Professional Documents
Culture Documents
LET REVIEW On Assessment
Uploaded by
June Dalumpines0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views4 pagesThe document discusses various concepts related to assessment including tests, measurement, assessment, and evaluation. It defines these terms and distinguishes between them. The document also covers different modes of assessment such as traditional, alternative, and authentic assessments. It provides examples and discusses the advantages and disadvantages of each. Finally, the document discusses purposes of assessment including formative and summative assessment and principles of high-quality assessment.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses various concepts related to assessment including tests, measurement, assessment, and evaluation. It defines these terms and distinguishes between them. The document also covers different modes of assessment such as traditional, alternative, and authentic assessments. It provides examples and discusses the advantages and disadvantages of each. Finally, the document discusses purposes of assessment including formative and summative assessment and principles of high-quality assessment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views4 pagesLET REVIEW On Assessment
Uploaded by
June DalumpinesThe document discusses various concepts related to assessment including tests, measurement, assessment, and evaluation. It defines these terms and distinguishes between them. The document also covers different modes of assessment such as traditional, alternative, and authentic assessments. It provides examples and discusses the advantages and disadvantages of each. Finally, the document discusses purposes of assessment including formative and summative assessment and principles of high-quality assessment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
1.
LET REVIEW On Assessment
2. 2. Four concepts associated with assessment Test MeasurementAssessment Evaluation
3. 3. TestAn instrument designed to measure any characteristic, ability or
knowledgeComprised of test items on the area it intends to measure
4. 4. MeasurementA process of quantifying the degree to which someone or something
possesses a given trait.A broader term than test because there are other ways of
measuring other than through test, like observation, use of checklist and rating scales.
5. 5. AssessmentA process of gathering and organizing quantitative or qualitative data into an
interpretable form to have a basis for judgment or decision-makingA broader term than
measurement and involves interpreting or placing such information in contextA prerequisite
to evaluation as it provides the information which enables evaluation to take place
6. 6. EvaluationA process of systematic collection and analysis of both qualitative and
quantitative data in order to make some judgment or decisionInvolves judgment about the
desirability of changes in students
7. 7. Modes of assessment Assessment Traditional Alternative Authentic Click on the
rectangles with this image Performance- based Portfolio
8. 8. Modes of assessment Assessment Traditional Alternative Authentic ADVANTAGES
Performance- AND DISADVANTAGES: DESCRIPTION: based EXAMPLES: objective of
Scoring is Pen and paper mode Administration is easy as students Standardized and
assessingtest at the same timeor take the any quality, skill teacher-made tests knowledge
Portfolio Time-consuming to prepare Prone to guessing and cheating
9. 9. Modes of assessment Assessment Traditional Alternative Authentic Performance- based
Portfolio
10. 10. ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES: Modes of assessmentDESCRIPTION: to
prepare Relatively easy Assessment EXAMPLES: students to Measures behavior that
cannot be Requires the Projects, practical test, perform a faked significant and Scoring tends
