Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Before The Procedure: 1.using A Flowchart, Provide The Whole Procedure of Lumbar Tap
Uploaded by
Colene MoresOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Before The Procedure: 1.using A Flowchart, Provide The Whole Procedure of Lumbar Tap
Uploaded by
Colene MoresCopyright:
Available Formats
MORES, MARY COLENE P.
BSMT 2G
MODULE 5 ENHANCEMENT QUESTIONS
CEREBROSPINAL FLUID (CSF)
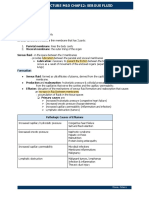
1.Using a flowchart, provide the whole procedure of lumbar tap.
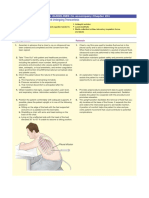
LUMBAR TAP PROCEDURE
Verify that no
contraindications exist.This Explain the procedure to the
Place the necessary orders
BEFORE THE may include doing a CT patient and answer all
so that the CSF tubes can be
head to rule out active questions. Obtain informed
PROCEDURE bleeding, midline shift, consent with appropriate
labeled after the procedure
is completed
space-occupying lesions or documentation.
signs of brain swelling.
Wash hands, open the
Position the patient either in Locate the L3/L4 space by
lumbar puncture tray
DURING THE lateral decubitus / fetal locating the superior iliac
without compromising
position, or sitting upright crests and placing your
sterility and consider any PROCEDURE leaning forward over a thumbs midline to the
extra supplies (i.e., spinal
small table spine.
needles or extra tubes)
Finish setting the LP tray
including opening the CSF Draw up and inject 10 mL of
Aseptically clean the skin Put on sterile gloves,
tubes in preparation to be 1% or 2% lidocaine
using chlorhexidine skin facemask, and protective
easily accessed, and apply (preservative free; without
prep gear per institutional policy
the sterile drapes to the epinephrine) to the area
patient
Insert the spinal needle The entry into the
directed at a slight cephalad subarachnoid space is
Attach the sterile
angle and with the bevel of commonly described as Have the patient slowly
manometer to the end of the
the needle oriented to the feeling a "pop" sensation, stretch out legs (if lying in
spinal needle to measure the
longitudinal fibers to the needle insert (obturator) lateral decubitus)
opening pressure
separate the fibers instead of is then removed and CSF
cutting them should begin to drip out
Reinsert the needle insert
Empty the manometer into
(obturator) and withdraw
CSF tube #1 and about 10 AFTER THE
Measure the closing the spinal needle and
drops of CSF into tubes #2 -
4 (note: some institutions
pressure (if indicated) immediately apply pressure PROCEDURE
and an adhesive bandage
use only 3 tubes)
over the insertion site
Document the procedure, Document the procedure,
Immediately label the CSF
Repeat neurologic number of attempts, number of attempts,
tubes have the tubes hand
assessment to evaluate for opening and closing opening and closing
carried/delivered to the lab
any changes post-LP pressure (if applicable), total pressure (if applicable), total
for analysis
amount of CSF drained amount of CSF drained
2.In a tabular form, give the cause and clinical significance of the different colors/appearance of CSF.
