Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Verb 1 CISS
Verb 1 CISS
Uploaded by
Fozia ShaikhCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Verb 1 CISS
Verb 1 CISS
Uploaded by
Fozia ShaikhCopyright:
Available Formats
CAMBRIDGE
Institute of Sure Success________ VERB_______________________________________
A verb is a doing word which shows some action or work.
Kinds of Verbs:
The verbs primarily have two kinds:
1. Helping / Auxiliary Verbs: These verbs do not directly show an action. These verbs also have
two kinds:
(a) Simple Auxiliaries / Helping Verbs: Is, am, are, was, were, be, been, being, has, have, had,
do, does, and did.
(b) Model Auxiliaries: Can, could, should, ought to, must, may, might, shall, will, would.
Dare, need, have to and used to also share some of the features of modal verbs.
2. Action / Main Verbs: These verbs directly show some action i.e. (He is writing a letter.)
3.
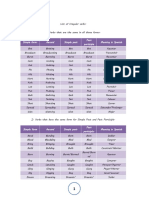
FORMS: Action / Main verbs have four forms:
Sr. # Forms of the Verb Names of the Forms Example
1. 1st form Present Catch
2. 2nd form Past Caught
rd
3. 3 Form Past Participle Caught
4. 4th Form Present Participle Catching
KINDS: Action / Main Verbs have two kinds:
1. Regular Verbs or Weak Verbs ( )
2. Irregular Verbs or Strong Verbs ( )
REGULAR VERBS
These verbs follow some rules to make their 2nd and 3rd forms out of their 1st form.
Rule: Add (d, ed, or ied) to the 1st form of a regular verb to make its 2nd and 3rd forms:
Sr. # 1st Form 2nd Form 3rd Form 4th form
1. Smile Smiled smiled Smiling
2. Recite Recited Recited Reciting
3. Carry Carried Carried Carrying
4. Apply Applied Applied Applying
5. Play Played Played Playing
6. Annoy Annoyed Annoyed Annoying
7. Watch Watched Watched Watching
8. Treat Treated Treated Treating
IRREGULAR VERBS
These verbs follow no specific rule. Their 1 st, 2nd and 3rd forms are often different.
By: Sir Aamir Abro
CAMBRIDGE
Institute of Sure Success________ VERB_______________________________________
Sr. # 1st Form 2nd Form 3rd Form 4th form
1. Beat Beat Beaten Beating
2. Buy Bought Bought Buying
3. Spread Spread Spread Spreading
4. Go Went Gone Going
5. Come Came Come Coming
6. Run Ran Run Running
7. Cut Cut Cut cutting
8. Read Read Read Reading
IRREGULARITIES IN BOTH REGULAR AND IRREGULAR VERBS
1. Omission of “e”: If a verb, whether regular or irregular, ends in an “e’, remove that “e” and
add “ing” for making its 4th i.e. present participle form:
Smile = Smiling Slide = Sliding
Reserve = Reserving Write = Writing
Recite = Reciting Ride = Riding
2. (a) Doubling the last consonant: If a verb starts with a consonant, ends in a consonant and
is preceded by a vowel, double the last consonant:
Cut = Cutting Run = Running
Hit = Hitting Ban = Banning / Banned
Sit = Sitting Fan = Fanning / fanned
Note: In case of four letters and three sounds, here also the last consonant will be doubled:
Shut = Shutting Stop = Stopping / Stopped
Chat = Chatting / chatted Wrap = Wrapping / Wrapped
(b) In case of five or more letters, if a verb ends in a consonant, is preceded by a vowel and
has a stress on the last consonant, double the last consonant:
Cancel = Cancelling / Cancelled Transfer = Transferring / Transferred
Compel = Compelling / Compelled Begin = Beginning
3. If a verb ends in “ie”, remove both “i & e” and add “ying” to make its 4th i.e. present participle
form: Die = Dying, Lie = Lying, Tie = Tying
4. If a verb ends in “ye”, don’t remove any letter, just add “ing” to make its 4th i.e. present participle
form: Dye = Dyeing, Eye = Eyeing / Eying
By: Sir Aamir Abro
You might also like
- Grammar, Spelling & Vocabulary Activity Book (Grade 4)Document66 pagesGrammar, Spelling & Vocabulary Activity Book (Grade 4)Dima Khaled100% (1)