to be subjective oralrelevant task Alternative and aural tests Traditional without rubrics
Authentic Time-consuming to administer Performance- based Portfolio
11. 11. Modes of assessment Assessment Traditional Alternative Authentic Performance- based
Portfolio
12. 12. Modes of assessment AssessmentADVANTAGES AND
DISADVANTAGES:DESCRIPTION: EXAMPLES: Measures students’ growth and
Dynamically and development Traditional Authentic Working Portfolios,Alternative
showcollaboratively gathers multiple Intelligence-fair indicators of isdocumentary portfolios,
time-consuming Development student progressRating tendsportfolios goals to support
course without to be subjective Performance- rubrics based Portfolio
13. 13. Modes of assessment Assessment Traditional Alternative Authentic Performance- based
Portfolio
14. 14. Modes of assessment AssessmentEXAMPLES: Traditional Alternative Authentic Could
be objective tests thatDESCRIPTION: reflect real life situations or Assessment methods that
Performance- alternative methods that are simulate true-to-life situations basedclose to what
we experience in real life Portfolio
15. 15. Purposes of Assessment FOR Learning Purposes of assessment AS OF Learning
Learning
16. 16. Purposes of Assessment FOR Learning PLACEMENT -Done before instruction
Purposes of -Determines mastery of prerequisites FORMATIVE assessment -Done before
instruction AS -Reinforce successful learning OF Learning DIAGNOSTIC Learning -Done
before instruction -Determines persistent difficulties
17. 17. Purposes of Assessment FOR Learning Purposes of assessment AS OF Learning
Learning
18. 18. Purposes of Assessment FOR For teachers to Learning understand and perform well
their role in assessment Purposes of assessment AS OF Learning Learning
19. 19. Purposes of Assessment FOR Learning Purposes of assessment AS OF Learning
Learning
20. 20. Purposes of Assessment Summative FOR Learning -Done after instruction -Certifies
mastery oflearning outcomes Purposes of assessment AS OF Learning Learning
21. 21. PRINCIPLES OF HIGH QUALITY ASSESSMENTContinuous process Takes place prior,
during and after instructionAppropriate methods Good match between learning targets and
assessment methodPracticality and efficiency The information should be worth the resources
and time required to obtain itAppropriate and clear learning Learning targets should be
clearlytargets stated and centers on what is importantBalance Should set targets in all
learning and intelligence domainsFairness Should provide students with equal opportunity to
demonstrate achievement
22. 22. PRINCIPLES OF HIGH QUALITY ASSESSMENTCommunication Targets, standards
and results should be communicated to studentsAuthenticity Meaningful task, clear
standards, transferable learningPositive consequences Should motivate both students and
teachers to improveEthics Should free students from misuse of assessment
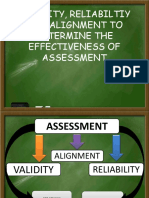
proceduresReliabilityValidity
23. 23. PERFORMANCE-BASED ASSESSMENT Description Reasons for Types Methodology
Others usingProcess of -Dissatisfaction Demonstra- 1. Identify the Criteria ingathering info
with limited tion type competenc selecting aabout learning info obtained y to be task:through
actual from certain demonstratdemonstration tests Creation ed -Generalizabilityof skills
and/or -Negative type 2. Describe -Authenticitycreation of impact of the task to
-Feasibilityproducts conventional be -Scorability tests performed -Fairness Appropriatene- 3.
Develop a -teachability ss in certain scoring approaches rubric like PBL reflecting the criteria
and the scores
24. 24. PORTFOLIO-BASED ASSESSMENT Description Reasons for Types Methodology
Others usingPurposeful, Offers multiple Working 1. set goals Underlyingongoing, indicators
of principles: portfolio(da 2. Collect Content (shoulddynamic, and students’collaborative
progress; y-to-day); 3. Select reflect Show 4. Organize importantprocess of Offers subject
