Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Inotropes and Vasopressors: Definition Recap
Uploaded by
Thistell Thistle0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views2 pagesOriginal Title
inotropes notes mrcs
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views2 pagesInotropes and Vasopressors: Definition Recap
Uploaded by
Thistell ThistleCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
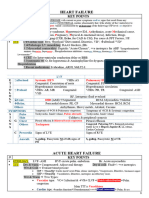
MRCS
Inotropes and Vasopressors
Definition Recap:
MAP = mean arterial pressure
CO = cardiac output
HR = heart rate
SV = stroke volume
SVR = systemic vascular resistance
EDV = end-diastolic volume
CO = HR x SV
Stroke volume = end-diastolic volume - end-systolic volume (80ml)
Ejection fraction = SV/ EDV (0.67)
Arterial pressure = CO x SVR
MAP estimation = diastolic pressure + 1/3(systolic pressure - diastolic pressure)
Pulse pressure = systolic pressure - diastolic pressure
Frank-Starling law - the stroke volume of the heart increases in response to the volume of blood
entering the heart (end diastolic volume). Note: An increase in myocardial contractility causes an
increase to the stroke volume.
Inotropic: Effects myocardial contractility i.e. +ve inotrope increases force of contraction - causes
an upward and left shift in the Starling curve.
Chronotropic: Effects heart rate i.e. +ve chronotrope increases rate
Dromotropic: Effects conduction speed and therefore rate of electrical impulses
Core receptors:
• Alpha adrenergic receptors -
• Increase systemic vascular resistance.
• Vasoconstriction of coronary arteries, venous constriction, reduced gut motility.
• A1 - smooth muscle contraction.
• A2 - negative feedback inhibits insulin release, NA release.
• Beta adrenergic receptors -
• B1 - Chronotropic/Dromotropic/Inotropic = increased CO, increases renin
secretion, increases ghrelin.
• B2 - Smooth muscle relaxation - bronchi/gi tract. Lipolysis, Anabolism, Insulin
secretion. Skeletal artery dilatation.
• Non-CNS Dopamine receptors -
• Various subtypes
• Vasodilatory, Inotropic
• Vasopressin receptors -
• V1 mediates constriction of vascular smooth muscle.
• V2 water reabsorption by enhancing renal collecting duct permeability.
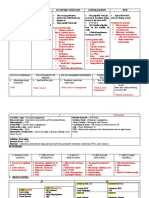
MRCS Inotropes and Vasopressors
Common Vaso-active Drugs:
Drug Receptor Effect Application Side Effects
Dopamine DA+++ +ve Inotrope. Often 1st Choice Hypotension,
β1++++ Low dose: splanchnic Shock - ventricular
α1+++ vasodilatation, increased Cardiogenic, arrhythmias,
β2++ renal and hepatic flow. Vasodilatory, cardiac/tissue
High dose: symptomatic ischaemia in high
vasoconstriction, bradycardia. doses.
increased SVR
Dobutamine β1+++ +ve Inotrope, weaker Low CO - Tachycardia
β2 ++ chronotrope. Decompensated Increased
α1+ Mild vasodilatation HF, Cardiogenic ventricular
shock. response rate in
patients with
Sepsis-induced atrial fibrillation
myocardial Ventricular
dysfunction, arrhythmias
Symptomatic Cardiac ischemia
bradycardia. Hypertension
Noradrenaline α1++++ Arteriolar Septic shock with Arrhythmias
β1++ vasoconstriction - low SVR Bradycardia
β2+ Increased systemic Peripheral
vascular resistance (digital) ischemia
Hypertension
Adrenaline α1++++ +ve Inotrope and Shock: Ventricular
β1++++ chronotrope Cardiogenic, arrhythmias
β2+++ High doses - septic. Severe
vasoconstriction Cardiac arrest hypertension risk
Bronchospasm/ of cerebral
anaphylaxis hemorrhage
Symptomatic Cardiac ischemia
bradycardia Sudden cardiac
death
Vasopressin V1, V2 Vasoconstriction, less Shock: Arrhythmias
(antidiuretic direct coronary/cerebral Vasodilatory, Hypertension
hormone) vasoconstriction. Cardiogenic. Decreased CO
