Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Carbohydrates 1.1
Uploaded by
Christian Paras0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views4 pagesCarbohydrates can be classified based on their carbon atom count and functional groups. Monosaccharides like glucose are the simplest sugars and cannot be broken down further. Disaccharides form when two monosaccharides join, while polysaccharides are long chains of monosaccharides linked together. Glucose is the primary energy source for humans and is absorbed from the small intestine. It enters the bloodstream and is either used immediately, stored as glycogen in the liver and muscles, or converted to fat. Hormones like insulin and glucagon tightly regulate blood glucose levels through pathways such as glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, and glycogenolysis.
Original Description:
INTROUCTION TO CARBOHYDRATES
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCarbohydrates can be classified based on their carbon atom count and functional groups. Monosaccharides like glucose are the simplest sugars and cannot be broken down further. Disaccharides form when two monosaccharides join, while polysaccharides are long chains of monosaccharides linked together. Glucose is the primary energy source for humans and is absorbed from the small intestine. It enters the bloodstream and is either used immediately, stored as glycogen in the liver and muscles, or converted to fat. Hormones like insulin and glucagon tightly regulate blood glucose levels through pathways such as glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, and glycogenolysis.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views4 pagesCarbohydrates 1.1
Uploaded by
Christian ParasCarbohydrates can be classified based on their carbon atom count and functional groups. Monosaccharides like glucose are the simplest sugars and cannot be broken down further. Disaccharides form when two monosaccharides join, while polysaccharides are long chains of monosaccharides linked together. Glucose is the primary energy source for humans and is absorbed from the small intestine. It enters the bloodstream and is either used immediately, stored as glycogen in the liver and muscles, or converted to fat. Hormones like insulin and glucagon tightly regulate blood glucose levels through pathways such as glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, and glycogenolysis.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
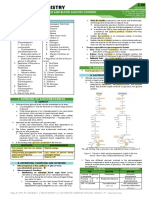
Carbohydrates - These are hydrates of aldehyde or 3.
Based on the number of sugars
ketone derivatives based on the location of the CO a. Monosaccharides- are simpler sugars that
functional group. cannot be hydrolyzed to simpler isomers. These
sugars can contain 3 or more carbon atom.
A. Classification Of Carbohydrates
Consists of
1. Based on CO functional group location
glucose and
a. The aldose form has a terminal carbonyl
fructose,
group(O=CH-) called an aldehyde group.
and
e.g. mannose and galactose
galactose
b. Disaccharide- are formed when two
monosaccharide units joined by a glycosidic
linkage. Sucrose, lactose, maltose
b. Ketose form has a carbonyl group (O=C) in the Lactase – located in intestine microvilli
middle linked between to two other carbon
atom called ketone group. e.g. fructose
c. Oligosaccharide- are chain of 2 to 10 units of
2. Based on Number of Carbon Atom sugar. e.g. raffinose
a. Trioses- contain three carbon atom. d. Polysaccharide- are formed by linkages of many
Glycol aldehyde- smallest carbohydrate (has monosaccharides. E.g. starch, cellulose, glycogen
three carbon compound) e.g. glyceraldehyde o Starch- major form of stored CHO in plants:
composed of mixtures of two substances
Amlyose- linear polysaccharide
Amylopectin- highly branched polysaccharide
b. Tetroses - contain four carbon atoms.
e.g. Erythrose
c. Pentoses- contain five carbon atoms
e.g. Ribose, deoxyribose o Cellulose- structural CHO that form cell walls and
other supporting tissues of plant cells
d. Hexoses- contain six carbon atoms
e.g. Glucose, fructose o Glycogen- the stored polysaccharide for animals:
also known as animal starch
c. Monosaccharides are absorbed from the
duodenum and ileum into blood.
