Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Math Study Guide
Uploaded by
Garnes Taahira0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views3 pagesThis document provides a study guide for geometry concepts including:
- Parts of a circle such as chords, arcs, secant lines, tangents, diameters, and radii.
- Formulas for circumference, area, radius, and diameter of a circle.
- The relationship between degrees and radians and how they can be used to measure arcs.
- Definitions of trigonometric ratios such as sine, cosine, and tangent.
- Laws of sines and cosines.
- The unit circle and how it relates x-coordinates to sines and y-coordinates to cosines.
- The triangle inequality theorem and how it can be used to determine if a triangle is possible.
- The
Original Description:
Original Title
Math study guide
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides a study guide for geometry concepts including:
- Parts of a circle such as chords, arcs, secant lines, tangents, diameters, and radii.
- Formulas for circumference, area, radius, and diameter of a circle.
- The relationship between degrees and radians and how they can be used to measure arcs.
- Definitions of trigonometric ratios such as sine, cosine, and tangent.
- Laws of sines and cosines.
- The unit circle and how it relates x-coordinates to sines and y-coordinates to cosines.
- The triangle inequality theorem and how it can be used to determine if a triangle is possible.
- The
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views3 pagesMath Study Guide
Uploaded by
Garnes TaahiraThis document provides a study guide for geometry concepts including:
- Parts of a circle such as chords, arcs, secant lines, tangents, diameters, and radii.
- Formulas for circumference, area, radius, and diameter of a circle.
- The relationship between degrees and radians and how they can be used to measure arcs.
- Definitions of trigonometric ratios such as sine, cosine, and tangent.
- Laws of sines and cosines.
- The unit circle and how it relates x-coordinates to sines and y-coordinates to cosines.
- The triangle inequality theorem and how it can be used to determine if a triangle is possible.
- The
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Taahira Garnes
April 26th, 2021
Ms.LaMagna - Study Guide
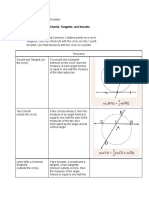
Parts of a Circle
A. Chord
B. Arc
C. Secant line
D. Tangent line
E. diameter
F. Radius
- Circumference > 2πr
- Area > πr2
- Radius > ½ D
- Diameter > 2r
Degrees v.s Radians
- Radians > Distance you rotated when you rotated the distance of the radius
π radians = ½ of a circle
1 radian ≈ ⅙ of a circle
- Another measure unit > can measure length of arcs
Degree = (180°/π)• radians
Radian = (π/180°) • degrees
Trig Ratios
Sin > Opposite / Hypotenuse
Cos >Adjacent/ Hypotenuse
Tan > Opposite / Adjacent
Law of Sines
Sin A/a = Sin B/b = Sin C/c
Law of Cosines
C2= a2 + b2 - 2ab(Cosc)
Unit Circle
- X Coordinate > Sine
- Y Coordinate > Cosine
- Tan > Y/X
Triangle Inequality theorem
- difference < third side < sum
- Used to determine if a triangle “works”
- Ex: 3,7,15 (3+7= 10) not larger than 15, doesn’t work
Pythagorean Theorem
a2 + b2 = c2
determining type of triangle ..
a2 + b2 = c2 > Right triangle
a2 + b2 < c2 > Obtuse Triangle
a2 + b2 > c2 > Acute Triangle
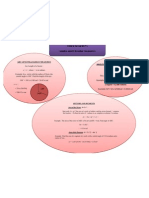
Relationships between inscribed angles, central angles, and subtended arcs
(a)Inscribed angle > the angle formed in the interior of a circle when two chords
intersect on the circle
(b)Central angle > an angle with its vertex at the center of a circle, with its sides
containing two radii of the circle
(c)Subtended arcs > an angle is subtended by an arc, line segment or any other
section of a curve when its two rays pass through the endpoints of that arc, line
segment or curve section
Relation: The measure of the inscribed angle is half the measure of the arc it
intercepts. If a central angle and an inscribed angle intercept the same arc, then the
central angle is double the inscribed angle, and the inscribed angle is half the central
angle.
