Professional Documents
Culture Documents
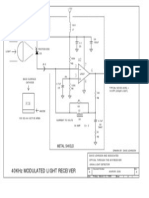
Cascode Light Receiver Circuit
Uploaded by
MEGA_ONEOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cascode Light Receiver Circuit
Uploaded by
MEGA_ONECopyright:
Available Formats
5v 5v 5v
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
Upper NPN transistor forms an emitter follower constant voltage source.
Q=1
Bottom NPN transistor forms a constant current sink.
The junction where the two circuits meet tries to keep the voltage and current constant.
2.2K
0.1 330K 1H TO NEXT Current changes fed into the node show up as current changes through the load impedance.
GAIN STAGE
The current from the photo diode is added to the node. Since the current is held
constant by the bottom circuit, any additional current fed into the node will result in a
Load impedance
current reduction through the load impedance.
5v
Ipd = photo diode current
3V 2N3904
Ia = upper NPN load current
Constant voltage source Ib = lower NPN current
0.1 3.3K Then: Ib = Ia + Ipd or Ia (load) = Ib - Ipd
0.1
2.5V
The circuit does not produce any current or voltage gain, it isolates the load from
CONSTANT VOLTAGE/ the PIN photo diode.
CURRENT NODE
C PIN photo diode current is translated into the load impedance.
Since the node voltage is held constant, the voltage across the photo diode is also fixed. The
PHOTODIODE
diode's capacitance effect on speed is therefore minimized.
A
With an inductive load, only current changes will produce a voltage drop across the impedance.
Constant current sink Ambient light induced current from the photo diode will not produce a voltage
across the inductive load.
3.3K 1.8V 5mA
5V However, the photo diode current must not be high enough to exceed the bottom
2N3904 NPN current sink level.
0.1 The resistor in parallel with the inductor is used to keep the Q of the circuit limited. For
1.8K 240
maximum bandwidth the Q should be held to a value of one or less.
DRAWN BY: DAVE JOHNSON
DAVID JOHNSON AND ASSOCIATES
Title
CASCODE LIGHT RECEIVER CIRCUIT
40KHz LIGHT RECEIVER FRONT-END CIRCUIT
Size Document Number Rev
A 40KRVR3A.DSN A
Date: Friday, February 15, 2002 Sheet 1 of 1
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- 8845physics Unit 3 Cheat Sheet 3Document2 pages8845physics Unit 3 Cheat Sheet 3Damon Hamilton100% (3)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- SMT Manual Handbook SMD Databook Surface Mount TechnologyDocument689 pagesSMT Manual Handbook SMD Databook Surface Mount TechnologyMEGA_ONE100% (2)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Circuits 1Document110 pagesCircuits 1Mark Ian Tanangonan Maravilloso100% (1)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- OZ Series LCD Backlight IC SDocument36 pagesOZ Series LCD Backlight IC SJUANNo ratings yet
- Smart Plant PotDocument95 pagesSmart Plant Potharshitha100% (1)
- UserManual - V Chem Plus (VEC 1.805)Document77 pagesUserManual - V Chem Plus (VEC 1.805)Dharmesh Patel100% (2)
- Sensors & Transducers MCQDocument25 pagesSensors & Transducers MCQSaquibh Shaikh75% (4)
- 40Khz TV-VCR Light Source Repeater: Size Document Number RevDocument1 page40Khz TV-VCR Light Source Repeater: Size Document Number RevMEGA_ONENo ratings yet
- CommandDocument8 pagesCommandMEGA_ONENo ratings yet
- The Harman Kardon FL8380 Service ManualDocument72 pagesThe Harman Kardon FL8380 Service ManualMEGA_ONENo ratings yet
- Great ResetDocument2 pagesGreat ResetMEGA_ONENo ratings yet
- Line Powered 60Hz Clock Generator Circuit DiagramDocument1 pageLine Powered 60Hz Clock Generator Circuit DiagramMEGA_ONENo ratings yet
- 75 MFBVRDocument1 page75 MFBVRMEGA_ONENo ratings yet
- 40 KRVR 3Document1 page40 KRVR 3Dhiietta YaqqiinNo ratings yet
- Explaining The Covid-49Document1 pageExplaining The Covid-49MEGA_ONENo ratings yet
- 30Khz - 50Khz Light Receiver Circuits: With Ambient Light CompensationDocument1 page30Khz - 50Khz Light Receiver Circuits: With Ambient Light CompensationMEGA_ONENo ratings yet
- 40Khz Light Receiver Front-End Circuit: TitleDocument1 page40Khz Light Receiver Front-End Circuit: TitleMEGA_ONENo ratings yet
- 50MHz BANDWIDTH LIGHT PROBEDocument1 page50MHz BANDWIDTH LIGHT PROBEMEGA_ONENo ratings yet
