Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Start System Introduction Wiki
Start System Introduction Wiki
Uploaded by
ronald allan livioco0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views2 pagesStart System Introduction Wiki
Start System Introduction Wiki
Uploaded by
ronald allan liviocoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Introduction
The function of the starter motor is to start up the combustion engine. An
electric motor forms the basis of the starter motor. When the starter switch
is turned on, the starter relay turns on the electric motor. This motor drives
the starter gear ring via the pinion gear.
The rotating movement of the starter motor is created through the
interaction of two magnetic fields. Starter motors come with permanent
magnets or with electromagnets. Each of these configurations has its own
specific characteristics.
The energy required by the starter motor is provided by the battery. The
starter motor requires a lot of start-up power. The battery must therefore
have sufficient capacity and any losses must be kept to a minimum. As
the starter motor begins to turn faster, start-up power is reduced. This is
caused by the inverse voltage generated.
Depending on temperature, diesel engines require starting assist systems.
In case of passenger cars, these facilities consist of a preheating system
that preheats the combustion chamber and the air it contains. Glow plugs
serve as heating elements. The glow period is regulated using a glow timer.
Start Systems
3
Theory
Starter Systems
4
Theory
Starter Systems
5
Theory
1 Function and Structure of the
Starter System
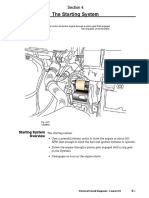
The starter system (Fig. 1) is responsible for turning the crankshaft until the
engine starts running.
The key components of the starter system are:
– Battery
– Starter (ignition) switch (part of the ignition lock)
– Starter relay
– Starter motor
– Starter gear ring mounted on the flywheel
The battery provides the required electrical energy during start--up. The
battery’s capacity and the power required for cold starts are key in this
regard. The battery must deliver sufficient power to allow the engine to turn
over for some time (several minutes maximum). In winter time, the chemical
reactions in the battery are slowed down and the battery’s capacity is
therefore lower in winter. The oil in the engine is also thicker then, which
means that it is more difficult to turn over the engine. This is why starting
problems are more likely to occur when temperatures are lower. The battery
is connected to the starter motor via thick cables. These wires must be
thick, because the starter current is very high. When the starter motor is
activated, the current can increase to several hundred amperes.
The starter switch is required to activate the starter system. When the
starter switch is activated, current flows to the starter relay. The starter
switch is often incorporated into the ignition lock. The starter position of
the ignition lock uses a spring-back mechanism. When the starter switch is
released it automatically reverts to its off position.
To be able to turn the engine, a gear ring has been mounted around the
flywheel (the starter gear ring). The starter motor turns the engine using a
small gear (pinion) that grips the starter gear ring.
Fig. 1 Starter System
Ignition lock
Starter gear ring
Starter relay
Starter Pinion
motor
Starter Systems
6
Theory
The transmission ratio between the pinion and the starter gear ring is about
10 : 1 to 15 : 1. This provides the starter motor with sufficiently high torque
to be able to turn over the engine.
The starter motor is activated by the starter relay. The starter relay is
controlled by the starter switch. When the starter relay is activated, it first
connects the starter motor with the starter gear ring. The starter current
is then switched on so that the starter motor will start turning. The starter
motor delivers the energy required to bring the engine up to the desired
level of start-up revolutions. The starter motor as such is an electric motor.
The capacity of a starter motor in a passenger car is about 800 W.
