Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DKASystem Disorder
DKASystem Disorder
Uploaded by
AA DDCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DKASystem Disorder
DKASystem Disorder
Uploaded by
AA DDCopyright:
Available Formats
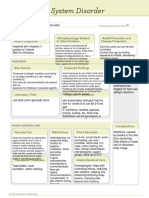
ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATE: System Disorder
STUDENT NAME______________________________________
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)
DISORDER/DISEASE PROCESS___________________________________________________________ REVIEW MODULE CHAPTER____________
Alterations in Pathophysiology Related Health Promotion and
Health (Diagnosis) to Client Problem Disease Prevention
-acute, life threatening condition characterized by
Diabetic Ketoacidosis uncontrolled hyperglycemia (> 300 mg/dl) resulting in the -smoking cessation -avoid
breakdown of body fat for energy, dehydration, metabolic
(DKA) acidosis and an accumulation of ketones in the blood and second hand smoke -use
urine protective equipment
ASSESSMENT SAFETY
CONSIDERATIONS
Risk Factors Expected Findings Wear medical
Lack of sufficient insulin related to polyuria, polydipsia, polyphagia, weight alert bracelet.
undiagnosed or untreated type 1 loss, GI effects, orthostatic hypotension, Rapid onset
fruity odor/breath, metabolic acidosis,
dm or inadequate disease kussamaul resp. mental status changes
management.
Laboratory Tests Diagnostic Procedures
Serum glucose >300 Na++: low, normal, high K: < c treatment BUN:
>30 Cr: >1.5 Ketones: present in serum and urine Osmolarity: High blood glucose, cbc, ph, ketones,
pH (ABG): <7.3 Polyuria, Polydipsia, Polyphagia, Wt loss, GI Effectts
(N/V Abd pain), Blurred vision, HA, weakness, orthostatic electrolytes, BUN, arterial or
hypotension, fruity odor of breath, kussmaul respirations, metabolic
acidosis, mental status change venous blood gases, urinalysis,
Chest x-ray, ecg or ekg
PATIENT-CENTERED CARE Complications
Nursing Care Medications Client Education acute, life threatening
condition,
Provide rapid isotonic fluid for perfusion to vital insulin aspart, insulin Teach clients how to monitor blood hypoglycemia,
organs. Monitor for fluid volume excess. Hypotonic glucose levels. Do not skip insulin
fluid 0.45 Na IV glucose if glucose >250 Administer glulisine, insulin hypokalemia fluids
doses. Maintain adequate fluids check
insulin Monitor K levels Administration of IV fluids, lispro, regular insulin, and insulin can drop
administration of short acting insulin, electrolyte urine for ketones, monitor glucose
replacement, assessment of mental status, record potassium chloride, every 4hrs when ill consume liquids potassium level this
I&O, central venous pressure monitoring. and sodium with carbs and electrolytes can impair the
bicarbonate
Medications 0.45% activities of heart,
Na fluid 0.9 % NaCl muscles and nerves.
Insulin Glucose via Cerebral edema. Left
Therapeutic Procedures IV to decrease Interprofessional Care untreated patient can
cerebral edema lose conscoiusness
Fluid replacement Electrolyte Potassium Hospitalization based on and it can be fatal.
replacement Insulin therapy. Find supplements Sodium
out if patients have trouble getting bicarbonate for pH circumstance. Outpatient,
insulin due to cost. Ensure clients less than 7.0 frequent communication
know how to administer insulins to Electrolytes with HCP,
keep glucose down.
ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATES
You might also like
- Case Simu 101Document5 pagesCase Simu 101Princess Levie CenizaNo ratings yet
- SOAP Note Example 32 Weeks OB CheckDocument4 pagesSOAP Note Example 32 Weeks OB CheckG. Crusor-PriceNo ratings yet
- Small Bowel Obstruction System - DisorderDocument1 pageSmall Bowel Obstruction System - DisorderMarina Wasem Netzlaff0% (1)
- Rhogam Medication TemplateDocument1 pageRhogam Medication TemplateAA DDNo ratings yet
- System Disorder GHDDocument1 pageSystem Disorder GHDSariahNo ratings yet
- Ati Medication Template KetorolacDocument1 pageAti Medication Template KetorolacSharee HaywoodNo ratings yet
- OB Session 1 Student Simulation Preparation Worksheet ObjectivesDocument3 pagesOB Session 1 Student Simulation Preparation Worksheet ObjectivesI Koffi100% (1)
- System Disorder CP CLDocument1 pageSystem Disorder CP CLSariahNo ratings yet
- DocDocument1 pageDocfelamendo0% (1)
- Aquifer Case 16Document4 pagesAquifer Case 16Dina KristevaNo ratings yet
- System Disorder: Renal CalculiDocument1 pageSystem Disorder: Renal CalculiHolly DeckelmanNo ratings yet
- System Disorder - Cystic FibrosisDocument1 pageSystem Disorder - Cystic Fibrosisjorge herreraNo ratings yet
- Waiters Rheumatoid Arthritis PDFDocument1 pageWaiters Rheumatoid Arthritis PDFmp1757100% (1)
- PDFDocument1 pagePDFGina GiammalvoNo ratings yet
- Ocne Competencies Updated 3 11 15Document8 pagesOcne Competencies Updated 3 11 15api-255767391No ratings yet
- What Is A PICO QuestionDocument3 pagesWhat Is A PICO QuestionBoid Gerodias100% (2)
- Final Check Off Soap NoteDocument4 pagesFinal Check Off Soap Notesana100% (1)
- H&P For ScriptDocument12 pagesH&P For ScriptAlina KievskyNo ratings yet
- ATI Medication TemplateDocument1 pageATI Medication Templatephoenix180No ratings yet
- Method Statement - Concealed ConduitDocument4 pagesMethod Statement - Concealed Conduitjoo2585No ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: System DisorderDocument1 pageThis Study Resource Was: System DisorderDeo FactuarNo ratings yet
- Waiters Osteoarthritis PDFDocument1 pageWaiters Osteoarthritis PDFmp1757No ratings yet
- Waiters Rhabdomyolysis PDFDocument1 pageWaiters Rhabdomyolysis PDFmp1757No ratings yet
- EBP & ResearchDocument6 pagesEBP & ResearchangieswensonNo ratings yet
- Focused ReviewDocument6 pagesFocused ReviewGina GiammalvoNo ratings yet
- Concept Map Due 04Document9 pagesConcept Map Due 04api-545711468No ratings yet
- Hypoxia: Lori HolmesDocument5 pagesHypoxia: Lori HolmesDanson Githinji ENo ratings yet
- Nursing AssessmentDocument16 pagesNursing AssessmentJihan Novita100% (1)
- System Disorder ADDocument1 pageSystem Disorder ADSariahNo ratings yet
- Nursing SkillDocument1 pageNursing SkillMarina Wasem NetzlaffNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Withdrawal ManagemetnDocument1 pageAlcohol Withdrawal ManagemetnerickaNo ratings yet
- Potential Complications Signs and SymptomsDocument2 pagesPotential Complications Signs and SymptomsJessica GomezNo ratings yet
- TMendoza CriticalCareConceptMap2Document5 pagesTMendoza CriticalCareConceptMap2Theresa Fernandez Mendoza0% (1)
- 6521 Advanced Pharmacology Final ExamDocument19 pages6521 Advanced Pharmacology Final ExamSandra JeffersonNo ratings yet
- 6 Physical AssessmentDocument26 pages6 Physical AssessmentAvyNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Community-Acquired Pneumonia Clinical Guideline PDFDocument1 pagePediatric Community-Acquired Pneumonia Clinical Guideline PDFJohn Vincent Dy OcampoNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer DiseaseDocument1 pagePeptic Ulcer DiseaseEunice CortésNo ratings yet