2. Metabolism in the blood
a. Energy production by conversion to carbon
dioxide and water
B. Representation model of CHO b. Storage as Glycogen in the liver
1. Fisher Projection - It has the aldehyde or ketone at c. Storage as triglycerides in the adipose
the top of drawing. The carbons are numbered tissues
starting the aldehyde or ketone end. The compound d. Conversion to ketoacidosis, amino acids or
may be represented as a straight chain or a cyclic proteins
(hemiacetal form)
F. Regulation of Glucose Concentration in the Blood
1. Pathway in Glucose Metabolism
a. Glycolysis - Metabolism of glucose molecule to
pyruvate or lactate to energy, 2 ATP generated
b. Gluconeogenesis - Formation of glucose – 6 –
2. Haworth Projection - Represents the cyclic form that phosphate from non – carbohydrate sources.
is more representative of the actual structure. Such as protein and fatty acids
c. Glycogenolysis - Breakdown of glycogen to
glucose for use as energy
d. Glycogenesis - Conversion of glucose to
glycogen for storage
e. Lipogenesis - Conversion of carbohydrates to
C. Stereoisomers fatty acids. Decrease in glucose
The central carbons of carbohydrates are f. Lipolysis - Breakdown of fats; fats are used as
asymmetrical (chiral) –four different groups are energy. Increase in glucose
attached to the carbon atoms. This allows for 2. Hormones Involved in Glucose Metabolism.
various spatial arrangements around each The liver, pancreas and other endocrine glands
asymmetric carbon also called stereogenic centers are involved in controlling blood glucose
forming molecules called stereoisomers. concentration in a narrow range
D. Chemical Properties of CHO a. Insulin
1. Reducing Substances - these CHO can reduce ✓ The primary hormone responsible for the
other compound. To be a reducing substance, entry of glucose in to the cells
the CHO must contain a ketone or aldehyde ✓ It is synthesized by β cells of islet of
group Langerhans in the pancreas
2. Non-Reducing Substances - do not have an ✓ It is normally released when glucose levels
active ketone or aldehyde group. sucrose is the are high.
only non-reducing substances ✓ Stored in liver, fats, muscle
E. Glucose metabolism ✓ Glycogenolysis
Glucose- is the primary source of energy for human.
b. Glucagon
1. Carbohydrate Digestion
✓ The primary hormone responsible for
a. Digestion starts in the mouth through the
increasing glucose level (hyperglycemic
enzyme ptyalin - salivary amylase
agent)
b. Alkaline pancreatic secretions increase the
pH of the intestines, enabling carbohydrate ✓ Release during stress and increase
digestion through pancreatic amylase catabolic fasting
(amylopsin) ✓ It is synthesized on the α cells of islet of
Langerhans in the pancreas.
✓ Fasting plasma glucagon concentrations 3. somatostatin
are normally 25-50 pg/ml
Pathway in Glucose Metabolism
✓ Glycogenolysis, Gluconeogenesis
c. Epinephrine Glycolysis
✓ Produced by the adrenal medulla
✓ Released during time of stress
✓ Increase plasma glucose by inhibiting
insulin secretion
✓ Increases glycogenolysis and promoting
lipogenesis
d. Glucocorticoids (Cortisol and Corticosteroid)
✓ Are secreted by the cells of the zona
fasciculate and zona reticularis of the
adrenal cortex
✓ They decrease intestinal entry of glucose in
to the cell
✓ Promote gluconeogenesis, liver glycogen
and lipolysis.
e. Catecholamines
✓ It is released by the chromaffin cells of the Gluconeogenesis
adrenal medulla
✓ Inhibits insulin secretion
✓ Promote glycogenolysis and lipolysis.
f. Growth hormone (Somatotrophic)
✓ It is secreted by the anterior pituitary gland
✓ It decreases entry of glucose in to the cell
✓ Promote glycogenolysis and glycolysis.
