Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Jurnal Profesi Medika: Jurnal Kedokteran Dan ISSN 0216-3438 (Print) - ISSN 2621-1122 (Online) Kesehatan
Uploaded by
NasriOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Jurnal Profesi Medika: Jurnal Kedokteran Dan ISSN 0216-3438 (Print) - ISSN 2621-1122 (Online) Kesehatan
Uploaded by
NasriCopyright:
Available Formats
Jurnal Profesi Medika : Jurnal Kedokteran dan
ISSN 0216-3438 (Print). ISSN 2621-1122 (Online) Kesehatan
PROVEN CASES OF DUODENAL ATRESIA ON PLAIN ABDOMINAL
RADIOGRAPHY IN CORRELATION WITH SURGICAL FINDINGS –
A CASE SERIES
Fiona1* , Ni Nyoman Margiani2 , Firman Parulian Sitanggang2
1 Faculty of Medicine, University of Udayana, Bali , Indonesia
2 Faculty of Medicine, Denpasar University, Bali, Indonesia
*Correspondence Email: fiona30jakarta@gmail.com
ABSTRACT
Duodenal atresia is a congenital emergency abnormality and the most common cause of proximal
bowel obstruction in neonates. The duodenum has not developed properly in embryogenesis with a
blind end that cannot be seen through gastric contents. The incidence of duodenal atresia is 1/10.000
live births that commonly affects boys than girls. In cases of neonatal bilious vomiting, the first choice
imaging modality is plain abdominal radiography. The purpose of this case report is to increase
radiologist and pediatrician awareness in duodenal atresia diagnosis through plain abdominal
radiography and to minimize radiation in the neonates. We report 3 cases of duodenal atresia found
in Sanglah Hospital, Denpasar, in 1 year for the period 2018 - 2019.Case 1: A 4-day-old baby girl
presented with bilious vomiting in the first 24 hours after birth.Case 2: A 4-day-old baby boy
presented with lethargy, weak crying, and groaning after birth. There is no history of passed
meconium in the first 24 hours of birth. Case 3: A newborn boy presented with bilious emesis after
breastfeeding and nonprojectile. From the 3 cases, a plain abdominal radiograph was examined, and
a double bubble sign with no intestinal gas distal was found.
Keywords: Duodenal Atresia; Bilious Vomiting; Double Bubble; Plain Abdominal Radiography;
Duodenoduodenostomy.
INTRODUCTION
Duodenal atresia is a proximal another congenital anomaly. Duodenal
congenital gastrointestinal obstruction that atresia is located at the junction of the 1st and
can cause bilious or non-bilious vomiting 2nd parts of the duodenum, found in 85% of
within the first 24-38 hours of birth, usually cases.2 Classification of duodenal atresia
after the first oral feeding. There is based on Gray and Scandalakis is divided
interference during the embryogenesis into three types. Type I is the most common
process. It produces a short fibrous cord that type and often occurs in neonates. Type II is
connects between the two blind ends of the the rarest type, about 1%, and type III occurs
atretic duodenum. This is considered the in about 7% of cases.
result of duodenal failure for recanalization, The diagnosis of duodenal atresia can
which begins at the 6th week of be made radiographically with a plain
embryogenesis development.1 Duodenal abdominal radiograph as the first step in
atresia is a congenital abnormality that evaluation. The double bubble sign with the
occurs in about 1/10.000 live births, which absence of distal intestinal gas is a
commonly affects boys than girls. More than pathognomonic sign for duodenal atresia.3
50% of duodenal atresia is associated with
Vol. 14 No 2 2020 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.33533/jpm.v14i2.2227 191
Jurnal Profesi Medika : Jurnal Kedokteran dan
ISSN 0216-3438 (Print). ISSN 2621-1122 (Online) Kesehatan
CASE SERIES
Case 1
A 4-day-old baby girl presented with
bilious vomiting within the first 24 hours of
birth, typically following after breastfeeding.
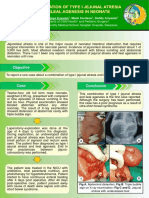
There was no history of passed meconium b. Duodenal atresia finding on
within the first 24 hours after birth. The duodenoduodenostomy laparoscopic and
patient had a history of cesarean delivery et anastomosis end to end is done.
causa re-cesarean section delivery with Figure 1. Plain abdominal radiography
normal gestational age, the 4th child, and birth and surgical findings in case 1.
weight is 3.100 gram and normal APGAR
score.
On physical abdominal examination, Case 2
there are supel, no distention, and normal A 4-day-old baby boy presented with
bowel sound. 20 cc residual from the lethargy, weak crying, and groaning after birth.
orogastric tube was obtained. There is a APGAR score 5-8-8. Respiratory distress (-),
normal laboratory blood examination. Plain cyanosis (-). 13 cc bilious material production in
abdominal radiography showed a double an orogastric tube after birth was obtained. No
bubble sign in the middle and left abdominal history of passed meconium within the first 24
cavity with the absence of distal bowel gas, so hours of birth. The patient is the 2nd child, with
impressed as duodenal atresia. premature gestational age (31 - 32 weeks) and
Duodenoduodenostomy laparoscopic is spontaneous delivery history, birth weight is
performed on the next day, duodenal atresia in 1.550 gram.
surgical findings, and anastomosis end to end On physical abdominal examination, there
is done. are supel, no distention, and normal bowel
sound. Bilious material production in the
orogastric tube remained. On plain abdominal
radiography showed double bubble sign with the
absence of bowel gas distally, so impressed as
duodenal atresia.
