Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Activity 3 Pastrana
Uploaded by
Ma. Paz PastranaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Activity 3 Pastrana
Uploaded by
Ma. Paz PastranaCopyright:
Available Formats
ACTIVITY 3.
CELLS AND MEMBRANE TRANSPORT
I. Define the term or briefly describe the function of the organelle (10 points)
1. Prokaryotic cell - a type of cell that does not have a true nucleus or membrane-bound organelles.
2. Cell membrane - encloses the cytoplasm and forms the boundary between material inside the cell
and material outside it, supports the cell contents, acts as a selective barrier that determines what
moves into and out of the cell, and plays a role in communication between cells.
3. Chloroplast – organelles in which photosynthesis takes place and are found in plants and green algae.
4. Rough endoplasmic reticulum – is specked with tiny granules or ribosomes and serves as site of
protein synthesis.
5. Mitochondria – tiny bodies similar to bacteria that serve as sites for ATP synthesis or energy
conversion and site of aerobic respiration.
6. Ribosomes – are tiny bodies that serve as sites for protein synthesis, some are found on the outer
surface of ER while others are found scattered elsewhere within the cell.
7. Nucleus – is a large bubble containing the cell’s genetic code or the deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and
the site of RNA synthesis and ribosomal subunit assembly.
8. Osmosis - the diffusion of water (a solvent) across a selectively permeable membrane, such as the cell
membrane, from a region of higher water concentration to one of lower water concentration
9. Active transport - is a carrier-mediated process that moves substances across the cell membrane
from regions of lower concentration to those of higher concentration against a concentration gradient
10. Endocytosis - is the uptake of material through the cell membrane by the formation of a vesicle. The
cell membrane invaginates (folds inward) to form a vesicle containing the material to be taken into the
cell. The vesicle then moves into the cytoplasm.
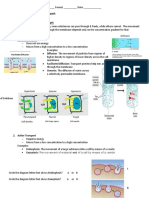
II. Identify the transport process and briefly explain the mechanism (10 points)
a. Exocytosis: a process where the secretory vesicles move to the cell membrane, where the membrane
of the vesicle fuses with the cell membrane, and the material in the vesicle is eliminated from the cell.
PASTRANA, MA. PAZ O. BS PSYCH 2B
b. Diffusion c. Facilitated Diffusion d. Active transport
- The passive movement - materials diffuse across the - a carrier-mediated process that
of particle moving plasma membrane with the the uses ATP as an energy
along with the help of membrane proteins source to transport molecules
gradient. across the membrane against its
concentration gradient.
ADP ATP
e. Secondary Active Transport f. Illustrate the process of g. Illustrate the process of
-uses the energy of one
osmosis endocytosis
substance moving
down its concentration (use diagram of (use diagram of
gradient to move
another substance lipid bilayer above) lipid bilayer above)
across the cell
membrane.
