Professional Documents
Culture Documents
English For Entertainment
Uploaded by
nursaida0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
46 views5 pagesOriginal Title
LK 1-4
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
46 views5 pagesEnglish For Entertainment
Uploaded by
nursaidaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
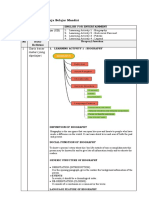
LK 4: Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri (Professional)
Judul Modul ENGLISH FOR ENTERTAINMENT
Judul Kegiatan Belajar (KB) 1. Biography
2. Historical Recount
3. Fables
4. Legends
No Butir Refleksi Respon/Jawaban
1 Daftar peta konsep 1. A biography, or simply bio, is a detailed
(istilah dan definisi) di description of a person's life. It involves
modul ini more than just the basic facts like
education, work, relationships, and
death; it portrays a person's experience of
these life events. and may include an
analysis of the subject's personality.
2. Characteristics of Biography
Biographical texts are not made by people
who are being told their life history, but
are told by other people in the perspective
of third people.
3. Generic Structure
Orientation (Introduction)
It is the opening paragraph, gives the
readers the background information of
the person. Usually contains narrated
biodata such as full name, place and
date of birth.
Events
In events, it should be a chronological
order. This stage is part of the events
or events experienced by the
character. It contains an explanation
of a good story in the form of problem
solving, career processes, and various
events that have been experienced by
the character to lead to success.
Re-Orientation (Closing)
It consists of a conclusion or a
comment or the writer. Tell about the
contribution or the contribution of the
person. In closing, this section
contains the views of the author of the
narrated character.
4. Historical recount is concerned with a
history of a place or an object.
5. Function of Historical recount.
To describe past historical experiences by
retelling chronological events by involving
the important dates, characters as well as
the place of the events.
6. Characteristics of Historical Recount
Retelling the past historical events
Upholding the history of a place or an
object
Written scientifically or imaginatively
Purposing to informing or entertaining
(can be both)
7. Grammar and language features
The participant of historical recount
must be specific, it could involve
persons, animals or things).
The of use correct pronouns referring
to the participants of the text.
It deals with the use of material
processes or actions verbs.
It uses some adverb phrased to
mention location, manner, and
frequency, such as in the afternoon,
carefully, and never.
It used the past tense in the sentences
because historical recount tells the
readers about past events,
It also requires the use of adjectives to
describe the objects.
The use of evaluative words are
absolutely needed to assess the
significance of something,
The historical recount should be
focusing on the ordered events which
were signaled by the use of time
connections like after that, ,after,
before, finally, etc
8. Fable is a story featuring animals, plants
or forces of nature which are
aanthropomorphized (given human
qualities). A fable always ends with a
moral value which was intended as the
lesson.
9. Social Function:
to amuse the readers
to give moral value
10. Grammar and language features
Using commn and nonspecific setting
Often taking place outside
Using past action verb: Climbed,
Turned, Brought
Using specific noun as pronoun of
person, animal in the story. Example:
The king, the queen, etc.
Using adjectives which are for noun
phrase. Example: Long black, hair,
two red apples, etc.
Using time connectives and
Conjunctions to arrange the events.
Examples: Then, before, after, soon,
etc.
Using adverbs and adverbial phrase to
show the location of events. Examples:
here, in the mountain, ever after, etc.
Using dialogue to elicit an emotional
response from the reader.
Using Past Tense.
Ending in happy resolution.
Using of variety of simple, compound
and complex sentences
11. Generic Structure
Orientation
Complication
resolution
12. Moral values of the fable
Persuasion is better than force
Liars may give themselves away
Make hay while the sun shines
Don’t just follow the crowd
Pride can be costly
13. Legend is a story about human events
or actions that has not been proved nor
documented in real history. Legends
are retold as if they are real events and
were believed to be historical accounts.
14. Function of Legend
to present the story of human actions
in such a way that they are perceived
by the the listeners or readers to be
true (in literature).