Surgical was performed and founded
duodenal atresia. Duodenoduodenostomy with
Kimura procedure is done.
a. Plain abdominal radiography showed a
double bubble sign in the middle and
left abdominal cavity and no distal
intestinal gas.
Figure 2. The plain abdominal radiograph
showed a double bubble sign with the absence
of bowel gas distally.
Vol. 14 No 2 2020 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.33533/jpm.v14i2.2227 192
Jurnal Profesi Medika : Jurnal Kedokteran dan
ISSN 0216-3438 (Print). ISSN 2621-1122 (Online) Kesehatan
Case 3 possibility of proximal bowel obstruction.
A newborn boy presented with bilious Other clinical symptoms and investigation
emesis after breastfeeding and nonprojectile. No examinations support it are carried out to
history of passed meconium within 24 hours after establish the diagnosis. In this case, the imaging
birth. The patient is the 1st child with cesarean modality plays an important role in establishing
delivery et causa polyhydramnios, birth weight the diagnosis. Complete history accompanied
is 2.680 gram, and a normal APGAR score. by information about the antenatal examination
Antenatal ultrasonography was obtained and in duodenal atresia can also be an adjunct in
revealed a double bubble appearance. establishing diagnoses such as polyhydramnios
On physical abdominal examination, there and double bubble sign on antenatal ultrasound.
are supel, no distention, and normal bowel The three serial cases of duodenal atresia were
sound. On the plain abdominal radiography obtained in the past year that was found at
showed double bubble sign with the absence of Sanglah Hospital, with bilious vomiting and no
bowel gas distally, so impressed as duodenal meconium passed in the first 24 hours of birth.
atresia. The duodenum is a small intestine C-
Atresia 2nd part of the duodenum was shaped that connects the stomach to the
founded in duodenoduodenostomy surgical with jejunum. The duodenum arches around the head
Kimura procedure and end to end anastomosis of the pancreas and forms the terminal or orifice
duodenoduodenostomy diamond shape is done. of the liver and pancreas' biliary apparatus
system. Besides, the duodenum is also the end
of the upper gastrointestinal tract.
Gastrointestinal is divided into upper and lower
parts by the presence of Treitz ligament (M.
suspensorius duodeni), which is located in the
duodenojejunalis flexura, which is the
boundary between the duodenum and jejunum.
The duodenum is located in the abdominal
cavity in the epigastric and umbilical regions.
The duodenum is divided into four parts:
superior part, descendens part, horizontalis
part, and ascendens part.4 Development of
a. Plain abdominal radiography showed a
duodenal embryology begins at the 5th week of
double bubble sign and no distal bowel
pregnancy, where the proliferating duodenal
gas. epithelium will completely block the duodenal
lumen in the 6th week. At the 7th week there will
be a vacuolization process. During this process,
the cell will undergo an apoptosis process that
arises in the lumen of the duodenum. Apoptosis
will cause epithelial cell degeneration. This
b. Atresia 2nd part of duodenum finding process results in recanalization of the duodenal
on duodenoduodenostomy surgical. lumen in the 9th week.
Atresia is a medical term describing a
Figure 3. Plain abdominal radiography condition where no opening or part of the body
and surgical findings in case 3. is closed.5 Duodenal atresia is defined as a
condition in which the duodenum does not
develop properly, so it is not an open channel of
DISCUSSION the stomach that does not allow food to travel
In newborns with vomiting, especially from the stomach to the intestine. In this
bilious vomiting, should be considered the
Vol. 14 No 2 2020 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.33533/jpm.v14i2.2227 193
Jurnal Profesi Medika : Jurnal Kedokteran dan
ISSN 0216-3438 (Print). ISSN 2621-1122 (Online) Kesehatan
condition, the duodenum can experience in this type, namely simple, fenestration and
complete narrowing, inhibiting food absorption windsock anomalies. Windsock anomalies may
from the stomach into the intestine.6 occur if the web is thin. The base of this
Congenital abnormalities are one of the membrane is the 2nd part of the duodenum. This
main causes of infant death. Based on WHO, type is the most common type of all duodenal
more than 8 million babies worldwide are born atresia (about 92%). This type of atresia may
every year with congenital abnormalities WHO partially obstruct and can, therefore, not be
states that congenital abnormalities cause 2.68 detected until solid food is given. Type II, the
million infant deaths, 11,3%. When compared two blind ends of the duodenum with the
with Southeast Asia, Indonesia is still the proximal and distal segments connected by short
country with a high prevalence of babies with fibrous cords. This type is the least common type
congenital abnormalities. The Ministry of of duodenal atresia, about 1%. Type III, the two
Health's surveillance results for the period of blind ends of the duodenum with the complete
September 2014 - March 2018 showed 1.085 discontinuity between the proximal and distal
infants with reported congenital abnormalities. segments, occurs in 7% of duodenal atresia cases.
However, there was no specific data regarding
intestinal atresia epidemiology because it was
still not well recorded.7 Congenital duodenal
atresia occurs in about 1 / 10.000 live births and
affecting boys more often than girls.