PASTRANA, MA. PAZ O. BS PSYCH 2B
You might also like
- Magic Frequencies: Excerpted From The Mixing Engineer's HandbookDocument5 pagesMagic Frequencies: Excerpted From The Mixing Engineer's HandbookmehmetkurtulusNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport - Module-3.09272021Document3 pagesCell Transport - Module-3.09272021Deps CesiNo ratings yet
- Pidlaoan, Coleen - Cell Structure PracticeDocument5 pagesPidlaoan, Coleen - Cell Structure PracticeColeenNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Processes Practice Worksheet: Name: Pidlaoan, Coleen LDocument5 pagesCell Structure and Processes Practice Worksheet: Name: Pidlaoan, Coleen LColeenNo ratings yet
- 11 - Active Transport - 2020Document24 pages11 - Active Transport - 2020tireddoodleNo ratings yet
- Active Vesicular TransportDocument14 pagesActive Vesicular Transportsarah abarcaNo ratings yet
- Biology - Module 4Document6 pagesBiology - Module 4ASHLEY MONICA PLATANo ratings yet
- Active TransportDocument11 pagesActive TransportDARLENE JANE MAYNESNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument6 pagesUntitled49 - Kaycee JoaquinNo ratings yet
- Group 4 G12 STEM Sept.30 General Biology Transport Mechanism in CellDocument38 pagesGroup 4 G12 STEM Sept.30 General Biology Transport Mechanism in CellAnime AddictNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 - The Cellular Level of OrganizationDocument82 pagesCHAPTER 3 - The Cellular Level of OrganizationMarin Jr., Reynaldo J.No ratings yet
- Cell 1Document48 pagesCell 1Mihai ChirniciniiNo ratings yet
- Act2 Bio SciDocument4 pagesAct2 Bio SciPamaran, Kristel DenishNo ratings yet
- GCSF 2013 AssignmentsDocument13 pagesGCSF 2013 AssignmentsHanNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Homeostasis and Transport Review PacketDocument9 pagesUnit 4 Homeostasis and Transport Review PacketShannon ErdmanNo ratings yet
- GenBio - 1st QuarterDocument13 pagesGenBio - 1st QuarterCc TvNo ratings yet
- (L9) Transport Across MembranesDocument22 pages(L9) Transport Across MembranesJhon TorresNo ratings yet
- Duma-Ha-Bi Ctnese833006 C03S5Document3 pagesDuma-Ha-Bi Ctnese833006 C03S5Cherifa AbdallahNo ratings yet
- Membrane Transport.Document2 pagesMembrane Transport.Adeaga ElizabethNo ratings yet
- NRS1102: Anatomy and Physiology (Lecture) 1 Semester 2020-2021 Ejfmania DMD, RN, MANDocument14 pagesNRS1102: Anatomy and Physiology (Lecture) 1 Semester 2020-2021 Ejfmania DMD, RN, MANEllen Mynelle MabulacNo ratings yet
- Prelim Session 3 Cellular Transport MembraneDocument33 pagesPrelim Session 3 Cellular Transport MembraneAnxi XiNo ratings yet
- Transport Across Cell Membrane - 43rd - BatchDocument7 pagesTransport Across Cell Membrane - 43rd - Batchshalukalakshanuni2021No ratings yet
- Biology Topic 2 NotesDocument12 pagesBiology Topic 2 NotesAasiya SultanaNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology 2 HoshmandDocument15 pagesCell Biology 2 HoshmandHoshmand HershNo ratings yet
- Part I: Cells: Overview of The Cellular Basis of LifeDocument5 pagesPart I: Cells: Overview of The Cellular Basis of LifeAldrin OjalesNo ratings yet
- Chap-11 - Transport in Plants (27) - EDocument56 pagesChap-11 - Transport in Plants (27) - ENithin RajanNo ratings yet
- 7 January 2017 Dept of Plant Biotechnology 1Document48 pages7 January 2017 Dept of Plant Biotechnology 1El Mata SuciasNo ratings yet
- S.N. Character Active Transport Passive TransportDocument2 pagesS.N. Character Active Transport Passive TransportFred SantosNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeDocument10 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeMega CyclopsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document15 pagesChapter 14Abhinav VermaNo ratings yet
