Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electrodeposition and Anodization
Uploaded by
Mahabub Alam Moon0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views3 pagesOriginal Title
Electrodeposition and anodization
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views3 pagesElectrodeposition and Anodization
Uploaded by
Mahabub Alam MoonCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
What is Electrodeposition? Discuss in brief.
• Electrodeposition is a well-known conventional surface modification method to improve the
surface characteristics, decorative an functional, of a wide variety of materials. Now,
electrodeposition is emerging as an accepted versatile technique for the preparation of
nanomaterial.
• Another name for electrodeposition is electroplating and this technique is an inexpensive one to
prepare thin layers of high quality metals over the inexpensive and easily available base
materials. It is an electrochemical process where metal ions are transferred from a solution and
are deposited as a thin layer onto surface of a cathode.
• It is used to coat electrically conductive textile materials with a metal layer by applying electrical
current which ends in forming a thick, stiff and heavy metal coat on textile. Some of the metals
that can be coated on fabric surfaces using this technique are cadmium, chromium, copper, gold,
iron, nickel, silver and zinc. The electrolytic cell, in which this electrodeposition process occurs,
contains an electrolyte and two electrodes.
What are the steps of Electrodeposition process?
Assembling an electric circuit.
Cleaning copper and zinc electrodes.
Installing the electrodes in a solution of zinc nitrate.
Turning the switch on to start the process.
Turning the copper electrode around at some point in the process so that both sides are
electrodeposited somewhat evenly.
Stopping electrodeposition when the copper electrode seems to be fairly well covered with
visible coating zinc.
Carefully putting the electrodes on a paper towel to dry before making measurements of the
length and width of the electroplated zinc metal.
Using scientific notation to calculate the thickness of the layer of zinc metal.
What are the steps for calculating the thickness of thin film by using Electrodeposition
Technique?
1. The number of electrons that zinc ions gained in a time period
2. The number of zinc atoms that formed
3. The number of atoms of zinc in a row across the width of the copper electrode
4. The number of atoms in a column along the length of the electrode that was in the solution
5. The number of atoms in one rectangular layer on one side of the copper electrode.
6. The number of atoms that formed a single layer on both sides of the copper electrode
7. The average number of layers of zinc atoms
8. The average thickness of the layer of zinc
Calculate thickness of thin film by using Electrodeposition technique.
Sample Data
Time of Trial: 5 minutes = 3.0 x seconds
Width of copper electrode in the solution 2 cm = 2.0 x meters
Length of electrode in the solution 5 cm = 5.0 x meters
Average ammeter reading 17 mill amperes
Average ammeter reading 0.017 ampere = 1.7 x Coulomb/sec
Step 1: Calculate the number of electrons that zinc ions gains in 5 minutes.
(1.7 x C/s)(6.24 x e/C)(3.0 x s) = 3.18 x e
Step 2: Calculate the number of zinc atoms that formed.
(3.18 x e)/ (2 electrons for each Zn ion) = 1.59 x atoms of Zn formed
A zinc atom has a diameter of 2.59 x meters
Step 3: Calculate the number of atoms of zinc in a row across the width of the copper electrode.
(2.0 x m ) / (2.59 x m/atom) = 7.72 x atoms in a row
Step 4: Calculate the number of atoms in a column along the length of the electrode that was in the
solution.
(5.0 x m ) / (2.59 x m/atom) = 1.93 x atoms in a column
Step 5: Calculate the number of atoms in one rectangular layer on one side of the copper electrode.
(7.72 x atoms in a row) x (1.93 x atoms in a column) = 1.49 x atoms
Zinc atoms were electrodeposited on both sides of the Copper Electrode.
Step 6: Calculate the number of atoms that formed a single layer on both sides of the copper electrode.
2 x 1.49 x atoms = 2.98 x atoms
Step 7: Calculate the average number of layers of zinc atoms.
(1.59 x atoms of zinc) / (2.98 x atoms / layer) = 5.34 x layers of atoms
Step 8: Calculate the average thickness of the layer of zinc.
5.34 x layers x 2.48 x m/layer = 13.24 x m
The calculation of the thickness was based on an assumption that there were an equal number of
zinc atoms in each layer.
Why choose Electrodeposition to make nanostructures?
The process is easy to manage and only needs simple equipment.
It is easy to control the deposition rate by manipulating voltage, current, and solution
concentrations.
What is Anodization? Discuss in brief.
Anodization is a unique electrochemical process to prepare oxide thin films of certain metals like
aluminium, niobium, tantalum, titanium, tungsten and zirconium in which aluminium, niobium and
tantalum oxide thin films play vital role as capacitor dielectrics in commercial and technological field.