You might also like
- Geometry Dba Study Guide 07.07Document3 pagesGeometry Dba Study Guide 07.07Tyler CosgroveNo ratings yet
- Work and Power LabDocument3 pagesWork and Power LabGarnes TaahiraNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry ReviewerDocument10 pagesTrigonometry ReviewerNiko Ramarama100% (1)
- Math Study GuideDocument3 pagesMath Study GuideGarnes TaahiraNo ratings yet
- Chord, Arcs, Central Angels, Tangents and SecantsDocument5 pagesChord, Arcs, Central Angels, Tangents and SecantsLucille BallaresNo ratings yet
- CircolDocument12 pagesCircol202130054No ratings yet
- Circles: Geometry 40 PointsDocument10 pagesCircles: Geometry 40 PointsAml AmlNo ratings yet
- Circular MeasurementsDocument15 pagesCircular Measurementsmihlemgoduka22No ratings yet
- Cliff S Notes GeometryDocument2 pagesCliff S Notes GeometryKamal SharmaNo ratings yet
- What Is The Circumference of A CircleDocument6 pagesWhat Is The Circumference of A Circleapi-126876773No ratings yet
- Circumference of A CircleDocument6 pagesCircumference of A Circleapi-126876773No ratings yet
- CurvesDocument26 pagesCurvesAsad BappiNo ratings yet
- TRIGONOMETRYDocument8 pagesTRIGONOMETRYurfriend_jjn05100% (1)
- Gr8 Math Notes (ch25)Document5 pagesGr8 Math Notes (ch25)Akshara ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Find The Circumference of A CircleDocument6 pagesFind The Circumference of A Circleapi-126876773No ratings yet
- Chapter - 12 Areas Related To CirclesDocument29 pagesChapter - 12 Areas Related To CirclesYash GoyalNo ratings yet
- Geometry: 3. Solid BodiesDocument40 pagesGeometry: 3. Solid BodiesEduardo Tello del PinoNo ratings yet
- What Is A CircleDocument10 pagesWhat Is A Circlevalli rajuNo ratings yet
- Makalah Bahasa Inggris MatematikaDocument8 pagesMakalah Bahasa Inggris MatematikaSofiyah Sitorus PaneNo ratings yet
- How To Find Circumference of A CircleDocument6 pagesHow To Find Circumference of A Circleapi-126876773No ratings yet
- Chapter 2.1 Mom1iDocument32 pagesChapter 2.1 Mom1iKarell Faye BatulanNo ratings yet
- 07 GemoetryDocument11 pages07 GemoetryKomanduri Murali SrinivasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 CirclesDocument9 pagesChapter 10 CirclesrachelbuchananNo ratings yet
- Circles PPTDocument69 pagesCircles PPTIfrah ZiaNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument3 pagesFormula SheetShelisa Michaela MuthukumaranaNo ratings yet
- Micro Project MathsDocument15 pagesMicro Project Mathsharshawardhan deshmukhNo ratings yet
- Segments of A CircleDocument25 pagesSegments of A CircleJoyce Estrevencion100% (1)
- Tangents and Sec Ants To The CircleDocument18 pagesTangents and Sec Ants To The CircleAnonymous 9uu04elNo ratings yet
- Center, Then They Are CongruentDocument9 pagesCenter, Then They Are CongruentAnwie ChuaNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 Areas Related To CirclesDocument30 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 Areas Related To Circlesjainsaarth297No ratings yet
- Module 5 TrigonometryDocument0 pagesModule 5 TrigonometryManish MishraNo ratings yet
- Areas Related To CirclesDocument23 pagesAreas Related To Circlesthinkiit80% (5)
- Pre Cal Exam Quarter 2Document6 pagesPre Cal Exam Quarter 2Hannah Balais100% (1)
- Mind MapDocument1 pageMind MapSiti Norfadilah RosmadiNo ratings yet
- CirclesDocument26 pagesCirclesNeha ThakurNo ratings yet
- All Math FormulasDocument27 pagesAll Math FormulasMubassher Ahmed Shoaib100% (1)
