Professional Documents
Culture Documents
04.01 Organization of Organisms Guided Notes: Objectives
Uploaded by
Kiyara Pelletier0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
52 views2 pagesThis document provides an overview of the hierarchical organization of organisms from atoms to organ systems. It identifies the seven levels of organization as atoms, molecules, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms. At each level, basic units are organized into increasingly complex structures, with atoms forming molecules, molecules forming cells, cells forming tissues, tissues forming organs, and organs working together in organ systems to form whole living organisms.
Original Description:
My 6th grade science notes.
Original Title
04_01_notes filled out already.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
ODT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an overview of the hierarchical organization of organisms from atoms to organ systems. It identifies the seven levels of organization as atoms, molecules, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms. At each level, basic units are organized into increasingly complex structures, with atoms forming molecules, molecules forming cells, cells forming tissues, tissues forming organs, and organs working together in organ systems to form whole living organisms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as ODT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
52 views2 pages04.01 Organization of Organisms Guided Notes: Objectives
Uploaded by
Kiyara PelletierThis document provides an overview of the hierarchical organization of organisms from atoms to organ systems. It identifies the seven levels of organization as atoms, molecules, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms. At each level, basic units are organized into increasingly complex structures, with atoms forming molecules, molecules forming cells, cells forming tissues, tissues forming organs, and organs working together in organ systems to form whole living organisms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as ODT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
04.
01 Organization of Organisms Guided Notes
Objectives:
In the lesson you will:
identify and organize atoms, molecules, cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems
describe patterns in the hierarchical organization of organisms
Big Ideas:
Key Questions and Terms Notes
What is a living organism? Give a few Animal, plant, and me
examples.
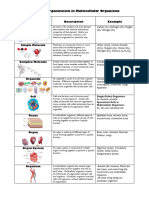
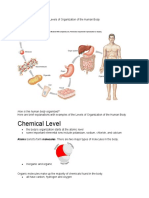
What are the levels of organization, including Atoms, molecules, cells, tissues, organs,
the organism? (Hint: There are seven.) organ systems, organisms.
what is an element? A substance that cannot be broken down into
simpler substances.
What elements are found in the human body? Carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen,
phosphorus and sulfur.
What is an atom?
What is a molecule? What are some A molecule is a combination of two or more
molecules found in the human body? atoms combined. Carbohydrates, lipids,
nucleic acids, proteins, and water.
How are atoms related to molecules? Atoms make up molecules, so atoms are
molecules.
What is a compound? Give an example. A molecule consisting of 2 or more atoms
made up of two elements like a water atom
mixed with an oxygen atom to create H,2,0.
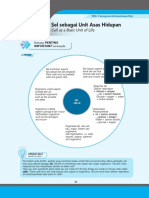
What is the basic unit of structure and Cells
function in all living organisms?
What is the difference between organisms that An unicellular organism is only made up of
are unicellular and organisms that are multi- one cell. An multi-cellular organism is made
cellular? of many cells.
What are some important functions cells Cells help you move your body and help your
perform in the human body? skins and bones function.
Briefly describe each group of specialized
cells.
Tissue: Are a certain type of cell a
muscle is one type of tissue.
Organs: are made up of lungs, the
heart, the brain, liver, stomach and the
kidneys.
Organ systems: Respiratory, digestive,
nervous, circulatory, skeletal, and
muscular.
How are organisms organized from simple to Atom, molecule, cell, tissue, organ, organ-
complex? system.