There are two suspected factors causing
duodenal atresia, namely, intrinsic and
extrinsic factors. Intrinsic factors are caused
due to failure of epithelial nerve Gambar 4. Classification of duodenal atresia
recanalization or excessive endodermal according to Gray and Scandalakis. (A) Type
proliferation.8 In contrast, the extrinsic factor I duodenal atresia; (B) Type II duodenal
of duodenal atresia is caused by the atresia, and (C) Type III duodenal atresia. 2
development of the disturbance of the
surrounding organ structure, such as the Duodenal atresia appears early in the birth
pancreas. The annular pancreas is a pancreatic
with bilious vomiting, usually within the first 24-
tissue surrounding the duodenum, especially 38 hours of birth after the first drink, and will
the duodenum descendens part.9 worsen if untreated. Infants with duodenal atresia
More than 50% of duodenal atresia is also appear in the early period with minimal
associated with congenital anomalies, namely abdominal distension, and 60-75% of neonates
trisomy 21 / Down Syndrome (about 30% of have no meconium release within the first 24
patients), as part of the VACTERL anomaly hours of birth. If there is a meconium release in
complex (Vertebral defects, Anal atresia, Cardiac neonates with atresia, usually a small amount of
defects, Tracheal Esophageal fistula, Renal meconium, a drier consistency, and a grayish
anomalies, and Limb abnormalities); 30% color than normal meconium. Obstruction often
isolated heart defects; 45% prematurity; 33%
occurs around the ampulla of Vater. If atresia
growth retardation; 25% other intestinal occurs in the distal ampulla of Vater in the 2nd
anomalies.2 part of the duodenum, bilious vomiting occurs. If
The classification of duodenal atresia, atresia occurs proximal to the ampulla of Vater,
according to Gray and Scandalakis is divided into non-bilious vomiting occurs. Dehydration,
three types, including :10 weight loss, and electrolyte imbalance can occur
Type I, characterized by the presence of a web or immediately unless fluid and electrolyte loss is
membrane that obstructs the duodenal lumen. replaced adequately.11 If the condition is not
There are three types of membrane abnormalities
Vol. 14 No 2 2020 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.33533/jpm.v14i2.2227 194
Jurnal Profesi Medika : Jurnal Kedokteran dan
ISSN 0216-3438 (Print). ISSN 2621-1122 (Online) Kesehatan
treated quickly, hypocalemia metabolic alkalosis
or hypochloremic can occur.
Plain abdominal radiography revealed a
double bubble sign accompanied by the
absence of gas in the distal part intestinal,
depicting obstruction of the stomach and
duodenum, which is pathognomonic for d. T2-weighted axial (left) and coronal
duodenal diagnosis atresia.12 If the stomach or (right) images of foetus showing
duodenum is decompressed by an orogastric distention stomach and duodenal bulb
tube or vomiting occurs, a double bubble sign giving a double bubble sign accompanied
may not be seen on the initial radiography. by an increased amniotic fluid suggestive
of polyhydramnios (S = stomach; D =
duodenal bulb; B = bladder.14
Gambar 5. Plain abdominal radiography,
contrast examination, abdominal
ultrasound, and abdominal MRI in
duodenal atresia
Plain abdominal radiography is and
continues to be a good and useful tool in
diagnosing neonatal intestinal obstruction.
a. Plain "double bubble sign" abdominal The sensitivity of plain abdominal
radiographs of duodenal atresia.
radiography in diagnosing neonatal
gastrointestinal obstruction is 85,2%. In
Malhotra's study in 1997, plain radiography
was diagnostic in 50-60% of neonatal small
bowel obstruction, equivocal in 20-30%, and
non-diagnostic in 10-20.15 In neonates with a
classic double bubble sign, an additional
radiological examination is not required. The
surgeon is prepared to plan the surgery
because all congenital cause of duodenal
obstruction requires surgery.16 An upper
b. Upper gastrointestinal contrast study gastrointestinal contrast study shows contrast
with a double bubble sign and no contrast filling of distended gastric and proximal
seen distally.13 duodenum with no visible contrast distally.
However, this examination is usually not
performed because plain radiography is
basically diagnostic. Duodenal atresia on
abdominal ultrasound is also seen as a typical
double bubble sign, depicting a fluid-filled
stomach and proximal duodenum separated
by narrowing at the location of the pylorus
c. Double bubble sign of duodenal atresia that is wider than normal.12
on abdominal ultrasound (ST = stomach; Duodenal atresia in neonates can be
D = duodenum) (13). diagnosed antenatally. A serial antenatal
examination can detect duodenal obstruction
Vol. 14 No 2 2020 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.33533/jpm.v14i2.2227 195
Jurnal Profesi Medika : Jurnal Kedokteran dan
ISSN 0216-3438 (Print). ISSN 2621-1122 (Online) Kesehatan
in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy. short transient ileus. Surgeons compared the
Polyhydramnios occurs during the 3rd laparoscopic and open approach on congenital
trimester in almost all cases of duodenal duodenal obstruction that laparoscopic group
atresia. So the diagnosis of antenatal duodenal can start feeding faster, full feeding, and
atresia can be made at 32-36 weeks gestation shorter length of stay in hospital. The
for cases with polyhydramnios.11 On weakness of laparoscopic surgery that has
ultrasonography and magnetic resonance been reported is postoperative leakage after
imaging (MRI), a typical double bubble sign conventional suturing techniques.17
is seen due to distention of the stomach and Postoperative complications are
duodenal bulb. The remaining small intestine uncommon, possible early complications
loops appear to collapse. Ultrasonography include leakage of anastomosis and
findings are enough to diagnose; however, constriction,17 easy dehydration, functional
MRI helps exclude several intestinal atresias duodenal obstruction, adhesion, and bowel
that have different postnatal prognosis and movement problems.8 But advanced
management. T2-weighted MRI images are complications (megaduodenum, blind loop
important in making a diagnosis that shows a syndrome, GERD, esophagitis, pancreatitis,
double bubble sign associated with cholecystitis, and intraabdominal sepsis)
hyperintense fluid in the stomach and occur in very rare cases.2
duodenal bulb at the level of obstruction. T1- The prognosis of duodenal atresia with
weighted MRI images help to exclude the early surgical intervention is very good. With
presence of additional atretic segments that surgical treatment, neonates' survival rate with
shows meconium in the distal loop of the duodenal atresia reaches more than 90% (12).
