Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Diss 3rd Module
Uploaded by
Edelyn A. BergantinOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Diss 3rd Module
Uploaded by
Edelyn A. BergantinCopyright:
Available Formats
Sacred Heart Academy
Loon, Bohol
SY 2020-2021
Member: Catholic Educational Association of the Philippines (CEAP)
and Bohol Association of Catholic Schools (BACS-Tagbilaran)
email add: sacredheartacademyloon@yahoo.com
tel #: (038) 505-8087
ACTIVITY SHEET NO. 3 – Q2
NAME: __________________________________________________ SECTION: ________________________________
Subject: DISS Grade Level: 11-HUMSS Date: ______________________ Score: _____
ACTIVITY TITLE: RATIONAL CHOICE
LEARNING COMPETENCY/S: Predict the social consequences of decision making based on scarcity.
LEARNING TARGET/S: 1. Define rational choice;
2. Identify the key concepts in Rational Choice Theory; and
3. Create a video presentation on rational choice theory as applied in social sciences.
REFERENCE/S: Gonzalez, Maria Carinnes P. Disciples and Ideas in the Social Sciences. Makati City: Diwa Learning
System Inc., 2016.pp. 136-141
CONCEPT NOTES
The rational choice theory explains that human action and behavior are products of choice. Individuals rationalize
their situations by processing between the most beneficial choice and the lesser individual cost. In the rational choice
theory, cost-benefit analysis is always performed in every given situation and is considered an instinctual response of every
human. Cost is something disadvantageous to or what is lost by an individual after making the choice. Some of the
questions commonly asked during a cost-benefit analysis are the following:
Will this benefit me?
How will this benefit me?
What will benefit me most?
How far am I willing to negotiate?
What will I have to sacrifice?
How much will it cost me?
For example, Sebastian has two classmates whom he wants to be friends with: Ethan, a social outcast but has the
newest action game, and Alyster, the most popular in the class but does not like to play action games. Sebastian’s first
level of cost-benefit analysis is choosing between having the chance to play the newest action game or not. His second
level of cost-level analysis is choosing whether he would like to be associated with a social outcast or with the most
popular student in class. The rational choice for Sebastian would then be dependent on which is more important to him
– to play the game or to be associated with the popular crowd. This example provides the basic principle of rational
choice theory wherein preference plays an important role in decision-making, while the individual rationalizes the
burden and benefits of the available choices. This example also highlights the basic assumptions of rational choice
theory which are the following:
1. Individuals act purely on self- interest.
2. Individuals understand their interests enough to rationally categorize them according to what they most prefer.
3. Preferences are transitive in nature. This means that choices have a hierarchical order and that the highest
preference will always be favored.
A famous example of rational choice theory is the prisoner’s dilemma. Two recently released convicts committed a
crime. However, investigators of the case lack sufficient evidence to prove their guilt. As a scheme, the investigators had the
two suspects held in separate rooms where they were told that if they tell on the other, they would be freed. This condition
allows one of them to go free, while the other faces incarceration. Since both will think that one is already betraying the
other, both would indeed decide to betray the other, causing both of them to be incarcerated. ThisFAITH
Prepared by: JEAN example
M. NOVALproves that
individual self-interest weighs heavily in the process of choice making. Reviewed by: NINO JAY C. GASTONES, MA- English
The underlying structure of the rational choice theory is the incentive to do what is beneficial to all; nevertheless,
SHS Coordinator
what weighs more heavily is the incentive to do what is beneficial to the individual. This structure
Approved by: NIÑObest
JAY C.explains
GASTONES,how this
MA-English
theory is readily applied to social phenomena and interactions. Academic Coordinator
Vision: An institution of God-fearing, God-loving, and well transformed individuals
Mission: To provide quality education and values formation
Goals: inspired by the school’s vision-mission statement and the Divine Providence, we commit ourselves to:
become person for others by sharing what we have and what we are;
have a harmonious relationship among administrators, teachers, parents and students based on Trinitarian Spirituality;
develop a pro-People, a pro-Nation, a pro-Earth, and a pro-God community
Parent’s/Guardian’s Signature over Printed Name: _________________________________________
Sacred Heart Academy
Loon, Bohol
SY 2020-2021
Member: Catholic Educational Association of the Philippines (CEAP)
and Bohol Association of Catholic Schools (BACS-Tagbilaran)
email add: sacredheartacademyloon@yahoo.com
tel #: (038) 505-8087
Key Concepts in Rational Choice Theory
Social Consequence of Scarcity-based Decision
Humanity’s unlimited wants and perpetual desires drove civilizations to either their prominence or destruction. With
natural resources being finite and the requirements of human ambition unending, the most rational choice is to conserve the
limited resources and share these with each other. However, the problem is that individuals only seek self-interest and
would end up deciding what benefits them the most.