- Cell, Cell Membrane, To Transport, Substances, Structure of The MembraneDocument4 pagesCell, Cell Membrane, To Transport, Substances, Structure of The MembraneИрина КривошеяNo ratings yet
- Transport 2 PDF Lecture Elalamein 2021-22Document5 pagesTransport 2 PDF Lecture Elalamein 2021-22Ahmed MagdyNo ratings yet
- Biology Short NoteDocument10 pagesBiology Short NotePatrix ParkerNo ratings yet
- 116 - Transport Mechanisms in CellsDocument4 pages116 - Transport Mechanisms in Cellslastjoe71100% (1)
- Worksheet Unit 6 - MembranesDocument2 pagesWorksheet Unit 6 - MembranesShooting StarNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport Recall Qs ANSDocument6 pagesCell Transport Recall Qs ANSzaynabaziz52No ratings yet
- Cell Membrane TransportDocument2 pagesCell Membrane TransportMARITIM GEOFFREY KIPLANGATNo ratings yet
- L9 Cellular TransportDocument2 pagesL9 Cellular TransportStephanie SyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Movement Into and Out of The Cell - Active TransportDocument12 pagesChapter 3 - Movement Into and Out of The Cell - Active TransportshammmssNo ratings yet
- Transport Across Plasma Membrane PDFDocument2 pagesTransport Across Plasma Membrane PDFTracie Curry100% (1)
- Report in Bio Transport MechanismDocument7 pagesReport in Bio Transport MechanismElaiza Nicole AccatanNo ratings yet
- Biom1070 L4 2022Document31 pagesBiom1070 L4 2022Kevin ZhangNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Chapter 3 Cell Structures and Their FunctionsDocument27 pagesAnaphy Chapter 3 Cell Structures and Their FunctionsVince Martin ManaigNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive TransportDocument2 pagesActive and Passive TransportMaricon TubonNo ratings yet
- Chapter Overview: Subject Name The Cell Topic 1 Week 1Document9 pagesChapter Overview: Subject Name The Cell Topic 1 Week 1VeiliLookNo ratings yet
- Heba Al Khasswenh 2019507339: Passive DiffusionDocument3 pagesHeba Al Khasswenh 2019507339: Passive DiffusionHEBA AL khassawenhNo ratings yet
- Heba Al Khasswenh 2019507339: Passive DiffusionDocument3 pagesHeba Al Khasswenh 2019507339: Passive DiffusionHEBA AL khassawenhNo ratings yet
- The Cell and Cellular Metabolism ReproductionDocument4 pagesThe Cell and Cellular Metabolism ReproductionApple AbriamNo ratings yet
- Transport Process: Active Transport Active TransportDocument1 pageTransport Process: Active Transport Active TransportbumbaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Cell Structures & Their Functions: Certain Molecules To Enter/exit The Cell)Document5 pagesChapter 3 Cell Structures & Their Functions: Certain Molecules To Enter/exit The Cell)Gellyace A.No ratings yet
- Movements Across Cell MembraneDocument30 pagesMovements Across Cell Membraneعلیزہ نعیمNo ratings yet
- Drug Absorption-WPS OfficeDocument6 pagesDrug Absorption-WPS Officeloknath sur parthoNo ratings yet
- Cells: DetailsDocument109 pagesCells: DetailsAishwarya SivakumarNo ratings yet
- 3 - kh201295 kh201295Document5 pages3 - kh201295 kh201295murtada gubaNo ratings yet
- 4 Movement of Substances Across The Cell MembraneDocument5 pages4 Movement of Substances Across The Cell MembraneVenice LoNo ratings yet
- Cueva-Cell TransportDocument15 pagesCueva-Cell TransportCristine Jane CuevaNo ratings yet
- Senior High School: Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (Stem) Specialized SubjectDocument53 pagesSenior High School: Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (Stem) Specialized Subjectpotato macchiatoNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Chapter 3 by GetteDocument13 pagesAnaphy Chapter 3 by GetteDUQUE, GEORGETTE FLOREANNE L.No ratings yet
- L2 the+Cell+MembraneDocument35 pagesL2 the+Cell+Membranebmnyandu2003No ratings yet