The thickness and properties of the thin films deposited in this method depend on the metal. Thick oxide
coatings of aluminium obtained by anodizing aluminium alloys in particular acidic electrolytes show high
density of microscopic pores which make them applicable as corrosion preventives in automobiles and
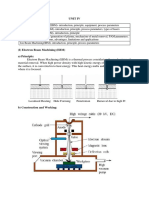
aerospace structures and also as electrical insulation. The anodizing cell contains the metal work piece as
anode by connecting it to the positive terminal of a dc power supply and any electronic conductor which
is inert in the anodizing bath as cathode by connecting to the negative terminal of the supply.
When the dc power supply is switched on, electrons are thrown out of the metal surface which acts as
a positive terminal leaving behind ions and these ions on the metal surface interact with water and form
an oxide layer upon the metal. Hydrogen gas is formed when the electrons react with the hydrogen ions in
the cathode during their return path. The electrolytes in the anodizing cell should be carefully selected so
that the oxide layer will be insoluble in it and also the bath composition should be carefully studied as the
formation of a barrier or a porous thin film depends mainly on it. 4-5 μm long nanotubes of mixed V2O5 –
TiO2 arrays were deposited on Ti-V alloy plates and Ti foils by anodization.
You might also like
- ELEC E8174 Homework 3 2019Document4 pagesELEC E8174 Homework 3 2019Joshua LunguNo ratings yet
- Nucleation and Growth of Metals: From Thin Films to NanoparticlesFrom EverandNucleation and Growth of Metals: From Thin Films to NanoparticlesNo ratings yet
- Nanoscale Electrodeposition: A Hands-On Activity for Teaching Atomic Structure and Self-AssemblyDocument24 pagesNanoscale Electrodeposition: A Hands-On Activity for Teaching Atomic Structure and Self-AssemblysobheysaidNo ratings yet
- Particle Characterization of Copper Nanoparticles by Electrochemical MethodDocument5 pagesParticle Characterization of Copper Nanoparticles by Electrochemical MethodIJSTENo ratings yet
- Electroplating Lab CHEM 401Document10 pagesElectroplating Lab CHEM 401anak gamerNo ratings yet
- Tiõng Anh Chuy N NG NH ®Iön-®Iön TöDocument21 pagesTiõng Anh Chuy N NG NH ®Iön-®Iön TöHungNo ratings yet
- Tieng Anh Chuyen Nganh Dien-Dien TuDocument95 pagesTieng Anh Chuyen Nganh Dien-Dien TuPhong Vũ VănNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 Chemical MethodsDocument99 pagesUnit-3 Chemical MethodsAkshay NachappaNo ratings yet
- 2365-202-01 - Electron Theory Day 1.Document4 pages2365-202-01 - Electron Theory Day 1.BillNo ratings yet
- Final DoneDocument12 pagesFinal DoneRockson YuNo ratings yet
- 11-13. Sample PreparationDocument37 pages11-13. Sample PreparationeyobNo ratings yet
- ECM and EDMDocument23 pagesECM and EDMVinay KumarNo ratings yet
- Electro-Chemical Machining: Presented By: Keisham Sushima Devi DIP/14/ME/12Document18 pagesElectro-Chemical Machining: Presented By: Keisham Sushima Devi DIP/14/ME/12Fawad HussainNo ratings yet
- AM Week 2 ECM NOTESDocument19 pagesAM Week 2 ECM NOTESa38659158No ratings yet
- Lecture 24 - ECMDocument32 pagesLecture 24 - ECMDivyam GargNo ratings yet
- Chem For Eng 1Document122 pagesChem For Eng 1Lindsay LabagnoyNo ratings yet
- Engineering MaterialsDocument9 pagesEngineering MaterialsJevan CalaqueNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The X-Ray Machine PDFDocument31 pagesAnatomy of The X-Ray Machine PDFbajarNo ratings yet
- BPUT Question Bank For Material ScienceDocument4 pagesBPUT Question Bank For Material ScienceMr.S UpenderNo ratings yet
- Nickel-Zinc Accordion-Fold Batteries With MicrofibrousDocument14 pagesNickel-Zinc Accordion-Fold Batteries With MicrofibrousMarco Antonio Miranda RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Practical 6Document7 pagesPractical 6Farid FazamyNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics (ES-112)Document49 pagesBasic Electronics (ES-112)Bharat LalNo ratings yet
- Chem For Eng 1Document123 pagesChem For Eng 1Am AsdfghjklNo ratings yet
- A 37 Elect Fund NoteDocument10 pagesA 37 Elect Fund NoteJeans BazzarNo ratings yet