- Critical Analysis: Skills by Stella Cottrell (2005, Palgrave Macmillan) Extremely Useful. in TheDocument11 pagesCritical Analysis: Skills by Stella Cottrell (2005, Palgrave Macmillan) Extremely Useful. in ThelisastricklandNo ratings yet
- Medicine1 Grand PE ScriptDocument10 pagesMedicine1 Grand PE ScriptCarmeline Santi BeronillaNo ratings yet
- Care of Pediatric Client With Dermatologic DisorderDocument3 pagesCare of Pediatric Client With Dermatologic DisorderAraw GabiNo ratings yet
- Behavioral Health Care PlanDocument12 pagesBehavioral Health Care Planapi-520841770100% (1)
- FAELDONEA - B. Concept MapDocument1 pageFAELDONEA - B. Concept MapPatricia Jean FaeldoneaNo ratings yet
- SOAP NoteDocument3 pagesSOAP NoteMagdala D'autruche100% (1)
- Mood Disorders: Advanced Practice Education AssociatesDocument11 pagesMood Disorders: Advanced Practice Education AssociatesAndrea100% (1)
- Hypothyroidism Concept MapDocument5 pagesHypothyroidism Concept Mapnursing concept maps0% (1)
- Concept Map Meningitis TheoryDocument3 pagesConcept Map Meningitis TheoryMia AuliaNo ratings yet
- Critical Appraisal of Healthcare Literature GuideDocument2 pagesCritical Appraisal of Healthcare Literature GuideGenevieve LawrenceNo ratings yet
- HEMATOLOGIC ONCOLOGIC IMMUNOLOGIC DISORDERS - BoardsDocument10 pagesHEMATOLOGIC ONCOLOGIC IMMUNOLOGIC DISORDERS - BoardsSoojung NamNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic - Procedure DoyleDocument1 pageDiagnostic - Procedure Doylemp1757No ratings yet
- Ampicillin Med InfoDocument1 pageAmpicillin Med InfoJan McgovernNo ratings yet
- Concept Map Week 2Document2 pagesConcept Map Week 2Ashley ChristensenNo ratings yet
- DX Infective Endocarditis PDFDocument7 pagesDX Infective Endocarditis PDFSherree HayesNo ratings yet
- Breast ModuleDocument2 pagesBreast ModuleDasha Vee100% (1)
- Nursing Management of Patient With Community Acquired PneumoniaDocument5 pagesNursing Management of Patient With Community Acquired PneumoniaSummer SuarezNo ratings yet
- Care Plan For CHFDocument6 pagesCare Plan For CHFclarimerNo ratings yet
- Template For NURSING NotesDocument2 pagesTemplate For NURSING Notesbngraham4No ratings yet
- Physical ExaminationDocument7 pagesPhysical ExaminationErwin MirandaNo ratings yet
- Pharma GI CardsDocument16 pagesPharma GI CardsDoctorsHangout.comNo ratings yet
- Mastitis Teaching PlanDocument2 pagesMastitis Teaching Planapi-252910411No ratings yet
- Evaluation and Management of Suspected Sepsis and Septic Shock in AdultsDocument62 pagesEvaluation and Management of Suspected Sepsis and Septic Shock in AdultsGiussepe Chirinos CalderonNo ratings yet
- The Nurse Practitioner in UrologyFrom EverandThe Nurse Practitioner in UrologyMichelle LajinessNo ratings yet
- Inflamed Trachea, (Tracheitis) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandInflamed Trachea, (Tracheitis) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Chest Pain System - DisorderDocument1 pageChest Pain System - DisorderAA DDNo ratings yet
- Medication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseDocument1 pageMedication: Expected Pharmacological Action Therapeutic UseAA DDNo ratings yet
- Ostomy CareNursing - SkillDocument1 pageOstomy CareNursing - SkillAA DDNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaSystem DisorderDocument1 pagePneumoniaSystem DisorderAA DDNo ratings yet
- Embodied IntelligenceDocument31 pagesEmbodied IntelligenceNagendra KumarNo ratings yet