- Oxford EAP - Intermediate B1 - 11.60Document224 pagesOxford EAP - Intermediate B1 - 11.60Vasile Ciorici84% (32)
- Worksheet 1: SUBJECT: Subject Pronouns and Verb " To Be "Document2 pagesWorksheet 1: SUBJECT: Subject Pronouns and Verb " To Be "Yami100% (1)
- Delf A1Document9 pagesDelf A1Alexia Pomoni100% (2)
- Gramatica Inglesa Tarea 1Document3 pagesGramatica Inglesa Tarea 1Luis AlfredoNo ratings yet
- Word Building ListDocument11 pagesWord Building ListARI100% (5)
- Unit 5 Week 2 PDFDocument5 pagesUnit 5 Week 2 PDFmanubadwl96No ratings yet
- Verb Forms: 1. What Is A Verb. Types of VerbsDocument3 pagesVerb Forms: 1. What Is A Verb. Types of VerbsCristina DediuNo ratings yet
- VERBS Active and Passive Voice Oct 27Document6 pagesVERBS Active and Passive Voice Oct 27Mhcc Mindanao CrusadersNo ratings yet
- Present Simple Test DvojhárokDocument2 pagesPresent Simple Test DvojhárokDominik RamžaNo ratings yet
- Activity 1Document1 pageActivity 1Gayzel Fanged - MauleonNo ratings yet
- Words Ending in - Ed: Practice SentencesDocument4 pagesWords Ending in - Ed: Practice SentencesBùi Mạnh GiỏiNo ratings yet
- Verb ListDocument4 pagesVerb ListAlejandro JacquatNo ratings yet
- The VerbsDocument6 pagesThe VerbsKenyo Ch-yNo ratings yet
- Gammer WordDocument10 pagesGammer WordPAhmed BabanNo ratings yet
- GRAMMAR Present SimpleDocument5 pagesGRAMMAR Present SimpleeugeneNo ratings yet
- Sound of Vowel YDocument7 pagesSound of Vowel YABHISHEK GOUTAMNo ratings yet
- Iiregular VerbDocument8 pagesIiregular VerbJanardhan ChakliNo ratings yet
- 01 ImperativeDocument21 pages01 ImperativeMercy Thandiwe MadhiNo ratings yet
- Module 2, Test A: ListeningDocument3 pagesModule 2, Test A: ListeningValeriaSantaCruzNo ratings yet
- W10.Strong Form and Weak FormDocument22 pagesW10.Strong Form and Weak FormHoang Hai ĐỗNo ratings yet
- Group 1-Central VowelDocument40 pagesGroup 1-Central VowelMinh An NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Maestro Trainer's ManualDocument197 pagesMaestro Trainer's ManualvvikashNo ratings yet
- The Present Tense of Regular - Er and - Ir VerbsDocument19 pagesThe Present Tense of Regular - Er and - Ir Verbsapi-536006520No ratings yet
- Verbs in French: They Are Mostly Identified Using Their Ending)Document28 pagesVerbs in French: They Are Mostly Identified Using Their Ending)Nandana JayakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - VerbalsDocument29 pagesLesson 1 - VerbalsEdrian Angelo KoNo ratings yet
- Unit 01Document14 pagesUnit 01Alfianita RakasiwiNo ratings yet
- Full Verb Auxiliary Verb Model Verb: To Be To Do To HaveDocument35 pagesFull Verb Auxiliary Verb Model Verb: To Be To Do To HaveImran MirzadNo ratings yet
- ED Ending PronunciationDocument4 pagesED Ending PronunciationCaioNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive VoiceDocument18 pagesActive and Passive Voiceritesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Present Continuous Spelling RulesDocument1 pagePresent Continuous Spelling RulesTae Drake100% (10)
- Lesson Plan in English Grade Three 3Document6 pagesLesson Plan in English Grade Three 3Imily AcmaNo ratings yet
- Voice and Accent SB Part 5 Revisado Octubre 2016Document14 pagesVoice and Accent SB Part 5 Revisado Octubre 2016Wilson LopezNo ratings yet
- (LMC) Level 1 - Lesson 2Document26 pages(LMC) Level 1 - Lesson 2Trà My NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Unit1 CertificacionDocument75 pagesUnit1 Certificacionchristian aguilar osorioNo ratings yet
- Taller InglesDocument5 pagesTaller Inglesoscar rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Actividad Present PDocument5 pagesActividad Present PJimmy Boscan TorresNo ratings yet
- Connect+Plus+4++Revision+Mr Mostafa Abd El-AalDocument64 pagesConnect+Plus+4++Revision+Mr Mostafa Abd El-AalMostafa MostafaNo ratings yet