Increased systemic Cardiac arrest Cardiac ischemia
vascular resistance. Peripheral
ischemia
Splanchnic
vasoconstriction
Reference:
Christopher B. Overgaard, Vladimír Džavík, Contemporary Reviews in Cardiovascular Medicine. Inotropes and
Vasopressors. Review of Physiology and Clinical Use in Cardiovascular Disease Circulation. 2008; 118: 1047-1056
You might also like
- Medicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtFrom EverandMedicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Cardiac Care and COVID-19: Perspectives in Medical PracticeFrom EverandCardiac Care and COVID-19: Perspectives in Medical PracticeNo ratings yet
- Classification and Management of HypertensionDocument20 pagesClassification and Management of HypertensionMaya Arum SariNo ratings yet
- ShockDocument39 pagesShockCut Ristina OlviaNo ratings yet
- High Risk AdultDocument7 pagesHigh Risk AdultJen IlaganNo ratings yet
- AkshayDocument35 pagesAkshaySheryl VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) / Decompensation Cordis Functional Class (DCFCDocument25 pagesCongestive Heart Failure (CHF) / Decompensation Cordis Functional Class (DCFCYUSRIL ZUMADINSYAHNo ratings yet
- Congestive Cardiac Failure - Batch 8 Feb 2015Document79 pagesCongestive Cardiac Failure - Batch 8 Feb 2015frankozed1No ratings yet
- Cardiogenic Shock: DR Putra Hendra SPPD UnibaDocument30 pagesCardiogenic Shock: DR Putra Hendra SPPD UnibaDian PuspaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular-Renal DrugsDocument114 pagesCardiovascular-Renal DrugsShahpoor Ahmad ShirzadaNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in The Treatment of Congestive Heart FailureDocument18 pagesDrugs Used in The Treatment of Congestive Heart Failurekarina azlia amandaNo ratings yet
- Endocarditis: (Post Strep Infection)Document8 pagesEndocarditis: (Post Strep Infection)Eben Ezar Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- ExaminationofpulseDocument6 pagesExaminationofpulsePeter Paul GollamudiNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure & Cardiac Arrest: Rony YuliwansyahDocument92 pagesHeart Failure & Cardiac Arrest: Rony YuliwansyahSasha ManoNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure: 10 July 2013Document8 pagesCongestive Heart Failure: 10 July 2013Michelle Vera GabunNo ratings yet
- P 3a Gagal JTGDocument35 pagesP 3a Gagal JTGAnaMariyaMaNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart FailureDocument25 pagesCongestive Heart FailuredevianiamalinaNo ratings yet
- Lect 8 & 9 - Cardiovascular and NSAIDsDocument29 pagesLect 8 & 9 - Cardiovascular and NSAIDsRaneem ShiferNo ratings yet
- Syok Kardiogenik Dr. Rani Maliawan, SP JPDocument59 pagesSyok Kardiogenik Dr. Rani Maliawan, SP JPLuh Leni AriniNo ratings yet
- Cardio PathDocument6 pagesCardio PathPranay ManiarNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failuretinayko100% (1)
- Pengantar Syok Pada Layanan PrimerDocument15 pagesPengantar Syok Pada Layanan PrimerabdmaliknasNo ratings yet
- Blood PressureDocument64 pagesBlood PressureSrishti GoenkaNo ratings yet
- Acute Heart Failure PDFDocument18 pagesAcute Heart Failure PDFRiaak ImNo ratings yet
- Treating Congestive Heart Failure with Diuretics, Inotropes, Vasodilators and ACE InhibitorsDocument18 pagesTreating Congestive Heart Failure with Diuretics, Inotropes, Vasodilators and ACE InhibitorsAnityo NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology: Cardiovascular SystemDocument314 pagesPharmacology: Cardiovascular SystemSharifa DarayanNo ratings yet
- Family Medicine EORDocument159 pagesFamily Medicine EORAndrew BowmanNo ratings yet
