 Findings: Summary/checklist: Table 3 Check List of FindingsRohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- All Climatology Seminar - 26Document1 pageAll Climatology Seminar - 26Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- GTP Introduction 071223GlobalTippingPointsReport2023Document22 pagesGTP Introduction 071223GlobalTippingPointsReport2023Maria Silvia Muylaert de AraujoNo ratings yet
- Climate Change Effects and SolutionsDocument1 pageClimate Change Effects and SolutionsGem CarmelNo ratings yet
- You Can Type Something HereDocument31 pagesYou Can Type Something HereLilibethNo ratings yet
- Activity 2. Weather and Natural Disasters Match The Words and The PicturesDocument2 pagesActivity 2. Weather and Natural Disasters Match The Words and The PicturesMorgana Luiza GranellaNo ratings yet
- Unit 6.in Re.t M I.re - Global Warning.11g.t M I, ReDocument3 pagesUnit 6.in Re.t M I.re - Global Warning.11g.t M I, ReLinh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Class Test Cop-27-1Document1 pageClass Test Cop-27-1Prachi AroraNo ratings yet
- Project 2Document20 pagesProject 2Gamaliel Luna CalderónNo ratings yet
- Climate Change CertificateDocument9 pagesClimate Change CertificateNaimish TewariNo ratings yet
- Children and Young People and The Climate Change ChallengeDocument2 pagesChildren and Young People and The Climate Change ChallengeIstiqamah PurnomoNo ratings yet
- News Lessons Climate Change Advanced Ws 940922Document5 pagesNews Lessons Climate Change Advanced Ws 940922IrrelevantNo ratings yet
- Module 4-Climate Change and Energy Crisis... STSDocument31 pagesModule 4-Climate Change and Energy Crisis... STSaljon.tolete.pbsNo ratings yet
- Evs ProjectDocument4 pagesEvs ProjectPragya RichhariyaNo ratings yet
- 1.0 1.1 Background To The StudyDocument82 pages1.0 1.1 Background To The StudyOko IsaacNo ratings yet
- NSTP ReviewerDocument29 pagesNSTP ReviewerUmoji KimNo ratings yet
- Global Warming Causes, Effects, and SolutionsDocument3 pagesGlobal Warming Causes, Effects, and SolutionsLouisa Alexis TanuraharjaNo ratings yet
- Electric Vehicle Charging InfrastructureDocument13 pagesElectric Vehicle Charging InfrastructureRajib DasNo ratings yet
- Global Warming and Climate ChangeDocument10 pagesGlobal Warming and Climate ChangeMuhammad WaseemNo ratings yet
- Pre-int/Intermediate Reading Text: Wild WeatherDocument6 pagesPre-int/Intermediate Reading Text: Wild WeatherAna Maria CruzNo ratings yet
- Identifying Assumptions and Conclusions in Practice QuestionsDocument2 pagesIdentifying Assumptions and Conclusions in Practice QuestionsJohn Patrick LaspiñasNo ratings yet
- Climatology AssignmentDocument6 pagesClimatology AssignmentPrince SiawNo ratings yet
- Zeng+et+al 2021 Environ. Res. Lett. 10.1088 1748-9326 Ac3f62Document25 pagesZeng+et+al 2021 Environ. Res. Lett. 10.1088 1748-9326 Ac3f62lucioNo ratings yet
- Carbon Program Introduction: January 2022Document14 pagesCarbon Program Introduction: January 2022Rahim DavisNo ratings yet
- Final Second Sum 3rd QuarterDocument2 pagesFinal Second Sum 3rd QuarterNavelle Grace AliteNo ratings yet
- Article Climate Change and Global WarmingDocument4 pagesArticle Climate Change and Global WarmingNurhusna IzmanNo ratings yet
- Gest Final ExamDocument2 pagesGest Final ExamLean Cris MaatNo ratings yet
- Climate Change Causes and Solutions in 40 CharactersDocument1 pageClimate Change Causes and Solutions in 40 CharactersPorcia ScriptsNo ratings yet
- IPCC AR6 WGIII FinalDraft FullReportDocument2,913 pagesIPCC AR6 WGIII FinalDraft FullReportarfa wainceNo ratings yet
- E ProofingDocument42 pagesE ProofingSusana AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- LCCAP TemplateDocument71 pagesLCCAP TemplateEmmanuel RecodoNo ratings yet
- Environment Global Warming Conversation Topics Dialogs Oneonone Activities Re 90781Document3 pagesEnvironment Global Warming Conversation Topics Dialogs Oneonone Activities Re 90781Monica Maria DogaruNo ratings yet