You might also like
- ME4555 TwoMass Control Spring2021 PART 1 2Document18 pagesME4555 TwoMass Control Spring2021 PART 1 2Rax UtaNo ratings yet
- Beauty Salon PDFDocument16 pagesBeauty Salon PDFAhmed El-Adawy50% (2)
- Mce 115Document14 pagesMce 115Kolawole folorunsho johnNo ratings yet
- Trosten Ahu CatalogueDocument88 pagesTrosten Ahu CatalogueJohn Son G80% (5)
- Generator Sizing by Hyundai PDFDocument5 pagesGenerator Sizing by Hyundai PDFflyzalNo ratings yet
- Ata-80 Aircraft Engine Starting Systems: Electrical Starter MotorsDocument13 pagesAta-80 Aircraft Engine Starting Systems: Electrical Starter MotorsBharath Kumar GoudNo ratings yet
- Self-Check Minor EESServiceDocument9 pagesSelf-Check Minor EESServiceMulugeta AbebeNo ratings yet
- Ata-80 Aircraft Engine Starting Systems: Electrical Starter MotorsDocument5 pagesAta-80 Aircraft Engine Starting Systems: Electrical Starter MotorsBharath Kumar GoudNo ratings yet
- Experiment Two: Starter MotorDocument10 pagesExperiment Two: Starter MotorFeras Al-AzzehNo ratings yet
- Starter MotorDocument4 pagesStarter MotorLong NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Starting System LGDocument22 pagesStarting System LGlahmetoNo ratings yet
- Electric StarterDocument3 pagesElectric StarterDio BrandoNo ratings yet
- The Cartridge StarterDocument1 pageThe Cartridge StarterlooserlooserNo ratings yet
- Ignition SystemDocument8 pagesIgnition SystemAsraNo ratings yet
- Electrical SystemDocument5 pagesElectrical SystemMoiz AamirNo ratings yet
- Automotive Electrical SystemDocument55 pagesAutomotive Electrical SystemMoriel J. NudoNo ratings yet
- Objective of The Experiment:: Starter MotorDocument15 pagesObjective of The Experiment:: Starter MotorFeras Al-AzzehNo ratings yet
- Engine Starting SystemsDocument6 pagesEngine Starting SystemsDaniel MkandawireNo ratings yet
- Tecnologia de VI Starter Alternator and Battery Tercer Bimestre 2022Document18 pagesTecnologia de VI Starter Alternator and Battery Tercer Bimestre 2022Nicolas Alexxander TavicoNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2: Dynamic Behavior of Electric DrivesDocument43 pagesChapter-2: Dynamic Behavior of Electric DrivesMuket AgmasNo ratings yet
- 6.starting SystemDocument13 pages6.starting SystemMari MuthuNo ratings yet
- Ignition SystemDocument11 pagesIgnition SystemSatyajitSahooNo ratings yet
- Engine Starting SystemsDocument19 pagesEngine Starting SystemsSal St0% (1)
- Chapter 8 - Ignition System-1Document23 pagesChapter 8 - Ignition System-1Yabtsega TadesseNo ratings yet
- Starting SystemDocument7 pagesStarting SystemEmad SatariNo ratings yet
- Starting SystemDocument15 pagesStarting SystemBULAN, LANCE KENNETH A.No ratings yet
- Charging System Leture and Quiz1Document5 pagesCharging System Leture and Quiz1Mae CherryNo ratings yet
- UNIT-2-Starter Motor and DrivesDocument34 pagesUNIT-2-Starter Motor and DrivesChandan135100% (1)
- Handbook ArranqueDocument18 pagesHandbook ArranqueChristian EchavarriaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document18 pagesChapter 5Malachi KeefeNo ratings yet
- Ggenerator AlternatorDocument4 pagesGgenerator AlternatorShakir FadzliNo ratings yet
- 11 - Electrical System PDFDocument31 pages11 - Electrical System PDFTanaji ShindeNo ratings yet
- Ignition SystemDocument25 pagesIgnition Systemahmed jemalNo ratings yet
- Ignition System and Types of Ignition SystemDocument4 pagesIgnition System and Types of Ignition SystemMuhammad ZamanNo ratings yet
- What Is Soft Starting?: Having ThyristorsDocument2 pagesWhat Is Soft Starting?: Having ThyristorsDanish MujibNo ratings yet
- Secondary Coil, and This Induces Within It An EHT VoltageDocument3 pagesSecondary Coil, and This Induces Within It An EHT VoltagePrerak Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Sistema de ArranqueDocument45 pagesSistema de ArranqueJulio CesarNo ratings yet
- Rotor Exp1Document4 pagesRotor Exp1Andrei John EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Starter Motor VehicleDocument8 pagesStarter Motor Vehiclemulengac276No ratings yet