g. Thyroid hormone (Thyroxine)
✓ Synthesized by the thyroid gland
✓ Promote glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis,
and intestinal absorption of glucose
h. Adrinocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
✓ It stimulates the release of cortisol from
adrenal cortex Glycogenolysis
✓ Promote glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis
i. Somatostatin
✓ It is produced by the delta cells of the islet
of Langerhans of the pancreas
✓ It also synthesized by the paraventricular
and arcuate nuclei of the hypothalamus (a
neuroendocrine hormone)
✓ It primarily inhibits the action of insulin,
growth hormone and glucagon
3 hormones synthesized in pancreas
1. Insulin
2. Glucagon
Glycogenesis
Lipogenesis
Lipolysis
Prepared by:
Christian Paras
BSMT-3B
You might also like
- 100 MCAT TipsDocument23 pages100 MCAT TipsJhilianne Batino100% (1)
- Biochemistry 101 PTC8 PDFDocument12 pagesBiochemistry 101 PTC8 PDFvNo ratings yet
- Sulfur Deficiency Stephanie SeneffDocument19 pagesSulfur Deficiency Stephanie Seneffgkebiz100% (1)
- Biochemistry - 2.08 - Gluconeogenesis and Blood Glucose ControlDocument9 pagesBiochemistry - 2.08 - Gluconeogenesis and Blood Glucose ControlJonathan Decena Jr.No ratings yet
- Review of Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument7 pagesReview of Anatomy and PhysiologyKyla CalzadoNo ratings yet
- (NOTES) Carbohydrates MetabolismDocument13 pages(NOTES) Carbohydrates MetabolismGabrielle SerranoNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Pathway of Carbohydrate and GlycolysisDocument22 pagesMetabolic Pathway of Carbohydrate and GlycolysisDarshansinh MahidaNo ratings yet
- 04 Physiology of The Pancreas PDFDocument66 pages04 Physiology of The Pancreas PDFMonesa Christy VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Learning Guides: Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument69 pagesLearning Guides: Carbohydrate MetabolismLeena MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lec (Part 3)Document17 pagesBiochem Lec (Part 3)Rainier Vincent LeonardoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry - Bishop WITH Answers - ANALYTIC TECHNIQUES Which of The Following Is Not - StudocuDocument61 pagesClinical Chemistry - Bishop WITH Answers - ANALYTIC TECHNIQUES Which of The Following Is Not - Studocum65b6hf9ffNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document28 pagesChapter 3skywalkerNo ratings yet
- Biochem MidtermsDocument25 pagesBiochem MidtermsYuki MendezNo ratings yet
- Midterm Lesson 1Document38 pagesMidterm Lesson 1Alexa QuizomNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: A Short CourseDocument31 pagesBiochemistry: A Short CourseEli JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4: Biomolecules: Major Types of Biomolecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids, Nucleic Acids, andDocument12 pagesLesson 4: Biomolecules: Major Types of Biomolecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids, Nucleic Acids, andJuselle Faith AtaNo ratings yet
- 1142 L6 CarbohydratesDocument27 pages1142 L6 CarbohydratesjanindujayathmaNo ratings yet
- Biochem Exam 2 Review.2Document31 pagesBiochem Exam 2 Review.2ashdmb217No ratings yet
- of CarbohydrateDocument19 pagesof CarbohydrateshraddhagosNo ratings yet
- CC ChekDocument105 pagesCC ChekMarie LlanesNo ratings yet
- BIOA111 SN17 SummaryDocument6 pagesBIOA111 SN17 SummaryDorothy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Nucleotide - Monomer of Nucleic AcidsDocument2 pagesNucleotide - Monomer of Nucleic AcidsMika Sophia GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Lesson On CarbohydratesDocument5 pagesLesson On CarbohydratesTweenieSumayanMapandiNo ratings yet
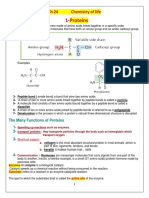
- 1-Proteins: CH 24 Chemistry of LifeDocument6 pages1-Proteins: CH 24 Chemistry of LifeXIBG21SANIANo ratings yet
- Structure of Carbohydrates FinalDocument8 pagesStructure of Carbohydrates FinalAnonymous KeHF7wbhFNo ratings yet