- RM C1 Pronunciation Worksheets TNsDocument9 pagesRM C1 Pronunciation Worksheets TNsHanna MykhalskaNo ratings yet
- Rules For Changing A Verb From The Active Voice Into The Passive VoiceDocument12 pagesRules For Changing A Verb From The Active Voice Into The Passive VoiceruchiNo ratings yet
- English Module Grade 6 Elementary SchoolDocument11 pagesEnglish Module Grade 6 Elementary SchoolDara FatimahNo ratings yet
- Past Simple Test RezolvatDocument3 pagesPast Simple Test RezolvatSerban ElenaNo ratings yet
- HjjujuiDocument6 pagesHjjujuiNhat Anh NguyenNo ratings yet
- List of Irregular VerbsDocument4 pagesList of Irregular VerbsJose Baruc Martinez RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Finite and Infinite Verbs PDFDocument4 pagesFinite and Infinite Verbs PDFMirza Haider RezaNo ratings yet
- Lecţia 6Document6 pagesLecţia 6Anonymous RMLf5aNo ratings yet
- Simple Present Tense PDFDocument95 pagesSimple Present Tense PDFPubg GamerNo ratings yet
- Guide 1 Activity 1. Read This Newspaper Article and Complete The Tasks BelowDocument4 pagesGuide 1 Activity 1. Read This Newspaper Article and Complete The Tasks Below604 PERDOMO CHICUE ISABELANo ratings yet
- Irregular VerbDocument25 pagesIrregular VerbConie NapolesNo ratings yet
- Past Simple Test Rezolvat Elena CORRECTEDDocument3 pagesPast Simple Test Rezolvat Elena CORRECTEDSerban ElenaNo ratings yet
- Enviando English For You NowDocument283 pagesEnviando English For You NowCarlos Vargas100% (1)
- FCE - Exam: B2 First For SchoolsDocument26 pagesFCE - Exam: B2 First For SchoolsNele Loubele PrivateNo ratings yet
- Phrases, Clauses, Finite and Non-Finite VerbsDocument3 pagesPhrases, Clauses, Finite and Non-Finite VerbsSanthosh SNo ratings yet
- Differences in American and British English GrammarDocument6 pagesDifferences in American and British English GrammarSenay Akar-Ben BeyNo ratings yet
- Hands On GrammarDocument78 pagesHands On Grammarsonia martinsNo ratings yet
- Material de Apoyo 2Document9 pagesMaterial de Apoyo 2nubia saavedraNo ratings yet
- Morphemes (Powerpoint)Document23 pagesMorphemes (Powerpoint)Bantfor TCườngNo ratings yet
- FR 1 Er VerbsDocument13 pagesFR 1 Er Verbsapi-290456510No ratings yet
- 2 Welcome Grade 11 StudentsDocument67 pages2 Welcome Grade 11 StudentsCristine CruzNo ratings yet
- English Grammar Form 4 - With SameecoDocument84 pagesEnglish Grammar Form 4 - With SameecoOmer WarsamehNo ratings yet
- Test 2 8 Form What's Your School LikeDocument2 pagesTest 2 8 Form What's Your School LikeІрина ПанченкоNo ratings yet
- Gerund or Infinitive - KeyDocument7 pagesGerund or Infinitive - KeyValter Pinheiro LimaNo ratings yet
- English Grammar BookDocument71 pagesEnglish Grammar Bookcleara stafanyNo ratings yet
- Daftar Irregular Verbs Beserta Artinya 3Document11 pagesDaftar Irregular Verbs Beserta Artinya 3nabilaafaz7No ratings yet
- 5 6332511923094946274Document2 pages5 6332511923094946274Fozia ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory of GasesDocument18 pagesKinetic Theory of GasesFozia ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Iso and PolymophismDocument17 pagesIso and PolymophismFozia Shaikh100% (1)
- Gas Laws: Boyle's Law Charles's Law Avogadro's LawDocument13 pagesGas Laws: Boyle's Law Charles's Law Avogadro's LawFozia ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Surface Tension 2Document11 pagesSurface Tension 2Fozia ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws: Boyle's Law Charles's Law Avogadro's LawDocument20 pagesGas Laws: Boyle's Law Charles's Law Avogadro's LawFozia ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Relative Atomic MassDocument21 pagesRelative Atomic MassFozia Shaikh100% (1)
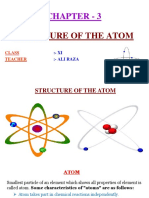