- "Feed With Responsibility You Mind and Body": Colegio Abraham LincolnDocument3 pages"Feed With Responsibility You Mind and Body": Colegio Abraham Lincolnsara barretoNo ratings yet
- BB 3002Document2 pagesBB 3002Leslie TaylorNo ratings yet
- ISO 8861 Blower Engine RoomDocument28 pagesISO 8861 Blower Engine Roommohammad choirul huda100% (1)
- Car Frontal ImpactDocument25 pagesCar Frontal Impactapi-3762972100% (1)
- BCA 5005 Minor Project Synopsis Format & GuidelinesDocument7 pagesBCA 5005 Minor Project Synopsis Format & GuidelinesAnu VermaNo ratings yet
- Benguet Folktales Bases For Tracing Family BloodlineDocument17 pagesBenguet Folktales Bases For Tracing Family BloodlineJohn Rey PelilaNo ratings yet
- Newton Papers Letter Nat Phil Cohen EdDocument512 pagesNewton Papers Letter Nat Phil Cohen EdFernando ProtoNo ratings yet
- Island Super Kinis Skim Coat White (RP)Document4 pagesIsland Super Kinis Skim Coat White (RP)coldfeetNo ratings yet
- 2b. TESDA-OP-CO-01-F14 TOOLSDocument2 pages2b. TESDA-OP-CO-01-F14 TOOLSRommel SelgaNo ratings yet
- PAMDocument14 pagesPAMRashed IslamNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Single Cylinder Solenoid EngineDocument7 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Single Cylinder Solenoid EngineVIVA-TECH IJRINo ratings yet
- CHEM2112 General Chemistry 1 First Quarter Exam 50 PDFDocument13 pagesCHEM2112 General Chemistry 1 First Quarter Exam 50 PDFviehazeNo ratings yet
- Mesoamerica: Where Civilizations Flourished, and Crashed, RepeatedlyDocument8 pagesMesoamerica: Where Civilizations Flourished, and Crashed, RepeatedlyEnvyAmarr •No ratings yet
- 5276Document52 pages5276Sean PorterNo ratings yet
- A 388 - A 388M - 03 - Qtm4oc9bmzg4tqDocument8 pagesA 388 - A 388M - 03 - Qtm4oc9bmzg4tqRod RoperNo ratings yet
- A Novel Wastewater Derived BiodieselDocument13 pagesA Novel Wastewater Derived BiodieselYuri ClaroNo ratings yet
- Concept Paper Group 1Document9 pagesConcept Paper Group 1Kaime KeilarNo ratings yet
- F5 BIG IP LTM 301A 301B Key Notes Feb 2023 1677506622Document63 pagesF5 BIG IP LTM 301A 301B Key Notes Feb 2023 1677506622MuhammadAbidHameedNo ratings yet
- Doosan Dielsel Forklift d35s 7 d40s 7 d45s 7 d50c 7 d55c 7 d40sc 7 d45sc 7 d50sc 7 d55sc 7 Part Book Sb1223e01Document22 pagesDoosan Dielsel Forklift d35s 7 d40s 7 d45s 7 d50c 7 d55c 7 d40sc 7 d45sc 7 d50sc 7 d55sc 7 Part Book Sb1223e01daleherrera100788nke100% (23)
- Mary Szybist On Visual Poetry Compressed PDFDocument5 pagesMary Szybist On Visual Poetry Compressed PDFcarlos.enrique.fonseca1440No ratings yet
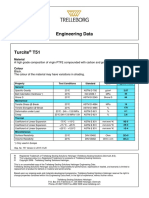
- Turcite T51 Engineering DataDocument1 pageTurcite T51 Engineering DataAntonio Rivera VillavicencioNo ratings yet
- Writing Good PI ObjectivesDocument42 pagesWriting Good PI Objectivesfrankiepaul06No ratings yet
- Response-2000 - Stalp 30x30Document1 pageResponse-2000 - Stalp 30x30tikianNo ratings yet
- Investigation Gr. 8Document6 pagesInvestigation Gr. 8Marthie van zylNo ratings yet
- O Level Physics ATP ReferencesDocument4 pagesO Level Physics ATP ReferencesHassan Ali BhuttaNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System PowerpointDocument20 pagesLymphatic System Powerpointabisantiago6131No ratings yet
- Measure Guide Air Cond DiagnosticsDocument70 pagesMeasure Guide Air Cond Diagnosticsayad60No ratings yet
- Yamaha Tank Removal wr250rDocument2 pagesYamaha Tank Removal wr250rMotoc Mircea-RazvanNo ratings yet
- Biomedical Uses and Applications of Inorganic Chemistry. An OverviewDocument4 pagesBiomedical Uses and Applications of Inorganic Chemistry. An OverviewHiram CruzNo ratings yet
- Basic SCBA: Self-Contained Breathing ApparatusDocument51 pagesBasic SCBA: Self-Contained Breathing ApparatusPaoloFregonaraNo ratings yet