small intestine and colon.14 According to Milar (2005), although the
Before surgery, the stomach and prognosis of duodenal atresia is generally good,
proximal duodenum are decompressed using the mortality rate is 7%. High mortality is
an orogastric tube, and intravenous fluid caused by prematurity and congenital
resuscitation is performed. Surgical abnormalities that accompany it.8
correction by duodenoduodenostomy can be
done with an open procedure or laparoscopy. CONCLUSION
The open approach is the most commonly Duodenal atresia is a congenital
used to correct duodenal atresia. The abnormality that was included in neonates'
duodenum was mobilized using the Kocher emergencies and common in proximal neonatal
maneuver. Duodenal atresia can also be gastrointestinal obstruction due to failure of
corrected with duodenoduodenostomy as recanalization during embryogenesis.10 This
described by Kimura. Transversal causes the stomach contents can't pass through
duodenotomy is made in a dilated proximal so that the symptoms of vomiting arise, often
segment and connected with a longitudinal bilious vomiting in the first 24 hours of birth
duodenotomy along the distal portion to form accompanied by the absence of meconium.
a diamond shape.2 Patients with duodenal atresia are often
Recent developments in laparoscopic associated with other congenital abnormalities.
equipment and techniques have triggered Baby with duodenal atresia associated with
changes in infant and pediatric surgical care. down syndrome in 30% of cases. Early signs of
The advanced laparoscopic technique in duodenal atresia are minimal abdominal
neonates has recently led to a new surgical distension, bilious vomiting, and no meconium
approach, laparoscopic duodeno- release in the first 24 hours of birth. The
duodenostomy. Comparison between imaging modality has an important role in
laparoscopic and open operations procedure establishing the diagnosis. In this case, the plain
allows a reduction in intestinal function and abdominal radiography as an initial modality
Vol. 14 No 2 2020 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.33533/jpm.v14i2.2227 196
Jurnal Profesi Medika : Jurnal Kedokteran dan
ISSN 0216-3438 (Print). ISSN 2621-1122 (Online) Kesehatan
that presents a double bubble sign and the 7. Kemenkes RI. InfoDATIN: Kelainan
absence of intestinal gas in the distal part, bawaan. Pus Data dan Inf Kemeterian
which is pathognomonic for duodenal atresia Kesehat RI [Internet]. 2018;1–6. Available
radiological examination is no need required. from:
The sensitivity of plain abdominal radiography http://www.depkes.go.id/download.php?file
is 85,2% in diagnosing neonatal gastrointestinal =download/pusdatin/infodatin/infodatin
obstruction. Selection of the right initial kelainan bawaan.pdf
imaging can minimize radiation in neonates. 8. Widiastuti IDA. Diagnosis dan Tatalaksana
Continuous vomiting caused dehydration, Atresia Duodenum [Internet]. Fakultas
weight loss, and electrolyte imbalance. Kedokteran Universitas Udayana; Available
Therefore adequate fluid and electrolyte from:
replacement must be carried out. After the file:///C:/Users/user/Downloads/5343-1-
patient is stable, fluid and electrolyte 8480-1-10-20130501 (3).pdf
replacement is resolved, surgery can be 9. Free EA, Gerald B. Duodenal Obstruction In
performed as a duodenal atresia treatment. The Newborn Duw To Annular Pancreas.
Am J Roentgenol [Internet]. 103(2):321–5.
REFERENCES Available from: https://www.ajronline.org/
1. Babić VB, Sjekavica I, Jurca I, Čolic A. doi/pdf/10.2214/ajr.103.2.321
Conventional radiological diagnostics of the 10. Gharpure V. Duodenal Atresia. J Neonatal
most common patological conditions of the Surg [Internet]. 2014;3(4):1–3. Available
gastrointestinal tract in newborns. Gynaecol from:
Perinatol. 2014;23(1):6–13. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/
2. Todd YH, Christine J. Chapter 83 - Surgical PMC4420424/
Conditions of the Small Intestine in Infants 11. Jagatiani N, Ariwala N, Shah J, Ghatala B,
and Children [Internet]. Eighth Edi. Dave a. n., Patel v. b. Antenatal Diagnosis
Elsevier. Elsevier Inc.; 2020. 970–990 p. of Duodenal Atresia. Ahmedabad:
Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/ GUJARAT MEDICAL JOURNAL; 2009. p.
B978-0-323-40232-3.00083-2 77–8.
3. Sigmon DF, Eovaldi BJ CH. Duodenal 12. Bilal A. Sethi. Intestinal obstruction and the
Atresia And Stenosis. NCBI [Internet]. double bubble sign. infant [Internet].
2020;1–11. Available from: 2016;12(5):175–8. Available from:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK4 https://medical.azureedge.net/pdf/2333.pdf
70548/?report=classic 13. Aydogdu B. Factors affecting early
4. Melinda V, Djajaludin. Diagnosis dan mortality and morbidity in congenital
Penatalaksaan Atresia Duodenum. 2013. duodenal obstruction: summary of a 20-year
5. Mak G, Lange P, Arca MJ. Duodenal Atresia experience. Int Surg [Internet]. 2012;6:1–14.
[Internet]. American Pediatric Surgical Available from: https://www.international
Association. 2016 [cited 2016 Feb 11]. p. 1. surgery.org/doi/pdf/10.9738/INTSURG-D-
Available from: https://eapsa.org/parents 15-00284.1
/learn-about-a-condition/a-e/duodenal- 14. Satapara J, Bahri N. Antenatal diagnosis of
atresia/ atresia : USG and MRI findings. Eurorad
6. Hayden CK, Schwartz MZ, Davis M, [Internet]. 2019;1–7. Available from:
Swischuk LE. Combined esophageal and https://www.eurorad.org/case/16488
duodenal atresia: Sonographic findings. Am
J Roentgenol [Internet]. 1983;140(2):225–6.
Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.
nih.gov/6600333/
Vol. 14 No 2 2020 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.33533/jpm.v14i2.2227 197
Jurnal Profesi Medika : Jurnal Kedokteran dan
ISSN 0216-3438 (Print). ISSN 2621-1122 (Online) Kesehatan
15. Malek A, Afzali N, Abasi N. Comparison of
Abdominal X-ray Findings and Results of
Surgery in Neonates with Gastrointestinal
Obstruction. Mashhad Univ Med Sci
[Internet]. 2019;7(1):8877–80. Available
from: http://ijp.mums.ac.ir/article_11422
html
16. Traubici J. The double bubble sign.
Radiology. 2001;220(2):463–4.
17. Fabio Chiarenza S, Bucci V, Luisa Conighi
M, Zolpi E, Costa L, Fasoli L, et al.
Duodenal Atresia: Open versus MIS Repair-
Analysis of Our Experience over the Last 12
Years. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017.
Vol. 14 No 2 2020 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.33533/jpm.v14i2.2227 198
You might also like
- Late Third Trimester Prenatal Ultrasound Diagnosis of Duodenal AtresiaDocument4 pagesLate Third Trimester Prenatal Ultrasound Diagnosis of Duodenal AtresiaIful SaifullahNo ratings yet
- Medicine: A Newborn Patient With Both Annular Pancreas and Meckel 'S DiverticulumDocument5 pagesMedicine: A Newborn Patient With Both Annular Pancreas and Meckel 'S DiverticulumAdrian UmbriaNo ratings yet
- Association of Duodenal Atresia, Malrotation, Ventricular Septal Defect, Endocardial Cushion Defect, Atrial Septal Defect, and Patent Ductus Arteriosus in A Down Syndrome PatientDocument3 pagesAssociation of Duodenal Atresia, Malrotation, Ventricular Septal Defect, Endocardial Cushion Defect, Atrial Septal Defect, and Patent Ductus Arteriosus in A Down Syndrome PatientasclepiuspdfsNo ratings yet
- Topics Pediatric SurgeryDocument6 pagesTopics Pediatric SurgeryPatrycjaSkierkaNo ratings yet
- Combined Duodenal and Jejunal Atresia Forming A BiDocument3 pagesCombined Duodenal and Jejunal Atresia Forming A BiOvamelia JulioNo ratings yet
- Poster WijayaDocument1 pagePoster Wijayawijaya kusumaNo ratings yet
- Duodenal Web at Bizarre LocationDocument22 pagesDuodenal Web at Bizarre LocationRAGHU NATH KARMAKERNo ratings yet
- Apple Peel Small Bowel, A Review of Four Cases: Surgical and Radiographic AspectsDocument8 pagesApple Peel Small Bowel, A Review of Four Cases: Surgical and Radiographic AspectsraecmyNo ratings yet
- 2726 UnrecognizedDocument4 pages2726 UnrecognizedXusetaSanzNo ratings yet
- Tubular Ileal Duplication Causing Small Bowel Obstruction in A ChildDocument5 pagesTubular Ileal Duplication Causing Small Bowel Obstruction in A ChildDiego Leonardo Herrera OjedaNo ratings yet
- A Pattern Based Approach To The Bowel Obstruction in The NewbornDocument12 pagesA Pattern Based Approach To The Bowel Obstruction in The Newborntiosam59100% (1)
- Successful Management of Giant Hydrocolpos in a LiDocument3 pagesSuccessful Management of Giant Hydrocolpos in a LiVictor FernandoNo ratings yet
- Duodenal Stenosis from Midgut Malrotation and Ladd's BandDocument1 pageDuodenal Stenosis from Midgut Malrotation and Ladd's BandKevinJuliusTanadyNo ratings yet
- Gastroenterology Cases PracticeDocument19 pagesGastroenterology Cases PracticeIbtissame BadadNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Atresia: A Case ReportDocument3 pagesIntestinal Atresia: A Case ReportOvamelia JulioNo ratings yet
- Imaging of Congenital Anomalies of The Gastrointestinal TractDocument12 pagesImaging of Congenital Anomalies of The Gastrointestinal TractMateen ShukriNo ratings yet
- Jejunojejunal Intussusception As Initial Presentation of Coeliac Disease: A Case Report and Review of LiteratureDocument6 pagesJejunojejunal Intussusception As Initial Presentation of Coeliac Disease: A Case Report and Review of Literatureellya theresiaNo ratings yet
- PDF TJP 2175Document5 pagesPDF TJP 2175husna fitriaNo ratings yet
- Keywords: Neonatal Appendicitis, Intestinal: Malrotation and Ladd's ProcedureDocument1 pageKeywords: Neonatal Appendicitis, Intestinal: Malrotation and Ladd's ProcedurePradnyanita MustikaNo ratings yet
- Diverticular Disease and Intestinal ObstructionDocument31 pagesDiverticular Disease and Intestinal ObstructionPauLa Cheneree Peña ÜNo ratings yet
- Uog 16935Document1 pageUog 16935Razi MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Case Report HisprungDocument11 pagesCase Report HisprungAnggun Dwi Jayanti0% (1)
- The Rapunzel Syndrome - A Case Report: Trichobezoar As A Cause of Intestinal PerforationDocument4 pagesThe Rapunzel Syndrome - A Case Report: Trichobezoar As A Cause of Intestinal PerforationSajag GuptaNo ratings yet
- Case 16737: Duodenal Atresia in A Fetus With Trisomy 21Document5 pagesCase 16737: Duodenal Atresia in A Fetus With Trisomy 21NasriNo ratings yet