Such is the structure of human nature when being described in the context of rational choice theory. The tragedy of
the commons further elaborates this structure. The tragedy of the commons is a scenario wherein a common piece of land
is shared for grazing by a community. Because the grass that grows on the land is limited, farmers need to limit their herd
when grazing so that the land could keep up with the requirements of the community. The tragedy in this scenario starts
when a farmer lets his herd graze more than what is allotted, thinking that such action would provide him with better profits.
If the farmers would all think of the same, the land will eventually become useless to the community. When the land is
already unusable, the farmer would just resort to letting his herd graze more because after all, there will be nothing left.
Plato discussed in his The Republic this very notion of exploitation by the unchecked freedoms of people. Without
justice, people would consume as much as they like and would eventually deplete the resources common to all. Thomas
Hobbes philosophized that the only thing that could prevent the pillaging of public or common goods is the absolute
monarch, which he calls Leviathan.
Activity # 1. What Have I Learned So Far? Answer the following questions in 2 to 3 sentences. Write your answers on a
separate sheet of paper.
1. What is rational choice theory?
2. How does preference affect decision-making?
3. How does incentive affect individual behavior?
4. What is the nature of humans?
5. What is the tragedy of the commons?
6. What is Plato’s argument on exploitation?
7. According to Hobbes, how can the exploitation of the commons be avoided?
PERFORMANCE TASK
Go to https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JaKMimJPxyA (last accessed on 29 February 2016) and watch a video
presentation on rational choice theory as applied in economics. Afterward, create a similar video that tackles any of the
other disciplines in social sciences (except for economics). Your output will be based on creativity (50%) and accuracy of
data (50%).
Prepared by: JEAN FAITH M. NOVAL
Reviewed by: NINO JAY C. GASTONES, MA- English
SHS Coordinator
Most Sacred Heart of Jesus, Have mercy on us. Immaculate Heart of Mary, Pray for us. St. Joseph, Pray for us.