- Overview of MetabolismDocument13 pagesOverview of Metabolismgabby chaanNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates Definition: Back To TopDocument10 pagesCarbohydrates Definition: Back To Topshree devNo ratings yet
- Outline: Biochemistry LEC CarbohydratesDocument8 pagesOutline: Biochemistry LEC CarbohydratesShardy Lyn RuizNo ratings yet
- Biochemlab CarbslipidsDocument61 pagesBiochemlab Carbslipidschpa.dalisay.auNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument22 pagesCarbohydratesMaris JoyceNo ratings yet
- Module 5 CarbohydratesDocument21 pagesModule 5 CarbohydratesSpongebob SquarepantsNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Biological Molecules General Biology 1 1 Quarter: 1. Carbohydrates and LipidsDocument5 pagesUnit 2: Biological Molecules General Biology 1 1 Quarter: 1. Carbohydrates and LipidsSophia AbatayNo ratings yet
- MODULE - FINALS - Biochem - 1Document5 pagesMODULE - FINALS - Biochem - 1Cyril CauilanNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate - Lecture NotesDocument7 pagesCarbohydrate - Lecture NotesKate Taylor100% (1)
- Lec 2 CarbohydratesDocument10 pagesLec 2 CarbohydratesIrish De VeraNo ratings yet
- HARPERS - IV Carbohydrates of Physiological SignificanceDocument4 pagesHARPERS - IV Carbohydrates of Physiological SignificancedandiNo ratings yet
- CARBOHYDRATESDocument5 pagesCARBOHYDRATESMicah YapNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Nutrition 9th Edition Wardlaw Solutions Manual 1Document15 pagesContemporary Nutrition 9th Edition Wardlaw Solutions Manual 1pamela100% (37)
- Macromolecules: Self-Preparation Biology Assessment TestDocument36 pagesMacromolecules: Self-Preparation Biology Assessment Testmay ann dimaanoNo ratings yet
- WEEK 3 ActivityDocument11 pagesWEEK 3 ActivityMai SasaNo ratings yet
- CHO Classification, Example, Chemical Structure, FuctiDocument108 pagesCHO Classification, Example, Chemical Structure, FuctiYo'el Onaznam50% (2)
- Biomolecules: A. Synthesis & Hydrolysis Reaction VocabDocument18 pagesBiomolecules: A. Synthesis & Hydrolysis Reaction Vocabrashmi_harryNo ratings yet
- The Chemical Constituents of Cells1Document14 pagesThe Chemical Constituents of Cells1ArnelBautistaNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculesDocument12 pagesBio MoleculesMohammed IliasNo ratings yet
- I. Carbohydrate Chemistry: Structure, Function and ClassificationDocument15 pagesI. Carbohydrate Chemistry: Structure, Function and ClassificationasdfNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 - Energy Giving Food - Carbohydrates (CHO)Document4 pagesCHAPTER 3 - Energy Giving Food - Carbohydrates (CHO)Ruby Jane LaquihonNo ratings yet
- Biochem 2.1 Introduction To MetabolismDocument5 pagesBiochem 2.1 Introduction To Metabolismlovelots1234No ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Classification of Carbohydrate Metabolism and Regulation of CarbohydrateDocument14 pagesCarbohydrate Classification of Carbohydrate Metabolism and Regulation of CarbohydratesukNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates, Lipids & Nucleic Acids:: Forms Chain Like Molecules-PolymersDocument8 pagesCarbohydrates, Lipids & Nucleic Acids:: Forms Chain Like Molecules-PolymersJojo LouNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit Review: I. CarbohydratesDocument11 pagesBiology Unit Review: I. CarbohydratesJOSHUA DICHOSONo ratings yet
- Topic Brief Outline: CarbohydratesDocument29 pagesTopic Brief Outline: CarbohydrateshunnylandNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism Presentation.Document27 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism Presentation.ViragNo ratings yet
- Organic MoleculesDocument7 pagesOrganic MoleculesJames CadizNo ratings yet
- Module 2.2 CarbohydratesDocument6 pagesModule 2.2 CarbohydratesZabelle BungarNo ratings yet
- Metabolism: An Overview: Prof. Dr. Gerhard GrüberDocument57 pagesMetabolism: An Overview: Prof. Dr. Gerhard GrüberBS1009 group5No ratings yet
- Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument12 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolismbingbong2231No ratings yet
