Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is Power Electronics?: 1957 1900 Late 1980s Mid 1970s
Uploaded by
B ANIL KUMAROriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Is Power Electronics?: 1957 1900 Late 1980s Mid 1970s
Uploaded by
B ANIL KUMARCopyright:
Available Formats
1. What is Power Electronics?
For descriptive purposes, it is frequently useful to divide the overall field of electrical engineering into
three areas of specialization: electronics, power, and control. The electronics area deals primarily with
devices and circuits for the processing of information; the power area deals with both rotating and static
equipment for the generation,transmission, distribution, and utilization of vast quantities of electrical
power; and the control area deals with the stability and response characteristics of
closed-loop systems using feedback on either a continuous or sampled-data basis.
Interstitial to all three of these areas is power electronics, which deals with the use of electronics for
the control and conversion of large amounts of electrical power.
The origins of power electronics can be traced back many years, at which time mercury-arc devices were
utilized for the rectification of AC to DC or the inversion of DC to AC. However, today’s rapidly
growing usage of power electronics has resulted from the development of solid-state power devices.
"Power electronics is the technology associated with the efficient conversion, control,
and conditioning of electric power by static means from its available input form into
the desire electrical output form."
Applicat ion of
fast- switching
Invention of fully- controlled
Thyristor semiconductor
devices GTO
Mercury arc rectifier IGBT
GTR
Vacuum- tube rectifier Power diode Power MOSFET
Power MOSFET
Thyratron Thyristor Thyristor
Thyristor
(DSP)
(microprocessor)
1900 1957 mid 1970s late 1980s
Pre-history 1st phase 2nd phase 3rd phase
Turn On And Turn Off Time
You might also like
- Expt-5 Lab Manual TE LabDocument10 pagesExpt-5 Lab Manual TE LabRuham RofiqueNo ratings yet
- Lect - 2 - 3 - Recent AdvancementDocument76 pagesLect - 2 - 3 - Recent AdvancementAreeba talpurNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Chapter 1 Introduction: Dr. Othman Hassan Assistant Professor SIUDocument38 pagesPower Electronics Chapter 1 Introduction: Dr. Othman Hassan Assistant Professor SIUAwe HughNo ratings yet
- Power ElectronicDocument66 pagesPower Electronicsalman shariff100% (1)
- Eletromagnetic - William HaytDocument11 pagesEletromagnetic - William HaytshubhNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices Used in Power Electronics Characteristics ComparisonDocument12 pagesElectronic Devices Used in Power Electronics Characteristics ComparisonEysha qureshiNo ratings yet
- Power Semiconductor Devices PosterDocument1 pagePower Semiconductor Devices PosterSai Pranahita KulithalaiNo ratings yet
- Power Switches and Their Drivers: Break Down Voltage Is Uptokv and and Forward Current Is KaDocument17 pagesPower Switches and Their Drivers: Break Down Voltage Is Uptokv and and Forward Current Is Kaabdi warfaaNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - SupplemantaryDocument13 pagesWeek 1 - SupplemantaryMohammad AmawiNo ratings yet
- Identifying and Mitigating The Problems PDFDocument4 pagesIdentifying and Mitigating The Problems PDFxvehicleNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics: OrientationDocument41 pagesPower Electronics: OrientationchandueeeNo ratings yet
