Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Department of Electrical Engineering
Uploaded by
goyal.167009Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Department of Electrical Engineering
Uploaded by
goyal.167009Copyright:
Available Formats
Department of Electrical Engineering
BEEG-1001 Session:2020-21 Tutorial sheet : 1
Electrical Engineering (Magnetic circuit) Odd Semester
1. A coil of insulated wire of 500 turns and resistance of 4Ω is closely wound on an iron ring. The
ring has a mean diameter of 0.25m and a uniform cross-sectional area of 700 mm 2. Calculate the
total flux in the ring when a dc supply of 6V is applied at the ends of winding. Assume a relative
permeability of 550.
[Ans: 0.462mWb]
2. A ring of mean diameter 30 cm is wound with 200 turns of copper wire carrying a current of 2
A. The x-section of the magnetic material of the ring is 12 cm 2 and its relative permeability is
1,000. Determine theflux through it.
[Ans: 0.64 m Wb]
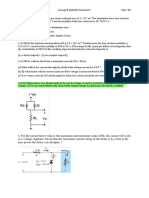
3. A rectangular shaped core is made of mild steel plate 15 mm x 20 mm cross-section. The mean
length of the magnetic path is 18 cm. The exciting coil has 300 turns and current 0.7
A. Calculate :
(i) Magnetic field intensity(H)
(ii) Flux density
(iii) Reluctance
(iv) Flux of magnetic circuit.
Assume relative permeability of mild steel is 940.
[Ans: (i) 1,166.67 AT/m, (ii) 1.378 T (iii) 50.794 x 10 4 AT/ Wb (iv) 4.134x10 -4Wb]
4. An iron ring of mean diameter 10 cm is uniformly wound with 2000 turns of wire. When a
current of 0.25 A is passed through the coil a flux density of 0.4 T is set up in the iron.
Find
(a) the magnetic field intensity
(b) the relative permeability of theiron under these conditions.
[Ans: 1592 A/m, 200]
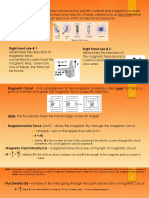
5. What are the difference between electric and magnetic circuit?
6. Define the terms: (a) MMF (b) Field strength (c) Flux density (d) Relative permeability (e)
Reluctance (f) Coercive force (g) residual flux density (h) leakage flux
You might also like
- Home-made Toy Motors: A practical handbook giving detailed instructions for building simple but operative electric motorsFrom EverandHome-made Toy Motors: A practical handbook giving detailed instructions for building simple but operative electric motorsNo ratings yet
- EEB326 Magnetic Circuits and ElectromagnetismDocument110 pagesEEB326 Magnetic Circuits and ElectromagnetismDerrick Maatla MoadiNo ratings yet
- MCQ DistributionDocument8 pagesMCQ Distributiongoyal.167009100% (2)
- Chapter 9. Electromagnetism Induction - PDFDocument10 pagesChapter 9. Electromagnetism Induction - PDFYakub ChannelNo ratings yet
- Synopsis FormatDocument5 pagesSynopsis Formatsgrpdl100% (1)
- Question Bank PS1Document3 pagesQuestion Bank PS1goyal.167009No ratings yet
- Power System Simulation Lab ManualDocument41 pagesPower System Simulation Lab ManualArivumani86% (14)
- Algoritma Genetika Dalam MatlabDocument94 pagesAlgoritma Genetika Dalam MatlabTomo Siagian50% (2)
- Inverted PendulumDocument73 pagesInverted PendulumDheeraj GaddiNo ratings yet
- Scada SystemDocument48 pagesScada SystemAbilraj PurathetharayilNo ratings yet
- Scada SystemDocument48 pagesScada SystemAbilraj PurathetharayilNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Aasign Set 2 For 2020-24 BatchDocument2 pagesUnit 1 Aasign Set 2 For 2020-24 BatchHARSHNI R 24EENo ratings yet
- Problems For PracticeDocument2 pagesProblems For PracticeFisher TigerNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Circuit Assignment SolvedDocument1 pageMagnetic Circuit Assignment SolvedVikash TiwariNo ratings yet
- Exercise On MagnetismDocument2 pagesExercise On Magnetismkirubel ayeleNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Energy Conversion Problem Set 1Document1 pageFundamentals of Energy Conversion Problem Set 1rebecca pullitan100% (1)