To entertain or to amuse the readers
about the interesting story (in general)
15. Characteristics of Legend
A legend is a set in specific place or
time
The main character is often heroic
The main character is a human, not a
God
A legend is a fictional story
Usually there is some historical truth
at the heart of every legend
Heroes perform great deeds with their
strength and their intelligence.
Exaggeration is usually involved in
retelling deeds.
Heroes often give up dreams of
happiness to help others
The hero is real but some parts of the
story are not completely true. They
have been stretched or expanded
upon.
Handed down through generation
The story was told orally and turned
into literary masterpieces
16. Generic Structure
Orientation (Introduction)
It tells about the text talks in general,
who involves in the text, when and
where it happens. It should include
the characters of the story.
Complication
It tells what happens with the
participants. It explores the conflict
among the participants.
Resolution
This phase tells how the participants
solve the problems aroused by the
conflict. It is not matter whether the
participants succeed or fail. The point
is the conflict becomes ended. The
problem must be resolved.
Re-Orientation
It tells the conclusion of the story. It
usually include the lesson from the
story.
17. Grammar and language features
The use of Adjective that form the
noun phrase. Example: the strong
crocodile.
Time connectives and conjunction.
Example: A long time ago.
The use of adverb and adverbial
phrases to indicate the location of the
incident or events. Example: In the
river.
The use of action verbs in the past
tense. Example: They curved her.
People then always talked.
The used of saying verbs that mark
remarks. Example : He said angrily.
The use of thinking verbs that mark
the thoughts, perceptions or feelings of
the characters in the story. Example:
The man then looked so curious.
The use of dialogue to elicit an
emotional response from the reader.
2 Daftar materi yang sulit 1. -
dipahami di modul ini
3 Daftar materi yang sering 1. -
mengalami miskonsepsi
You might also like
- LK 1 - Modul 4 ProfesionalDocument5 pagesLK 1 - Modul 4 ProfesionalAnang SusantoNo ratings yet
- Biography, Historical Recount, Fables and Legends in English LearningDocument7 pagesBiography, Historical Recount, Fables and Legends in English LearningtyaoktrianiNo ratings yet
- LK 0.1 Lembar Kerja Mandiri Modul Profesional 4Document4 pagesLK 0.1 Lembar Kerja Mandiri Modul Profesional 4liaNo ratings yet
- Profesional - Modul 4Document4 pagesProfesional - Modul 4agustina kurnianingsihNo ratings yet
- LK Modul 4 English For EntertainmentDocument7 pagesLK Modul 4 English For EntertainmentSari FebriantiNo ratings yet
- LK 1 Profesional Modul 4Document5 pagesLK 1 Profesional Modul 4Farra PramitaNo ratings yet
- English For Entertainment: Reflecting on Biographies, Historical Recounts, Fables, and LegendsDocument10 pagesEnglish For Entertainment: Reflecting on Biographies, Historical Recounts, Fables, and LegendsIweNo ratings yet
- LK 0.1 Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri - Modul Profesional 2Document4 pagesLK 0.1 Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri - Modul Profesional 2sanniahmadNo ratings yet
- LK 1 - Modul 4 - Ade Permata Sari - Bahasa InggrisDocument7 pagesLK 1 - Modul 4 - Ade Permata Sari - Bahasa InggrisAde Permata SariNo ratings yet