matter)gathering opportunities portfolio 5. Reflect Learning (shouldmultiple for students to
(best works) 6. Evaluate enable studentsindicators of document Documentar 7. exhibit
become activethe learner’s reflections of learners)growth and theirs; y Equity
(shoulddevelopment Offers (combinatio allow students teachers new n) to demonstrate their
learning roles in the styles assessment process
25. 25. Assessment Methods OBJECTIVE-Multiple choice-true or false-matching-short answer-
completion test
26. 26. Assessment Methods ESSAY--restricted response-extended response ORAL
QUESTION-Oral examination-Interview
27. 27. Assessment Methods PERFORMANCE-BASED-Projects-Presentations-Portfolios
28. 28. Assessment Methods OBSERVATION-Informal observation-Formal observation SELF-
REPORT-Questionnaires-Attitude survey-Sociometric devices
29. 29. What is a rubric?Contains characteristics of a desirable trait Measure the degree to
which a performance or product work or has been satisfied by one’sRater checks the ones
observe in one’s performance performanceat least 3 levels or product -is a measuring
instrument usually Uses used in rating performance-based tasks-is a cross between a
checklist and a rating scale
30. 30. Types of rubricHolistic Rubric-describes the overall quality of aperformance or product;
there isonly one rating given to the entire work or performance
31. 31. Holistic Rubric -allows fast assessment-provides one score to describe the overall
performance or quality of work-can indicate the general strengths and weaknesses of the
work or performance
32. 32. Holistic Rubric -does not clearly describe thedegree of the criterion satisfied ornot
satisfied by the performance or product -does not permit differential weighting of he qualities
of a product or performance
33. 33. Types of rubricAnalytic Rubric -describes the quality of aperformance or product in terms
of the identified dimensions and/or criteria which are rated independently to give a better
picture of the quality of work or performance
34. 34. Analytic rubric-Clearly describes the degree of thecriterion satisfied or not satisfied by the
performance or product -permits differential weighting of the qualities of a product or a
performance-helps raters pinpoint specific areas of strengths and weaknesses
35. 35. Analytic rubric--more time consuming to use -more difficult to construct
36. 36. Important elements found in a rubric -competency to be tested (requires either a
demonstration or creation of products of learning -performance task (should be authentic and
feasible) -evaluative criteria and their indicators (should be made clear using observable
traits)
37. 37. Important elements found in a rubric -performance levels (at least 3) -qualitative and
quantitative descriptions of each performance level (must be observable)
38. 38. What is a test? -a test is an instrument or systematic procedure, whichtypically consists a
set of questions for measuring any characteristic, quality, ability, skill or knowledge
39. 39. Different types of tests scope & purpose interpretation contentTime limit & level
According language of difficulty to mode manner of Manner of Effect ofadministration
construction biases
40. 40. According to purpose What the test measuresEducational test-aims to measure the
results ofinstruction; administered after theinstructional process Achievement test-what the
studenthas achieved at the end of instruction;what has been learned
41. 41. According to purpose What the test measuresEx:Aptitude test-areas where the student
will likelysucceed; specifically measures different mentalprocesses like verbal, numerical,
spatial, andmechanical reasoning; also judgment, analysis & logicPersonality test- student’s
personal traitsIntelligence test- student’s mental ability;innate/inherent capacity of the mind
without anybackground training