- Svaritm 2010Document26 pagesSvaritm 2010j.doe.hex_87No ratings yet
- Family Medicine Study GuideDocument240 pagesFamily Medicine Study GuideJeremy Christmann100% (1)
- MANAGING PATIENTS WITH HEART FAILURE COMPLICATIONSDocument8 pagesMANAGING PATIENTS WITH HEART FAILURE COMPLICATIONSkristine keen buanNo ratings yet
- Factors Leading to Heart FailureDocument3 pagesFactors Leading to Heart Failurejacj2010No ratings yet
- Cariology FinalDocument7 pagesCariology FinalBell GatesNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Blood Pressure: Short and Long Term MechanismsDocument38 pagesRegulation of Blood Pressure: Short and Long Term Mechanismsvikrant gholapNo ratings yet
- Drugs for Heart FailureDocument39 pagesDrugs for Heart FailureOngKahYeeNo ratings yet
- HYPERTENSIONSSSSDocument1 pageHYPERTENSIONSSSSJulianne Jeamer FabroaNo ratings yet
- MT MS ArrythmiaDocument3 pagesMT MS ArrythmiaChuchai AmbongNo ratings yet
- 12 Days CHF Neurohumoral PDFDocument37 pages12 Days CHF Neurohumoral PDFJoeNo ratings yet
- Brex CVS DrugsDocument287 pagesBrex CVS DrugsKate EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Kelompok 14 Skenario 2Document11 pagesKelompok 14 Skenario 2Rachmad SammuliaNo ratings yet
- Cardiomyopathy PathogenesisDocument3 pagesCardiomyopathy PathogenesisThrift AdvisoryNo ratings yet
- PHARMACOLOGY OF ANTIHYPERTENSIVE AGENTSDocument8 pagesPHARMACOLOGY OF ANTIHYPERTENSIVE AGENTSL2 - MAKILALA, Zion joy B.No ratings yet
- Ramipril For CHFDocument13 pagesRamipril For CHFYennyTjuatjaNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesHeart Failure Cheat SheetNicolle GaleNo ratings yet
- Dopa MineDocument1 pageDopa MineJon Corpuz AggasidNo ratings yet
- ShockDocument30 pagesShockLập Trương Minh QuốcNo ratings yet
- Differences Between Left and Right Heart Failure: Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument118 pagesDifferences Between Left and Right Heart Failure: Diagnosis and TreatmentMirza Thaariq HapsitoNo ratings yet
- Cardiac DysrhytmiasDocument60 pagesCardiac DysrhytmiasPY 01No ratings yet
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) : Pathogenesis RFDocument5 pagesCoronary Artery Disease (CAD) : Pathogenesis RFJennyu Yu100% (1)
- REVIEWER2Document6 pagesREVIEWER2Lorielyn Ashlee GaiteNo ratings yet
- CHFDocument45 pagesCHFAry 01No ratings yet
- Heart Failure: Understanding the Definition, Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument48 pagesHeart Failure: Understanding the Definition, Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentSanjay SathasevanNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument20 pagesCardiovascular SystemFisco DessereiNo ratings yet
- Angina Pectoris PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesAngina Pectoris Pathophysiologydana86% (7)
- 8A - Heart FailureDocument114 pages8A - Heart FailureShahpoor Ahmad ShirzadaNo ratings yet
- Rhythm Packet: Normal ECG CriteriaDocument19 pagesRhythm Packet: Normal ECG CriteriaRegina MithaNo ratings yet
- CHFDocument22 pagesCHFshazia kaziNo ratings yet
- AHeart DisordersDocument30 pagesAHeart DisordersArnold TemporosaNo ratings yet
- Cardiogenic Shock Dr. ArieDocument40 pagesCardiogenic Shock Dr. Arierio kristianNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis&Manajemen ShockDocument8 pagesDiagnosis&Manajemen ShockHJKIMNo ratings yet
- TourniquetDocument1 pageTourniquetThistell ThistleNo ratings yet
- Principles of Resuscitation, Anaesthetics, Medicine, Imaging and Laboratory InvestigationsDocument2 pagesPrinciples of Resuscitation, Anaesthetics, Medicine, Imaging and Laboratory InvestigationsThistell ThistleNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology Revision2155 160125092509Document47 pagesOphthalmology Revision2155 160125092509Thistell Thistle100% (1)