- LK 1 Modul 4 English For EntertanmentDocument10 pagesLK 1 Modul 4 English For Entertanmentjauhar muttaqinNo ratings yet
- LK 1-Profesional - Bahasa Inggris - Modul 4Document6 pagesLK 1-Profesional - Bahasa Inggris - Modul 4adi67% (3)
- LK 1-Modul 4Document5 pagesLK 1-Modul 4mita mustikaNo ratings yet
- LK 0.1 mODUL 4 Bahasa InggrisDocument5 pagesLK 0.1 mODUL 4 Bahasa InggrisArieNo ratings yet
- LK 0.1 - Modul4Document4 pagesLK 0.1 - Modul4muhalib alibNo ratings yet
- LK 1: Understanding English Text TypesDocument9 pagesLK 1: Understanding English Text Typesprasetyoeko19889No ratings yet
- Modul 4 LK 0.1Document5 pagesModul 4 LK 0.1Yohanes ChristianNo ratings yet
- MODUL 4 LK 0.1 Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri ANIZA PUSPITADocument8 pagesMODUL 4 LK 0.1 Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri ANIZA PUSPITAAniza PuspitaNo ratings yet
- Understanding English Text TypesDocument4 pagesUnderstanding English Text TypesMohammad Daifi Ibrahim100% (3)
- LK Modul English For Entertaiment Modul 4Document6 pagesLK Modul English For Entertaiment Modul 4Nopita RinggoNo ratings yet
- LK Modul English For EntertaimentDocument6 pagesLK Modul English For EntertaimentNopita RinggoNo ratings yet
- LK Modul English For Entertaiment Modul 4Document6 pagesLK Modul English For Entertaiment Modul 4Nopita RinggoNo ratings yet
- LK 0.1 Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri Modul Bahasa Inggris 4 Tedi KurniawanDocument7 pagesLK 0.1 Lembar Kerja Belajar Mandiri Modul Bahasa Inggris 4 Tedi KurniawanKoko KurniaNo ratings yet
- LK 0.1 Modul 4 ProfesionalDocument5 pagesLK 0.1 Modul 4 ProfesionalAsmawatiNo ratings yet
- LK 1.1 Modul 4 ProfesionalDocument5 pagesLK 1.1 Modul 4 ProfesionalDwi Wahyuni100% (1)
- Modul 4: English For Entertainment: Non-FictionDocument13 pagesModul 4: English For Entertainment: Non-Fictionayu dindaNo ratings yet
- LK Modul 4 ProfesionalDocument7 pagesLK Modul 4 Profesionalsri lestariNo ratings yet
- FICTIONDocument13 pagesFICTIONjayvee CaguimbalNo ratings yet
- LK 0.1: Lembar Kerja Belajar MandiriDocument3 pagesLK 0.1: Lembar Kerja Belajar MandiriAna AthiyahNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Prose FictionDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Prose FictionTaaboNo ratings yet
- LK 4 - Williantika RahayuDocument4 pagesLK 4 - Williantika RahayuWilliantika RahayuNo ratings yet
- CNF Module Week 1 and 2Document3 pagesCNF Module Week 1 and 2Jaja CabaticNo ratings yet
- LK 1 - Modul 4 English For Entertainment - 201506473786 Syamsul BahriDocument6 pagesLK 1 - Modul 4 English For Entertainment - 201506473786 Syamsul Bahriabu Hanifah100% (4)
- Modul Profesional 4Document6 pagesModul Profesional 4ainul yaqinNo ratings yet
- LK 1: Lembar Kerja Belajar MandiriDocument4 pagesLK 1: Lembar Kerja Belajar MandirimelvaNo ratings yet
- щпора ее теорииDocument1 pageщпора ее теорииЛеша ЗадворныхNo ratings yet
- LK 0.1 PPG Bahasa InggrisDocument11 pagesLK 0.1 PPG Bahasa InggrisAnnah SwanNo ratings yet
- Cnf-Q3-Week 6Document11 pagesCnf-Q3-Week 6guiaNo ratings yet
- 21ST Century NotesDocument4 pages21ST Century NotesEinNo ratings yet
- LK 0.1 Profesional Modul 4Document6 pagesLK 0.1 Profesional Modul 4Devi Eva FianyNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Short StoryDocument7 pagesLesson Plan in Short StoryAries Roy Saplagio Aungon0% (1)
