Professional Documents
Culture Documents
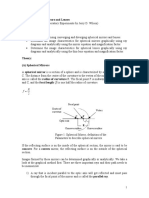
Week 7 - Ray Diagram - Concave
Week 7 - Ray Diagram - Concave
Uploaded by
Danlie ArcigalOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Week 7 - Ray Diagram - Concave
Week 7 - Ray Diagram - Concave
Uploaded by
Danlie ArcigalCopyright:
Available Formats
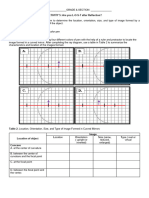
Name:
Ray Diagrams for Concave Mirrors
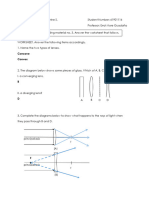
For the following mirrors and corresponding object positions, construct ray diagrams. Then describe the
Location of the image, Orientation (upright or inverted) of the image, the relative Size of the image
(larger or smaller than object), and the Type of image (real or virtual). For Case 4, merely construct the
ray diagram.
NOTE: 1) All light rays have arrowheads that indicate the direction of travel of the ray.
2) Always draw in the image once located (an arrow is a good representation).
3) Exactness counts. Use a straightedge and be accurate.
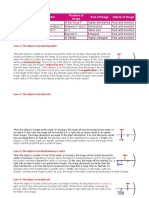
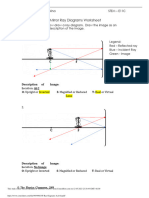
Case 1: If the object is located "beyond" the center of curvature.
Description of Image:
Location:
O: Upright or Inverted S: Magnified or Reduced T: Real or Virtual
Case 2: If the object is located at the center of curvature.
Description of Image:
Location:
O: Upright or Inverted S: Magnified or Reduced T: Real or Virtual
Case 3: If the object is located between the center of curvature and the focal point.
Description of Image:
Location:
O: Upright or Inverted S: Magnified or Reduced T: Real or Virtual
Case 4: If the object is located at the focal point.
No Description Required
Case 5: If the object is
located between the
focal point and the
mirror.
Description of Image:
Location:
O: Upright or Inverted S: Magnified or Reduced T: Real or Virtual
You might also like
- This Study Resource Was: Table 1: Convex LensDocument4 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Table 1: Convex Lenschidi100% (1)
- Homework #15 (Phy 112) SolutionsDocument23 pagesHomework #15 (Phy 112) SolutionsKvn4N6100% (1)
- Lab 10 Spherical Mirrors and LensesDocument16 pagesLab 10 Spherical Mirrors and LensesOtto ManNo ratings yet
- Ray Diagrams For Concave MirrorsDocument2 pagesRay Diagrams For Concave MirrorsShanne IsraelNo ratings yet
- Refln7 PDFDocument2 pagesRefln7 PDFJoseph LopezNo ratings yet
- Concave Diagrams - KeyDocument3 pagesConcave Diagrams - KeyOnie BerolNo ratings yet
- Concave LensDocument2 pagesConcave LensMau BautistaNo ratings yet
- Refln8 PDFDocument1 pageRefln8 PDFJoanna SeproNo ratings yet
- Concave and Convex MirrorsDocument3 pagesConcave and Convex MirrorsghgguNo ratings yet
- Curved Mirrors WSDocument2 pagesCurved Mirrors WSMariella Del Rio0% (1)
- F1 ADUCTANTE Lyka Marie T. - Activity 5 Mirror Ray DiagramDocument4 pagesF1 ADUCTANTE Lyka Marie T. - Activity 5 Mirror Ray DiagramShane GendranoNo ratings yet
- Q2 Module 3Document34 pagesQ2 Module 3Ryza AcunaNo ratings yet
- Ray DiagrammingDocument1 pageRay DiagrammingFELIX ROBERT VALENZUELANo ratings yet
- Plane Mirror Reflection PhysicsDocument14 pagesPlane Mirror Reflection PhysicsMark BelsondaNo ratings yet
- Lesson NotesDocument44 pagesLesson NotesZildjian Apud100% (1)
- LensesDocument58 pagesLensesmacmac bugananNo ratings yet
- Lecture 23Document46 pagesLecture 23Manivannan S MNo ratings yet
- Plane Mirrors.: Today's AgendaDocument45 pagesPlane Mirrors.: Today's AgendaRaym CallejaNo ratings yet
- F Ray Diagrams Activity PDFDocument3 pagesF Ray Diagrams Activity PDFzenqdumbasfNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics & Optical Instrument Most WantedDocument17 pagesRay Optics & Optical Instrument Most Wantedramianx01No ratings yet
- Convex MirrorsDocument10 pagesConvex MirrorsheteroNo ratings yet
- Science 10 - Week 17Document9 pagesScience 10 - Week 17Mira Verano80% (5)
- Phys4C Lecture45Document29 pagesPhys4C Lecture45tatinnnnn.diokno00No ratings yet