- 1.introduction To P Es - NewDocument60 pages1.introduction To P Es - Newbarkat mughalNo ratings yet
- Svcet: EE6503 - Power ElectronicsDocument11 pagesSvcet: EE6503 - Power ElectronicsSatyanarayana GurramNo ratings yet
- Industrial Electronics: Anela L. SalvadorDocument148 pagesIndustrial Electronics: Anela L. SalvadorJames SuarezNo ratings yet
- Thyristor TypesDocument5 pagesThyristor TypesMustafa AnwarNo ratings yet
- Insulated-Gate Bipolar TransistorDocument12 pagesInsulated-Gate Bipolar TransistorMustafa ErcümenNo ratings yet
- 3U VNB PED-Unit-IDocument113 pages3U VNB PED-Unit-IgautamNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics - QB - Final - PECDocument52 pagesPower Electronics - QB - Final - PECmanoj kumarNo ratings yet
- 2 Power Semiconductor DevicesDocument128 pages2 Power Semiconductor DevicesSaif Ahmed 1520628645No ratings yet
- Chapter I, II, III, IV PDFDocument84 pagesChapter I, II, III, IV PDFAsmaNo ratings yet
- Thyrister (MKU)Document4 pagesThyrister (MKU)Elavazhagan NilakkottaiNo ratings yet
- Ee6503 - Power Electronics: 2 Marks and 16 Marks-Question Bank Unit 1 - Introduction Two MarksDocument30 pagesEe6503 - Power Electronics: 2 Marks and 16 Marks-Question Bank Unit 1 - Introduction Two Marksdishore312No ratings yet
- Lec-1 (Introduction To Power ElectroDocument37 pagesLec-1 (Introduction To Power ElectroEngr Muhammad Faisal YaqoobNo ratings yet
- Mepe516 L04Document551 pagesMepe516 L04tawanda daniel denguNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics IntroductionDocument18 pagesPower Electronics Introductionsagar378No ratings yet
- PPT Introduction To Power Electronics (Benny Yeung) PDFDocument32 pagesPPT Introduction To Power Electronics (Benny Yeung) PDFHamza Mustafa100% (1)
- A Pulsed Magnetron Microwave Generator Based On A Solid-State SwitchDocument6 pagesA Pulsed Magnetron Microwave Generator Based On A Solid-State SwitchPhong Phan CôngNo ratings yet
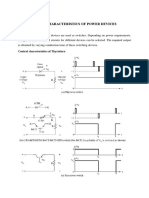
- Control Characteristics of Power DevicesDocument2 pagesControl Characteristics of Power Devicesprashansa basavarajNo ratings yet
- UE23EE643A - Unit 1 - Class 2 - Classification of Power Semiconductor DevicesDocument10 pagesUE23EE643A - Unit 1 - Class 2 - Classification of Power Semiconductor DevicesGAYATHRI DEVI BNo ratings yet
- Power ElectronicsDocument12 pagesPower Electronicssherwincalma189No ratings yet
- Ferrite Circulator SwitchesDocument2 pagesFerrite Circulator SwitchesAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- I2sg-Hw1-Scet-Ee-2k16-Group No.8Document24 pagesI2sg-Hw1-Scet-Ee-2k16-Group No.8Ab CNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics EngineeringDocument30 pagesPower Electronics Engineeringiamjarvis990No ratings yet
- Advancements in P.esDocument30 pagesAdvancements in P.esSifar TeenNo ratings yet
- 5500 Fire OptionDocument5 pages5500 Fire Optionانعام مىمونNo ratings yet
- Power Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument27 pagesPower Bipolar Junction TransistorNikhil Kushwaha50% (2)
- Module 1Document30 pagesModule 1Sathya Prakash PNo ratings yet
- ETT Vs LTTDocument13 pagesETT Vs LTTGoyito MuñozNo ratings yet
- Compare BJTDocument2 pagesCompare BJTNISHANT395No ratings yet
- Circuits Devices and ApplicationsDocument30 pagesCircuits Devices and ApplicationsTe NgNo ratings yet
- Mgiter-Navsari Electrical Engineering Department Lesson PlanningDocument3 pagesMgiter-Navsari Electrical Engineering Department Lesson PlanningJAY S TANDELNo ratings yet