CSF COLOR CAUSE CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE
Normal
CRYSTAL CLEAR
White Blood Cells (WBCs)(over Meningitis
HAZY, TURBID, MILKY,
200 cells/µl)
CLOUDY
Microorganisms Meningitis
(bacteria, fungi, amebas)
Proteins Disorders that affect blood-brain
barrier
Production of IgG within the CNS
Radiographic contrast media
OILY
Red Blood Cells (RBCs) Hemorrhage
BLOODY
Traumatic Tap
Hemoglobin Old hemorrhage
XANTHOCHROMIC
Lysed dells from traumatic tap
Bilirubin RBC degradation
Elevated serum bilirubin level
Carotene Increased serum levels
Protein Disorders affecting blood-brain
barrier
Melanin Meningeal melanosarcoma
REFERENCES
https://www.ebmconsult.com/articles/procedure-lumbar-puncture
https://slideplayer.com/slide/5846519/
You might also like
- Lumbar PunctureDocument4 pagesLumbar PuncturewlNo ratings yet
- Anesthesiology Resident Manual of Procedures: A Step-by-Step GuideFrom EverandAnesthesiology Resident Manual of Procedures: A Step-by-Step GuideNo ratings yet
- Rectal and Prostate Examination Assessment SheetDocument3 pagesRectal and Prostate Examination Assessment Sheetد.أبوجعفر البراء أبوشُنّارNo ratings yet
- The Kybernetics of Natural Systems: A Study in Patterns of ControlFrom EverandThe Kybernetics of Natural Systems: A Study in Patterns of ControlNo ratings yet
- Assisting The Patient Undergoing Thoracentesis PDFDocument2 pagesAssisting The Patient Undergoing Thoracentesis PDFSITTIE JOBAISAH TOMINAMAN ALINo ratings yet
- 15 Lumber PunctureDocument18 pages15 Lumber PunctureAisha mohammedNo ratings yet
- Rosenwasser - Use of A Pedicled Adipose Flap As A Sling For Anterior Subcutaneous Transposition of The Ulnar NerveDocument4 pagesRosenwasser - Use of A Pedicled Adipose Flap As A Sling For Anterior Subcutaneous Transposition of The Ulnar NervedanielpohlmanNo ratings yet
- Operative Dictations in OphthalmologyFrom EverandOperative Dictations in OphthalmologyEric D. RosenbergNo ratings yet
- Thora Procedure 1Document10 pagesThora Procedure 1E PadzNo ratings yet
- Breathing SkillsDocument3 pagesBreathing SkillsydtrgnNo ratings yet
- Lumbar PunctureDocument25 pagesLumbar Punctureomar kmr97No ratings yet
- High Resolution and High Definition Anorectal ManometryFrom EverandHigh Resolution and High Definition Anorectal ManometryMassimo BelliniNo ratings yet
- Care of CLIENT With Neurologic ProblemsDocument20 pagesCare of CLIENT With Neurologic ProblemsArianne LasamNo ratings yet
- Sequential Compression DeviceDocument2 pagesSequential Compression Deviceal-obinay shereen0% (1)
- Lumbar Puncture in PediatricsDocument5 pagesLumbar Puncture in PediatricsMarsianus UslNo ratings yet
- Lumbar Puncture in Pediatrics PDFDocument5 pagesLumbar Puncture in Pediatrics PDFSarah AgustinNo ratings yet
- SPINAL AnaesthesiaDocument54 pagesSPINAL Anaesthesiadarsh bhattiNo ratings yet
- ACB Dan FIBCDocument21 pagesACB Dan FIBCharjunaNo ratings yet
- Spinal Anesthesia Output To PrintDocument5 pagesSpinal Anesthesia Output To PrintTin SumangaNo ratings yet
- Prostate Cancer NCPDocument1 pageProstate Cancer NCPKathleen Dimacali0% (1)
- NCM 112 Lab (Prelims)Document14 pagesNCM 112 Lab (Prelims)Erica Mei CapiliNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Lumbar PunctureDocument19 pagesLesson Plan Lumbar PunctureLoma Waghmare (Jadhav)No ratings yet
- Neonatal Chest X-Ray Interpretation: Prof. Praveen KumarDocument7 pagesNeonatal Chest X-Ray Interpretation: Prof. Praveen KumarRaji MohanNo ratings yet
- Trans Versus Abdominis Plane BlockDocument7 pagesTrans Versus Abdominis Plane BlockIvette M. Carroll D.No ratings yet
- AnesthesiaDocument24 pagesAnesthesiaakufahabaNo ratings yet
- Lumbal PungsiDocument20 pagesLumbal PungsiRk NNo ratings yet
- EncefalitisDocument5 pagesEncefalitisnataly yañezNo ratings yet
- Lumbar Puncture in PediatricsDocument9 pagesLumbar Puncture in PediatricsAulia Rahardjo100% (1)