- Image Characteristics For Concave MirrorsDocument17 pagesImage Characteristics For Concave MirrorsZeinab ElkholyNo ratings yet
- Image Formation and Ray Diagrams Involving MirrorsDocument75 pagesImage Formation and Ray Diagrams Involving Mirrorsjohn charles garalde100% (1)
- B09 Ryan Delacruz - Q2 Cont - Module3Document7 pagesB09 Ryan Delacruz - Q2 Cont - Module3Mark SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Spherical Mirrors PDFDocument9 pagesSpherical Mirrors PDFAditya SudhakarNo ratings yet
- ReflectionDocument16 pagesReflectiongiyu72623No ratings yet
- Physics Cl10 Assign3Document2 pagesPhysics Cl10 Assign3Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Study Material Class 10Document19 pagesStudy Material Class 10Shivam Tiwari100% (2)
- Plane Mirrors.: Today's LectureDocument29 pagesPlane Mirrors.: Today's LectureDedar RashidNo ratings yet
- Reflection and Refraction NotesDocument18 pagesReflection and Refraction Notessundeepika2008No ratings yet
- curvedmirrors-160510115732Document23 pagescurvedmirrors-160510115732Lidelyn Jane CañalitaNo ratings yet
- 3.0 Plane Mirror-Lecture-3Document3 pages3.0 Plane Mirror-Lecture-3NIMISH GARGNo ratings yet
- OpticsDocument89 pagesOpticsKarunya nidhi100% (1)
- Task2.2 - (Optics and Waves)Document3 pagesTask2.2 - (Optics and Waves)Catherine TuliaoNo ratings yet
- 1.5 Lens Science Iv FinalDocument27 pages1.5 Lens Science Iv FinalJohn Lester GenizeraNo ratings yet
- Activity 6Document2 pagesActivity 6Charm Banlaoi100% (1)
- Curvedmirrors 160510115732 PDFDocument23 pagesCurvedmirrors 160510115732 PDFIan Frederick Sidayon CerveraNo ratings yet
- Urved Mirrors Concave and Convex: Sophia Marie D. Verdeflor Grade 10-1 STEDocument23 pagesUrved Mirrors Concave and Convex: Sophia Marie D. Verdeflor Grade 10-1 STEImman Ray Loriezo AguilarNo ratings yet
- Convex and Concave LensesDocument21 pagesConvex and Concave LensesJuniel BarriosNo ratings yet
- Lenses Notes: Convex or Converging LensDocument9 pagesLenses Notes: Convex or Converging LensAthena HuynhNo ratings yet
- Ray OpticsDocument62 pagesRay OpticsmrdaddydaddaNo ratings yet
- CLASS 10 LIGHT - REFLECTION NotesDocument14 pagesCLASS 10 LIGHT - REFLECTION NotesDeepti KashyapNo ratings yet
- CH 10 Light (Reflection 1)Document22 pagesCH 10 Light (Reflection 1)Mohammad MujtabaNo ratings yet
- Reflection of Light FINALDocument8 pagesReflection of Light FINALPrakritiNo ratings yet
- Activity 3 (B) Aim: TheoryDocument3 pagesActivity 3 (B) Aim: TheoryMeghan KumarNo ratings yet
- General Physics2 Lesson 6 PDFDocument7 pagesGeneral Physics2 Lesson 6 PDFJohn Renzo MolinarNo ratings yet
- Reflection in Curved MirrorDocument32 pagesReflection in Curved MirrorHoney Jane Romano-MoradaNo ratings yet
- PowerPoint Presentation of Convex MirrorDocument25 pagesPowerPoint Presentation of Convex MirrorPanuncialman, Johanna Mary B.No ratings yet
- Science 10th PDFDocument189 pagesScience 10th PDFMD Moon100% (1)
- Year of The YouthDocument13 pagesYear of The YouthJustin A VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Mirrors and LensesDocument49 pagesMirrors and LensesjosephrandalldeiparineNo ratings yet
- M.E.S Indian School, Doha - Qatar Notes 2024 - 2025Document10 pagesM.E.S Indian School, Doha - Qatar Notes 2024 - 2025Rafiya95z MynirNo ratings yet
- Lecture23 Part 4 Concave MirrorsDocument13 pagesLecture23 Part 4 Concave MirrorsTeresa Abing SalazarNo ratings yet
- Learning Guide SLM 56Document13 pagesLearning Guide SLM 56Kate Megan ApuliNo ratings yet
- Lecture 36: Spherical Refracting Surfaces & Thin LensesDocument7 pagesLecture 36: Spherical Refracting Surfaces & Thin LensesparveezNo ratings yet
- Ray OpticsDocument41 pagesRay Opticssangitat082No ratings yet
- Science 10q2w5Document8 pagesScience 10q2w5Cara's Vlogger.No ratings yet
- Digital Manga Composition & Perspective: A Guide for Comic Book ArtistsFrom EverandDigital Manga Composition & Perspective: A Guide for Comic Book ArtistsNo ratings yet