- Tutorial 3Document1 pageTutorial 3Goral Nakum Prof.No ratings yet
- Tutorial 5Document2 pagesTutorial 5lucky meNo ratings yet
- TUT 3 (Electromagnetism)Document1 pageTUT 3 (Electromagnetism)Tbos ThabisoNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering Assignment 1 (Unit-1)Document1 pageBasic Electrical Engineering Assignment 1 (Unit-1)14 Tejaswini PawarNo ratings yet
- sheet 1 مقدمة فى الالاتDocument13 pagessheet 1 مقدمة فى الالاتahmed shaban alsaidNo ratings yet
- AC and DC Machinery Review QuestionsDocument4 pagesAC and DC Machinery Review Questionsedwinjayar50% (6)
- SheetDocument2 pagesSheetabosalah1223334444100% (1)
- Magnetic Circuit Problems From HughesDocument2 pagesMagnetic Circuit Problems From Hughesutkarsh singh100% (1)
- Sheet (1) : An Iron Ring Has A Cross-Sectional Area of 3 CMDocument2 pagesSheet (1) : An Iron Ring Has A Cross-Sectional Area of 3 CMKhalifa MohamedNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism Problem SheetDocument1 pageElectromagnetism Problem Sheetud54100% (1)
- Tut 5 - Magnetic Circuits and Electromagnetic InductionDocument3 pagesTut 5 - Magnetic Circuits and Electromagnetic InductionAVINASH PATILNo ratings yet
- Class Test 3Document1 pageClass Test 3jayeshdiwanNo ratings yet
- Three phase circuits and magnetic circuitsDocument4 pagesThree phase circuits and magnetic circuitsMahesh SinghNo ratings yet
- 2 A ElectromagnetismDocument4 pages2 A ElectromagnetismSyed AzzizNo ratings yet
- Tutsheet 3Document2 pagesTutsheet 3rohanNo ratings yet
- Eee3352 L5Document42 pagesEee3352 L5Desmond CheweNo ratings yet
- ECE 330 homework problems magnetic fields circuits phasorsDocument2 pagesECE 330 homework problems magnetic fields circuits phasorsHuynh BachNo ratings yet
- Machine Tutorial 1Document3 pagesMachine Tutorial 1Rajeev YadavNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document2 pagesTutorial 2Srinath PvtNo ratings yet
- BEEG1001 Assignment 1: Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument1 pageBEEG1001 Assignment 1: Basic Electrical EngineeringSakshat LakhianiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - Magnetic CircuitsDocument4 pagesAssignment 1 - Magnetic CircuitsPravish Zeus100% (1)
- DC MachinesDocument34 pagesDC MachinesCristele Mae GarciaNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Flux and Density ProblemsDocument3 pagesMagnetic Flux and Density ProblemsAliaa TarekNo ratings yet
- 4 - Simple Magnetic Circuits - 2019Document22 pages4 - Simple Magnetic Circuits - 2019ZAINAB MOFFATNo ratings yet
- CE6306 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS PART-B TOPICSDocument8 pagesCE6306 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS PART-B TOPICSnkchandruNo ratings yet
- Machine Work Sheet With AnswerDocument20 pagesMachine Work Sheet With AnswerTeklu AnbeseNo ratings yet
- DC Machines Module 2Document17 pagesDC Machines Module 2Joshua Roberto GrutaNo ratings yet
- T1-T7Q Ee2005 NtuDocument10 pagesT1-T7Q Ee2005 NtuamosmarongshengNo ratings yet
- Bee - Cse - ItDocument1 pageBee - Cse - ItTân ChipNo ratings yet
- Understanding Electro MagnetismDocument22 pagesUnderstanding Electro MagnetismkarnatisharathNo ratings yet
- EE 321 Assignment No. 1Document2 pagesEE 321 Assignment No. 1johnpaulshobayanNo ratings yet
- Exam 4 Set BDocument9 pagesExam 4 Set BDummy AccountNo ratings yet
- Questions of Magnetic Circuit and TransformerDocument1 pageQuestions of Magnetic Circuit and Transformerm_mustaqeemNo ratings yet
- SheetDocument3 pagesSheetBarun BeheraNo ratings yet
- Problem SetDocument1 pageProblem SetEmilee Noven RamirezNo ratings yet
- ElectroTechnology 1 Nov 2009Document5 pagesElectroTechnology 1 Nov 2009Fraidy mhlongoNo ratings yet