Approved by: NIÑO JAY C. GASTONES, MA-English
Academic Coordinator
Vision: An institution of God-fearing, God-loving, and well transformed individuals
Mission: To provide quality education and values formation
Goals: inspired by the school’s vision-mission statement and the Divine Providence, we commit ourselves to:
become person for others by sharing what we have and what we are;
have a harmonious relationship among administrators, teachers, parents and students based on Trinitarian Spirituality;
develop a pro-People, a pro-Nation, a pro-Earth, and a pro-God community
Parent’s/Guardian’s Signature over Printed Name: _________________________________________
You might also like
- 15 Understanding Culture, Society and PoliticsDocument8 pages15 Understanding Culture, Society and PoliticsMc Clarens Laguerta93% (27)
- Cosmology: Beyond The Big BangDocument60 pagesCosmology: Beyond The Big BangHaris_IsaNo ratings yet
- Review of Quality and Reliability HandbookDocument282 pagesReview of Quality and Reliability HandbookMohamed AbdelAzizNo ratings yet
- Zero Carbon Building StandardsDocument32 pagesZero Carbon Building Standardsjoslinmtg100% (1)
- Disciplines and Ideas in Social SciencesDocument5 pagesDisciplines and Ideas in Social SciencesLeah Navarro0% (1)
- Sociological Foundation of CurriculumDocument9 pagesSociological Foundation of CurriculumJhoy ManuelNo ratings yet
- The Analysis of Equity Vs EqualityDocument5 pagesThe Analysis of Equity Vs Equalityapi-384543912No ratings yet
- Hotel Facility Design and Architectural ConstructionDocument67 pagesHotel Facility Design and Architectural ConstructionM RAJESH BABHUNo ratings yet
- 200+ TOP RADIOLOGY Online Quiz Questions - Exam Test 2023Document24 pages200+ TOP RADIOLOGY Online Quiz Questions - Exam Test 2023Ayub Alam100% (1)
- IGEM-UP-1C Draft For Comment - 2nd Consultation (IGEM-TSP-10-122)Document54 pagesIGEM-UP-1C Draft For Comment - 2nd Consultation (IGEM-TSP-10-122)eastway98100% (2)
- Computer Systems Servicing (CSS) : Flexible Instructional Delivery Plan (Fidp)Document5 pagesComputer Systems Servicing (CSS) : Flexible Instructional Delivery Plan (Fidp)Edelyn A. BergantinNo ratings yet
- Reflection On TRC Calls To Action - AssignmentDocument4 pagesReflection On TRC Calls To Action - Assignmentapi-547138479No ratings yet
- #PTC - The Sociology of EducationDocument49 pages#PTC - The Sociology of EducationRaffy Jay JaminNo ratings yet
- Functional Biology NOTESDocument113 pagesFunctional Biology NOTESRebecca Amy JennerNo ratings yet
- Socialization and Education: Education and LearningFrom EverandSocialization and Education: Education and LearningNo ratings yet
- Understanding Culture, Society and Politics: Quarter 2 LearningDocument11 pagesUnderstanding Culture, Society and Politics: Quarter 2 LearningG19 Domino, MarionNo ratings yet
- Smart AntennasDocument40 pagesSmart AntennasMeeraNo ratings yet
- Vendetta by Catherine Doyle EXCERPTDocument33 pagesVendetta by Catherine Doyle EXCERPTI Read YA50% (2)
- Beed Ii-B - Nobleza, Kim Eduard Module 5 - Prof Ed. 6Document7 pagesBeed Ii-B - Nobleza, Kim Eduard Module 5 - Prof Ed. 6Kim Nobleza50% (4)
- The Institution For Better LifeDocument2 pagesThe Institution For Better Lifezanderhero30No ratings yet
- Moral Education: Building On Ideals and Fostering CompetenciesDocument15 pagesMoral Education: Building On Ideals and Fostering Competencieskmdd1234No ratings yet
- Theory Paper 2 PortfolioDocument7 pagesTheory Paper 2 Portfolioapi-444220771No ratings yet