- Local/Regional/Spinal Anaesthesia: DefinitionDocument4 pagesLocal/Regional/Spinal Anaesthesia: DefinitionThistell ThistleNo ratings yet
- Maternal Death 6.0Document20 pagesMaternal Death 6.0Thistell ThistleNo ratings yet
- RECOVER ANKLE FRACTUREDocument2 pagesRECOVER ANKLE FRACTUREThistell ThistleNo ratings yet
- Gynecology Notes Ebook PDFDocument51 pagesGynecology Notes Ebook PDFThistell Thistle100% (1)
- Contraceptive Choices For Young People May 2019Document33 pagesContraceptive Choices For Young People May 2019Thistell ThistleNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology Notes on Red Eye, Glaucoma, Uveitis & Sudden Vision LossDocument2 pagesOphthalmology Notes on Red Eye, Glaucoma, Uveitis & Sudden Vision LossThistell ThistleNo ratings yet
- Resp Meds 2017Document25 pagesResp Meds 2017Thistell ThistleNo ratings yet
- Ent Lecture NotesDocument2 pagesEnt Lecture NotesThistell ThistleNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Disease in Pregnancy AO38v3.1Document9 pagesThyroid Disease in Pregnancy AO38v3.1Thistell ThistleNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Cases For Osces - Dec14Document14 pagesPaediatric Cases For Osces - Dec14Thistell ThistleNo ratings yet
- MAA Paeds Conditions - Chromosomal and GeneticDocument8 pagesMAA Paeds Conditions - Chromosomal and GeneticThistell ThistleNo ratings yet
- Neck ExamsDocument1 pageNeck ExamsThistell ThistleNo ratings yet
- PACES Revision Obstetrics and Gynaecology: 27/04/2012 Amrita Banerjee & Ola MarkiewiczDocument62 pagesPACES Revision Obstetrics and Gynaecology: 27/04/2012 Amrita Banerjee & Ola MarkiewiczThistell ThistleNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Cardiology Guide to ASD, Coarctation, Heart Failure & Kawasaki DiseaseDocument13 pagesPaediatric Cardiology Guide to ASD, Coarctation, Heart Failure & Kawasaki DiseaseThistell ThistleNo ratings yet
- Child Development LectureDocument1 pageChild Development LectureThistell ThistleNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Ultrasound For Postgraduates in ObstetricsDocument33 pagesDiagnostic Ultrasound For Postgraduates in Obstetricsg1381821No ratings yet
- Child Development LectureDocument44 pagesChild Development LectureThistell ThistleNo ratings yet
- Paediatrics Notes PDFDocument111 pagesPaediatrics Notes PDFhafizahhoshniNo ratings yet
- Unbalanced Recovery of Regulatory and Effector T Cells PaperDocument13 pagesUnbalanced Recovery of Regulatory and Effector T Cells PaperThistell ThistleNo ratings yet
- Allogeneic Stem Cell TransplantDocument3 pagesAllogeneic Stem Cell TransplantThistell ThistleNo ratings yet
- Allopurinol May Help Calcium Oxalate Kidney Stone Formation by Inhibiting Uric Acid CrystallizationDocument2 pagesAllopurinol May Help Calcium Oxalate Kidney Stone Formation by Inhibiting Uric Acid CrystallizationThistell ThistleNo ratings yet
- Surgery For Finals 2010Document58 pagesSurgery For Finals 2010Kay Bristol100% (1)
- Paediatrics Notes PDFDocument111 pagesPaediatrics Notes PDFhafizahhoshniNo ratings yet
- Common Drugs For F1Document7 pagesCommon Drugs For F1Thistell ThistleNo ratings yet
- Common Drugs For F1Document7 pagesCommon Drugs For F1Thistell ThistleNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Cardiac Glycosides, Antianginals, and Antidysrhythmics - AntiarrhythmmicsDocument40 pagesLesson 1 Cardiac Glycosides, Antianginals, and Antidysrhythmics - AntiarrhythmmicsXiamen Magsino NolascoNo ratings yet
- PacemakersDocument8 pagesPacemakersVIVEK Kumar Prajapati 72No ratings yet