- Sheet 2 2Document2 pagesSheet 2 2Fatma AbdoNo ratings yet
- Electron Beam WeldingDocument19 pagesElectron Beam WeldingRajan BhadoriyaNo ratings yet
- Unit Iii NotesDocument29 pagesUnit Iii NotesSadhasivam CNo ratings yet
- Chemi ProjectDocument9 pagesChemi ProjectCh'ng Song ShuNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 (Praful Rawat 160970104033)Document5 pagesAssignment 2 (Praful Rawat 160970104033)as hgfNo ratings yet
- MPS HW (10) Soln 011518Document4 pagesMPS HW (10) Soln 011518Renaldi NafiawanNo ratings yet
- UNIT-1 Conducting Materials NotesDocument21 pagesUNIT-1 Conducting Materials NotesAdarsh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Wire-Cut EdmDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Wire-Cut EdmZamree Bin HarunNo ratings yet
- QA-Chemical Effects of Electric CurrentDocument6 pagesQA-Chemical Effects of Electric CurrentNikita RajNo ratings yet
- Deposition of Tungsten Nitride On Stainless Steel Substrates Using Plasma FocusDocument5 pagesDeposition of Tungsten Nitride On Stainless Steel Substrates Using Plasma FocusAli HussnainNo ratings yet
- ElectroplatingDocument5 pagesElectroplatingmatiyasNo ratings yet
- 10351Document32 pages10351sanyengereNo ratings yet
- COSIDO-CHEM-LAB-REPORTDocument7 pagesCOSIDO-CHEM-LAB-REPORTVladimer CosidoNo ratings yet
- Particle Strengthening of The Surface of Copper Electrode For Electrical Discharge MachiningDocument7 pagesParticle Strengthening of The Surface of Copper Electrode For Electrical Discharge MachiningMariana Hernández PérezNo ratings yet
- EcmhjghjgjDocument19 pagesEcmhjghjgjhfhtgfhgNo ratings yet
- Nano Wire Electrical ContactsDocument7 pagesNano Wire Electrical ContactsalfaesiNo ratings yet
- What is NanotechnologyDocument52 pagesWhat is NanotechnologyOmkar SheteNo ratings yet
- PDF 16 WorkingElecDocument5 pagesPDF 16 WorkingElecThoifahMuthohharohNo ratings yet
- Beam WeldingDocument10 pagesBeam Weldingpatel ketanNo ratings yet
- 1.1intro - RCA CleaningDocument47 pages1.1intro - RCA CleaningSiddhant BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- NTM Unit4Document8 pagesNTM Unit4saravana kumarNo ratings yet
- Multi-Cathode Cell With Flow-Through Electrodes For The Production of Iron (Ii) - Triethanolamine ComplexesDocument8 pagesMulti-Cathode Cell With Flow-Through Electrodes For The Production of Iron (Ii) - Triethanolamine ComplexestanveerhusseinNo ratings yet
- L-6 Nanorods SynthesisDocument27 pagesL-6 Nanorods SynthesisAshutosh BaghelNo ratings yet
- Advanced Materials Letters: Accepted ManuscriptDocument14 pagesAdvanced Materials Letters: Accepted ManuscripttarquitaNo ratings yet
- Simulation ElectrochemistryDocument12 pagesSimulation Electrochemistryain kasbiNo ratings yet
- Second Semester PH2161 - ENGINEERING Physics-II Important 2 - Mark Questions Unit Wise - 2013 EditionDocument3 pagesSecond Semester PH2161 - ENGINEERING Physics-II Important 2 - Mark Questions Unit Wise - 2013 EditionaeroherozNo ratings yet
- Reference: Diffusion Bonded EDM Electrode With Micro Holes For Jetting Dielectric Liquid, CIRP Annals - Manufacturing Technology, 2006Document11 pagesReference: Diffusion Bonded EDM Electrode With Micro Holes For Jetting Dielectric Liquid, CIRP Annals - Manufacturing Technology, 2006EdinNo ratings yet
- Document 1Document8 pagesDocument 1sadiqali4244No ratings yet
- Influence of Titanium Oxide Films On Copper Nucleation During ElectrodepositionDocument12 pagesInfluence of Titanium Oxide Films On Copper Nucleation During Electrodepositionapi-19973331No ratings yet
- Hybrid Metal FoamsDocument11 pagesHybrid Metal FoamsSEP-PublisherNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Electron TheoryDocument23 pagesChapter 1 Electron TheoryJames Ryan GarmaNo ratings yet
- Diode Semiconductor 2022Document255 pagesDiode Semiconductor 2022suryakant mahariNo ratings yet
- Electroforming: What Is Electroforming? The Electroforming Process The Electroforming AnimationDocument10 pagesElectroforming: What Is Electroforming? The Electroforming Process The Electroforming AnimationJatin GadhokNo ratings yet