- Belonging A Review of Conceptual Issues An Integrative Framework and Directions For Future ResearchDocument17 pagesBelonging A Review of Conceptual Issues An Integrative Framework and Directions For Future Researchjuniki.mariaNo ratings yet
- Kelly On BrufeefDocument11 pagesKelly On BrufeefJim KellyNo ratings yet
- Ludwig Van Bedolla TapiaDocument5 pagesLudwig Van Bedolla TapiaBrenda BedollaNo ratings yet
- Learning Activities: Republic of The Philippines City of Catbalogan, Samar College EducationDocument8 pagesLearning Activities: Republic of The Philippines City of Catbalogan, Samar College EducationCalagos Mary JoyceNo ratings yet
- Sidharth Nambiar FSS BBALLB 2021Document10 pagesSidharth Nambiar FSS BBALLB 2021Sidharth NambiarNo ratings yet
- Topic 14 Social StratificationDocument5 pagesTopic 14 Social StratificationAbegail BlancoNo ratings yet
- Caste Identity in Education SystemDocument7 pagesCaste Identity in Education SystemkanishaNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Social Science and Theories and Thier Implicants To EducationDocument4 pagesModule 4 - Social Science and Theories and Thier Implicants To EducationRose Ann ProcesoNo ratings yet
- q.1 Val - Ed 9 Done Lesson 1Document9 pagesq.1 Val - Ed 9 Done Lesson 1Abby QuiñanolaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 14: Social Stratification: San Jose Community CollegeDocument5 pagesLesson 14: Social Stratification: San Jose Community CollegeSeongyuk ImNo ratings yet
- Cesc Perspective John Paul O. GonzalesDocument4 pagesCesc Perspective John Paul O. GonzalesKrystal ReyesNo ratings yet
- Midterm Module in EthicsDocument19 pagesMidterm Module in EthicsAlvin Kris AlicNo ratings yet
- FRANZ A World of Ideas1Document2 pagesFRANZ A World of Ideas1Franz Soriano IINo ratings yet
- Coun 502 Poverty in SchoolsDocument5 pagesCoun 502 Poverty in Schoolsapi-202005625No ratings yet
- W2 - LM Uts The Sociological Perspective of SelfDocument8 pagesW2 - LM Uts The Sociological Perspective of SelfRyan LaspiñasNo ratings yet
- Herbert Blumer - Coined The Term "Symbolic Interactionism" and Outlined These Basic Premises: HumansDocument4 pagesHerbert Blumer - Coined The Term "Symbolic Interactionism" and Outlined These Basic Premises: HumansAnabel BahintingNo ratings yet
- I. Lesson Lesson 1: Exploring Groups Within Society Specific ObjectivesDocument14 pagesI. Lesson Lesson 1: Exploring Groups Within Society Specific ObjectivesAni Vie MaceroNo ratings yet
- The Interdependence HypothesisDocument21 pagesThe Interdependence HypothesisCarlos PlazasNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheets Week 2Document5 pagesActivity Sheets Week 2Glen Ruzzel ElleveraNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0010027720302602 MainDocument15 pages1 s2.0 S0010027720302602 MainAzmil XinanNo ratings yet
- Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion 1Document15 pagesDiversity, Equity, and Inclusion 1api-378481314No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 FTCDocument23 pagesChapter 3 FTCEricson PandesNo ratings yet
- Savani - A Choice Mind-Set Increases The Acceptance and Maintenance of Wealth InequalityDocument10 pagesSavani - A Choice Mind-Set Increases The Acceptance and Maintenance of Wealth Inequalityselena pNo ratings yet
- J. P. Rizal Ext., West Rembo, Makati City: University of Makati Higher School NG Umak Department of Social SciencesDocument3 pagesJ. P. Rizal Ext., West Rembo, Makati City: University of Makati Higher School NG Umak Department of Social SciencesmaricrisNo ratings yet
- Concept Paper ETHICS. MarzoDocument4 pagesConcept Paper ETHICS. MarzoJune Maylyn Marzo100% (1)
- Educ 13 - Midterm ExamDocument22 pagesEduc 13 - Midterm ExamJea Mae G. BatiancilaNo ratings yet