42. 42. According to purpose What the test measuresPsychological test-aims to measure
students’ intelligence ormental ability in a large degree withoutreference to what the student
has learned;intangible aspects of an individual;administered before the instructional process
43. 43. According to interpretation How the test is interpretedNorm-referenced test-result is
interpreted by comparing onestudent with other students-some will really pass-there is
competition for a limited percentageof high score-describes student’s performance
comparedto others
44. 44. According to interpretation How the test is interpretedCriterion-referenced test-result is
interpreted by comparing a studentagainst a set of criteria-all or none may pass-there is NO
competition for a limitedpercentage of high score-describes student’s mastery of the
courseobjective
45. 45. According to the scope and contentSurvey-covers a broad range of objectives-measures
general achievement in certainsubjects-is constructed by trained professionalMastery Test-
covers a specific learning objective-measures fundamental skills and abilities-is typically
constructed by the teacher
46. 46. According to time limit and level of difficultyPower-consists of items of increasing level of
difficultybut taken with ample time-measures a student’s ability to answer more andmore
difficult itemsMastery Test-covers a specific learning objective-measures fundamental skills
and abilities-is typically constructed by the teacher
You might also like
- BISAYA Project GutenbergDocument2,026 pagesBISAYA Project GutenbergJune DalumpinesNo ratings yet
- 2 - Basic Assessment in TrainingDocument32 pages2 - Basic Assessment in TrainingDevan MollyNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 DESIGNING AND DEVELOPING ASSESSMENTDocument46 pagesUnit 3 DESIGNING AND DEVELOPING ASSESSMENTSherilyn Cercado Emanil100% (2)
- Devolution and DecentralizationDocument10 pagesDevolution and DecentralizationkofiadrakiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Performance Assessment - Written ReportDocument18 pagesUnit 2 Performance Assessment - Written ReportKayla Albay100% (1)
- Qatar PetroleumDocument22 pagesQatar PetroleumPrathmesh Uddhav Pawar100% (3)
- 1 - Personal Development For Teachers PDFDocument5 pages1 - Personal Development For Teachers PDFShai Reen100% (2)
- Properties of Assessment MethodDocument8 pagesProperties of Assessment MethodEstrella P. AgotNo ratings yet
- Learning Assessment 1Document43 pagesLearning Assessment 1Christine Joy Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Ethics Nicole McDowellDocument3 pagesEthics Nicole McDowellAuguste Riedl100% (1)
- Module 1 - Assessment Tools Measuring The Cognitive DomainDocument28 pagesModule 1 - Assessment Tools Measuring The Cognitive DomainApril Ann Estrada Lim100% (1)
- Principles and Purposes of Assessment - Practicality, Validity, and Washback (Cosme, Camille P.)Document7 pagesPrinciples and Purposes of Assessment - Practicality, Validity, and Washback (Cosme, Camille P.)Camille Pavico CosmeNo ratings yet
- 1st 10 SalemDocument15 pages1st 10 SalempogsNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Training and DevelopmentDocument59 pagesEvaluation of Training and Developmentaiswarya888888No ratings yet
- Chapter 2:stakeholder Relationships, Social Responsibility, and Corporate GovernanceDocument43 pagesChapter 2:stakeholder Relationships, Social Responsibility, and Corporate GovernanceKhoai TâyNo ratings yet
- Principles of High Quality AssessmentDocument52 pagesPrinciples of High Quality AssessmentKathleen de LeonNo ratings yet
- Evaluation and Educational Programs in Nursing Course and Program NSG Education.Document10 pagesEvaluation and Educational Programs in Nursing Course and Program NSG Education.Akanksha NikunjNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Nature of Performance-Based AssessmentDocument33 pagesChapter 3 Nature of Performance-Based AssessmentTes Carandang-Marasigan86% (7)