- Lumber Puncture ProcedureDocument8 pagesLumber Puncture ProcedureDimpal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Lumber Puncture ProcedureDocument8 pagesLumber Puncture ProcedureDimpal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound-Guided Interscalene Brachial Plexus Block - NYSORADocument16 pagesUltrasound-Guided Interscalene Brachial Plexus Block - NYSORAEarn TipananNo ratings yet
- Postoperative Urinary Retention: Anesthetic and Perioperative ConsiderationsDocument19 pagesPostoperative Urinary Retention: Anesthetic and Perioperative Considerationspooria shNo ratings yet
- Lumbar Puncture: STEP 1 - Prepare The PatientDocument2 pagesLumbar Puncture: STEP 1 - Prepare The Patientnbp2009No ratings yet
- 5 PPH - Scenario 1Document4 pages5 PPH - Scenario 1mjgmhgfvNo ratings yet
- TRANS Porno MyocardialDocument3 pagesTRANS Porno MyocardialChristy Joy AvilaNo ratings yet
- Lumber PDFDocument13 pagesLumber PDFPrasann RoyNo ratings yet
- Venipuncture Techniques in Chelonian Species: Lab Animal August 2008Document3 pagesVenipuncture Techniques in Chelonian Species: Lab Animal August 2008david alonsoNo ratings yet
- Guía ClínicaDocument4 pagesGuía ClínicaingenieroaggNo ratings yet
- Channel Palpation PDFDocument7 pagesChannel Palpation PDFJose Gregorio Parra100% (1)
- Lesson Plan Lumbar PunctureDocument25 pagesLesson Plan Lumbar PunctureValarmathi50% (4)
- Basic FESS - Step-By-Step Guide With Surgical Videos PDFDocument20 pagesBasic FESS - Step-By-Step Guide With Surgical Videos PDFMujeeb MohammedNo ratings yet
- Skill 34 (1) ..EVD Maintaining System at Correct Level and FunctioningDocument2 pagesSkill 34 (1) ..EVD Maintaining System at Correct Level and FunctioningnetsquadNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Spinal Anaesthetic Block: ReferencesDocument3 pagesAssessment of Spinal Anaesthetic Block: ReferencesAlyssa MadriagaNo ratings yet
- AnesthesiaDocument26 pagesAnesthesiaezkina14No ratings yet
- Procedure On Lumber PunctureDocument8 pagesProcedure On Lumber PunctureDimpal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument8 pagesCase StudyKrisianne Mae Lorenzo FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Lumbar PunctureDocument4 pagesLumbar Puncturerupali gahalianNo ratings yet
- Endoscopic Wedge Excisions With CO2 Laser For Subglottic Stenosis, 2020Document5 pagesEndoscopic Wedge Excisions With CO2 Laser For Subglottic Stenosis, 2020Araceli BarreraNo ratings yet
- Obtaining An Abg SampleDocument20 pagesObtaining An Abg Samplemohannadalkwiese3No ratings yet
- No. 3 Lumbar PunctureDocument4 pagesNo. 3 Lumbar PunctureGrant Wynn ArnucoNo ratings yet
- Invasive Neuromonitoring TechniqueDocument20 pagesInvasive Neuromonitoring TechniqueReza ManefoNo ratings yet
- External Ventricular Drain Care and Management-3Document11 pagesExternal Ventricular Drain Care and Management-3nitsauNo ratings yet
- Cobb - Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel ReleaseDocument8 pagesCobb - Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel ReleaseJohnny WangNo ratings yet
- Op3. Lumbar PunctureDocument5 pagesOp3. Lumbar PunctureRusseiNo ratings yet
- Expt. 2 Buffer CapacityDocument12 pagesExpt. 2 Buffer CapacityColene MoresNo ratings yet
- Expt 7 LipidsDocument34 pagesExpt 7 LipidsColene MoresNo ratings yet
- Expt 5 CarbohydratesDocument49 pagesExpt 5 CarbohydratesColene MoresNo ratings yet
- Mores, Mary Colene P. BSMT 2GDocument3 pagesMores, Mary Colene P. BSMT 2GColene MoresNo ratings yet
- Expt 1 PH MeasurementDocument33 pagesExpt 1 PH MeasurementColene MoresNo ratings yet
- Brief Description That Differs From Other Imaging Procedure (Answer Should Be in Bullet Form) Examples of Medical Conditions That Is Being DiagnosedDocument3 pagesBrief Description That Differs From Other Imaging Procedure (Answer Should Be in Bullet Form) Examples of Medical Conditions That Is Being DiagnosedColene MoresNo ratings yet