- Plasma Etching Processes for CMOS Devices RealizationFrom EverandPlasma Etching Processes for CMOS Devices RealizationNicolas PossemeNo ratings yet
- Floor FinishesDocument42 pagesFloor FinishesLawrence TingNo ratings yet
- Experimental and Numerical Investigations of Athletic Prosthetic Feet Made of Fiber Glass Reinforced EpoxyDocument6 pagesExperimental and Numerical Investigations of Athletic Prosthetic Feet Made of Fiber Glass Reinforced EpoxyMohsin NooriNo ratings yet
- Rubber Products SairamDocument24 pagesRubber Products SairamHina Thetenders.comNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Cementation ProductsDocument20 pagesMechanical Cementation Productstafhim rashidNo ratings yet
- Building Technology Flashcards Study GuideDocument9 pagesBuilding Technology Flashcards Study GuideXYRHEN ZEEJAY GONZALESNo ratings yet
- Winters Productoverview2Document12 pagesWinters Productoverview2JOSE DEL CARMEN TOLEDONo ratings yet
- EcoFlame B-971 MSDSDocument8 pagesEcoFlame B-971 MSDSZirve PolimerNo ratings yet
- Analysis Geological Minerals Using ARL EQUINOX 41102Document2 pagesAnalysis Geological Minerals Using ARL EQUINOX 41102Daniel AguifNo ratings yet
- The Hermes Wide Belt Product Family For Sanding Particleboard and FiberboardDocument8 pagesThe Hermes Wide Belt Product Family For Sanding Particleboard and FiberboardFlavioNo ratings yet
- Museum conservation methodsDocument4 pagesMuseum conservation methodsRitikNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Investigatory Project 2018-19: Setting of CementDocument18 pagesChemistry Investigatory Project 2018-19: Setting of CementNitin Sai AvirneniNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Analysis of Lipids LectureDocument48 pagesQualitative Analysis of Lipids LectureAlessandra Franchesca CortezNo ratings yet
- Combination Flame Arrester & Free VentDocument4 pagesCombination Flame Arrester & Free Ventyulianus_srNo ratings yet
- B21 5530 EnglishDocument20 pagesB21 5530 EnglishWillianNo ratings yet
- FichaTecnicaBacker ModifiedDocument1 pageFichaTecnicaBacker ModifiedEdwin HernandezNo ratings yet
- Cold Formed Steel Sections - IDocument37 pagesCold Formed Steel Sections - IsskamalakannanNo ratings yet
- Automobile Air Condition System Using Exahust GasDocument19 pagesAutomobile Air Condition System Using Exahust GasEr. Ramji TripathiNo ratings yet
- Ch. 1 - Semiconductor Diodes SummaryDocument2 pagesCh. 1 - Semiconductor Diodes SummaryJesryniel PlazaNo ratings yet
- Methodology For Definition of Bending Radius and Pullback Force in HDD Operations Danilo Machado L. Da Silva, Marcos V. Rodrigues, Asle Venås Antonio Roberto de MedeirosDocument8 pagesMethodology For Definition of Bending Radius and Pullback Force in HDD Operations Danilo Machado L. Da Silva, Marcos V. Rodrigues, Asle Venås Antonio Roberto de MedeirosMAHESH CHAND100% (1)
- Resume of Curtismccauley54Document2 pagesResume of Curtismccauley54api-27883418No ratings yet
- Science Fest Script 3Document9 pagesScience Fest Script 3vaibhavi singhNo ratings yet
- (MCQS) On "Solar Radiation"-MergedDocument115 pages(MCQS) On "Solar Radiation"-MergedMahavirsinh PadheriyaNo ratings yet
- Business PlanDocument10 pagesBusiness Planryzabuhayan24No ratings yet
- "Hot Topics": Effect of Carbon in Ductile IronDocument4 pages"Hot Topics": Effect of Carbon in Ductile IronAdeel BhattiNo ratings yet
- Welder Job Clearance Card for Ali QurbanDocument43 pagesWelder Job Clearance Card for Ali QurbanDhanush NairNo ratings yet
- E155 15 PDFDocument4 pagesE155 15 PDFOscar Gomez GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Heat Eachner DesignDocument32 pagesHeat Eachner DesignCH1253No ratings yet
- Molykote 1000 Paste MSDSDocument9 pagesMolykote 1000 Paste MSDSNikola Polimenov100% (1)
- The Comparative Study On Corrosion Behaviour of Steel and Basalt Fibre Reinforced Polymer (BFRP) Rebar in Concrete"Document9 pagesThe Comparative Study On Corrosion Behaviour of Steel and Basalt Fibre Reinforced Polymer (BFRP) Rebar in Concrete"Abhijeet SableNo ratings yet
- The Dependable Selection: For Excellent PerformanceDocument8 pagesThe Dependable Selection: For Excellent PerformanceJovanDiNo ratings yet