- Diagnóstico Tardio de MARDocument8 pagesDiagnóstico Tardio de MARthedoctor1986No ratings yet
- Abdominal Pain and Vomiting in a Boy: Magnet IngestionDocument3 pagesAbdominal Pain and Vomiting in a Boy: Magnet IngestionMonica LeeNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument28 pagesPDFFauziyah ZiyahNo ratings yet
- Small Intestine Obstruction in Patients Due To Phytobezoar: Case Report of Four PatientsDocument4 pagesSmall Intestine Obstruction in Patients Due To Phytobezoar: Case Report of Four PatientsInt Journal of Recent Surgical and Medical SciNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Obstruction and The Double Bubble SignDocument10 pagesIntestinal Obstruction and The Double Bubble SignHelgaNo ratings yet
- Diagnosing Ileal Atresia The Role of Clinical CorrDocument4 pagesDiagnosing Ileal Atresia The Role of Clinical CorrMohammad Hamim SultoniNo ratings yet
- Abstract1 SDDocument1 pageAbstract1 SDKevinJuliusTanadyNo ratings yet
- Duodenal Stenosis PDFDocument9 pagesDuodenal Stenosis PDFDorcas KafulaNo ratings yet
- 12 - Paediatric Abdomen RadiologyDocument74 pages12 - Paediatric Abdomen RadiologyMaria DoukaNo ratings yet
- Trilogy of Foregut Midgut and Hindgut Atresias PreDocument5 pagesTrilogy of Foregut Midgut and Hindgut Atresias PreEriekafebriayana RNo ratings yet
- Kayatsha - Gastroschisis and Omphalocele A Case ReportDocument4 pagesKayatsha - Gastroschisis and Omphalocele A Case ReportAffannul HakimNo ratings yet
- Small BowelDocument5 pagesSmall BowelFachry MuhammadNo ratings yet
- 1 PBDocument6 pages1 PBrizalakbarsyaNo ratings yet
- PeritonitisDocument7 pagesPeritonitisrina yulianaNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology Clinical Presentation: AssociationsDocument3 pagesEpidemiology Clinical Presentation: AssociationsMaria JozilynNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2210261221012268 MainDocument4 pages1 s2.0 S2210261221012268 Mainzenatihanen123No ratings yet
- Case Report: The Combination of Gastroschisis, Jejunal Atresia, and Colonic Atresia in A NewbornDocument5 pagesCase Report: The Combination of Gastroschisis, Jejunal Atresia, and Colonic Atresia in A NewbornAnonymous PmfX227No ratings yet
- Esophageal AtresiaDocument18 pagesEsophageal AtresiaNeha RathoreNo ratings yet
- Balloon and Bougie Dilation of Benign Esophageal Strictures: Ajay George, Vikas SinhaDocument3 pagesBalloon and Bougie Dilation of Benign Esophageal Strictures: Ajay George, Vikas SinhaAgus KarsetiyonoNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Malrotation in Neonates With Nonbilious Emesis: Perinatal/Neonatal Case PresentationDocument3 pagesIntestinal Malrotation in Neonates With Nonbilious Emesis: Perinatal/Neonatal Case PresentationSaurav SultaniaNo ratings yet
- Imaging Patients With Acute Abdominal PainDocument16 pagesImaging Patients With Acute Abdominal PainNaelul IzahNo ratings yet
- Trichobezoar With Large Bowel Obstruction in Children - Case ReportDocument3 pagesTrichobezoar With Large Bowel Obstruction in Children - Case ReportSajag GuptaNo ratings yet
- Prune Belly SyndromeDocument33 pagesPrune Belly SyndromePrasanna KumarNo ratings yet
- Acute Gastric VolvulusDocument3 pagesAcute Gastric Volvuluskhumaira1982No ratings yet
- Gomella Sec03 p0167 0300Document134 pagesGomella Sec03 p0167 0300Gabriela GheorgheNo ratings yet
- Pediatric (S) 2023 Final 7th SemDocument226 pagesPediatric (S) 2023 Final 7th SemSyed NoorNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Ileocolica Invagination Case ReportDocument5 pagesPediatric Ileocolica Invagination Case Reportdaily of sinta fuNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound "Whirlpool Sign" For Midgut Volvulus: Muktachand L. Rokade, Sushila Yamgar, Devesh TawriDocument3 pagesUltrasound "Whirlpool Sign" For Midgut Volvulus: Muktachand L. Rokade, Sushila Yamgar, Devesh TawrizzzNo ratings yet
- Congenital Pyloric Atresia With Distal Duodenal Atresia-Role of CT ScanDocument3 pagesCongenital Pyloric Atresia With Distal Duodenal Atresia-Role of CT Scanhaidar HumairNo ratings yet
- Urosepsis Is The Most Common Complication of Purn-Belly SyndromeDocument4 pagesUrosepsis Is The Most Common Complication of Purn-Belly Syndromeraisa desti ardiantyNo ratings yet
- 44 Danfulani EtalDocument3 pages44 Danfulani EtaleditorijmrhsNo ratings yet
- Prenatal diagnosis of gastroschisis by ultrasoundDocument5 pagesPrenatal diagnosis of gastroschisis by ultrasoundhakimrosliNo ratings yet
- Duodenal Stenosis in A Child: A. Y. Kshirsagar, Sanjitsingh R. Sulhyan, Gaurav Vasisth, Yogesh P. NikamDocument3 pagesDuodenal Stenosis in A Child: A. Y. Kshirsagar, Sanjitsingh R. Sulhyan, Gaurav Vasisth, Yogesh P. Nikameka nurjanahNo ratings yet