- S8 Defibrillator/monitor: - Share With The WorldDocument19 pagesS8 Defibrillator/monitor: - Share With The WorldKarl MamarilNo ratings yet
- VVIR Vs DDDRDocument2 pagesVVIR Vs DDDRNITACORDEIRONo ratings yet
- Pharmacological Management of Cardiac Arrhythmias in The Fetal andDocument16 pagesPharmacological Management of Cardiac Arrhythmias in The Fetal andcristhian mendezNo ratings yet
- Cardiology PDFDocument9 pagesCardiology PDFFC Mekar AbadiNo ratings yet
- Management of A Case of Ventricular Bigeminy UsingDocument2 pagesManagement of A Case of Ventricular Bigeminy UsingAlfian AlfianNo ratings yet
- d4 Medical Examiner Report For A Lorry or Bus Driving LicenceDocument8 pagesd4 Medical Examiner Report For A Lorry or Bus Driving LicenceSimplyMore25No ratings yet
- Ecg Interpretation New TemplateDocument88 pagesEcg Interpretation New TemplateJonathan NgNo ratings yet
- HDO Leaflet PTDocument12 pagesHDO Leaflet PTErickson Fabian CastilloNo ratings yet
- Mitral Valve ProlapseDocument6 pagesMitral Valve ProlapseMary Joy FrancoNo ratings yet
- Avant Review Lesson 1-8 ECG Rhythm Strip InterpretationDocument28 pagesAvant Review Lesson 1-8 ECG Rhythm Strip InterpretationphoebjaetanNo ratings yet
- Rigel Uni-SimDocument6 pagesRigel Uni-SimMatíasNo ratings yet
- Oral Contributions: JACC March 9, 2010 ABSTRACTS: Cardiac Arrhythmias A1Document217 pagesOral Contributions: JACC March 9, 2010 ABSTRACTS: Cardiac Arrhythmias A1Apner Calvin SuNo ratings yet
- Why Animals: Don't GetDocument308 pagesWhy Animals: Don't Getioan ispasNo ratings yet
- What Is A Cardiac Dysrhythmia?Document6 pagesWhat Is A Cardiac Dysrhythmia?Megan N. ReyesNo ratings yet
- Cardiology The ABC's of The PQRSTDocument2 pagesCardiology The ABC's of The PQRSTMardiya MahmoudNo ratings yet
- DefibrillatorDocument44 pagesDefibrillatorDipika JangpangiNo ratings yet
- 7 Cardiac RehabilitationDocument63 pages7 Cardiac RehabilitationgilangbpNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Drugs in Intensive Care GuideDocument6 pagesHandbook of Drugs in Intensive Care GuideardriangollerNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs: AmiodaroneDocument32 pagesAntiarrhythmic Drugs: Amiodaroneabd hamzaNo ratings yet
- Zoll M MCCT Series Defibrillator ManualDocument111 pagesZoll M MCCT Series Defibrillator Manualjuan alberto florez coteNo ratings yet
- Hipokalemia: KaliumDocument49 pagesHipokalemia: KaliumIqbalAmriFauzalNo ratings yet
- Cardiac ImDocument22 pagesCardiac ImmetNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Antiarrhythmic Drugs - RecordedDocument33 pagesPharmacology of Antiarrhythmic Drugs - RecordedSarah SabtiNo ratings yet
- Perceived Competence in Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation, Knowledge and Skills, Amongst 50 Qualified NursesDocument6 pagesPerceived Competence in Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation, Knowledge and Skills, Amongst 50 Qualified NursesYannis ZoldenbergNo ratings yet
- Vital Signs Simulator Saves Time and MoneyDocument2 pagesVital Signs Simulator Saves Time and MoneyRamadhan FebriNo ratings yet
- Dynamical Model ECG v3Document30 pagesDynamical Model ECG v3Nada Fitrieyatul HikmahNo ratings yet
- Fuster Et Al 2001 Acc Aha Esc Guidelines For The Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation Executive Summary ADocument33 pagesFuster Et Al 2001 Acc Aha Esc Guidelines For The Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation Executive Summary AAlfita RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- UW - Cardiovascular - Educational ObjectivesDocument52 pagesUW - Cardiovascular - Educational ObjectivesUsama BilalNo ratings yet