- Biases in Niche ConstructionDocument32 pagesBiases in Niche ConstructionGONZALO VELASCO ARIASNo ratings yet
- Theory Paper #1Document6 pagesTheory Paper #1Ona FisherNo ratings yet
- UCSP Module 6Document2 pagesUCSP Module 6jonalyn obinaNo ratings yet
- Social Exchange TheoryDocument10 pagesSocial Exchange TheoryOh Lee100% (1)
- Learning Task No.3Document2 pagesLearning Task No.3Rosemarie Cabuco RazNo ratings yet
- g12 SSC 121 - Understanding Culture, Socity and PoliticsDocument61 pagesg12 SSC 121 - Understanding Culture, Socity and Politicsibnolyn2003No ratings yet
- Understanding Culture, Society and PoliticsDocument42 pagesUnderstanding Culture, Society and Politicsemeemarieson.belvisNo ratings yet
- 9 28 Equity Diversity TeamDocument40 pages9 28 Equity Diversity Teamapi-470244531No ratings yet
- Students EthicDocument5 pagesStudents Ethicchiorean_robertNo ratings yet
- Sensoy and DiangeloDocument9 pagesSensoy and DiangeloConnor JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Theories of Cohesion and Integration - EditedDocument2 pagesTheories of Cohesion and Integration - EditedCowbee WritingsNo ratings yet
- Stands and Values of Our Society Today RevisedDocument8 pagesStands and Values of Our Society Today RevisedAlatariel SabridoNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 Values Ed. Ma049 Carmen QuizDocument8 pagesQuiz 1 Values Ed. Ma049 Carmen QuizJOHNERROL CARCELLARNo ratings yet
- Ged109 MRR2 Agustin PDFDocument2 pagesGed109 MRR2 Agustin PDFSeth Jarl G. AgustinNo ratings yet
- Towards Greater Realism in Learning For Sustainability: June 2012Document14 pagesTowards Greater Realism in Learning For Sustainability: June 2012karinNo ratings yet
- RRE 2025 CallForProposalsDocument7 pagesRRE 2025 CallForProposalsCarlos DecioNo ratings yet
- Desarrollo Auto, Social y MoralDocument14 pagesDesarrollo Auto, Social y MoralKitzia AveiriNo ratings yet
- Ijre 020101Document6 pagesIjre 020101Luan OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Housing A Homeless Shelter - A Case Study of Community DeliberatioDocument12 pagesHousing A Homeless Shelter - A Case Study of Community Deliberatiojudy ann vidalNo ratings yet
- 25 Page (96-120)Document12 pages25 Page (96-120)Krista BashyalNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet No. 2-Q3: 11 Learning Competency/S: Learning Target/SDocument9 pagesActivity Sheet No. 2-Q3: 11 Learning Competency/S: Learning Target/SEdelyn A. BergantinNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet No. 3-Q3Document4 pagesActivity Sheet No. 3-Q3Edelyn A. BergantinNo ratings yet
- Form Factor Dimensions (WXDXH, In) Case Style Motherboard Connectors Case Form Factor Output VoltagesDocument4 pagesForm Factor Dimensions (WXDXH, In) Case Style Motherboard Connectors Case Form Factor Output VoltagesEdelyn A. BergantinNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet No. 4-Q3: 11 Learning Competency/S: Learning Target/SDocument5 pagesActivity Sheet No. 4-Q3: 11 Learning Competency/S: Learning Target/SEdelyn A. BergantinNo ratings yet
- 11-1Q4 Planning and Preparing For MaintenanceDocument6 pages11-1Q4 Planning and Preparing For MaintenanceEdelyn A. BergantinNo ratings yet
- 2 Creating Network CablesDocument6 pages2 Creating Network CablesEdelyn A. BergantinNo ratings yet
- Activity Title:: Activity Sheet No. 3-Q3Document5 pagesActivity Title:: Activity Sheet No. 3-Q3Edelyn A. BergantinNo ratings yet
- 1 Understanding Network DevicesDocument4 pages1 Understanding Network DevicesEdelyn A. BergantinNo ratings yet
- 4 Configuring The Wireless NetworkDocument5 pages4 Configuring The Wireless NetworkEdelyn A. BergantinNo ratings yet