- Cause (Causative Agent) Pathophysiolo Gic Mechanism Manifestation (Signs & Symptoms)Document5 pagesCause (Causative Agent) Pathophysiolo Gic Mechanism Manifestation (Signs & Symptoms)Colene MoresNo ratings yet
- AUBF Lecture Module 8 Chapter 10: SEMINALYSIS: Semen AnalysisDocument9 pagesAUBF Lecture Module 8 Chapter 10: SEMINALYSIS: Semen AnalysisColene MoresNo ratings yet
- Cerebrospinal Fluid LectureDocument5 pagesCerebrospinal Fluid LectureColene MoresNo ratings yet
- Aubf Lec - Serous FluidDocument12 pagesAubf Lec - Serous FluidColene MoresNo ratings yet
- Synovial FluidDocument7 pagesSynovial FluidColene MoresNo ratings yet
- Ob AssignmntDocument4 pagesOb AssignmntOwais AliNo ratings yet
- NI 43-101 Technical Report - Lithium Mineral Resource Estimate Zeus Project, Clayton Valley, USADocument71 pagesNI 43-101 Technical Report - Lithium Mineral Resource Estimate Zeus Project, Clayton Valley, USAGuillaume De SouzaNo ratings yet
- 5Document3 pages5Carlo ParasNo ratings yet
- CALIDocument58 pagesCALIleticia figueroaNo ratings yet
- Iii. The Impact of Information Technology: Successful Communication - Key Points To RememberDocument7 pagesIii. The Impact of Information Technology: Successful Communication - Key Points To Remembermariami bubuNo ratings yet
- 19-Microendoscopic Lumbar DiscectomyDocument8 pages19-Microendoscopic Lumbar DiscectomyNewton IssacNo ratings yet
- Mohak Meaning in Urdu - Google SearchDocument1 pageMohak Meaning in Urdu - Google SearchShaheryar AsgharNo ratings yet
- Weird Tales v14 n03 1929Document148 pagesWeird Tales v14 n03 1929HenryOlivr50% (2)
- Food NutritionDocument21 pagesFood NutritionLaine AcainNo ratings yet
- VIII and IXDocument56 pagesVIII and IXTinn ApNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: Personal InformationDocument2 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Personal InformationtyasNo ratings yet
- Community Service Learning IdeasDocument4 pagesCommunity Service Learning IdeasMuneeb ZafarNo ratings yet
- Walt Whitman Video Worksheet. CompletedDocument1 pageWalt Whitman Video Worksheet. CompletedelizabethannelangehennigNo ratings yet
- Game Theory Presentation: Big BrotherDocument11 pagesGame Theory Presentation: Big BrotherNitinNo ratings yet
- Haloperidol PDFDocument4 pagesHaloperidol PDFfatimahNo ratings yet
- Ra 7877Document16 pagesRa 7877Anonymous FExJPnCNo ratings yet
- Repair and Field Service BrochureDocument4 pagesRepair and Field Service Brochurecorsini999No ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management: A Framework of Understanding D. Du Toit & P.J. VlokDocument14 pagesSupply Chain Management: A Framework of Understanding D. Du Toit & P.J. VlokchandanaNo ratings yet
- Novedades Jaltest CV en 887Document14 pagesNovedades Jaltest CV en 887Bruce LyndeNo ratings yet
- Hanumaan Bajrang Baan by JDocument104 pagesHanumaan Bajrang Baan by JAnonymous R8qkzgNo ratings yet
- LBST 2102 Final EssayDocument9 pagesLBST 2102 Final Essayapi-318174977No ratings yet
- Karnataka BankDocument6 pagesKarnataka BankS Vivek BhatNo ratings yet
- Annals of The B Hand 014369 MBPDocument326 pagesAnnals of The B Hand 014369 MBPPmsakda HemthepNo ratings yet
- DE1734859 Central Maharashtra Feb'18Document39 pagesDE1734859 Central Maharashtra Feb'18Adesh NaharNo ratings yet
- Lesson 17 Be MoneySmart Module 1 Student WorkbookDocument14 pagesLesson 17 Be MoneySmart Module 1 Student WorkbookAry “Icky”100% (1)
- A Practical Guide To Transfer Pricing Policy Design and ImplementationDocument11 pagesA Practical Guide To Transfer Pricing Policy Design and ImplementationQiujun LiNo ratings yet
- School Games Calendar Part-1Document5 pagesSchool Games Calendar Part-1Ranadhir Singh100% (2)
- HDFC Bank-Centurion Bank of Punjab: Presented By: Sachi Bani Perhar Mba-Ib 2010-2012Document40 pagesHDFC Bank-Centurion Bank of Punjab: Presented By: Sachi Bani Perhar Mba-Ib 2010-2012Sumit MalikNo ratings yet
- Elements of PoetryDocument5 pagesElements of PoetryChristian ParkNo ratings yet
- Frbiblio PDFDocument16 pagesFrbiblio PDFreolox100% (1)