- 1.1.1 The Fuel and Energy RelationshipDocument10 pages1.1.1 The Fuel and Energy RelationshipRomeo San GasparNo ratings yet
- 21-CoV10069-Ruslan Bin HashimDocument1 page21-CoV10069-Ruslan Bin HashimHERU EKO PRAYOGONo ratings yet
- LOTTE Chemical Pakistan LTD (LOTCHEM) : Recovery in Primary Margins To Drive ProfitabilityDocument13 pagesLOTTE Chemical Pakistan LTD (LOTCHEM) : Recovery in Primary Margins To Drive ProfitabilityAli CheenahNo ratings yet
- NEM - Main Guidelines & Schedule 1 (Amendment 2019)Document29 pagesNEM - Main Guidelines & Schedule 1 (Amendment 2019)Tan Kang YaoNo ratings yet
- PDF 20221128 184203 0000Document20 pagesPDF 20221128 184203 0000Ana StolpovencoNo ratings yet
- Fraser MapDocument1 pageFraser MapbackdoorburpNo ratings yet
- 2B201-313E - B - Aquilion16PC Basic Operation PDFDocument230 pages2B201-313E - B - Aquilion16PC Basic Operation PDFLuis Daniel Gutierrez100% (1)
- Automatic Condensate Drains Eco Drain Series: For Compressor Capacities Up To 1,700 M /minDocument7 pagesAutomatic Condensate Drains Eco Drain Series: For Compressor Capacities Up To 1,700 M /minCatalin Frincu100% (1)
- A Pansophic Diagram On Letters: Translation From Latin by Christine EikeDocument7 pagesA Pansophic Diagram On Letters: Translation From Latin by Christine EikeSupremus33No ratings yet
- Bezier CurveDocument9 pagesBezier CurvePathul02No ratings yet
- Self-Directed Neuroplasticity: Rick Hanson, PH.DDocument80 pagesSelf-Directed Neuroplasticity: Rick Hanson, PH.DkabshielNo ratings yet
- Louwe Kooijmans - Bronze Age Multiple Burial at WassenaarDocument20 pagesLouwe Kooijmans - Bronze Age Multiple Burial at Wassenaarapi-3703833No ratings yet
- Linear Actuator: Component Maintenance ManualDocument67 pagesLinear Actuator: Component Maintenance ManualTAR AEROLINEASNo ratings yet
- KVS PGT Syllabus PDFDocument36 pagesKVS PGT Syllabus PDFMondar Deb0% (1)
- Technical Object First Draft & Peer Reviews - EditedDocument5 pagesTechnical Object First Draft & Peer Reviews - EditedJohn MainaNo ratings yet
- CompendiumDocument116 pagesCompendiumKämÿ LīäNo ratings yet
- Explorations Introduction To Astronomy 8th Edition Arny Test Bank 1Document36 pagesExplorations Introduction To Astronomy 8th Edition Arny Test Bank 1brandonpoolecjptayorfn100% (24)
- The Secret To: Japanese SuccessDocument44 pagesThe Secret To: Japanese Successmaria neneng bulakNo ratings yet
- 1st - 4th Yr Subjects With InstructorDocument6 pages1st - 4th Yr Subjects With InstructorEddie GuiribaNo ratings yet
- UT Dallas Syllabus For Phys3411.001.11f Taught by Paul Mac Alevey (Paulmac)Document14 pagesUT Dallas Syllabus For Phys3411.001.11f Taught by Paul Mac Alevey (Paulmac)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupNo ratings yet
- King of All Days by Hillsong UnitedDocument2 pagesKing of All Days by Hillsong UnitedPaul NietoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Trans Design RequirementsDocument63 pagesChapter 1 Trans Design RequirementstetojogoldenboyNo ratings yet
- Cotech 9264341418014Document48 pagesCotech 9264341418014paktenNo ratings yet
- Apgenco Set A1880Document16 pagesApgenco Set A1880Srimannarayana NandamNo ratings yet
- Rent To Own FlyerDocument2 pagesRent To Own FlyerKobe BinamiraNo ratings yet
- DOWSIL™ 33 Additive: Features & BenefitsDocument3 pagesDOWSIL™ 33 Additive: Features & BenefitsNiranjan GoriwaleNo ratings yet
- GIA Ruby Montepuez Mozambique PDFDocument84 pagesGIA Ruby Montepuez Mozambique PDFVaishali JhaveriNo ratings yet
- Technical Data Sheet: DescriptionDocument3 pagesTechnical Data Sheet: DescriptionFrancesco VignaliNo ratings yet