- Active Gate Voltage Control of Turn-On$di/dt$and Turn-Off$dv/dt$in Insulated Gate TransistorsDocument8 pagesActive Gate Voltage Control of Turn-On$di/dt$and Turn-Off$dv/dt$in Insulated Gate TransistorsAbraham GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document40 pagesChapter 2Nabil IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Concept Map Electron Devices and CircuitsDocument1 pageConcept Map Electron Devices and CircuitsAnusooya VNo ratings yet
- Basics of Power Electronics Updated Version PDFDocument34 pagesBasics of Power Electronics Updated Version PDFSritaran BalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Training Agenda: General Electronics Thyristor TrainingDocument40 pagesTraining Agenda: General Electronics Thyristor Trainingjitu19784No ratings yet
- @1b - Semiconductors Diodes and ApplicationsDocument269 pages@1b - Semiconductors Diodes and Applicationsminh vũNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics: Elektronika DayaDocument32 pagesPower Electronics: Elektronika Dayawilliam MusapelalanNo ratings yet
- EEE 338 Power ElectronicsDocument28 pagesEEE 338 Power ElectronicsdaudNo ratings yet
- G. Pulla Reddy Engineering College (Autonomous) : Kurnool Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering Power Electronics (PEP) Laboratory (Scheme-2013)Document87 pagesG. Pulla Reddy Engineering College (Autonomous) : Kurnool Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering Power Electronics (PEP) Laboratory (Scheme-2013)Sreenath SreenathNo ratings yet
- Materi 2 Saklar ElektronikDocument18 pagesMateri 2 Saklar ElektronikAnonymous X7WdfpfwgNo ratings yet
- Introduction High Power System TransmitterDocument14 pagesIntroduction High Power System Transmittersiddhartha2862No ratings yet
- IGBT Review PaperDocument4 pagesIGBT Review PaperAJIT PRAJAPATINo ratings yet
- 1) Power Switching Devices EE-442-642Document17 pages1) Power Switching Devices EE-442-642Mehmet DALNo ratings yet
- Thyristors and Controlled Rectifiers: EE328 Power Electronics Assoc. Prof. Dr. Mutlu BOZTEPE Ege University, Dept. of E&EDocument79 pagesThyristors and Controlled Rectifiers: EE328 Power Electronics Assoc. Prof. Dr. Mutlu BOZTEPE Ege University, Dept. of E&ESilvana JimenezNo ratings yet
- Gate Turn Off Thyristors GTODocument16 pagesGate Turn Off Thyristors GTOElrich Joseph JalandoniNo ratings yet
- Transistor EnglishDocument5 pagesTransistor EnglishArif KusumaNo ratings yet
- EE 442 642 Power Switching DevicesDocument16 pagesEE 442 642 Power Switching Devicesthienvuong90No ratings yet
- Hand Gesture HOME AUTOMATIONDocument4 pagesHand Gesture HOME AUTOMATIONAman ForuNo ratings yet
- Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1From EverandNewnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- SMC1Document6 pagesSMC1B ANIL KUMARNo ratings yet
- LST H4Document46 pagesLST H4B ANIL KUMARNo ratings yet
- Proposed Area of Research Maximum Power Point Tracking Under Partial Shading Conditions For Solar Photovoltaic SystemsDocument1 pageProposed Area of Research Maximum Power Point Tracking Under Partial Shading Conditions For Solar Photovoltaic SystemsB ANIL KUMARNo ratings yet
- Control Systems Mcq'sDocument33 pagesControl Systems Mcq'sB ANIL KUMARNo ratings yet
- Elect Ckt-Session PlanDocument5 pagesElect Ckt-Session PlanB ANIL KUMARNo ratings yet
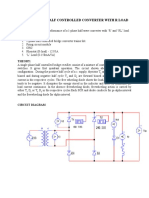
- Single Phase Half Controlled Converter With R LoadDocument3 pagesSingle Phase Half Controlled Converter With R LoadB ANIL KUMARNo ratings yet