- Research II: Quarter 1 - Module 4: Methods in Scientific Research Reports (IMRAD)Document28 pagesResearch II: Quarter 1 - Module 4: Methods in Scientific Research Reports (IMRAD)johnston100% (1)
- Meet Generation Z - The Second Generation Within The Giant Millenial CohortDocument13 pagesMeet Generation Z - The Second Generation Within The Giant Millenial CohortChristopher Ryan Isidro AdalemNo ratings yet
- Models of Curriculum EvaluationDocument30 pagesModels of Curriculum EvaluationJaymar MagtibayNo ratings yet
- Salamera v. SandiganbayanDocument1 pageSalamera v. SandiganbayanCars Carandang100% (1)
- Unit 2Document93 pagesUnit 2Jean MarceloNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document14 pagesLesson 3Khyla Mae Bassig CondeNo ratings yet
- Course Overview, CBA, OBADocument64 pagesCourse Overview, CBA, OBAJade TijamNo ratings yet
- AssessInLearn2 Lesson 3Document30 pagesAssessInLearn2 Lesson 3sadsadako111No ratings yet
- How Do You Conduct Performance AssessmentDocument2 pagesHow Do You Conduct Performance AssessmentAlexander ReyesNo ratings yet
- How Do You Conduct Performance Assessment?Document12 pagesHow Do You Conduct Performance Assessment?jeno purisimaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document42 pagesLecture 1Izlaikha AzizNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Evaluation & Curriculum Change: Mrs. Shiji Thomas Caritas College of NursingDocument56 pagesCurriculum Evaluation & Curriculum Change: Mrs. Shiji Thomas Caritas College of NursingShijiThomasNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam 3rd Tri 2019-2020Document5 pagesMidterm Exam 3rd Tri 2019-2020tsinitongmaestroNo ratings yet
- Assessment in Learning 2Document12 pagesAssessment in Learning 2BUEN, RENZZELLE JOY B.No ratings yet
- Determining Appropriate Evaluation Instruments REPORTDocument12 pagesDetermining Appropriate Evaluation Instruments REPORTJerameel Mangubat ArabejoNo ratings yet
- Evaluation in Education: Overnment College of Education Sector ChandigarhDocument30 pagesEvaluation in Education: Overnment College of Education Sector ChandigarhHarpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Validity, Reliabiltiy and Alignment To Determine The Effectiveness of AssessmentDocument25 pagesValidity, Reliabiltiy and Alignment To Determine The Effectiveness of AssessmentCaryll Apellanes BaylonNo ratings yet
- Written Write UpsDocument9 pagesWritten Write UpsMarianne MadeloNo ratings yet
- Acob - Module 9.curriculum AssessmentDocument7 pagesAcob - Module 9.curriculum AssessmentJoy AcobNo ratings yet
- MAN 205 ReportDocument26 pagesMAN 205 ReportAPRIL LYNNo ratings yet
- Health Ed 2nd ReviewerDocument25 pagesHealth Ed 2nd ReviewerDency Mae AbreNo ratings yet
- A Practical Guide For Educators: Classroom AssessmentDocument24 pagesA Practical Guide For Educators: Classroom AssessmentAgni RudraNo ratings yet
- Chargie P. San JuanDocument45 pagesChargie P. San Juanसचिन उरुणकरNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENTDocument16 pagesUnit 2 PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENTsteffiii dawnNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Learning Chapter-1Document14 pagesAssessment of Learning Chapter-1Aiza Grail BotangenNo ratings yet
- Design and DevelopDocument8 pagesDesign and Developtangwanlu9177No ratings yet
- Edassl Topic 4Document17 pagesEdassl Topic 4POSADAS, MA. KRISTINE L.No ratings yet
- 6 Tests and Evaluation, Report WritingDocument29 pages6 Tests and Evaluation, Report WritingA KNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document28 pagesChapter 1Kim VenturaNo ratings yet
- Defination of Training and EvaluationDocument13 pagesDefination of Training and EvaluationUmika SawhneyNo ratings yet
- OBEDocument73 pagesOBEJiwa AbdullahNo ratings yet