- Invaginasi 16903495Document4 pagesInvaginasi 16903495Fadhillawatie MaanaiyaNo ratings yet
- Duodenal Duplication, Intestinal Malrotation and Volvulus. An Unusual Cause of Intestinal ObstructionDocument3 pagesDuodenal Duplication, Intestinal Malrotation and Volvulus. An Unusual Cause of Intestinal ObstructionDiego Leonardo Herrera OjedaNo ratings yet
- Case Series: Newborn Haemorrhagic Disorders: About 30 CasesDocument8 pagesCase Series: Newborn Haemorrhagic Disorders: About 30 CasesNasriNo ratings yet
- Hemorrhagic Disease of Newborn: A Prospective Study of Clinical Features and OutcomeDocument5 pagesHemorrhagic Disease of Newborn: A Prospective Study of Clinical Features and OutcomeIan SutejaNo ratings yet
- Penanganan Hipotiroid Pada Anak Dengan Sindrom Nefrotik: Bernadetha NadeakDocument14 pagesPenanganan Hipotiroid Pada Anak Dengan Sindrom Nefrotik: Bernadetha NadeakMuh FardiansyahNo ratings yet
- Vitamin K Deficiency Bleeding A Case Study: Advances in Neonatal Care December 2013Document7 pagesVitamin K Deficiency Bleeding A Case Study: Advances in Neonatal Care December 2013NasriNo ratings yet
- Innocent Blood: A History of Hemorrhagic Disease of The NewbornDocument7 pagesInnocent Blood: A History of Hemorrhagic Disease of The NewbornNasriNo ratings yet
- Vitamin K Deficiency: A Case Report and Review of Current GuidelinesDocument5 pagesVitamin K Deficiency: A Case Report and Review of Current GuidelinesRB M ESNo ratings yet
- Vitamin K deficiency bleeding of newborn masquerading haemophilia BDocument5 pagesVitamin K deficiency bleeding of newborn masquerading haemophilia BNasriNo ratings yet
- Mutius SlidesCarnivalDocument29 pagesMutius SlidesCarnivaldinar aimcNo ratings yet
- L2 - RELATO DE CASO - ABC71 - InglesDocument3 pagesL2 - RELATO DE CASO - ABC71 - InglesNasriNo ratings yet
- FIT Clinical Decision Making: Severe Mitral Stenosis and Pulmonary Hypertension in Pregnancy: When To ActDocument1 pageFIT Clinical Decision Making: Severe Mitral Stenosis and Pulmonary Hypertension in Pregnancy: When To ActNasriNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Right Ventricular Dysfunction in Patients With Mitral Stenosis: A Speckle Tracking StudyDocument6 pagesAssessment of Right Ventricular Dysfunction in Patients With Mitral Stenosis: A Speckle Tracking StudyNasriNo ratings yet
- Degenerative Mitral Stenosis: Interpreting The Meaning of Mean GradientDocument3 pagesDegenerative Mitral Stenosis: Interpreting The Meaning of Mean GradientNasriNo ratings yet
- Case ReportDocument6 pagesCase ReportNasriNo ratings yet
- 5105 11336 3 PB 2Document18 pages5105 11336 3 PB 2Taufik 81No ratings yet
- L2 - RELATO DE CASO - ABC71 - InglesDocument3 pagesL2 - RELATO DE CASO - ABC71 - InglesNasriNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Arrest in PregnancyDocument4 pagesCardiac Arrest in PregnancyNasriNo ratings yet
- Cordelia SlidesCarnivalDocument40 pagesCordelia SlidesCarnivalEnzo Alcívar ThomasNo ratings yet
- Degenerative Mitral Stenosis: Interpreting The Meaning of Mean GradientDocument3 pagesDegenerative Mitral Stenosis: Interpreting The Meaning of Mean GradientNasriNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Right Ventricular Dysfunction in Patients With Mitral Stenosis: A Speckle Tracking StudyDocument6 pagesAssessment of Right Ventricular Dysfunction in Patients With Mitral Stenosis: A Speckle Tracking StudyNasriNo ratings yet
- Cardiorespiratory ArrestDocument5 pagesCardiorespiratory Arrestore wa IzzampNo ratings yet
- FIT Clinical Decision Making: Severe Mitral Stenosis and Pulmonary Hypertension in Pregnancy: When To ActDocument1 pageFIT Clinical Decision Making: Severe Mitral Stenosis and Pulmonary Hypertension in Pregnancy: When To ActNasriNo ratings yet
- Degenerative Mitral Stenosis: Interpreting The Meaning of Mean GradientDocument3 pagesDegenerative Mitral Stenosis: Interpreting The Meaning of Mean GradientNasriNo ratings yet
- L2 - RELATO DE CASO - ABC71 - InglesDocument3 pagesL2 - RELATO DE CASO - ABC71 - InglesNasriNo ratings yet
- Low-Gradient Severe Mitral Stenosis: Hemodynamic Pro Files, Clinical Characteristics, and OutcomesDocument12 pagesLow-Gradient Severe Mitral Stenosis: Hemodynamic Pro Files, Clinical Characteristics, and OutcomesNasriNo ratings yet
- Severe Mitral Stenosis in Patients With Severe Mitral Annular Calci FicationDocument3 pagesSevere Mitral Stenosis in Patients With Severe Mitral Annular Calci FicationNasriNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Right Ventricular Dysfunction in Patients With Mitral Stenosis: A Speckle Tracking StudyDocument6 pagesAssessment of Right Ventricular Dysfunction in Patients With Mitral Stenosis: A Speckle Tracking StudyNasriNo ratings yet