- Chapter - 3: Structure of The AtomDocument34 pagesChapter - 3: Structure of The AtomFozia ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Significant Figures: Created By: Sir. Ali RazaDocument40 pagesSignificant Figures: Created By: Sir. Ali RazaFozia ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Solid StateDocument12 pagesSolid StateFozia ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Structure of Atom.Document18 pagesStructure of Atom.Fozia ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Three States of MatterDocument36 pagesThree States of MatterFozia ShaikhNo ratings yet
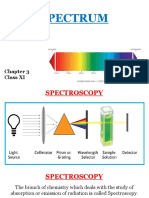
- SpectrumDocument11 pagesSpectrumFozia ShaikhNo ratings yet
- E.F and M.FDocument21 pagesE.F and M.FFozia ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Hell Is Empty and All Devils Are HereDocument2 pagesHell Is Empty and All Devils Are HereFozia ShaikhNo ratings yet
- And Cooking With Chemicals: StoichiometryDocument19 pagesAnd Cooking With Chemicals: StoichiometryFozia ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Liquid StateDocument16 pagesLiquid StateFozia ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Test 2Document2 pagesChapter 1 Test 2Fozia ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Test 3Document2 pagesChapter 1 Test 3Fozia ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Mobile A Bane or BoonDocument2 pagesMobile A Bane or BoonFozia ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Institucion Educativa Departamental Serrezuela JM: You NeedDocument4 pagesInstitucion Educativa Departamental Serrezuela JM: You Needjuan beltranNo ratings yet
- PhonologyDocument4 pagesPhonologyAce Cuison100% (1)
- GST 111 - Cours-WPS OfficeDocument31 pagesGST 111 - Cours-WPS Officebadejokosarah08No ratings yet
- Soft Skills I Unit IDocument23 pagesSoft Skills I Unit IArshNo ratings yet
- Business English 2: Unit 1 Verb "Be" & Personal Information QuestionsDocument9 pagesBusiness English 2: Unit 1 Verb "Be" & Personal Information QuestionsalbertoNo ratings yet
- Guía de Inglés IIDocument39 pagesGuía de Inglés IIAlan Jose Schwarck LeonesNo ratings yet
- Ficha-Ingl-4to. A-B - Semana 3Document3 pagesFicha-Ingl-4to. A-B - Semana 3wilder chiroqueNo ratings yet
- Second Year Scientific Streams: Budding Scientist/Second Term Test.Document2 pagesSecond Year Scientific Streams: Budding Scientist/Second Term Test.Brahim Belit100% (3)
- Chapter 4. Syntax: LinguisticsDocument35 pagesChapter 4. Syntax: LinguisticsNicoleNo ratings yet
- Eng9 Las q2 w4 AdverbsDocument4 pagesEng9 Las q2 w4 AdverbsRossmond Brigge RonquilloNo ratings yet
- Tas 3 ADocument2 pagesTas 3 AsilverpenNo ratings yet
- PELC GrammarDocument229 pagesPELC Grammaraqil zada100% (2)
- Iet FixDocument4 pagesIet FixzeliaNo ratings yet
- Deixis Presentation G01Document41 pagesDeixis Presentation G01Aulia TaufiqiNo ratings yet
- Mandarin TensesDocument11 pagesMandarin TensesShaira Nicole PelaezNo ratings yet
- English Grammar by Bhuoinder SinghDocument60 pagesEnglish Grammar by Bhuoinder SinghUmakanta DashNo ratings yet
- Grammar Space 3 Student BookDocument51 pagesGrammar Space 3 Student BookJasmin Manio50% (2)
- Unit 1Document5 pagesUnit 1Diego PerezNo ratings yet
- Noun (Subject) + Verb + The + Superlative Adjective + Noun (Object)Document6 pagesNoun (Subject) + Verb + The + Superlative Adjective + Noun (Object)anaNo ratings yet
- Soal Tes TOEFLDocument8 pagesSoal Tes TOEFLBerkat BuuloloNo ratings yet
- Progress Test AnswersDocument4 pagesProgress Test AnswersGrace AraujoNo ratings yet
- Indice Modulo 2Document5 pagesIndice Modulo 2JESUS LADRON DE GUEVARA MIRANDANo ratings yet
- Future Tenses Mind MapDocument1 pageFuture Tenses Mind MapMaripinkyNo ratings yet
- 5 Grammar Pet PeevesDocument3 pages5 Grammar Pet Peevesapi-301320346No ratings yet