You might also like
- Anatomy 101: From Muscles and Bones to Organs and Systems, Your Guide to How the Human Body WorksFrom EverandAnatomy 101: From Muscles and Bones to Organs and Systems, Your Guide to How the Human Body WorksRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (19)
- 20 - Levels of Biological OrganizatonDocument31 pages20 - Levels of Biological Organizatonammy adeNo ratings yet
- Webster 2018 Life Science ReviewDocument88 pagesWebster 2018 Life Science Reviewapi-312162583No ratings yet
- Unit-2, (Lecture-4th) Characterstics To Living OrganismDocument24 pagesUnit-2, (Lecture-4th) Characterstics To Living OrganismNavneet ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- 1.discuss The Different Levels of Organization's in The BodyDocument6 pages1.discuss The Different Levels of Organization's in The BodyJasper jay DumalagNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology 01Document5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology 01vara prasadNo ratings yet
- Principles of Organisation 1Document9 pagesPrinciples of Organisation 1María Lau WongNo ratings yet
- Principles of Organisation 1 ScienseDocument9 pagesPrinciples of Organisation 1 ScienseMaría Lau WongNo ratings yet
- Levels of OrganizationDocument32 pagesLevels of OrganizationZayra GomezNo ratings yet
- Structural Level of An OrganismDocument4 pagesStructural Level of An OrganismxoxogeloNo ratings yet
- A221 Module 1 Cell and Tissue PDFDocument10 pagesA221 Module 1 Cell and Tissue PDFAkmal Danish100% (1)
- Levels of Organization HandoutDocument2 pagesLevels of Organization HandoutsallynourlbNo ratings yet
- Precision Nutrition Certification Level 1 - Chapter 1Document76 pagesPrecision Nutrition Certification Level 1 - Chapter 1trungchinh8xxx100% (2)
- Anatomy NoteDocument8 pagesAnatomy Notechiamaka anthonyNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Earth and Life Science Organ SystemDocument11 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Earth and Life Science Organ SystemRodelyn Dahay CalluengNo ratings yet
- Sel Sebagai Unit Asas Hidupan: Cell As A Basic Unit of LifeDocument13 pagesSel Sebagai Unit Asas Hidupan: Cell As A Basic Unit of Lifejulia ahmadNo ratings yet
- BIO - 103 - L2 - Fall, 2018Document27 pagesBIO - 103 - L2 - Fall, 2018Demi RoseNo ratings yet
- Human Body Study Guide AnswersDocument2 pagesHuman Body Study Guide Answersapi-325864985No ratings yet
- Levels of Organization of Human BodyDocument1 pageLevels of Organization of Human Bodyandersonmack047No ratings yet
- BPE102 Anatomy Physiology of Human MovementDocument9 pagesBPE102 Anatomy Physiology of Human MovementBasiwa AprilNo ratings yet
- ORGANIZATION LEVELS OF LIVING ORGANISM - Ms - RisdqaDocument9 pagesORGANIZATION LEVELS OF LIVING ORGANISM - Ms - RisdqaMangattt UghteaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Guide: Molecules of LifeDocument4 pagesLesson 1 Guide: Molecules of LifeKyle PontonNo ratings yet
- Lesson Biological OrganizationDocument49 pagesLesson Biological OrganizationReinalyn MendozaNo ratings yet
- Bab 2 Tingkatan 1Document13 pagesBab 2 Tingkatan 1brandonvico94No ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument1 pageUntitled DocumentLoveleen HeartsNo ratings yet
- The Hierarchical Organization of Life: Web Tutorial 1.2Document2 pagesThe Hierarchical Organization of Life: Web Tutorial 1.2api-456882628No ratings yet
- Cells Are The Starting PointDocument2 pagesCells Are The Starting PointDONABEL ESPANONo ratings yet
- Biological Rganizatio of LifeDocument19 pagesBiological Rganizatio of LifeJerry De Leon TaayNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Structural Organization of The Human BodyDocument6 pages1.2 Structural Organization of The Human BodyHarshitha ReddyNo ratings yet
- UNIT 5 Livings BeingsDocument8 pagesUNIT 5 Livings BeingsAlba etceteraNo ratings yet
- Chapter.1 Doc.1Document4 pagesChapter.1 Doc.1Enju ChipepeNo ratings yet