- Ignition Systems B SNIsTDocument18 pagesIgnition Systems B SNIsTmilan mottaNo ratings yet
- The Starting SystemDocument20 pagesThe Starting SystemRuth MwendaNo ratings yet
- JLKDocument13 pagesJLKharshavardan1987No ratings yet
- Hanna Gwapa1Document8 pagesHanna Gwapa1Bhea Veiy GamayaoNo ratings yet
- IgnitionDocument13 pagesIgnitionडॉ. इन्द्रसेन सिंहNo ratings yet
- Diesel Engine Starting SystemDocument25 pagesDiesel Engine Starting SystemAbrar Hussain100% (1)
- Hệ Thống Khởi ĐộngDocument18 pagesHệ Thống Khởi ĐộngPeterNo ratings yet
- Automotive Charging SystemDocument61 pagesAutomotive Charging SystemMark100% (1)
- h7 Toyota Starting SystemsDocument11 pagesh7 Toyota Starting Systemstechtrain5199No ratings yet
- Engine Systems (p1)Document27 pagesEngine Systems (p1)dfgNo ratings yet
- The Charging System Has Three Main Components: The Alternator, The Voltage Regulator, and The BatteriesDocument20 pagesThe Charging System Has Three Main Components: The Alternator, The Voltage Regulator, and The BatteriesMae CherryNo ratings yet
- CBLM-Auto Starting SystemDocument16 pagesCBLM-Auto Starting Systemace ebradoNo ratings yet
- Car Starting and Ignition SystemDocument10 pagesCar Starting and Ignition Systemduyvu422004No ratings yet
- Qip Ice 16 Ignition - SystemsDocument60 pagesQip Ice 16 Ignition - SystemsAjay KumarNo ratings yet
- GT InfoDocument1 pageGT InfoHafizNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document52 pagesModule 1HimanshuNo ratings yet
- Automotive Startingsystem 140819070116 Phpapp02Document19 pagesAutomotive Startingsystem 140819070116 Phpapp02RamParvathaneniNo ratings yet
- Ignition SystemDocument16 pagesIgnition SystemShuguta LatiNo ratings yet
- Ignition SystemDocument23 pagesIgnition SystemGemedaNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Ignition SystemDocument14 pagesGroup 3 Ignition SystemOne Love Jah LoveNo ratings yet
- 17me655 Module 3.2Document10 pages17me655 Module 3.2VinayakNo ratings yet
- What Is A Stepper MotorDocument12 pagesWhat Is A Stepper MotorteddiyfentawNo ratings yet
- Battery:: Starter SwitchDocument3 pagesBattery:: Starter SwitchKaine WrightNo ratings yet
- Starting SystemDocument21 pagesStarting SystemKeno Domingo100% (1)
- Marine Electrics Made Simple or How to Keep the Batteries ChargedFrom EverandMarine Electrics Made Simple or How to Keep the Batteries ChargedNo ratings yet
- Urban Quality and Designing of Spaces: Case Study For Nasr City, CairoDocument11 pagesUrban Quality and Designing of Spaces: Case Study For Nasr City, CairoAhmed El-AdawyNo ratings yet
- 370 PDFDocument16 pages370 PDFAhmed El-AdawyNo ratings yet
- MNHD Cons FS 12 2018EDocument40 pagesMNHD Cons FS 12 2018EAhmed El-AdawyNo ratings yet
- Diamedica Glostavent Helix Anaesthesia System - User ManualDocument30 pagesDiamedica Glostavent Helix Anaesthesia System - User ManualAhmed El-AdawyNo ratings yet
- Statistical Characteristics of Extreme Rainfall Events in EgyptDocument9 pagesStatistical Characteristics of Extreme Rainfall Events in EgyptAhmed El-AdawyNo ratings yet
- The Red Sea and Gulf of Aden BasinsDocument46 pagesThe Red Sea and Gulf of Aden BasinsAhmed El-AdawyNo ratings yet
- SalmonFacts PDFDocument9 pagesSalmonFacts PDFAhmed El-AdawyNo ratings yet
- Program 3 PDFDocument62 pagesProgram 3 PDFAhmed El-AdawyNo ratings yet
- The Red Sea and Gulf of Aden BasinsDocument46 pagesThe Red Sea and Gulf of Aden BasinsAhmed El-AdawyNo ratings yet
- Article 1646Document16 pagesArticle 1646Ahmed El-AdawyNo ratings yet
- Assessmentofgroundwaterqualityin West Sohag EgyptDocument9 pagesAssessmentofgroundwaterqualityin West Sohag EgyptAhmed El-AdawyNo ratings yet
- Hend Hafez PaperDocument42 pagesHend Hafez PaperAhmed El-AdawyNo ratings yet
- Ismaili Age A PenDocument117 pagesIsmaili Age A PenAhmed El-AdawyNo ratings yet
- Environmental Action Plan Fayoum Governorate: State Ministry of Environment Fayoum Governorate Eeaa EMUDocument139 pagesEnvironmental Action Plan Fayoum Governorate: State Ministry of Environment Fayoum Governorate Eeaa EMUAhmed El-AdawyNo ratings yet