- EDUC3 Module2Document5 pagesEDUC3 Module2Dahlia GalimbaNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Learning: (Test Measurement and Evaluation)Document39 pagesAssessment of Learning: (Test Measurement and Evaluation)Centienne BatemanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Development of Classroom Assessment ToolsDocument87 pagesLecture 3 Development of Classroom Assessment ToolsMiss'ElNo ratings yet
- Let Review Assessment EvaluationDocument5 pagesLet Review Assessment EvaluationRaffy Jay TamameoNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document33 pagesModule 1Rosalie AbaoNo ratings yet
- Aicte Exam Reforms Guidelines: by Prof. B.A.KhivsaraDocument49 pagesAicte Exam Reforms Guidelines: by Prof. B.A.KhivsaraSabha NayaghamNo ratings yet
- Bett - Phase 5Document34 pagesBett - Phase 5Anuja DamleNo ratings yet
- Designing An Effective Evaluation StrategyDocument17 pagesDesigning An Effective Evaluation StrategyANA LEE MENDOZANo ratings yet
- Summative and Formative Evaluation in The Process of Curriculum DevelopmentDocument15 pagesSummative and Formative Evaluation in The Process of Curriculum DevelopmentSelvyn EzekielNo ratings yet
- Information Sheet 1.1.1a: Assessment MethodologyDocument3 pagesInformation Sheet 1.1.1a: Assessment MethodologyRona Mei TiangcoNo ratings yet
- A - Principles of AssessmentDocument29 pagesA - Principles of AssessmentRomneRyanPortacionNo ratings yet
- Planning Classroom TestDocument24 pagesPlanning Classroom TestYa Ganak90% (10)
- Chapter 2 Trainees Current CompetenciesDocument24 pagesChapter 2 Trainees Current CompetenciesJia Mae Sapico ApantiNo ratings yet
- Performance Assessment ReportDocument16 pagesPerformance Assessment ReportAilyn LacandulaNo ratings yet
- E204-Grp-4-Report - PPTX 20240306 202022 0000Document13 pagesE204-Grp-4-Report - PPTX 20240306 202022 0000aynz3fellicbataoilNo ratings yet
- 8 EvaluationofHRDProgramDocument10 pages8 EvaluationofHRDProgramOrooj Siddiqui QaziNo ratings yet
- Assessment Report Partial 1Document1 pageAssessment Report Partial 1Imma CharNo ratings yet
- Training Evaluation: 6 Edition Raymond A. NoeDocument28 pagesTraining Evaluation: 6 Edition Raymond A. Noepanthoh1No ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Modes of AssessmentDocument2 pagesLesson 2 Modes of AssessmentINAHID, GLAYDELNo ratings yet
- ASSES Mod1Week1 Def&TermsDocument4 pagesASSES Mod1Week1 Def&TermsJasmin RelorcasaNo ratings yet
- How to Practice Before Exams: A Comprehensive Guide to Mastering Study Techniques, Time Management, and Stress Relief for Exam SuccessFrom EverandHow to Practice Before Exams: A Comprehensive Guide to Mastering Study Techniques, Time Management, and Stress Relief for Exam SuccessNo ratings yet
- DTR RecordsDocument1 pageDTR RecordsJune DalumpinesNo ratings yet
- About Me Experience / Seminar Workshop: St. Peter's College of Ormoc IncDocument2 pagesAbout Me Experience / Seminar Workshop: St. Peter's College of Ormoc IncJune DalumpinesNo ratings yet
- Enduring Understandings and Essential QuestionsDocument1 pageEnduring Understandings and Essential QuestionsJune DalumpinesNo ratings yet
- JabberwockyDocument36 pagesJabberwockyJune DalumpinesNo ratings yet
- Elem Ed MeasurementsDocument1 pageElem Ed MeasurementsJune DalumpinesNo ratings yet
- Multiplication of FractionsDocument8 pagesMultiplication of FractionsJune DalumpinesNo ratings yet
- LITERACYDocument1 pageLITERACYJune DalumpinesNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Heredity and Variation Demo1Document2 pagesLesson Plan Heredity and Variation Demo1June DalumpinesNo ratings yet
- Bleaching Property of Powder DetergentDocument2 pagesBleaching Property of Powder DetergentJune DalumpinesNo ratings yet
- ANNOTATIONS For Teachers IDocument14 pagesANNOTATIONS For Teachers IJune DalumpinesNo ratings yet
- PROFED2 AssignmentsDocument10 pagesPROFED2 AssignmentsJune DalumpinesNo ratings yet