- Reading Levels of OrganizationDocument12 pagesReading Levels of OrganizationVanessaMolinaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATIONDocument27 pagesLesson 1 STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATIONRichville PenetranteNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.2 The Organisation of Living Organisms - Grade 9Document12 pagesLesson 2.2 The Organisation of Living Organisms - Grade 9SAMI DHAOUINo ratings yet
- 2 Levels of Structural OrganizationDocument2 pages2 Levels of Structural OrganizationLance StrikerNo ratings yet
- Anglais-Français (A M G'DO) 4Document12 pagesAnglais-Français (A M G'DO) 4Aly GuindoNo ratings yet
- Human Body: How Is The Human Body Similar To A Well-Tuned Machine?Document9 pagesHuman Body: How Is The Human Body Similar To A Well-Tuned Machine?Montse GilNo ratings yet
- Cells, Tissues, Organs, and SystemsDocument11 pagesCells, Tissues, Organs, and SystemsJay-ar AlzonaNo ratings yet
- Science Form 1 - Chapter 2Document20 pagesScience Form 1 - Chapter 2Beevy GB85% (39)
- Invertebrates 1 @chetanbhagatDocument269 pagesInvertebrates 1 @chetanbhagatEka Dyah ANo ratings yet
- Study Guide For Science Periodic 2 Term 2 6 Grade Life Science-Sections 1.1, 1.2, & 1.3Document7 pagesStudy Guide For Science Periodic 2 Term 2 6 Grade Life Science-Sections 1.1, 1.2, & 1.3api-270387817No ratings yet
- Body Systems OrganizationDocument12 pagesBody Systems Organizationmegha139No ratings yet
- Cell OrganellesDocument24 pagesCell Organellesmetasynthronos748No ratings yet
- Chemical Level: How Is The Human Body Organized?Document5 pagesChemical Level: How Is The Human Body Organized?Dhea BugnaNo ratings yet
- Cells Tissues Organs and Systems Power PointDocument11 pagesCells Tissues Organs and Systems Power PointNidonama E. KabmatNo ratings yet
- Four Systems For Happy YogaDocument109 pagesFour Systems For Happy YogaAwanish PandeyNo ratings yet
- Cells: The Building Blocks of LifeDocument8 pagesCells: The Building Blocks of LifeAniza Nimozalophefriendz AndsainczclueNo ratings yet
- 4 - Levels of Organization of Living ThingsDocument20 pages4 - Levels of Organization of Living ThingsFrancisco jezziel dominguez fernandezNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Structural Organization of The Human Body - Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument8 pages1.2 Structural Organization of The Human Body - Anatomy and PhysiologyAlexander Acevedo100% (1)
- Stages of The Biological Organization Subatomic ParticlesDocument4 pagesStages of The Biological Organization Subatomic ParticlesBéla JózsiNo ratings yet
- AbbyDocument2 pagesAbbyGiancarlo PerezNo ratings yet
- Biology - Module 1Document6 pagesBiology - Module 1ASHLEY MONICA PLATANo ratings yet
- Levels of OrganizationDocument11 pagesLevels of OrganizationLeo Cambaya Lascuña Jr.No ratings yet
- From Cells To Tissue To Organs To Organ Systems: LS1.A: Structure and FunctionDocument3 pagesFrom Cells To Tissue To Organs To Organ Systems: LS1.A: Structure and FunctionSaleh AlsowayanNo ratings yet
- Science 7 Unit 5 Study GuideDocument15 pagesScience 7 Unit 5 Study GuideMae RicañaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 BC SC Probe 8Document24 pagesChapter 2 BC SC Probe 8api-265180883100% (1)
- Introduction To The Human BodyDocument2 pagesIntroduction To The Human BodyjonelbambaNo ratings yet
- Cells Tissues Organs and Systems Power PointDocument10 pagesCells Tissues Organs and Systems Power PointRamyRamia ElzantNo ratings yet
- Cells, Tissues and Organs Animal and Plant CellsDocument5 pagesCells, Tissues and Organs Animal and Plant CellsAmisha VastaniNo ratings yet
- Zikri Aiman-Cell Organization in AnimalsDocument37 pagesZikri Aiman-Cell Organization in AnimalsZikriAimanNo ratings yet