- Low-Gradient Severe Mitral Stenosis: Hemodynamic Pro Files, Clinical Characteristics, and OutcomesDocument12 pagesLow-Gradient Severe Mitral Stenosis: Hemodynamic Pro Files, Clinical Characteristics, and OutcomesNasriNo ratings yet
- Calcific Mitral Stenosis: Echoes of AgingDocument3 pagesCalcific Mitral Stenosis: Echoes of AgingNasriNo ratings yet
- Doacs in Patients With Mitral Stenosis and Atrial FibrillationDocument3 pagesDoacs in Patients With Mitral Stenosis and Atrial FibrillationNasriNo ratings yet
- Outcomes of Direct Oral Anticoagulants in Patients With Mitral StenosisDocument9 pagesOutcomes of Direct Oral Anticoagulants in Patients With Mitral StenosisNasriNo ratings yet
- Bohemian Flower Face Mask by Maya KuzmanDocument8 pagesBohemian Flower Face Mask by Maya KuzmanDorca MoralesNo ratings yet
- Viennot - 1979 - Spontaneous Reasoning in Elementary DynamicsDocument18 pagesViennot - 1979 - Spontaneous Reasoning in Elementary Dynamicsjumonteiro2000No ratings yet
- Transportation Chapter 3Document17 pagesTransportation Chapter 3Tuan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Qy130v633 Operation ManualDocument414 pagesQy130v633 Operation ManualumamNo ratings yet
- Gas Mixtures: Seventh Edition in SI UnitsDocument13 pagesGas Mixtures: Seventh Edition in SI Unitshamed farzanehNo ratings yet
- Project On Honda Two WheelersDocument46 pagesProject On Honda Two WheelersC SHIVASANKARNo ratings yet
- ANNEXURE IV Dec 2022 enDocument17 pagesANNEXURE IV Dec 2022 enadvocacyindyaNo ratings yet
- Quick Reference To Psychotropic Medications: AntidepressantsDocument2 pagesQuick Reference To Psychotropic Medications: AntidepressantsNaiana PaulaNo ratings yet
- Manual de Partes 501-601Document27 pagesManual de Partes 501-601camilo bautista100% (2)
- BW Query GuidelinesDocument10 pagesBW Query GuidelinesyshriniNo ratings yet
- Cowell - The Wizards of Once PDFDocument315 pagesCowell - The Wizards of Once PDFtatoes n lases100% (1)
- Business Continuity Generaly Accepted Practices GAP v2.1 (Disaster Recovery Journal 2015) PDFDocument140 pagesBusiness Continuity Generaly Accepted Practices GAP v2.1 (Disaster Recovery Journal 2015) PDFducuhNo ratings yet
- Nature and Purpose of CommunicationDocument17 pagesNature and Purpose of CommunicationEdmond Dantès100% (4)
- GC 1999 03 Minas BrethilDocument5 pagesGC 1999 03 Minas BrethilErszebethNo ratings yet
- A319/A320/A321 Technical Training Manual Mechanics / Electrics & Avionics Course 33 LightsDocument224 pagesA319/A320/A321 Technical Training Manual Mechanics / Electrics & Avionics Course 33 LightsAhmedHamdyElsaidy100% (3)
- CENELEC RA STANDARDS CATALOGUEDocument17 pagesCENELEC RA STANDARDS CATALOGUEHamed AhmadnejadNo ratings yet
- Parison of Dia para FerroDocument4 pagesParison of Dia para FerroMUNAZIRR FATHIMA F100% (1)
- Yatendra Kumar Sharma ResumeDocument3 pagesYatendra Kumar Sharma ResumeDheeraj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Hercules Segers - Painter EtchterDocument4 pagesHercules Segers - Painter EtchterArtdataNo ratings yet
- Readings On The History and System of The Common Law - Roscoe PoundDocument646 pagesReadings On The History and System of The Common Law - Roscoe PoundpajorocNo ratings yet
- "Network Security": Alagappa UniversityDocument1 page"Network Security": Alagappa UniversityPRADEEPRAJANo ratings yet
- Al-Jahiz (781-869) : ZoologyDocument25 pagesAl-Jahiz (781-869) : ZoologyJA QuibzNo ratings yet
- TN Govt RecruitmentDocument12 pagesTN Govt RecruitmentPriyanka ShankarNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Pediatric Nursing The Critical Components of Nursing Care 2nd Edition Kathryn Rudd Diane KociskoDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Pediatric Nursing The Critical Components of Nursing Care 2nd Edition Kathryn Rudd Diane Kociskolaurencelittlehdcj100% (26)
- Cultural DiffusionDocument2 pagesCultural DiffusionNicole Aguarin SwinNo ratings yet
- 4 Types and Methods of Speech DeliveryDocument2 pages4 Types and Methods of Speech DeliveryKylie EralinoNo ratings yet
- Rguhs Dissertation PharmacyDocument6 pagesRguhs Dissertation PharmacyWhatAreTheBestPaperWritingServicesSingapore100% (1)
- A Critical Review: Constructive Analysis in English and Filipino 1 SEMESTER 2021-2022Document4 pagesA Critical Review: Constructive Analysis in English and Filipino 1 SEMESTER 2021-2022roseNo ratings yet
- PREXC Operational Definition and Targets CY 2019 - 2020Document12 pagesPREXC Operational Definition and Targets CY 2019 - 2020iamaj8No ratings yet
- Super BufferDocument41 pagesSuper Bufferurallalone100% (1)