- Ismailia Public Free Zone About UsDocument3 pagesIsmailia Public Free Zone About UsAhmed El-AdawyNo ratings yet
- Egypt's Mega Projects: Blueprints For Long-Term Growth: The New Suez CanalDocument2 pagesEgypt's Mega Projects: Blueprints For Long-Term Growth: The New Suez CanalAhmed El-AdawyNo ratings yet
- IsmailiaDocument337 pagesIsmailiaAhmed El-AdawyNo ratings yet
- Water Ways Sustainable Rural TransportDocument65 pagesWater Ways Sustainable Rural TransportAhmed El-AdawyNo ratings yet
- November 2017 Surplus Record Machinery & Equipment DirectoryDocument728 pagesNovember 2017 Surplus Record Machinery & Equipment DirectorySurplus RecordNo ratings yet
- Yaskawa Sigma V 02Document430 pagesYaskawa Sigma V 02thanh_cdt01100% (1)
- Harmonics in Transformer: B.TechDocument31 pagesHarmonics in Transformer: B.TechSaheli MazumderNo ratings yet
- 2021 Update of The Canadian CSA Z462 Electrical Safety StandardDocument49 pages2021 Update of The Canadian CSA Z462 Electrical Safety Standardachour louniNo ratings yet
- RD 5700 SpecificationsDocument6 pagesRD 5700 SpecificationsGomathi sankarNo ratings yet
- Major Project Report grp-1Document21 pagesMajor Project Report grp-1Sachin Kumar 47No ratings yet
- Module 4 Single Phase Induction Motor 1Document43 pagesModule 4 Single Phase Induction Motor 1saravananNo ratings yet
- Position Sensorless Control For An Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor SVM Drive With ANN Based Stator Flux EstimatorDocument6 pagesPosition Sensorless Control For An Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor SVM Drive With ANN Based Stator Flux EstimatorKamrul HasanNo ratings yet
- Manual VSD Ls Ig5aDocument109 pagesManual VSD Ls Ig5arochimunNo ratings yet
- AppliancesDocument38 pagesAppliancesHardik RavalNo ratings yet
- GCM02 MT Ing4newDocument57 pagesGCM02 MT Ing4newGeorge BarsoumNo ratings yet
- 1.SF-QRV 1-4HP 2P Ip55Document2 pages1.SF-QRV 1-4HP 2P Ip55Lê ThứcNo ratings yet
- KDT Evo-General CharacteristicsDocument2 pagesKDT Evo-General CharacteristicsDjelloul AbdelhadiNo ratings yet
- Alarm Code Servo OkumaDocument4 pagesAlarm Code Servo OkumaSửa Máy Cnc LoinguyenNo ratings yet
- Upa 150c Ing.Document7 pagesUpa 150c Ing.Alfredo HerreraNo ratings yet
- A Direct Torque Controller For Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor DrivesDocument6 pagesA Direct Torque Controller For Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor DrivesGo GoNo ratings yet
- Power Generation Using Speed BreakerDocument18 pagesPower Generation Using Speed BreakerGauravNo ratings yet
- Sandvik Hl1060T Hydraulic Rock Drill: Technical SpecificationDocument2 pagesSandvik Hl1060T Hydraulic Rock Drill: Technical SpecificationLUIS ORLANDO RONDO LAYZANo ratings yet
- EMI NotesDocument13 pagesEMI Notesdfgh athtNo ratings yet
- ECD-KEB F5 VF Installation Manual (Feb 02, 2021)Document24 pagesECD-KEB F5 VF Installation Manual (Feb 02, 2021)Eric EmmsNo ratings yet
- Central Luzon State University: Plant Watering PumpDocument14 pagesCentral Luzon State University: Plant Watering PumpJohn Henry TenorioNo ratings yet
- Deep Vibro TechniquesDocument40 pagesDeep Vibro TechniquesChong Boon HanNo ratings yet
- Specifications Systems Operation Testing & Adjusting: Microcontroller Control SystemDocument133 pagesSpecifications Systems Operation Testing & Adjusting: Microcontroller Control SystemHandy LeeNo ratings yet
- 10 Science Exemplar Chapter 13Document5 pages10 Science Exemplar Chapter 13senjicsNo ratings yet
- Rockwell Automation TechED 2018 - SY08 - Lab Manual - Integrated Architecture® Tools Motion Analyzer and Automation Device Objects Basic LabDocument30 pagesRockwell Automation TechED 2018 - SY08 - Lab Manual - Integrated Architecture® Tools Motion Analyzer and Automation Device Objects Basic LabAlex RivasNo ratings yet
- B) BelowDocument10 pagesB) BelowsatishNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth Based 360 Degree Rotating MachineDocument69 pagesBluetooth Based 360 Degree Rotating Machinesakethdandu628No ratings yet