- Routine Maintenance For External Water Tank Pump and Circulation Pump On FID Tower and Rack 2017-014Document5 pagesRoutine Maintenance For External Water Tank Pump and Circulation Pump On FID Tower and Rack 2017-014CONVIERTE PDF JPG WORDNo ratings yet
- H.mohamed Ibrahim Hussain A Study On Technology Updatiing and Its Impact Towards Employee Performance in Orcade Health Care PVT LTD ErodeDocument108 pagesH.mohamed Ibrahim Hussain A Study On Technology Updatiing and Its Impact Towards Employee Performance in Orcade Health Care PVT LTD ErodeeswariNo ratings yet
- Dash8 200 300 Electrical PDFDocument35 pagesDash8 200 300 Electrical PDFCarina Ramo LakaNo ratings yet
- Patricio Gerpe ResumeDocument2 pagesPatricio Gerpe ResumeAnonymous 3ID4TBNo ratings yet
- Ziarek - The Force of ArtDocument233 pagesZiarek - The Force of ArtVero MenaNo ratings yet
- Categories of Cargo and Types of ShipsDocument14 pagesCategories of Cargo and Types of ShipsVibhav Kumar100% (1)
- Resa Auditing Theorydocx - CompressDocument64 pagesResa Auditing Theorydocx - CompressMaeNo ratings yet
- ABHIGYAN 2020 E-InvitationDocument2 pagesABHIGYAN 2020 E-Invitationchirag sabhayaNo ratings yet
- 2012 Conference NewsfgfghsfghsfghDocument3 pages2012 Conference NewsfgfghsfghsfghabdNo ratings yet
- Wood ReportDocument36 pagesWood Reportメルヴリッ クズルエタNo ratings yet
- 1 - DIASS Trisha Ma-WPS OfficeDocument2 pages1 - DIASS Trisha Ma-WPS OfficeMae ZelNo ratings yet
- Ericsson For Sale From Powerstorm 4SA03071242Document8 pagesEricsson For Sale From Powerstorm 4SA03071242wd3esaNo ratings yet
- RseDocument60 pagesRseH S Vishwanath ShastryNo ratings yet
- Influence of Freezing and Pasteurization of The Physical Condition of The Plastik (PE, PP and HDPE) As Selar Fish Packaging (Selaroides Leptolepis) in Sendang Biru, Malang, East Java. IndonesiaDocument7 pagesInfluence of Freezing and Pasteurization of The Physical Condition of The Plastik (PE, PP and HDPE) As Selar Fish Packaging (Selaroides Leptolepis) in Sendang Biru, Malang, East Java. IndonesiaInternational Network For Natural SciencesNo ratings yet
- Rate If Iodine and PropanoneDocument3 pagesRate If Iodine and Propanoneshareef1No ratings yet
- LET-English-Structure of English-ExamDocument57 pagesLET-English-Structure of English-ExamMarian Paz E Callo80% (5)
- Chapter S1 (Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation)Document28 pagesChapter S1 (Celestial Timekeeping and Navigation)Марко Д. Станковић0% (1)
- Model 900 Automated Viscometer: Drilling Fluids EquipmentDocument2 pagesModel 900 Automated Viscometer: Drilling Fluids EquipmentJazminNo ratings yet
- Group 4&5 Activity Syntax AnalyzerDocument6 pagesGroup 4&5 Activity Syntax AnalyzerJuan PransiskoNo ratings yet
- PRINCIPLES OF TEACHING NotesDocument24 pagesPRINCIPLES OF TEACHING NotesHOLLY MARIE PALANGAN100% (2)
- NZ2016SH (32k) - e - NSC5026D 3.3V +100ppmDocument2 pagesNZ2016SH (32k) - e - NSC5026D 3.3V +100ppmDumarronNo ratings yet
- Ceo DualityDocument3 pagesCeo Dualitydimpi singhNo ratings yet
- Ocr A Level History Russia CourseworkDocument7 pagesOcr A Level History Russia Courseworkbcrqhr1n100% (1)
- PC Engines APU2 Series System BoardDocument11 pagesPC Engines APU2 Series System Boardpdy2No ratings yet
- Weekly Lesson Plan: Pry 3 (8years) Third Term Week 1Document12 pagesWeekly Lesson Plan: Pry 3 (8years) Third Term Week 1Kunbi Santos-ArinzeNo ratings yet
- Report On Monitoring and Evaluation-Ilagan CityDocument5 pagesReport On Monitoring and Evaluation-Ilagan CityRonnie Francisco TejanoNo ratings yet
- Deloitte - Introduction To TS&A - CloudDocument2 pagesDeloitte - Introduction To TS&A - Cloudsatyam100% (1)
- Schermer 1984Document25 pagesSchermer 1984Pedro VeraNo ratings yet
- Beng (Hons) Telecommunications: Cohort: Btel/10B/Ft & Btel/09/FtDocument9 pagesBeng (Hons) Telecommunications: Cohort: Btel/10B/Ft & Btel/09/FtMarcelo BaptistaNo ratings yet
- Early Christian ArchitectureDocument38 pagesEarly Christian ArchitectureInspirations & ArchitectureNo ratings yet