- Lecture4 BiochemistryDocument35 pagesLecture4 BiochemistryEssam HassanNo ratings yet
- Biological MacromoleculesDocument4 pagesBiological MacromoleculesHabiba AmrNo ratings yet
- Biomolecule: Carbohydrates: Philippine Christian Gospel SchoolDocument9 pagesBiomolecule: Carbohydrates: Philippine Christian Gospel SchoolTashi OngNo ratings yet
- CARBOHYDRATESDocument23 pagesCARBOHYDRATESClassen Mudenda KundaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: The Chemical Building Blocks of Life: Enantiomers . These Are Mirror Images of Each Other. MirroredDocument17 pagesChapter 3: The Chemical Building Blocks of Life: Enantiomers . These Are Mirror Images of Each Other. Mirroredapi-524244445No ratings yet
- 2019 Chapter5 Carbohydrates Students PDFDocument32 pages2019 Chapter5 Carbohydrates Students PDFyoNo ratings yet
- محاضرات الكيمياء كاملة PDFDocument124 pagesمحاضرات الكيمياء كاملة PDFفراس الموسويNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Changes of Diabetes MellitusDocument4 pagesBiochemical Changes of Diabetes MellitusGerardLum100% (3)
- Pharm-D 011014 PDFDocument106 pagesPharm-D 011014 PDFSeethalakshmiNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism: MR - Tapeshwar YadavDocument108 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism: MR - Tapeshwar YadavbashiriNo ratings yet
- Nutrition For Sport and Exercise 4Th Edition J Andrew Doyle Full ChapterDocument50 pagesNutrition For Sport and Exercise 4Th Edition J Andrew Doyle Full Chaptercharles.martinez668100% (5)
- Glucose Levels Maintaining MechanicsDocument7 pagesGlucose Levels Maintaining MechanicsSukhdeep KumarNo ratings yet
- L1.clinical ChemistryDocument37 pagesL1.clinical Chemistrysini gangNo ratings yet
- Mind Maps in Biochemistry - (Metabolism of Carbohydrates)Document23 pagesMind Maps in Biochemistry - (Metabolism of Carbohydrates)Gus LionsNo ratings yet
- Metabolism Interaction and Hormone Regulation.Document81 pagesMetabolism Interaction and Hormone Regulation.fikaduNo ratings yet
- CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Part II (Glycolysis)Document9 pagesCARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Part II (Glycolysis)InshaNo ratings yet
- PPSC Lecturer Zoology Past Paper PDFDocument5 pagesPPSC Lecturer Zoology Past Paper PDFfaisal maqbool50% (2)
- Physiology of The PancreasDocument4 pagesPhysiology of The PancreasClayton VerBerkmösNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Integration in The Fed and Starve States: Endocrine Module - Med 7524 (Biochemistry)Document61 pagesMetabolic Integration in The Fed and Starve States: Endocrine Module - Med 7524 (Biochemistry)Rohith KumarNo ratings yet
- Insulin and GlucagonDocument11 pagesInsulin and GlucagonNaman GuptaNo ratings yet
- GLIKOGENESISDocument45 pagesGLIKOGENESISChrista24796No ratings yet
- Human Metabolism Pathways and Clinical AspectsDocument8 pagesHuman Metabolism Pathways and Clinical AspectsSanjaya SenevirathneNo ratings yet
- Basics in Clinical Nutrition: Carbohydrate Metabolism: Luc TappyDocument4 pagesBasics in Clinical Nutrition: Carbohydrate Metabolism: Luc Tappymarliana100% (1)
- Diabetes Mellitus and Laboratory Tests of DiabetesDocument24 pagesDiabetes Mellitus and Laboratory Tests of DiabetesturkiNo ratings yet
- Path Phys3Document73 pagesPath Phys3Наталія Вікторівна ДавиденкоNo ratings yet
- MODULE - FINALS - Biochem - 1Document5 pagesMODULE - FINALS - Biochem - 1Cyril CauilanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 MCQs SolutionsDocument4 pagesTutorial 3 MCQs SolutionsEmmanuel ChendaNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument53 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolismjehram navalesNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates - Part - 1 - MazenDocument35 pagesCarbohydrates - Part - 1 - MazenAhmed GaberNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates MetabolismDocument6 pagesCarbohydrates MetabolismAisha ShahfiqueeNo ratings yet
- Mbs1 - k3 - Carbohydrate Metabolism 1. NewDocument18 pagesMbs1 - k3 - Carbohydrate Metabolism 1. NewDian Permana BurlandNo ratings yet