- Gate Firing Circuits For SCR'S R-C Triggering CircuitDocument3 pagesGate Firing Circuits For SCR'S R-C Triggering CircuitB ANIL KUMARNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 Ac - DC ConvertersDocument10 pagesUnit-2 Ac - DC ConvertersB ANIL KUMARNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document4 pagesChapter 6Indu SusmiNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 Ac-Ac ConvertersDocument8 pagesUnit-3 Ac-Ac ConvertersB ANIL KUMARNo ratings yet
- 7.induction Motor EceDocument13 pages7.induction Motor EceB ANIL KUMARNo ratings yet
- 3.DC MotorsDocument3 pages3.DC MotorsB ANIL KUMARNo ratings yet
- Induction MotorDocument28 pagesInduction MotorB ANIL KUMARNo ratings yet
- Intel CPU Install PDFDocument30 pagesIntel CPU Install PDFcernatandNo ratings yet
- Horn AntennaDocument18 pagesHorn AntennaMuhammad HashimNo ratings yet
- SDC Confidential DocumentDocument11 pagesSDC Confidential DocumentAlexander MonteroNo ratings yet
- Brochure Dolphin 2014 BD-new PDFDocument20 pagesBrochure Dolphin 2014 BD-new PDFlolo100% (1)
- Automate Productqrg Li-Ion q2-0Document2 pagesAutomate Productqrg Li-Ion q2-0ArturoMayGomezNo ratings yet
- Good PDSPDocument39 pagesGood PDSPJ HARSHA YADAVNo ratings yet
- Sony HCD S500 800 PDFDocument20 pagesSony HCD S500 800 PDFvideosonNo ratings yet
- SPF 5189zDocument10 pagesSPF 5189zAparna BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Projects List - 1271 Raspberry PI ProjectsDocument47 pagesProjects List - 1271 Raspberry PI ProjectsAshrafNo ratings yet
- Magnetics Design: 11/21/21 Dept. of Electrical & Electronics Engg., MIT - Manipal 1Document107 pagesMagnetics Design: 11/21/21 Dept. of Electrical & Electronics Engg., MIT - Manipal 1timothybijuvNo ratings yet
- Benix PLC Trainer System SDocument2 pagesBenix PLC Trainer System SAbhay tiwariNo ratings yet
- Mipi Csi2Document11 pagesMipi Csi2Varun Shanker Trivedi0% (1)
- 2 Marks-Unit-4Document27 pages2 Marks-Unit-4Thenappan SNo ratings yet
- 765kV Greater Noida-Mainpuri Line - Rev 0Document24 pages765kV Greater Noida-Mainpuri Line - Rev 0Abhisek SurNo ratings yet
- Motor Forward and Reverse Direction Control Using A PLCDocument5 pagesMotor Forward and Reverse Direction Control Using A PLCChalez ZengeretsiNo ratings yet
- 4 X 13 W Dual/quad Power Amplifier: FeaturesDocument25 pages4 X 13 W Dual/quad Power Amplifier: FeaturesDaruslan StrNo ratings yet
- Noc18 Ee32 Assignment9Document4 pagesNoc18 Ee32 Assignment9sangeethasNo ratings yet
- OTA Structures2Document13 pagesOTA Structures2Debopam DattaNo ratings yet
- Form STODocument1 pageForm STOMuhammad FarhanNo ratings yet
- Thermistor 10K: Tip+ Tip-Tip - Check - 1 Tip - Check - 2Document1 pageThermistor 10K: Tip+ Tip-Tip - Check - 1 Tip - Check - 2darioNo ratings yet
- Topic On Microwave XPIC-BDocument20 pagesTopic On Microwave XPIC-BHUgo Medrano100% (4)
- Design and Construction of An FM TransmitterDocument3 pagesDesign and Construction of An FM Transmitterhealth is priorityNo ratings yet
- Virtualization BasicsDocument8 pagesVirtualization BasicsarchiebearNo ratings yet
- Yamaha YSTSW45 ActsubDocument17 pagesYamaha YSTSW45 ActsubvasconiNo ratings yet
- Features: Parameter Unit Parameter UnitDocument1 pageFeatures: Parameter Unit Parameter UnitEliecer MenesesNo ratings yet
- Apollo Hardware ManualDocument36 pagesApollo Hardware ManualSebastian RehbeinNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7,8 and 9Document15 pagesExperiment 7,8 and 9Katherine OsicosNo ratings yet
- Keithly 225 Current SourceDocument38 pagesKeithly 225 Current SourcerombernaNo ratings yet
- Gprs ModemDocument2 pagesGprs ModemAdityaNo ratings yet