- Short Story ElementsDocument4 pagesShort Story ElementsJasmin PejoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document6 pagesLesson 3Lerramie Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- Learning Explorations 5Document7 pagesLearning Explorations 5Rebecca Marasigan TripulcaNo ratings yet
- 03 Handout 1Document4 pages03 Handout 1King CjNo ratings yet
- Elements of A Literary AnalysisDocument3 pagesElements of A Literary AnalysisANNAH GOMEZNo ratings yet
- Colegio de San Jose Activity GuideDocument8 pagesColegio de San Jose Activity GuideJoelina March Jaspe HuangNo ratings yet
- Key Points For Understanding: Dr. Eden Regala Flores ENG611M Week 3 Page 1 of 5Document5 pagesKey Points For Understanding: Dr. Eden Regala Flores ENG611M Week 3 Page 1 of 5Nguyen HalohaloNo ratings yet
- LP For CotDocument8 pagesLP For CotGracey Sagario Dela TorreNo ratings yet
- Creative Non-FictionDocument4 pagesCreative Non-FictionAlexa San ValentinNo ratings yet
- Lit Expressive Elements of FictionDocument3 pagesLit Expressive Elements of FictionuyandrieNo ratings yet
- Jargon in Prose FictionDocument6 pagesJargon in Prose FictionAdeosun OyindamolaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4Document26 pagesLesson 4Chennille Ann Bleu GundayaoNo ratings yet
- The Elements Prose-1Document14 pagesThe Elements Prose-1Ridwan AndriansyahNo ratings yet
- FICTION and Dead StarsDocument4 pagesFICTION and Dead Starsjohn mark escalaNo ratings yet
- English - Elements of Literary TextDocument8 pagesEnglish - Elements of Literary TextFlora Mae Mesolis Rodeno IINo ratings yet
- Life stories, history, fables and legendsDocument4 pagesLife stories, history, fables and legendsFrian SaputraNo ratings yet
- Modul 4 Profesional PPG Bahasa InggrisDocument4 pagesModul 4 Profesional PPG Bahasa InggrisSiti Nurzuliana100% (1)
- Creative Writing: Universal Scholastic Academe Sinisian East, Lemery, BatangasDocument5 pagesCreative Writing: Universal Scholastic Academe Sinisian East, Lemery, BatangasCharlieNo ratings yet
- CREATIVE Nonfiction WEEK 1-2Document19 pagesCREATIVE Nonfiction WEEK 1-2ailynjoy ManacapNo ratings yet
- English For EntertainmentDocument5 pagesEnglish For EntertainmentnursaidaNo ratings yet
- Professional English Text TypesDocument4 pagesProfessional English Text Typesnursaida100% (1)
- LK 1-1Document4 pagesLK 1-1nursaida100% (2)
- English For Personal CommunicationDocument2 pagesEnglish For Personal CommunicationnursaidaNo ratings yet
- English For Social CommunicationDocument2 pagesEnglish For Social CommunicationnursaidaNo ratings yet
- English For Personal CommunicationDocument2 pagesEnglish For Personal CommunicationnursaidaNo ratings yet
- LK 1-1Document4 pagesLK 1-1nursaida100% (2)
- Professional English Text TypesDocument4 pagesProfessional English Text Typesnursaida100% (1)
- Bab 3 4Document7 pagesBab 3 4nursaidaNo ratings yet
- English For Social CommunicationDocument2 pagesEnglish For Social CommunicationnursaidaNo ratings yet
- GoalsDocument5 pagesGoalsnursaidaNo ratings yet
- Infinitive Phrases ExplainedDocument1 pageInfinitive Phrases ExplainedChrisBaruelNo ratings yet
- Ucapan Terimakasih Dalam Berbagai BahsaDocument4 pagesUcapan Terimakasih Dalam Berbagai BahsaionebaceroNo ratings yet
- Jam Cgrammar FinalDocument51 pagesJam Cgrammar Finalعبدالحفيظ الشراديNo ratings yet
- Anymore Vs No LongerDocument4 pagesAnymore Vs No Longermpedraza-1No ratings yet