- Member: Catholic Educational Association of The Philippines (CEAP) and Bohol Association of Catholic Schools (BACS-Tagbilaran) Tel #: (038) 505-8087Document4 pagesMember: Catholic Educational Association of The Philippines (CEAP) and Bohol Association of Catholic Schools (BACS-Tagbilaran) Tel #: (038) 505-8087Edelyn A. BergantinNo ratings yet
- Diss 2nd ModuleDocument3 pagesDiss 2nd ModuleEdelyn A. BergantinNo ratings yet
- Sacred Heart Academy Loon, Bohol SY 2020-2021Document12 pagesSacred Heart Academy Loon, Bohol SY 2020-2021Edelyn A. BergantinNo ratings yet
- Computer Systems Servicing NC II CG - Spideylab - Com - 2017Document36 pagesComputer Systems Servicing NC II CG - Spideylab - Com - 2017Edelyn A. BergantinNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map EmtechDocument10 pagesCurriculum Map EmtechEdelyn A. BergantinNo ratings yet
- Solve Business-Related Problems and To Apply Logic To Real-Life Situations. Making DecisionsDocument3 pagesSolve Business-Related Problems and To Apply Logic To Real-Life Situations. Making DecisionsEdelyn A. BergantinNo ratings yet
- Classroom Instruction Delivery Alignment Map (Cidam)Document10 pagesClassroom Instruction Delivery Alignment Map (Cidam)Edelyn A. Bergantin100% (1)
- Linear RegressionDocument541 pagesLinear Regressionaarthi devNo ratings yet
- Power Transmission, Distribution and Utilization: Lecture# 13 &14: Underground CablesDocument29 pagesPower Transmission, Distribution and Utilization: Lecture# 13 &14: Underground CablesPhD EENo ratings yet
- Served POsDocument21 pagesServed POsYay DumaliNo ratings yet
- Honey Python TestingDocument2 pagesHoney Python Testinger.honeyraj2016No ratings yet
- Epson C82 Service ManualDocument48 pagesEpson C82 Service ManualPablo RothNo ratings yet
- Who Can Learn Diploma CivilDocument19 pagesWho Can Learn Diploma CivilGururaj TavildarNo ratings yet
- K01299 - 20211018160945 - SBF3043 Chapter 3 - Digestive SystemDocument52 pagesK01299 - 20211018160945 - SBF3043 Chapter 3 - Digestive SystemChimChim UrkNo ratings yet
- Krohne mfc300 Manual PDFDocument180 pagesKrohne mfc300 Manual PDFJorge GilNo ratings yet
- Us-Conversion CycleDocument3 pagesUs-Conversion CycleThessaloe B. FernandezNo ratings yet
- Manual PelucheraDocument7 pagesManual Pelucheralvplus0% (1)
- Robert BurnsDocument4 pagesRobert BurnsMilana SavicNo ratings yet
- Tacticity, Geometric IsomerismDocument7 pagesTacticity, Geometric IsomerismbornxNo ratings yet
- Digital Photography in OrthodonDocument48 pagesDigital Photography in OrthodonSrinivasan BoovaraghavanNo ratings yet
- Caced Set2Document19 pagesCaced Set2Anonymous SEDun6PWNo ratings yet
- Golf Ball Paper Final DraftDocument18 pagesGolf Ball Paper Final DraftSiva RajNo ratings yet
- Numerical ReasoningDocument10 pagesNumerical ReasoningJen LeonardoNo ratings yet
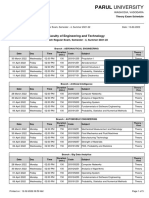
- Parul University: Faculty of Engineering and TechnologyDocument5 pagesParul University: Faculty of Engineering and TechnologySudhanshu SinghNo ratings yet
- An Accurate DDS Method Using Compound Frequency Tuning Word and Its FPGA ImplementationDocument14 pagesAn Accurate DDS Method Using Compound Frequency Tuning Word and Its FPGA ImplementationKit CornNo ratings yet
- Mobile: +91 9245560892 Objective: N.RaghunathanDocument3 pagesMobile: +91 9245560892 Objective: N.RaghunathanRagunathan NarayananNo ratings yet
- The 8051 Microcontroller and Embedded Systems: Motor Control: Relay, PWM, DC and Stepper MotorsDocument51 pagesThe 8051 Microcontroller and Embedded Systems: Motor Control: Relay, PWM, DC and Stepper MotorsAmAnDeepSingh100% (1)