- Baptism 2Document2 pagesBaptism 2June DalumpinesNo ratings yet
- Business Name and TaglineDocument3 pagesBusiness Name and TaglineJune DalumpinesNo ratings yet
- 1bisaya Rare-Tagalog-Words EnglishDocument28 pages1bisaya Rare-Tagalog-Words EnglishJune DalumpinesNo ratings yet
- Moby DickDocument4 pagesMoby DickJune DalumpinesNo ratings yet
- IshmaelDocument5 pagesIshmaelJune DalumpinesNo ratings yet
- The Canterbury TalesDocument9 pagesThe Canterbury TalesJune DalumpinesNo ratings yet
- Bisay Rare-Tagalog-Words EnlishDocument29 pagesBisay Rare-Tagalog-Words EnlishJune DalumpinesNo ratings yet
- Sight Words (Dolch and Fry Lists) and Sight Word PhrasesDocument9 pagesSight Words (Dolch and Fry Lists) and Sight Word PhrasesJune DalumpinesNo ratings yet
- SCM Template For ViewDocument2 pagesSCM Template For ViewJune DalumpinesNo ratings yet
- DEP ED Report CardDocument301 pagesDEP ED Report CardJune DalumpinesNo ratings yet
- Class Record I-ADocument198 pagesClass Record I-AJune DalumpinesNo ratings yet
- THC 1 Prelim OutputDocument3 pagesTHC 1 Prelim OutputJune DalumpinesNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Cambacbac Elementary SchoolDocument3 pagesDepartment of Education: Cambacbac Elementary SchoolJune DalumpinesNo ratings yet
- A Public Health Perspective of Road Traffic AccidentsDocument5 pagesA Public Health Perspective of Road Traffic AccidentsJune DalumpinesNo ratings yet
- AER Application Form V3.3.2018-PakkamDocument20 pagesAER Application Form V3.3.2018-PakkamMARIVEL BASANo ratings yet
- 2006 Annual ReportDocument84 pages2006 Annual ReportcattleyajenNo ratings yet
- What Is A Group DiscussionDocument8 pagesWhat Is A Group DiscussionTavishNo ratings yet
- Top Modular Construction Solution Companies in India: 1. Champion PrefabsDocument9 pagesTop Modular Construction Solution Companies in India: 1. Champion PrefabsNishant GauravNo ratings yet
- GUIDELINES & TIPS FOR FINAL EXAM Sem IIDocument9 pagesGUIDELINES & TIPS FOR FINAL EXAM Sem IIIam ThineshNo ratings yet
- 1 2018 Take Home Exam Dated 27 Sept 2018Document5 pages1 2018 Take Home Exam Dated 27 Sept 2018mgbautistallaNo ratings yet
- VSO Application FormDocument7 pagesVSO Application Formapi-3807120100% (1)
- Jayee Rajguru by Ramswaroop PadhyDocument20 pagesJayee Rajguru by Ramswaroop PadhyRam SwaroopNo ratings yet
- Agronomy 2010Document87 pagesAgronomy 2010Muhammad AonNo ratings yet
- Unified Communications Engineer: Certification CoursesDocument2 pagesUnified Communications Engineer: Certification CoursesMd RNo ratings yet
- Notes CPCDocument15 pagesNotes CPCmuhammad wafiNo ratings yet
- Confidential Recommendation Letter SampleDocument1 pageConfidential Recommendation Letter SamplearcanerkNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 Thinking Like An EconomistDocument19 pagesChapter 02 Thinking Like An EconomistTasfia Rahman RivaNo ratings yet
- Government College University Hyderabad (Gcuh) : Application FormDocument2 pagesGovernment College University Hyderabad (Gcuh) : Application FormNauman IrfanNo ratings yet
- M&Ét´Πøwühé - Ò"E Østt+Ãsy‡Yót+ (Ÿ S¡÷. 1,000/'≈£Î Ô - + - Ü⁄: Government Of Andhra PradeshDocument1 pageM&Ét´Πøwühé - Ò"E Østt+Ãsy‡Yót+ (Ÿ S¡÷. 1,000/'≈£Î Ô - + - Ü⁄: Government Of Andhra PradeshSAMICDPNo ratings yet
- Survey CampDocument2 pagesSurvey CampAnil MarsaniNo ratings yet
- Externally Advertised Vacancies PDFDocument2 pagesExternally Advertised Vacancies PDFZama Cheezozo MankayiNo ratings yet
- SMK Taman Widuri Cefr Daily Lesson Plan 2020Document5 pagesSMK Taman Widuri Cefr Daily Lesson Plan 2020Ramzan Khairunnisaa AliNo ratings yet
- Urban Mass Transit Brochure 2021Document2 pagesUrban Mass Transit Brochure 2021aditya34No ratings yet
- InfosysDocument16 pagesInfosysDivyank SinghNo ratings yet
- GHSS Arimalam - 10 Result AnalysisDocument4 pagesGHSS Arimalam - 10 Result AnalysisAnburaja KNo ratings yet