- Test Bank For Medical Terminology Systems 8th Edition by GylysDocument10 pagesTest Bank For Medical Terminology Systems 8th Edition by GylysSergio Perez100% (28)
- Article PublicationDocument14 pagesArticle PublicationAan DhienNo ratings yet
- Engvid Series by Teachers' Library PDFDocument122 pagesEngvid Series by Teachers' Library PDFSaad Aslam0% (1)
- Gerunds and InfinitivesDocument3 pagesGerunds and InfinitivesFanny Bettina Lubo LozadaNo ratings yet
- Clive Oxenden Christina Latham-Koenig: Paul SeligsonDocument14 pagesClive Oxenden Christina Latham-Koenig: Paul SeligsonAdam ThorsteinsonNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Extra PracticeDocument2 pagesUnit 2: Extra PracticeJésica Anahí FogelNo ratings yet
- Sanskrit Language - 1 Day-01-April-29-2016Document27 pagesSanskrit Language - 1 Day-01-April-29-2016Linga ReddyNo ratings yet
- Estambul High School WorksheetDocument4 pagesEstambul High School WorksheetDiana TangarifeNo ratings yet
- Word OrderDocument7 pagesWord OrderDavidNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Framework and Method of Research 2.1. Theoretical Framework 2.1.1. Compound WordDocument7 pagesTheoretical Framework and Method of Research 2.1. Theoretical Framework 2.1.1. Compound Worddyah oktaNo ratings yet
- Practice About Relative Pronouns - Who-Whose-WhomDocument4 pagesPractice About Relative Pronouns - Who-Whose-WhomLisbeth JiménezNo ratings yet
- III BGU Plan Semanal 5 II QuimestreDocument8 pagesIII BGU Plan Semanal 5 II QuimestreKarelyz RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Minna No Nihongo II - Trans - Text PDFDocument191 pagesMinna No Nihongo II - Trans - Text PDFTakumi JapaneseNo ratings yet
- Grammar Games ChallengeDocument5 pagesGrammar Games Challengedr0alexanderNo ratings yet
- The Ranieri-Roberts Approach To Ancient GreekDocument39 pagesThe Ranieri-Roberts Approach To Ancient Greekmenajo4864No ratings yet
- Course Syllabus: The University of Danang University of Foreign Language StudiesDocument13 pagesCourse Syllabus: The University of Danang University of Foreign Language StudiesThúy HiềnNo ratings yet
- Language Map - SB: Question Syllabus Vocabulary Grammar Speaking & SkillsDocument2 pagesLanguage Map - SB: Question Syllabus Vocabulary Grammar Speaking & SkillsCassiaNo ratings yet
- Javanese - Aké and - Akən A Short HistoryDocument14 pagesJavanese - Aké and - Akən A Short HistoryResistBookNo ratings yet
- Athenaze 1 Chapter 7a Jun 18th 2145Document3 pagesAthenaze 1 Chapter 7a Jun 18th 2145maverickpussNo ratings yet
- FRESNOS JEOPARDY GAME 4th GRADE 2021Document57 pagesFRESNOS JEOPARDY GAME 4th GRADE 2021Teresa Eugenia Aguírre TarascoNo ratings yet
- Verbs Subjunctive MoodDocument2 pagesVerbs Subjunctive MoodIrina MargineanuNo ratings yet
- Form SentencesDocument11 pagesForm SentencesHelna InaNo ratings yet
- Speak Now 1 Count and Noncount Nouns Grammar PresentationDocument27 pagesSpeak Now 1 Count and Noncount Nouns Grammar PresentationSheena SuicoNo ratings yet
- Present Participle vs. GerundsDocument3 pagesPresent Participle vs. GerundsDanny J. Pinto-GuerraNo ratings yet
- Persatuan Dwibahasa SK Ayer Jernih Animal Word Scramble Persatuan Dwibahasa SK Ayer Jernih Food Word ScrambleDocument3 pagesPersatuan Dwibahasa SK Ayer Jernih Animal Word Scramble Persatuan Dwibahasa SK Ayer Jernih Food Word ScrambleJaime GlassNo ratings yet
- Structure and Written ExpressionDocument72 pagesStructure and Written ExpressionChoirull RizalNo ratings yet