- 175 KRVRDocument1 page175 KRVRNicolas MigneaultNo ratings yet
- 40 KRVR 1Document1 page40 KRVR 1Tomas ErnestoNo ratings yet
- 175Khz Ring Generator: Size Document Number RevDocument1 page175Khz Ring Generator: Size Document Number RevPraveen StarkingNo ratings yet
- LOW POWER 30KHz LIGHT RECEIVER AMPDocument1 pageLOW POWER 30KHz LIGHT RECEIVER AMPMEGA_ONENo ratings yet
- Rem SwitchDocument1 pageRem Switchdr_best_001No ratings yet
- 200Mhz - 400Mhz Vco: Size Document Number RevDocument1 page200Mhz - 400Mhz Vco: Size Document Number RevMEGA_ONENo ratings yet
- 24 VexcDocument1 page24 VexcMEGA_ONENo ratings yet
- 20 MRVR 2Document1 page20 MRVR 2MEGA_ONENo ratings yet
- 20 MHZLSRDocument1 page20 MHZLSRMEGA_ONENo ratings yet
- 4 PhostatDocument1 page4 PhostatMEGA_ONENo ratings yet
- 9 V Pulse GeneratorDocument1 page9 V Pulse GeneratorAlex AnthonyNo ratings yet
- 5 Watt Fluorescent Lamp Modulation Test CircuitDocument1 page5 Watt Fluorescent Lamp Modulation Test CircuitGeorge MucutaNo ratings yet
- 40KHz LASER BURST TRANSMITTERDocument1 page40KHz LASER BURST TRANSMITTERMEGA_ONENo ratings yet
- 5MHz OPTICAL FIBER LIGHT PROBEDocument1 page5MHz OPTICAL FIBER LIGHT PROBEMEGA_ONENo ratings yet
- Charge Pump Voltage DividerDocument1 pageCharge Pump Voltage DividerMEGA_ONENo ratings yet
- 5v Touch SwitchDocument1 page5v Touch Switchthanu20No ratings yet
- 3 Vledfs 1Document1 page3 Vledfs 1MEGA_ONENo ratings yet
- Phototransistor-Ired Data BookDocument72 pagesPhototransistor-Ired Data BookvishunjeetNo ratings yet
- Free Space Optics - A Technical Seminar ReportDocument35 pagesFree Space Optics - A Technical Seminar Reportkarthik DC100% (4)
- PhotodetectorsDocument46 pagesPhotodetectorsShivam AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Fire Alarm and Water Turbine Sprinkler Using Zener DiodeDocument23 pagesFire Alarm and Water Turbine Sprinkler Using Zener DiodeJonathan SaydeNo ratings yet
- Optical FuzeDocument7 pagesOptical FuzegattiantonioNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor NotesDocument14 pagesSemiconductor NotesBansariNo ratings yet
- Technical Answers For Real World Problems (TARP) Assignment-7Document3 pagesTechnical Answers For Real World Problems (TARP) Assignment-7Anup PatelNo ratings yet
- Kasturba Institute of Technology: Minor ProjectDocument15 pagesKasturba Institute of Technology: Minor ProjectRiya KumariNo ratings yet
- Optical Sources DetectorsDocument72 pagesOptical Sources DetectorsDivyank BhardwajNo ratings yet
- An MLX75308 - System DesignDocument14 pagesAn MLX75308 - System DesignSantosh GoudarNo ratings yet
- Discovery Product Guide PP2052Document32 pagesDiscovery Product Guide PP2052Carlos TorresNo ratings yet
- Fiber OpticsDocument86 pagesFiber OpticsChristopher Oares100% (1)
- Smart Waste Management System Using ARDUINO: November 2019Document7 pagesSmart Waste Management System Using ARDUINO: November 2019Rajesh KannanNo ratings yet
- PM100A ManualDocument64 pagesPM100A Manualblues3gattoNo ratings yet
- Navneet Eced Lab ExpDocument16 pagesNavneet Eced Lab ExpNAVNEET KUMARNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3: Light SensorsDocument5 pagesAssignment 3: Light SensorsChimmy ChangaNo ratings yet
- BPW96B, BPW96C: Vishay SemiconductorsDocument5 pagesBPW96B, BPW96C: Vishay SemiconductorsHùng CậnNo ratings yet
- A Swing with a Falling Weight: Speeds and FrequenciesDocument60 pagesA Swing with a Falling Weight: Speeds and Frequenciesais3000No ratings yet
- Test Methods and PracticesDocument30 pagesTest Methods and PracticesBảo BìnhNo ratings yet
- Saint Louis University School of Engineering and Architecture Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument18 pagesSaint Louis University School of Engineering and Architecture Department of Mechanical EngineeringHero CourseNo ratings yet
- CatalogueDocument122 pagesCatalogueportocala12No ratings yet
- Brochures Hochiki AddressableDocument18 pagesBrochures Hochiki AddressableEdward Chan AcostaNo ratings yet
- Photo DetectorsDocument47 pagesPhoto DetectorsShubham SinghNo ratings yet
- Syllabus BE MergedDocument95 pagesSyllabus BE MergedSANGITA CHIRANJIBI POKHRELNo ratings yet