- Trigonometry BasicsDocument9 pagesTrigonometry Basicsapi-265481804No ratings yet
- Trigonometry Notes and Solved Examples For SSCDocument16 pagesTrigonometry Notes and Solved Examples For SSCTarique HassanNo ratings yet
- Mensuration: Ac B Ab C BC ADocument9 pagesMensuration: Ac B Ab C BC AhiyyearNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2.1 Handout PDFDocument5 pagesCHAPTER 2.1 Handout PDFAcuña ShineNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Revision Notes Areas Related To CirclesDocument4 pagesClass 10 Revision Notes Areas Related To CirclesArzhel BoissinotNo ratings yet
- Day 8 Plane Geometry December 01 20212Document51 pagesDay 8 Plane Geometry December 01 20212Free student100% (1)
- 10 - Angles and Their MeasurementDocument34 pages10 - Angles and Their MeasurementFrederick Patriarca OmalzaNo ratings yet
- Geometry 1st ChapterDocument20 pagesGeometry 1st ChaptersanthoshNo ratings yet
- Math 23Document34 pagesMath 23Sajed RahmanNo ratings yet
- Obj. 17 Radian Measure: Unit 5 Trigonometric and Circular FunctionsDocument13 pagesObj. 17 Radian Measure: Unit 5 Trigonometric and Circular FunctionsSandra MillerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document33 pagesChapter 13Ramesh NaiduNo ratings yet
- CirclesDocument2 pagesCirclesArie AbdillahNo ratings yet
- Math GR10T3 LA2 & AU3 ReviewerDocument5 pagesMath GR10T3 LA2 & AU3 ReviewerGab AquinoNo ratings yet
- Netcircle Problems With SolutionsDocument34 pagesNetcircle Problems With SolutionsFynn NiallNo ratings yet
- Simple Curves (Part 1)Document2 pagesSimple Curves (Part 1)Karo LiNo ratings yet
- Geom - 10.1-10.4 PowerPointDocument19 pagesGeom - 10.1-10.4 PowerPointAnanthuNo ratings yet
- Maths & Mech FormulasDocument19 pagesMaths & Mech FormulasgunasekaranNo ratings yet
- ROUTE SURVEY-for StudentsDocument71 pagesROUTE SURVEY-for StudentsUsama IsmailNo ratings yet
- Math 2: Lazaro, Mark Vincent J. BS CriminologyDocument13 pagesMath 2: Lazaro, Mark Vincent J. BS CriminologyArrojo Rhiane Hilary MaeNo ratings yet
- Institut Kemahiran MARA Sungai Petani, Kedah: Information SheetDocument6 pagesInstitut Kemahiran MARA Sungai Petani, Kedah: Information Sheetilzam_lilyNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Angles, Triangles and other PolygonsFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Angles, Triangles and other PolygonsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Unit 4 Homework Packet #1 Lessons 4 - 6Document5 pagesUnit 4 Homework Packet #1 Lessons 4 - 6Garnes TaahiraNo ratings yet
- Homework: Check-In: Find The Length of Each Arc. For Questions 3 and 4, Find The Radian Measure As WellDocument2 pagesHomework: Check-In: Find The Length of Each Arc. For Questions 3 and 4, Find The Radian Measure As WellGarnes TaahiraNo ratings yet
- Let's Assume The Following Circle Has A Radius of 1 Unit. Find The Coordinates of Each Position. Leave As A Fraction And/or RadicalDocument1 pageLet's Assume The Following Circle Has A Radius of 1 Unit. Find The Coordinates of Each Position. Leave As A Fraction And/or RadicalGarnes TaahiraNo ratings yet
- Science Lab # 2Document3 pagesScience Lab # 2Garnes TaahiraNo ratings yet
- Christian Humanist: Northern Writers Try To Reform SocietyDocument1 pageChristian Humanist: Northern Writers Try To Reform SocietyGarnes TaahiraNo ratings yet
- CH 11 Sec 5Document4 pagesCH 11 Sec 5Garnes TaahiraNo ratings yet