- Physics II ProblemsDocument1 pagePhysics II ProblemsBOSS BOSSNo ratings yet
- Ckt3 Plate 2Document3 pagesCkt3 Plate 2'Wendell BernardinoNo ratings yet
- Questions MagneticDocument3 pagesQuestions MagneticEmmanuelNo ratings yet
- CH 05 More QuestionsDocument17 pagesCH 05 More Questionswoboc79249No ratings yet
- ELL100 Group B Tutorial 1 Nov ‘22Document1 pageELL100 Group B Tutorial 1 Nov ‘22Priyanka kataria [IIT DELHI]No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Electrical MachineryDocument33 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Electrical MachineryShikoyeniNo ratings yet
- EMI NumericalDocument3 pagesEMI Numericalpraveen godaraNo ratings yet
- Answer Any THREE Questions From This SectionDocument3 pagesAnswer Any THREE Questions From This SectionKirk PatrickNo ratings yet
- Serway 6 e Problems 27Document12 pagesSerway 6 e Problems 27Diego CañonNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1 Magnetic CircuitsDocument3 pagesProblem Set 1 Magnetic CircuitsYaraNo ratings yet
- Strain energy stored in stretched cables and wiresDocument2 pagesStrain energy stored in stretched cables and wiresLiuJiewChuan100% (1)
- Tutorial Sheet IV Inductance Magnetic Flux Transformer ProblemsDocument2 pagesTutorial Sheet IV Inductance Magnetic Flux Transformer ProblemsRishav ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- HW - EE331 - No 5Document12 pagesHW - EE331 - No 575wpt82qvyNo ratings yet
- Taller Sobre Propiedades Eléctricas-2016-2Document2 pagesTaller Sobre Propiedades Eléctricas-2016-2alejo ossaNo ratings yet
- Hooke's Law and Stress-Strain Relationship for Mechanical EngineersDocument7 pagesHooke's Law and Stress-Strain Relationship for Mechanical Engineersrkrajesh86No ratings yet
- Network SynthesisDocument7 pagesNetwork Synthesisgoyal.167009No ratings yet
- Interference OverheadDocument1 pageInterference Overheadgoyal.167009No ratings yet
- Heat Generation CablesDocument1 pageHeat Generation Cablesgoyal.167009No ratings yet
- Filters 1Document40 pagesFilters 1goyal.167009No ratings yet
- Insulated Cables EEDocument36 pagesInsulated Cables EEgoyal.167009No ratings yet
- Comparison HVDC EHVACDocument2 pagesComparison HVDC EHVACgoyal.167009No ratings yet
- workTheoryObj SampleDocument7 pagesworkTheoryObj Samplegoyal.167009No ratings yet
- Distribution SystemDocument28 pagesDistribution Systemgoyal.167009No ratings yet
- Tute 4Document1 pageTute 4goyal.167009No ratings yet
- Bundle ConductorsDocument1 pageBundle Conductorsgoyal.167009No ratings yet
- Cable FaultsDocument1 pageCable Faultsgoyal.167009No ratings yet
- EEC - 604 Assign - 3Document1 pageEEC - 604 Assign - 3goyal.167009No ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - TDDocument7 pagesMicrosoft Word - TDgoyal.167009No ratings yet
- Basics of Distribution SubstationDocument16 pagesBasics of Distribution Substationgoyal.167009No ratings yet
- GLA University, Mathura Department of Electrical EngineeringDocument2 pagesGLA University, Mathura Department of Electrical Engineeringgoyal.167009No ratings yet
- Insulated Cables Subject Power SystemsDocument7 pagesInsulated Cables Subject Power Systemsgoyal.167009No ratings yet
- (M. Rasul) Thermal Power PlantsDocument274 pages(M. Rasul) Thermal Power Plantsgoyal.167009100% (1)
- Editionname:The Times of India Pageno:013Document1 pageEditionname:The Times of India Pageno:013goyal.167009No ratings yet
- Robust Energy Management of A Hybrid WindDocument13 pagesRobust Energy Management of A Hybrid Windgoyal.167009No ratings yet
- Inverted Pendulum Control System DesignDocument36 pagesInverted Pendulum Control System Designstephanie-tabe-1593No ratings yet
- 2006 07Document4 pages2006 07goyal.167009No ratings yet